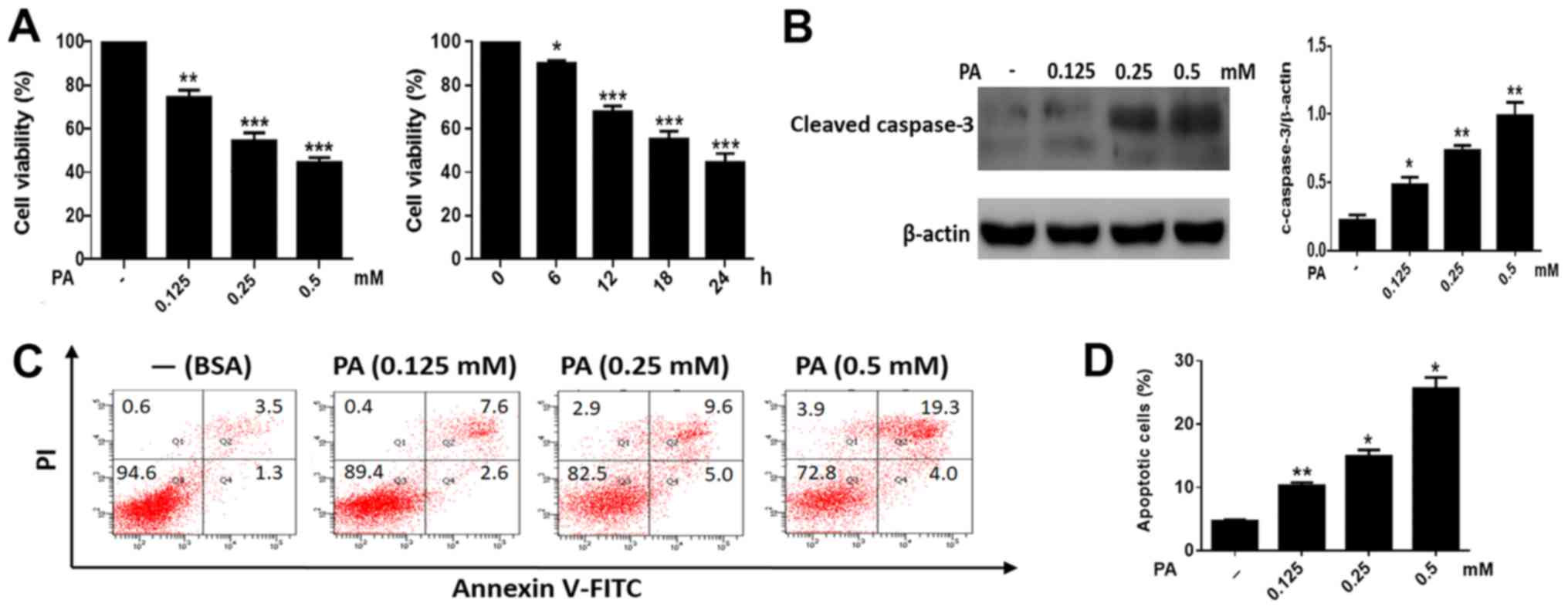
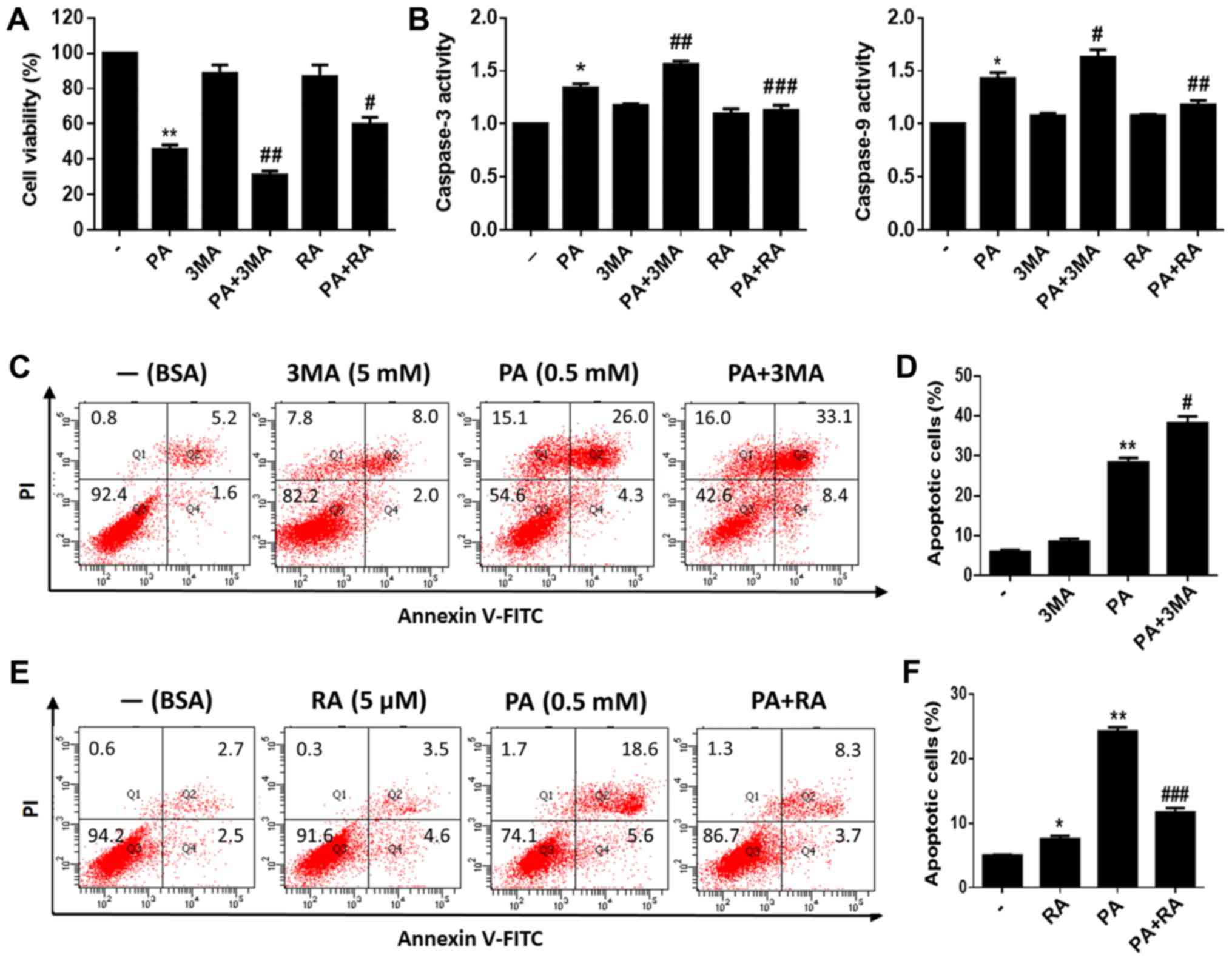
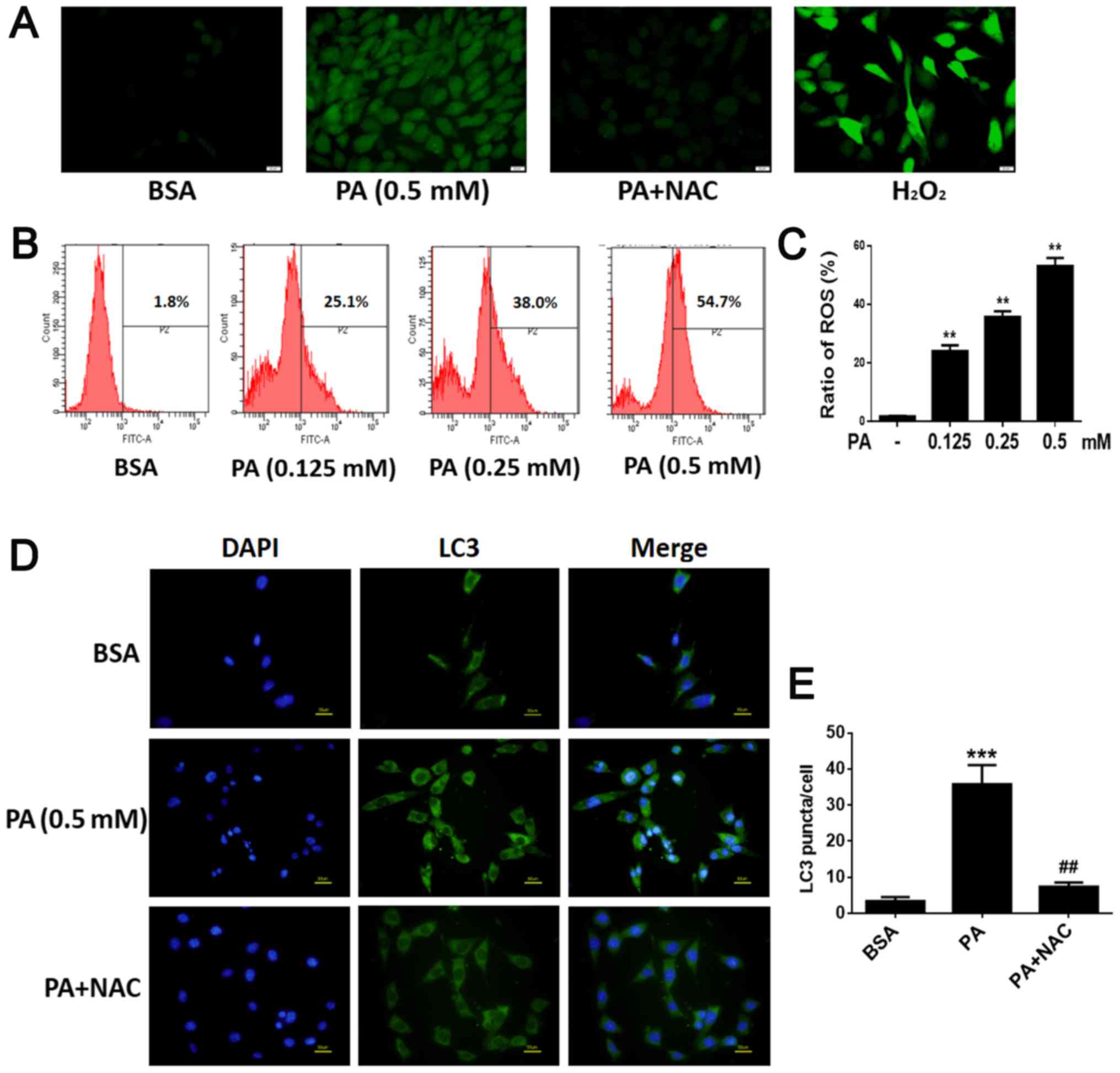
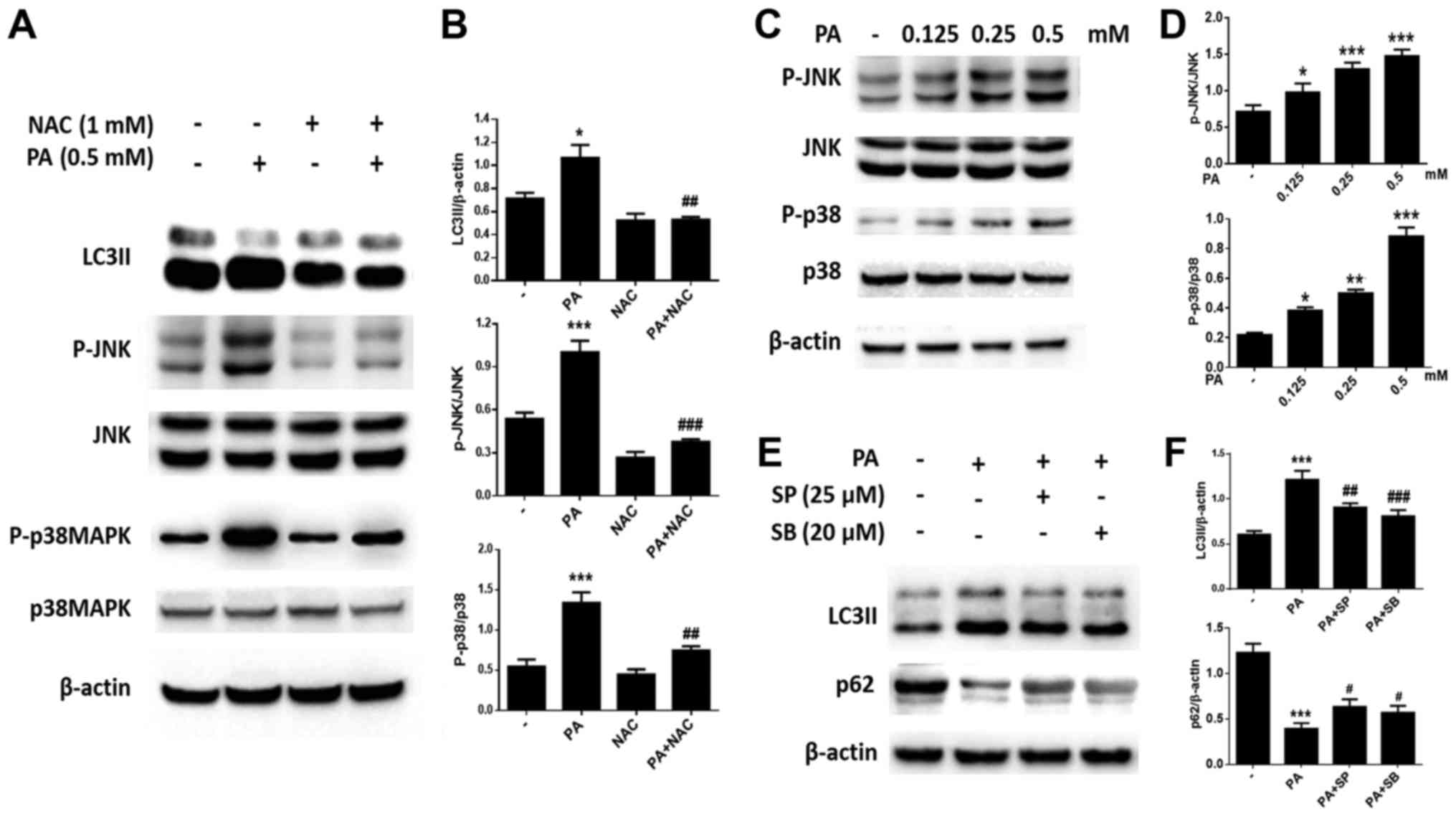
|
1
|
Brown SA and Rosen CJ: Osteoporosis. Med
Clin North Am. 87:1039–1063. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Gimble JM, Zvonic S, Floyd ZE, Kassem M
and Nuttall ME: Playing with bone and fat. J Cell Biochem.
98:251–266. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Rosen CJ and Bouxsein ML: Mechanisms of
disease: Is osteoporosis the obesity of bone? Nat Clin Pract
Rheumatol. 2:35–43. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Pei L and Tontonoz P: Fat's loss is bone's
gain. J Clin Invest. 113:805–806. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Elbaz A, Wu X, Rivas D, Gimble JM and
Duque G: Inhibition of fatty acid biosynthesis prevents adipocyte
lipotoxicity on human osteoblasts in vitro. J Cell Mol Med.
14:982–991. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Orchard TS, Cauley JA, Frank GC, Neuhouser
ML, Robinson JG, Snetselaar L, Tylavsky F, Wactawski-Wende J, Young
AM, Lu B and Jackson RD: Fatty acid consumption and risk of
fracture in the Women's Health Initiative. Am J Clin Nutr.
92:1452–1460. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Turpin SM, Lancaster GI, Darby I, Febbraio
MA and Watt MJ: Apoptosis in skeletal muscle myotubes is induced by
ceramides and is positively related to insulin resistance. Am J
Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 291:E1341–E1350. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Malhi H, Bronk SF, Werneburg NW and Gores
GJ: Free fatty acids induce JNK-dependent hepatocyte lipoapoptosis.
J Biol Chem. 281:12093–12101. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kim JE, Ahn MW, Baek SH, Lee IK, Kim YW,
Kim JY, Dan JM and Park SY: AMPK activator, AICAR, inhibits
palmitate-induced apoptosis in osteoblast. Bone. 43:394–404. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
de Bruin EC and Medema JP: Apoptosis and
non-apoptotic deaths in cancer development and treatment response.
Cancer Treat Rev. 34:737–749. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Levine B and Kroemer G: Autophagy in the
pathogenesis of disease. Cell. 132:27–42. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Eisenberg-Lerner A, Bialik S, Simon HU and
Kimchi A: Life and death partners: Apoptosis, autophagy and the
cross-talk between them. Cell Death Differ. 16:966–975. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hocking LJ, Whitehouse C and Helfrich MH:
Autophagy: A new player in skeletal maintenance? J Bone Miner Res.
27:1439–1447. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Caramés B, Taniguchi N, Otsuki S, Blanco
FJ and Lotz M: Autophagy is a protective mechanism in normal
cartilage, and its aging-related loss is linked with cell death and
osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 62:791–801. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lu J, Wang Q, Huang L, Dong H, Lin L, Lin
N, Zheng F and Tan J: Palmitate causes endoplasmic reticulum stress
and apoptosis in human mesenchymal stem cells: Prevention by AMPK
activator. Endocrinology. 153:5275–5284. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gillet C, Spruyt D, Rigutto S, Dalla Valle
A, Berlier J, Louis C, Debier C, Gaspard N, Malaisse WJ, Gangji V
and Rasschaert J: Oleate abrogates palmitate-induced lipotoxicity
and proinflammatory response in human bone marrow-derived
mesenchymal stem cells and osteoblastic cells. Endocrinology.
156:4081–4093. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Dong X, Bi L, He S, Meng G, Wei B, Jia S
and Liu J: FFAs-ROS-ERK/P38 pathway plays a key role in adipocyte
lipotoxicity on osteoblasts in co-culture. Biochimie. 101:123–131.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Li Y, Luo Q, Yuan L, Miao C, Mu X, Xiao W,
Li J, Sun T and Ma E: JNK-dependent Atg4 upregulation mediates
asperphenamate derivative BBP-induced autophagy in MCF-7 cells.
Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 263:21–31. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sui X, Kong N, Ye L, Han W, Zhou J, Zhang
Q, He C and Pan H: p38 and JNK MAPK pathways control the balance of
apoptosis and autophagy in response to chemotherapeutic agents.
Cancer Lett. 344:174–179. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Choi SE, Lee SM, Lee YJ, Li LJ, Lee SJ,
Lee JH, Kim Y, Jun HS, Lee KW and Kang Y: Protective role of
autophagy in palmitate-induced INS-1 beta-cell death.
Endocrinology. 150:126–134. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Martino L, Masini M, Novelli M, Beffy P,
Bugliani M, Marselli L, Masiello P, Marchetti P and De Tata V:
Palmitate activates autophagy in INS-1E β-cells and in isolated rat
and human pancreatic islets. PLoS One. 7:e361882012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Xie W, Zhai Z, Yang Y, Kuang T and Wang C:
Free fatty acids inhibit TM-EPCR expression through JNK pathway: An
implication for the development of the prothrombotic state in
metabolic syndrome. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 34:468–474. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Griffith JF, Yeung DK, Ahuja AT, Choy CW,
Mei WY, Lam SS, Lam TP, Chen ZY and Leung PC: A study of bone
marrow and subcutaneous fatty acid composition in subjects of
varying bone mineral density. Bone. 44:1092–1096. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Justesen J, Stenderup K, Ebbesen EN,
Mosekilde L, Steiniche T and Kassem M: Adipocyte tissue volume in
bone marrow is increased with aging and in patients with
osteoporosis. Biogerontology. 2:165–171. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hardouin P, Pansini V and Cortet B: Bone
marrow fat. Joint Bone Spine. 81:313–319. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wren TA, Chung SA, Dorey FJ, Bluml S,
Adams GB and Gilsanz V: Bone marrow fat is inversely related to
cortical bone in young and old subjects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.
96:782–786. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Shen W, Chen J, Gantz M, Punyanitya M,
Heymsfield SB, Gallagher D, Albu J, Engelson E, Kotler D, Pi-Sunyer
X and Gilsanz V: MRI-measured pelvic bone marrow adipose tissue is
inversely related to DXA-measured bone mineral in younger and older
adults. Eur J Clin Nutr. 66:983–988. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Fazeli PK, Horowitz MC, MacDougald OA,
Scheller EL, Rodeheffer MS, Rosen CJ and Klibanski A: Marrow fat
and bone-new perspectives. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 98:935–945.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ahima RS and Flier JS: Adipose tissue as
an endocrine organ. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 11:327–332. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Frühbeck G, Gómez-Ambrosi J, Muruzábal FJ
and Burrell MA: The adipocyte: A model for integration of endocrine
and metabolic signaling in energy metabolism regulation. Am J
Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 280:E827–E847. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lecka-Czernik B: Marrow fat metabolism is
linked to the systemic energy metabolism. Bone. 50:534–539. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Rosen CJ, Ackert-Bicknell C, Rodriguez JP
and Pino AM: Marrow fat and the bone microenvironment:
Developmental, functional, and pathological implications. Crit Rev
Eukaryot Gene Expr. 19:109–124. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kawai M, de Paula FJ and Rosen CJ: New
insights into osteoporosis: The bone-fat connection. J Intern Med.
272:317–329. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Maurin AC, Chavassieux PM, Frappart L,
Delmas PD, Serre CM and Meunier PJ: Influence of mature adipocytes
on osteoblast proliferation in human primary cocultures. Bone.
26:485–489. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Clabaut A, Delplace S, Chauveau C,
Hardouin P and Broux O: Human osteoblasts derived from mesenchymal
stem cells express adipogenic markers upon coculture with bone
marrow adipocytes. Differentiation. 80:40–45. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wang D, Haile A and Jones LC:
Dexamethasone-induced lipolysis increases the adverse effect of
adipocytes on osteoblasts using cells derived from human
mesenchymal stem cells. Bone. 53:520–530. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Corwin RL, Hartman TJ, Maczuga SA and
Graubard BI: Dietary saturated fat intake is inversely associated
with bone density in humans: Analysis of NHANES III. J Nutr.
136:159–165. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Fibbe WE and Noort WA: Mesenchymal stem
cells and hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Ann N Y Acad
Sci. 996:235–244. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Manolagas SC and Parfitt AM: What old
means to bone. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 21:369–374. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Komiya K, Uchida T, Ueno T, Koike M, Abe
H, Hirose T, Kawamori R, Uchiyama Y, Kominami E, Fujitani Y and
Watada H: Free fatty acids stimulate autophagy in pancreatic
β-cells via JNK pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 401:561–567.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Bjørkøy G, Lamark T, Brech A, Outzen H,
Perander M, Overvatn A, Stenmark H and Johansen T: p62/SQSTM1 forms
protein aggregates degraded by autophagy and has a protective
effect on huntingtin-induced cell death. J Cell Biol. 171:603–614.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Liu J, Chang F, Li F, Fu H, Wang J, Zhang
S, Zhao J and Yin D: Palmitate promotes autophagy and apoptosis
through ROS-dependent JNK and p38 MAPK. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
463:262–267. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Cai N, Zhao X, Jing Y, Sun K, Jiao S, Chen
X, Yang H, Zhou Y and Wei L: Autophagy protects against
palmitate-induced apoptosis in hepatocytes. Cell Biosci. 4:282014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Song C, Song C and Tong F: Autophagy
induction is a survival response against oxidative stress in bone
marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cells. Cytotherapy.
16:1361–1370. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Kiffin R, Bandyopadhyay U and Cuervo AM:
Oxidative stress and autophagy. Antioxid Redox Signal. 8:152–162.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Gao D, Nong S, Huang X, Lu Y, Zhao H, Lin
Y, Man Y, Wang S, Yang J and Li J: The effects of palmitate on
hepatic insulin resistance are mediated by NADPH Oxidase 3-derived
reactive oxygen species through JNK and p38MAPK pathways. J Biol
Chem. 285:29965–29973. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Sato Y, Fujimoto S, Mukai E, Sato H,
Tahara Y, Ogura K, Yamano G, Ogura M, Nagashima K and Inagaki N:
Palmitate induces reactive oxygen species production and β-cell
dysfunction by activating nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide
phosphate oxidase through Src signaling. J Diabetes Investig.
5:19–26. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Wei CD, Li Y, Zheng HY, Tong YQ and Dai W:
Palmitate induces H9c2 cell apoptosis by increasing reactive oxygen
species generation and activation of the ERK1/2 signaling pathway.
Mol Med Rep. 7:855–861. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Zhang M, Wang CM, Li J, Meng ZJ, Wei SN,
Li J, Bucala R, Li YL and Chen L: Berberine protects against
palmitate-induced endothelial dysfunction: Involvements of
upregulation of AMPK and eNOS and downregulation of NOX4. Mediators
Inflamm. 2013:2604642013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Klaunig JE, Kamendulis LM and Hocevar BA:
Oxidative stress and oxidative damage in carcinogenesis. Toxicol
Pathol. 38:96–109. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Ghosh J, Das J, Manna P and Sil PC:
Taurine prevents arsenic-induced cardiac oxidative stress and
apoptotic damage: Role of NF-kappa B, p38 and JNK MAPK pathway.
Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 240:73–87. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Manolagas SC: From estrogen-centric to
aging and oxidative stress: A revised perspective of the
pathogenesis of osteoporosis. Endocr Rev. 31:266–300. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Maiuri MC, Zalckvar E, Kimchi A and
Kroemer G: Self-eating and self-killing: Crosstalk between
autophagy and apoptosis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 8:741–752. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Zhang YH, Wu YL, Tashiro S, Onodera S and
Ikejima T: Reactive oxygen species contribute to oridonin-induced
apoptosis and autophagy in human cervical carcinoma HeLa cells.
Acta Pharmacol Sin. 32:1266–1275. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Lv XC and Zhou HY: Resveratrol protects
H9c2 embryonic rat heart derived cells from oxidative stress by
inducing autophagy: role of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase.
Can J Physiol Pharm. 90:655–662. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Dolado I, Swat A, Ajenjo N, De Vita G,
Cuadrado A and Nebreda AR: p38alpha MAP kinase as a sensor of
reactive oxygen species in tumorigenesis. Cancer Cell. 11:191–205.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
West RJ and Sweeney ST: Oxidative stress
and autophagy: Mediators of synapse growth? Autophagy. 8:284–285.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Haberzettl P and Hill BG: Oxidized lipids
activate autophagy in a JNK-dependent manner by stimulating the
endoplasmic reticulum stress response. Redox Biol. 1:56–64. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Xie CM, Chan WY, Yu S, Zhao J and Cheng
CH: Bufalin induces autophagy-mediated cell death in human colon
cancer cells through reactive oxygen species generation and JNK
activation. Free Radic Biol Med. 51:1365–1375. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|