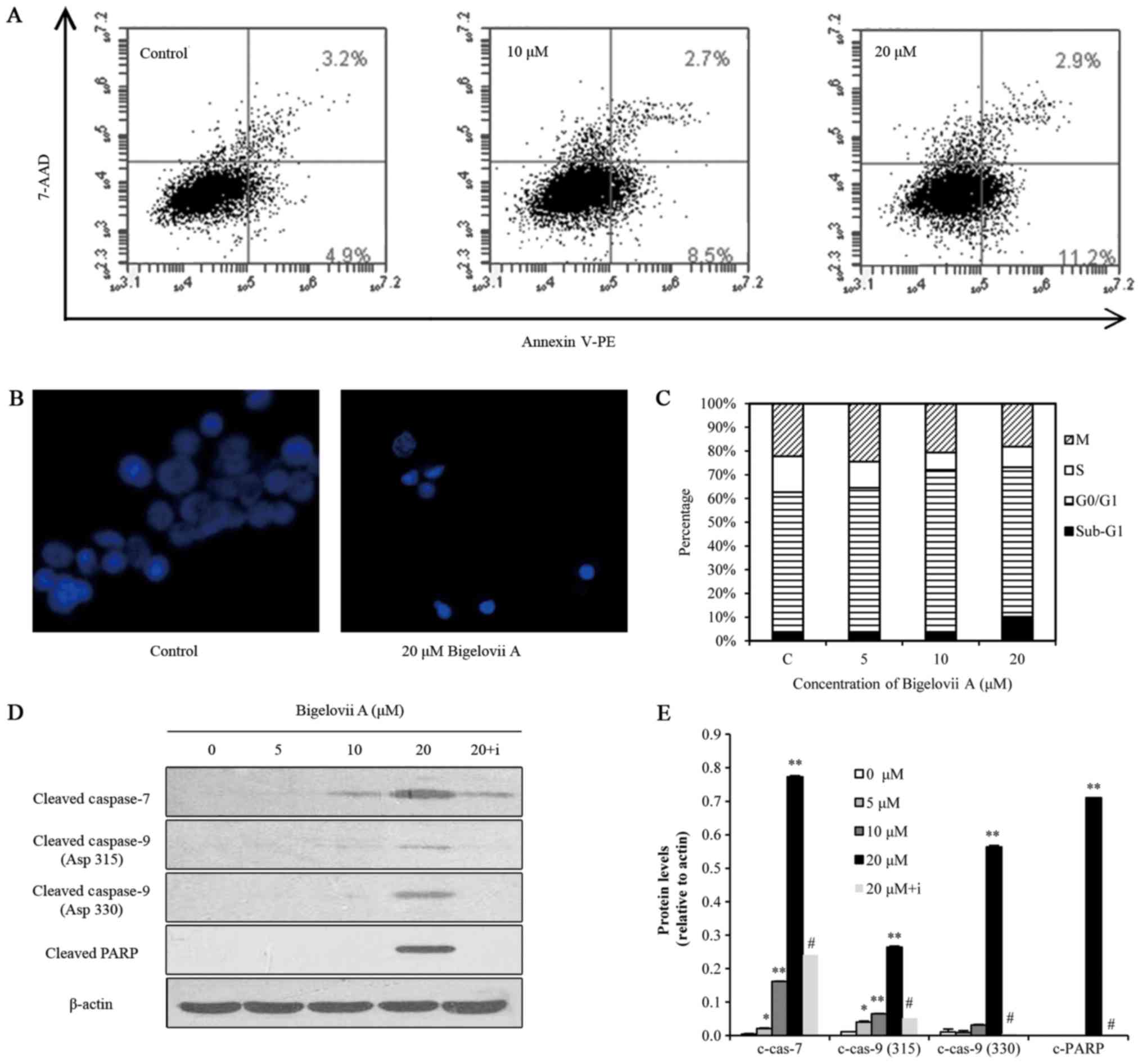
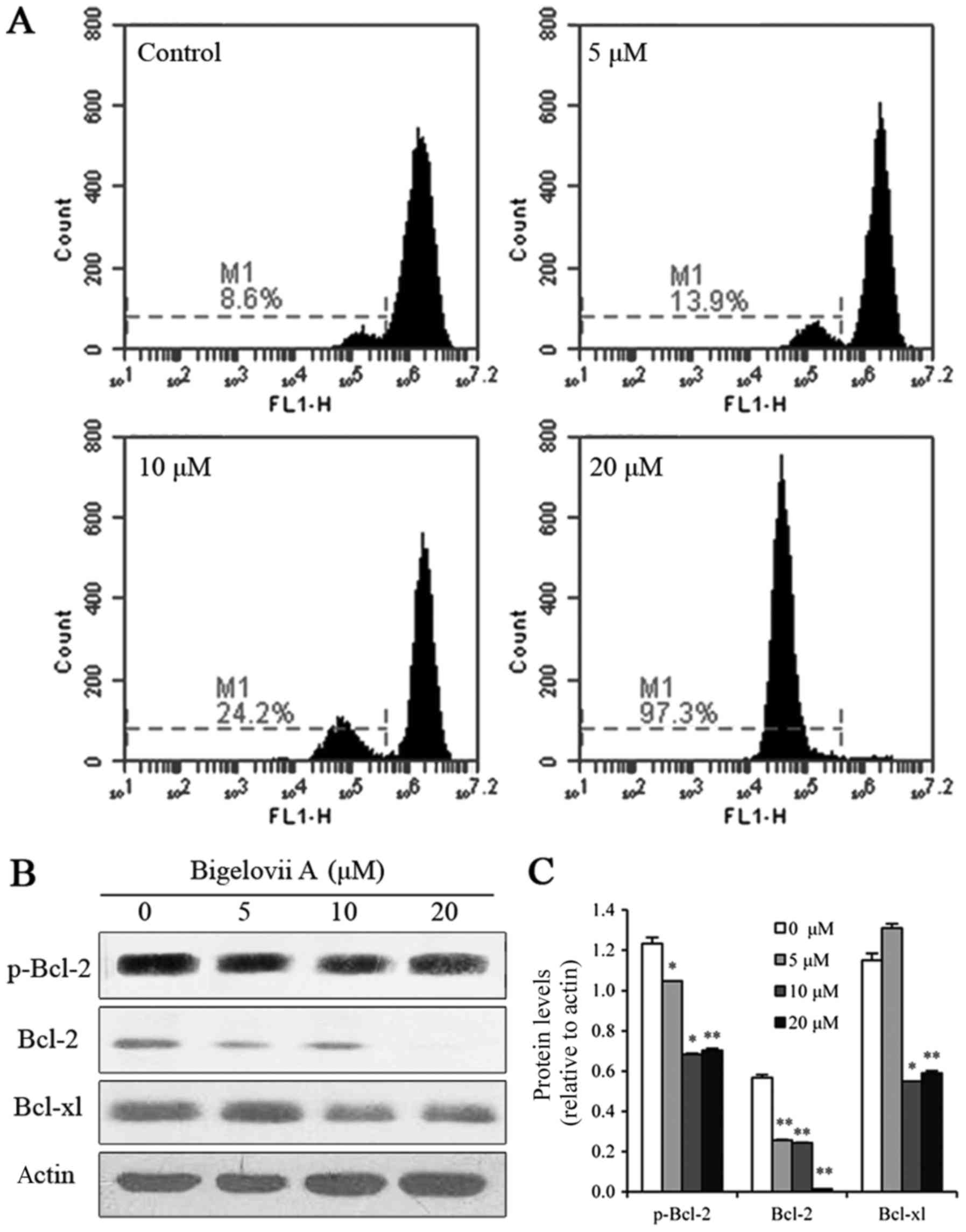
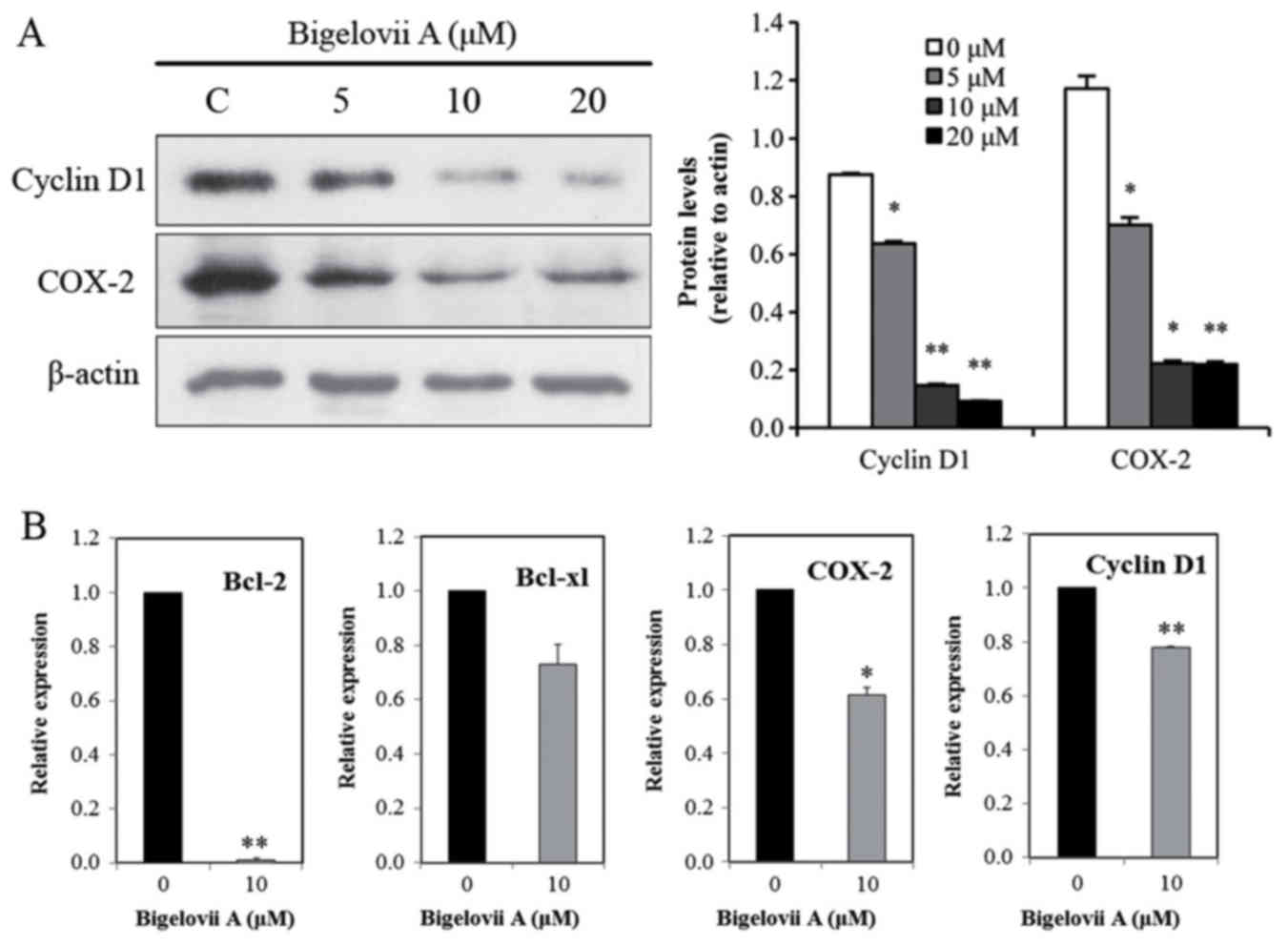
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 65:5–29. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Santa-Maria CA and Gradishar WJ: Changing
treatment paradigms in metastatic breast cancer: Lessons learned.
JAMA Oncol. 1:528–534. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
O'Shaughnessy J: Extending survival with
chemotherapy in metastatic breast cancer. Oncologist. 10:20–29.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ruland J: Return to homeostasis:
Downregulation of NF-κB responses. Nat Immunol. 12:709–714. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chaturvedi MM, Sung B, Yadav VR, Kannappan
R and Aggarwal BB: NF-κB addiction and its role in cancer: ‘One
size does not fit all’. Oncogene. 30:1615–1630. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Fornier MN, Rathkopf D, Shah M, Patil S,
O'Reilly E, Tse AN, Hudis C, Lefkowitz R, Kelsen DP and Schwartz
GK: Phase I dose finding study of weekly docetaxel followed by
flavopiridol for patients with advanced solid tumors. Clin Cancer
Res. 13:5841–5846. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Guan FQ, Shan Y, Zhao YY, Wang QZ, Wang M,
Sun H, Chen Y, Yin M and Feng X: Research development on
pharmacological activities and mechanism of Salicornia
plants. Chin Pharm Bull. 29:1188–1191. 2013.
|
|
8
|
Wang QZ, Liu XF, Shan Y, Guan FQ, Chen Y,
Wang XY, Wang M and Feng X: Two new nortriterpenoid saponins from
Salicornia bigelovii Torr. and their cytotoxic activity.
Fitoterapia. 83:742–749. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yan C, Guan F, Shen Y, Tang H, Yuan D, Gao
H and Feng X: Bigelovii a protects against
lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury by blocking NF-κB and
CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein δ pathways. Mediators Inflamm.
2016:92016042016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Guan FQ, Wang HT, Shan Y, Zhang DM, Zhao
YY, Chen Y, Wang QZ, Wang M and Feng X: Bigelovii A induces
apoptosis of HL60 human acute promyelocytic leukaemia cells. Mol
Med Rep. 7:1585–1590. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Guan F, Wang Q, Wang M, Shan Y, Chen Y,
Yin M, Zhao Y, Feng X, Liu F and Zhang J: Isolation, identification
and cytotoxicity of a new noroleanane-type triterpene saponin from
Salicornia bigelovii Torr. Molecules. 20:6419–6431. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wang F, Cai HY, Zhao Q, Xing T, Li JH and
Wang NS: Epinephrine evokes renalase secretion via
α-adrenoceptor/NF-κB pathways in renal proximal tubular epithelial
cells. Kidney Blood Press Res. 39:252–259. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang F, Zhang G, Lu Z, Geurts A M, Usa K,
Jacob HJ, Cowley AW, Wang N and Liang M: Antithrombin III/SerpinC1
insufficiency exacerbates renal ischemia/reperfusion injury. Kidney
Int. 88:796–803. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Rabi T and Banerjee S: Novel Synthetic
triterpenoid methyl 25-hydroxy-3-oxoolean-12-en-28-oate induces
apoptosis through JNK and p38 MAPK pathways in human breast
adenocarcinoma MCF-7 cells. Mol Carcinog. 47:415–423. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yip KW and Reed JC: Bcl-2 family proteins
and cancer. Oncogene. 27:6398–6406. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sevilla L, Zaldumbide A, Pognonec P and
Boulukos KE: Transcriptional regulation of the bcl-x gene encoding
the antiapoptotic Bcl-xL protein by Ets, Rel/NF-κB, STAT and AP1
transcription factor families. Histol Histopathol. 16:595–601.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zandi E and Karin M: Bridging the gap:
Composition, regulation and physiological function of the IκB
kinase complex. Mol Cell Biol. 19:4547–4551. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Pahl HL: Activators and target genes of
Rel/NF-κB transcription factors. Oncogene. 18:6853–6866. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Plummer SM, Holloway KA, Manson MM, Munks
RJ, Kaptein A, Farrow S and Howells L: Inhibition of
cyclo-oxygenase 2 expression in colon cells by the chemopreventive
agent curcumin involves inhibition of NF-κB activation via the
NIK/IKK signalling complex. Oncogene. 18:6013–6020. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
DeSantis C, Siegel R, Bandi P and Jemal A:
Breast cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 61:409–418. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Bishayee A, Ahmed S, Brankov N and Perloff
M: Triterpenoids as potential agents for the chemoprevention and
therapy of breast cancer. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 16:980–996.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ouyang L, Shi Z, Zhao S, Wang FT, Zhou TT,
Liu B and Bao JK: Programmed cell death pathways in cancer: A
review of apoptosis, autophagy and programmed necrosis. Cell
Prolif. 45:487–498. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ashe PC and Berry MD: Apoptotic signaling
cascades. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 27:199–214.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Gambi N, Tramontano F and Quesada P: Poly
(ADPR)polymerase inhibition and apoptosis induction in cDDP-treated
human carcinoma cell lines. Biochem Pharmacol. 75:2356–2363. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Scovassi AI and Poirier GG: Poly
(ADP-ribosylation) and apoptosis. Mol Cell Biochem. 199:125–137.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Goldberg JE and Schwertfeger KL:
Proinflammatory cytokines in breast cancer: Mechanisms of action
and potential targets for therapeutics. Curr Drug Targets.
11:1133–1146. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Liu B, Sun L, Liu Q, Gong C, Yao Y, Lv X,
Lin L, Yao H, Su F, Li D, et al: A cytoplasmic NF-κB interacting
long noncoding RNA blocks IκB phosphorylation and suppresses breast
cancer metastasis. Cancer Cell. 27:370–381. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wang J, Zhao B, Yi Y, Zhang W, Wu X, Zhang
L and Shen Y: Mycoepoxydiene, a fungal polyketide inhibits MCF-7
cells through simultaneously targeting p53 and NF-κB pathways.
Biochem Pharmacol. 84:891–899. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Shanmugam MK, Dai X, Kumar AP, Tan BK,
Sethi G and Bishayee A: Oleanolic acid and its synthetic
derivatives for the prevention and therapy of cancer: Preclinical
and clinical evidence. Cancer Lett. 346:206–216. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Baldwin AS: Regulation of cell death and
autophagy by IKK and NF-κB: Critical mechanisms in immune function
and cancer. Immunol Rev. 246:327–345. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|