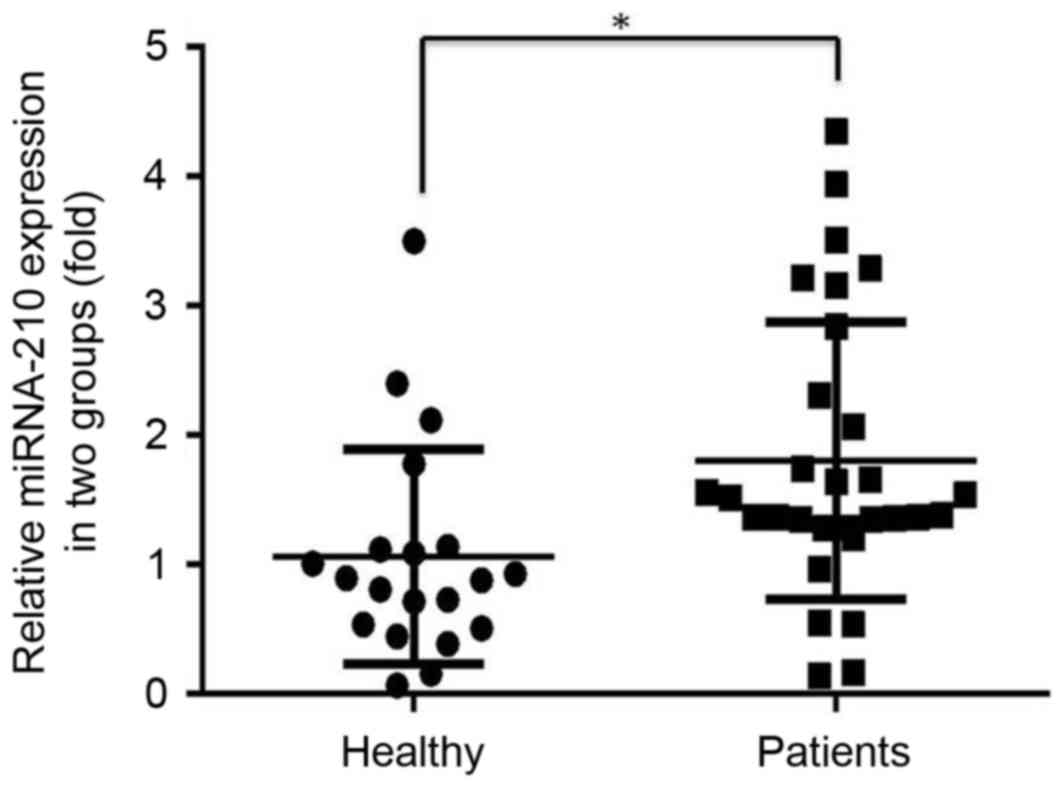
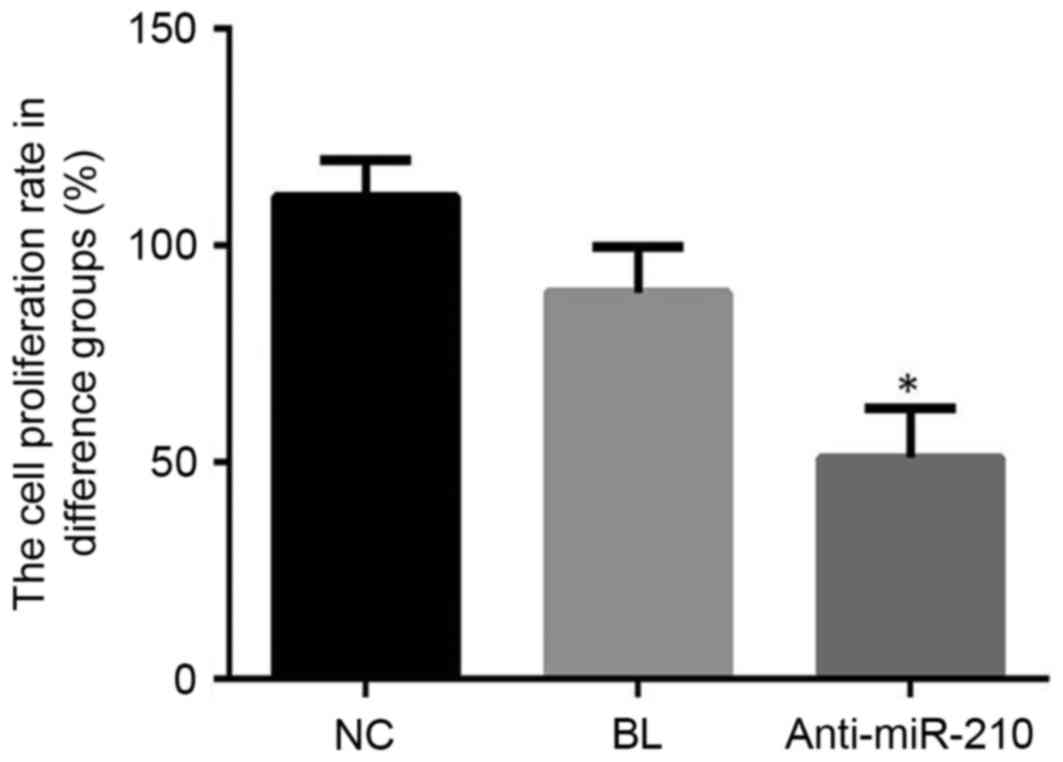
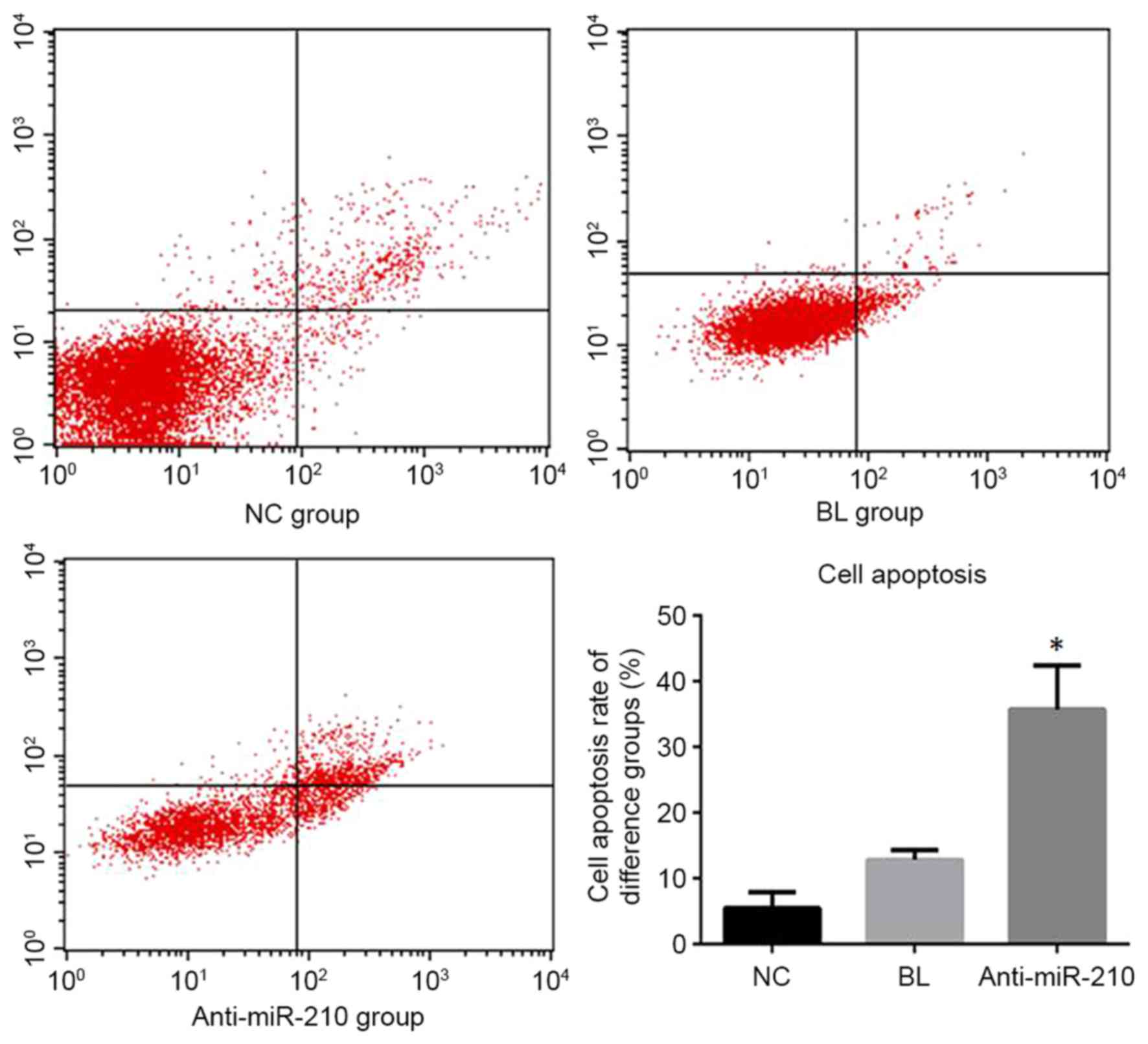
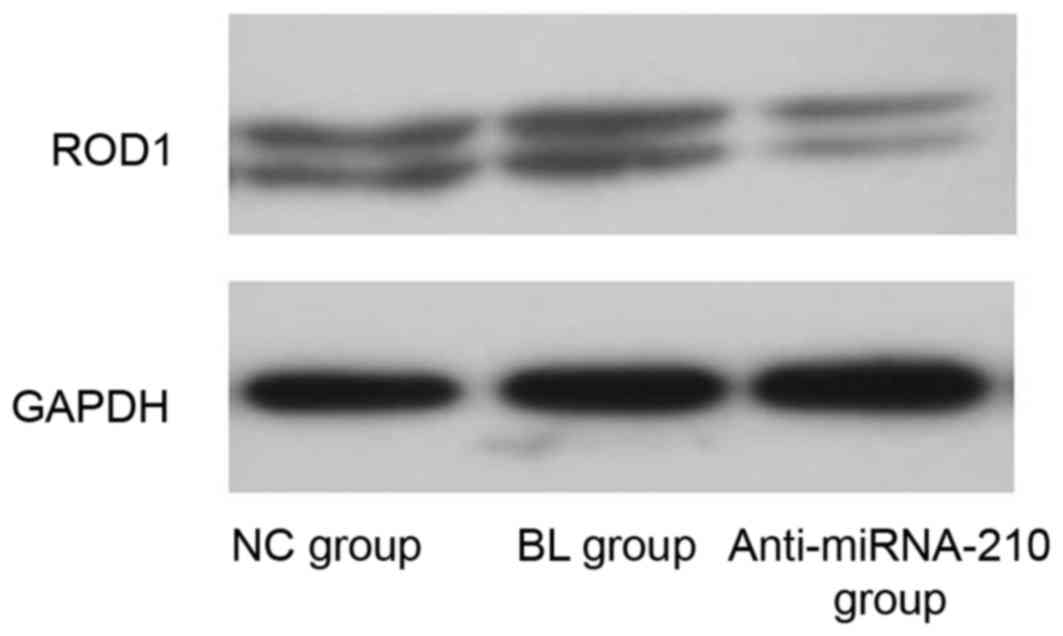
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics 2016. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:7–30. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Santanam U, Banach-Petrosky W, Abate-Shen
C, Shen MM, White E and DiPaola RS: Atg7 cooperates with Pten loss
to drive prostate cancer tumor growth. Genes Dev. 30:399–407. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Miftakhova R, Hedblom A, Semenas J,
Robinson B, Simoulis A, Malm J, Rizvanov A, Heery DM, Mongan NP,
Maitland NJ, et al: Cyclin A1 and P450 aromatase promote metastatic
homing and growth of stem-like prostate cancer cells in the bone
marrow. Cancer Res. 76:2453–2464. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Negrini M and Calin GA: Breast cancer
metastasis: A microRNA story. Breast Cancer Res. 10:2032008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Redova M, Poprach A, Besse A, Iliev R,
Nekvindova J, Lakomy R, Radova L, Svoboda M, Dolezel J, Vyzula R
and Slaby O: MiR-210 expression in tumor tissue and in vitro
effects of its silencing in renal cell carcinoma. Tumour Biol.
34:481–491. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bakirzi K, Law IK, Xue X, Iliopoulos D,
Shah YM and Pothoulakis C: Neurotensin promotes the development of
colitis and intestiinal angiogenesis via Hif-1α-miR-210 signaling.
J Immunol. 196:4311–4321. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Rane JK, Scaravilli M, Ylipää A, Pellacani
D, Mann VM, Simms MS, Nykter M, Collins AT, Visakorpi T and
Maitland NJ: MicroRNA expression profile of primary prostate cancer
stem cells as a source of biomarkers and therapeutic targets. Eur
Urol. 67:7–10. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Alhasan AH, Scott AW, Wu JJ, Feng G, Meeks
JJ, Thaxton CS and Mirkin CA: Circulating microRNA signature for
the diagnosis of very high-risk prostate cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 113:10655–10660. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Li X, Wan X, Chen H, Yang S, Liu Y, Mo W,
Meng D, Du W, Huang Y, Wu H, et al: Identification of miR-133b and
RB1CC1 as independent predictors for biochemical recurrence and
potential therapeutic targets for prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res.
20:2312–2325. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Toyama T, Kondo N, Endo Y, Sugiura H,
Yoshimoto N, Iwasa M, Takahashi S, Fujii Y and Yamashita H: High
expression of microRNA-210 is an independent factor indicating a
poor prognosis in Japanese triple-negative breast cancer patients.
Jpn J Clin Oncol. 42:256–263. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Eilertsen M, Andersen S, Al-Saad S,
Richardsen E, Stenvold H, Hald SM, Al-Shibli K, Donnem T, Busund LT
and Bremnes RM: Positive prognostic impact of miR-210 in non-small
cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 83:272–278. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Neal CS, Michael MZ, Rawlings LH, Van der
Hoek MB and Gleadle JM: The VHL-dependent regulation of microRNAs
in renal cancer. BMC Med. 8:642010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lai NS, Dong QS, Ding H, Miao ZL and Lin
YC: MicroRNA-210 overexpression predicts poorer prognosis in glioma
patients. J Clin Neurosci. 21:755–760. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Cai H, Lin L, Cai H, Tang M and Wang Z:
Prognostic evaluation of microRNA-210 expression in pediatric
osteosarcoma. Med Oncol. 30:4992013.Andersen S, Richardsen E, Moi
L, Donnem T, Nordby Y, Ness N, Holman ME, Bremnes RM and Busund LT:
Fibroblast miR-210 overexpression is independently associated with
clinical failure in prostate cancer-a multicenter (in situ
hybridization) study. Sci Rep 6: 36573, 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bray F and Soerjomataram I: The changing
global burden of cancer: Transitions in human development and
implications for cancer prevention and controlCancer: Disease
Control Priorities. Gelband H, Jha P, Sankaranarayanan R and Horton
S: 3. 3rd edition. The International Bank for Reconstruction and
Development/The World Bank; Washington, DC: 2015
|
|
17
|
Zhang K, Bangma CH and Roobol MJ: Prostate
cancer screening in Europe and Asia. Asian J Urol. 4:86–95. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Riquelme I, Saavedra K, Espinoza JA, Weber
H, García P, Nervi B, Garrido M, Corvalán AH, Roa JC and Bizama C:
Molecular classification of gastric cancer: Towards a
pathway-driven targeted therapy. Oncotarget. 6:24750–24779. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Taylor DD and Gecel-Taylor C: MicroRNA
signatures of tumor-derived exosomes as diagnostic biomarkers of
ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 110:13–21. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chen X, Ba Y, Ma L, Cai X, Yin Y, Wang K,
Guo J, Zhang Y, Chen J, Guo X, et al: Characterization of microRNAs
in serum: A novel class of biomarkers for diagnosis of cancer and
other diseases. Cell Res. 18:997–1006. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Dumont N and Tlsty TD: Reflections on
miR-ing effects in metastais. Cancer Cell. 16:3–4. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Volinia S, Calin GA, Liu CG, Ambs S,
Cimmino A, Petrocca F, Visone R, Iorio M, Roldo C, Ferracin M, et
al: A microRNA expression signature of human solid tumors defines
cancer gene targets. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:2257–2261. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sylvestre Y, De Guire V, Querido E,
Mukhopadhyay UK, Bourdeau V, Major F, Ferbeyre G and Chartrand P:
An E2F/miR-20a autoregulatory feedback loop. J Biol Chem.
282:2135–2143. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
McCormick R, Buffa FM, Ragoussis J and
Harris AL: The role of hypoxia regulated microRNAs in cancer. Curr
Top Microbiol Immunol. 345:47–70. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Tsuchiya S, Fujiwara T, Sato F, Shimada Y,
Tanaka E, Sakai Y, Shimizu K and Tsujimoto G: MicroRNA-210
regulates cancer cell proliferation through targeting fibroblast
growth factor receptor-like 1 (FGFRL1). J Biol Chem. 286:420–428.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
White NM, Bao TT, Grigull J, Youssef YM,
Girgis A, Diamandis M, Fatoohi E, Metias M, Honey RJ, Stewart R, et
al: miRNA profiling for clear cell renal cell carcinoma: Biomarker
discovery and identification of potential controls and consequences
of miRNA dysregulation. J Urol. 186:1077–1083. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhao A, Li G, Péoc'h M, Genin C and
Gigante M: Serum miR-210 as a biomarker for molecular diagnosis of
clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Exp Mol Pathol. 94:115–120. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Shen J, Liu Z, Todd NW, Zhang H, Liao J,
Yu L, Guarnera MA, Li R, Cai L, Zhan M and Jiang F: Diagnosis of
lung cancer in individuals with solitary pulmonary nodules by
plasma microRNA biomarkers. BMC Cancer. 11:3742011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ho AS, Huang X, Cao H, Christman-Skieller
C, Bennewith K, Le QT and Koong AC: Circulating miR-210 as a novel
hypoxia marker in pancreatic cancer. Transl Oncol. 3:109–113. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhang S, Lai N, Liao K, Sun J and Lin Y:
MicroRNA-210 regulates cell proliferation and apoptosis by
targeting regulator of differentiation 1 in glioblastoma cells.
Folia Neuropathol. 53:236–244. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Fasanaro P, Romani S, Voellenkie C,
Maimone B, Capogrossi MC and Martelli F: ROD1 is a seedless target
gene of hypoxia-induced miR-210. PLoS One. 7:e446512012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|