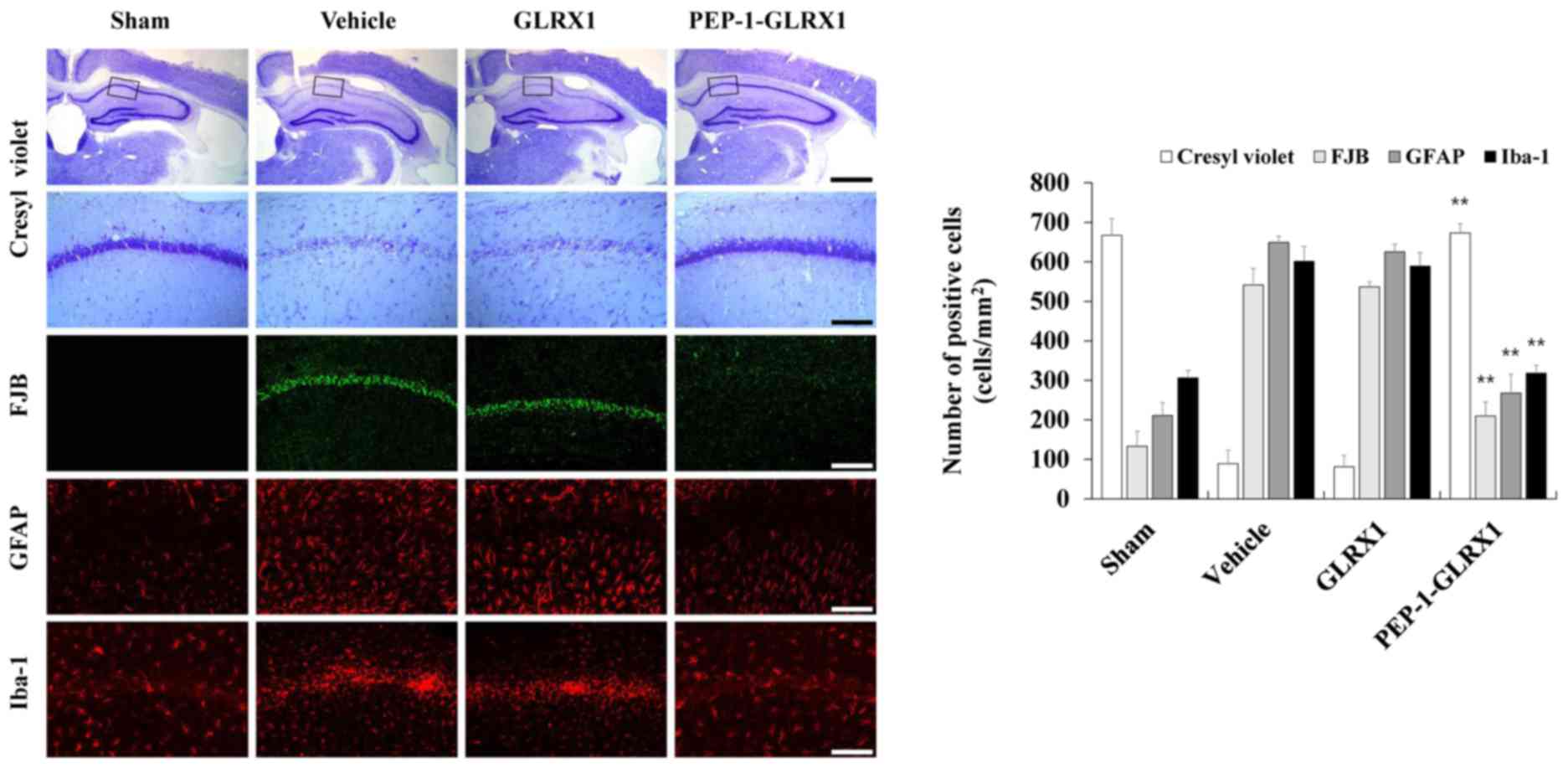
|
1
|
Kirkinezos IG and Moraes CT: Reactive
oxygen species and mitochondrial diseases. Semin Cell Dev Biol.
12:449–457. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Matés JM: Effects of antioxidant enzymes
in the molecular control of reactive oxygen species toxicology.
Toxicology. 153:83–104. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Rice ME, Forman RE, Chen BT, Avshalumov
MV, Cragg SJ and Drew KL: Brain antioxidant regulation in mammals
and anoxia-tolerant reptiles: Balanced for neuroprotection and
neuromodulation. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Phamacol.
133:515–525. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Poljsak B, Šuput D and Milisav I:
Achieving the balance between ROS and antioxidants: When to use the
synthetic antioxidants. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2013:9567922013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Son Y, Cheong YK, Kim NH, Chung HT, Kang
DG and Pae HO: Mitogen-activated protein kinases and reactive
oxygen species: How can ROS activate MAPK pathways? J Signal
Transduct. 2011:7926392011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Saeed U, Durgadoss L, Valli RK, Joshi DC,
Joshi PG and Ravindranath V: Knockdown of cytosolic Glutaredoxin 1
leads to loss of mitochondrial membrane potential: Implication in
neurodegenerative diseases. PLoS One. 3:e24592008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sanderson TH, Reynolds CA, Kumar R,
Przyklenk K and Hüttemann M: Molecular mechanisms of
ischemia-reperfusion injury in brain: Pivotal role of the
mitochondrial membrane potential in reactive oxygen species
generation. Nol Neurobiol. 47:9–23. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Jao SC, Ospina English SM, Berdis AJ,
Starke DW, Post CB and Mieyal JJ: Computational and mutational
analysis of human glutaredoxin (thioltransferase): Probing the
molecular basis of the low pKa of cysteine 22 and its role in
catalysis. Biochemistry. 45:4785–4796. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Okuda M, Inoue N, Azumi H, Seno T, Sumi Y,
Hirata KI, Kawashima S, Hayashi Y, Itoh H, Yodoi J and Yokoyama M:
Expression of glutaredoxin in human coronary arteries: Its
potential role in antioxidant protection against atherosclerosis.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 21:1483–1487. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Pai HV, Starke DW, Lesnefsky EJ, Hoppel CL
and Mieyal JJ: What is the functional significance of the unique
location of glutaredoxin 1 (GRx1) in the intermembrane space of
mitochondria? Antioxid Redox Signal. 9:2027–2033. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Peltoniemi M, Kaarteenaho-Wiik R, Säily M,
Sormunen R, Pääkkö P, Holmgren A, Soini Y and Kinnula VL:
Expression of glutaredoxin is highly cell specific in human lung
and is decreased by transforming growth factor-beta in vitro and in
interstitial lung diseases in vivo. Hum Pathol. 35:1000–1007. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Cater MA, Materia S, Xiao Z, Wolyniec K,
Ackland SM, Yap YW, Cheung NS and La Fontaine S: Glutaredoxin1
protects neuronal cells from copper-induced toxicity. Biometals.
27:661–672. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
El-Andaloussi S, Holm T and Langel U:
Cell-penetrating peptides: Mechanisms and applications. Curr Pharm
Des. 11:3597–3611. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Beerens AM, Al Hadithy AF, Rots MG and
Haisma HJ: Protein transduction domains and their utility in gene
therapy. Curr Gene Ther. 3:486–494. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Morris MC, Depollier J, Mery J, Heitz F
and Divita G: A peptide carrier for the delivery of biologically
active proteins into mammalian cells. Nat Biotechonol.
19:1173–1176. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Ahn EH, Kim DW, Shin MJ, Kim HR, Kim SM,
Woo SJ, Eom SA, Jo HS, Kim DS, Cho SW, et al: PEP-1-PEA-15 protects
against toxin-induced neuronal damage in a mouse model of
Parkinson's disease. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1840:1686–1700. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kim DW, Lee SH, Shin MJ, Kim K, Ku SK,
Youn JK, Cho SB, Park JH, Lee CH, Son O, et al: PEP-1-FK506BP
inhibits alkali burn-induced corneal inflammation on the rat model
of corneal alkali injury. BMB Rep. 48:618–623. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kim HR, Kim DW, Jo HS, Cho SB, Park JH,
Lee CH, Choi YJ, Yeo EJ, Park SY, Kim ST, et al: Tat-biliverdin
reductase A inhibits inflammatory response by regulation of MAPK
and NF-κB pathways in Raw 264.7 cells and edema mouse model. Mol
Immunol. 63:355–366. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kim MJ, Park M, Kim DW, Shin MJ, Son O, Jo
HS, Yeo HJ, Cho SB, Park JH, Lee CH, et al: Transduced PEP-1-PON1
proteins regulate microglial activation and dopaminergic neuronal
death in a Parkinson's disease model. Biomaterials. 64:45–56. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kim YN, Jung HY, Eum WS, Kim DW, Shin MJ,
Ahn EH, Kim SJ, Lee CH, Yong JI, Ryu EJ, et al: Neuroprotective
effects of PEP-1-carbonyl reductase 1 against
oxidative-stress-induced ischemic neuronal cell damage. Free Radic
Biol Med. 69:181–196. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Jo HS, Yeo HJ, Cha HJ, Kim SJ, Cho SB,
Park JH, Lee CH, Yeo EJ, Choi YJ, Eum WS and Choi SY: Transduced
Tat-DJ-1 protein inhibits cytokines-induced pancreatic RINm5F cell
death. BMB Rep. 49:297–302. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Shin MJ, Kim DW, Jo HS, Cho SB, Park JH,
Lee CH, Yeo EJ, Choi YJ, Kim JA, Hwang JS, et al: Tat-PRAS40
prevent hippocampal HT-22 cell death and oxidative stress induced
animal brain ischemic insults. Free Radic Biol Med. 97:250–262.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Bradford MM: A rapid and sensitive method
for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing
the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 72:248–254.
1976. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
An SY, Youn GS, Kim H, Choi SY and Park J:
Celastrol suppresses expression of adhesion molecules and
chemokines by inhibiting JNK-STAT1/NF-κB activation in
poly(I:C)-stimulated astrocytes. BMB Rep. 50:25–30. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Jo HS, Kim DS, Ahn EH, Kim DW, Shim MJ,
Cho SB, Park JH, Lee CH, Yeo EJ, Choi YJ, et al: Protective effects
of Tat-NQO1 against oxidative stress-induced HT-22 cell damage, and
ischemic injury in animals. BMB Rep. 49:617–622. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sohn EJ, Shin MJ, Kim DW, Son O, Jo HS,
Cho SB, Park JH, Lee CH, Yeo EJ, Choi YJ, et al: PEP-1-GSTpi
protein enhanced hippocampal neuronal cell survival after oxidative
damage. BMB Rep. 49:382–387. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Niizuma K, Yoshioka H, Chen H, Kim GS,
Jung JE, Katsu M, Okami N and Chan PH: Mitochondrial and apoptotic
neuronal death signaling pathways in cerebral ischemia. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1802:92–99. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Pradeep H, Diya JB, Shashikumar S and
Rajanikant GK: Oxidative stress-assassin behind the ischemic
stroke. Folia Neuropathol. 50:219–230. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yu JT, Lee CH, Yoo KY, Choi JH, Li H, Park
OK, Yan B, Hwang IK, Kwon YG, Kim YM, et al: Maintenance of
anti-inflammatory cytokines and reduction of glial activation in
the ischemic hippocampal CA1 region preconditioned with
lipopolysaccharide. J Neurol Sci. 296:69–78. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Bachschmid MM, Xu S, Maitland-Toolan KA,
Ho YS, Cohen RA and Matsui R: Attenuated cardiovascular hypertrophy
and oxidant generation in response to angiotensin II infusion in
glutaredoxin-1 knockout mice. Free Radic Biol Med. 49:1221–1229.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Murata H, Ihara Y, Nakamura H, Yodoi J,
Sumikawa K and Kondo T: Glutaredoxin exerts an antiapoptotic effect
by regulating the redox state of Akt. J Biol Chem. 278:50226–50233.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Akterin S, Cowburn RF, Miranda-Vizuete A,
Jiménez A, Bogdanovic N, Winblad B and Cedazo-Minguez A:
Involvement of glutaredoxin-1 and thioredoxin-1 in beta-amyloid
toxicity and Alzheimer's disease. Cell Death Differ. 13:1454–1465.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Joliot A and Prochiantz A: Transduction
peptides: From technology to physiology. Nat Cell Biol. 6:189–196.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Dietz GP: Cell-penetrating peptide
technology to deliver chaperones and associated factors in diseases
and basic research. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 11:167–174. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Popiel HA, Nagai Y, Fujikake N and Toda T:
Protein transduction domain-mediated delivery of QBP1 suppresses
polyglutamine-induced neurodegeneration in vivo. Mol Ther.
15:303–309. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Barrera G: Oxidative stress and lipid
peroxidation products in cancer progression and therapy. ISRN
Oncol. 2012:1372892012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Emerit J, Edeas M and Bricaire F:
Neurodegenerative diseases and oxidative stress. Biomed
Pharmacother. 58:39–46. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ho YS, Xiong Y, Ho DS, Gao J, Chua BH, Pai
H and Mieyal JJ: Targeted disruption of the glutaredoxin 1 gene
does not sensitize adult mice to tissue injury induced by
ischemia/reperfusion and hyperoxia. Free Radic Biol Med.
43:1299–1312. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Valavanidis A, Vlachogianni T and Fiotakis
C: 8-hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine (8-OHdG): A critical biomarker of
oxidative stress and carcinogenesis. J Environ Sci Health C Environ
Carcinog Ecotoxicol Rev. 27:120–139. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Lahair MM, Howe CJ, Rodriguez-Mora O,
McCubrey JA and Franklin RA: Molecular pathways leading to
oxidative stress-induced phosphorylation of Akt. Antioxid Redox
signal. 8:1749–1756. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Kwon SH, Hong SI, Kim JA, Jung YH, Kim SY,
Kim HC, Lee SY and Jang CG: The neuroprotective effects of
Lonicera japonica THUNB. Against hydrogen peroxide-induced
apoptosis via phosphorylation of MAPKs and PI3K/Akt in SH-SY5Y
cells. Food Chem Toxicol. 49:1011–1019. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Hwang SL and Yen GC: Modulation of Akt,
JNK, and p38 activation is involved in citrus flavonoid-mediated
cytoprotection of PC12 cells challenged by hydrogen peroxide. J
Agric Food Chem. 57:2576–2582. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Yang B, Oo TN and Rizzo V: Lipid rafts
mediate H2O2 prosurvival effects in cultured endothelial cells.
FASEB J. 20:1501–1503. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Ruffels J, Griffin M and Dickenson JM:
Activation of ERK1/2, JNK and PKB by hydrogen peroxide in human
SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells: Role of ERK1/2 in H2O2-induced cell
death. Eur J Pharmacol. 483:163–173. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Liu X, Jann J, Xavier C and Wu H:
Glutaredoxin 1 (Grx1) protects human retinal pigment epithelial
cells from oxidative damage by preventing AKT glutathionylation.
Invest Ophtalmol Vis Sci. 56:2821–2832. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Fulda S, Gorman AM, Hori O and Samali A:
Cellular stress responses: Cell survival and cell death. Int J Cell
Biol. 2010:2140742010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Villegas SN, Njaine B, Linden R and Carri
NG: Glial-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) prevents ethanol
(EtOH) induced B92 glial cell death by both PI3K/AKT and MEK/ERK
signaling pathways. Brain Res Bull. 71:116–126. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Reddy PH: Role of mitochondria in
neurodegenerative diseases: Mitochondria as a therapeutic target in
Alzheimer's disease. CNS Spectr. 14 8 Suppl 7:8–13; discussion
16-8. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Gupta S, Kass GE, Szeqezdi E and Joseph B:
The mitochondrial death pathway: A promising therapeutic target in
diseases. J Cell Mol Med. 13:1004–1033. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Gu ZT, Wang H, Li L, Liu YS, Deng XB, Huo
SF, Yuan FF, Liu ZF, Tong HS and Su L: Heat stress induces
apoptosis through transcription-independent p53-mediated
mitochondrial pathways in human umbilical vein endothelial cell.
Sci Rep. 4:44692014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Niizuma K, Endo H and Chan PH: Oxidative
stress and mitochondrial dysfunction as determinants of ischemic
neuronal death and survival. J Neurochem. 1 109 Suppl:133–138.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Zhang S, Ong CN and Shen HM: Involvement
of proapoptotic Bcl-2 family members in parthenolide-induced
mitochondrial dysfunction and apoptosis. Cancer Lett. 211:175–188.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Würstle ML, Laussmann MA and Rehm M: The
central role of initiator caspase-9 in apoptosis signal
transduction and the regulation of its activation and activity on
the apoptosome. Exp Cell Res. 318:1213–1220. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Kalogeris T, Baines CP, Krenz M and
Korthuis RJ: Cell biology of ischemia/reperfusion injury. Int Rev
Cell Mol Biol. 298:229–317. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Ito D, Tanaka K, Suzuki S, Dembo T and
Fukuuchi Y: Enhanced expression of Iba1, ionized calcium-binding
adapter molecule 1, after transient focal cerebral ischemia in rat
brain. Stroke. 32:1208–1215. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Chen Y and Swanson RA: Astrocytes and
brain Injury. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 23:137–149. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|