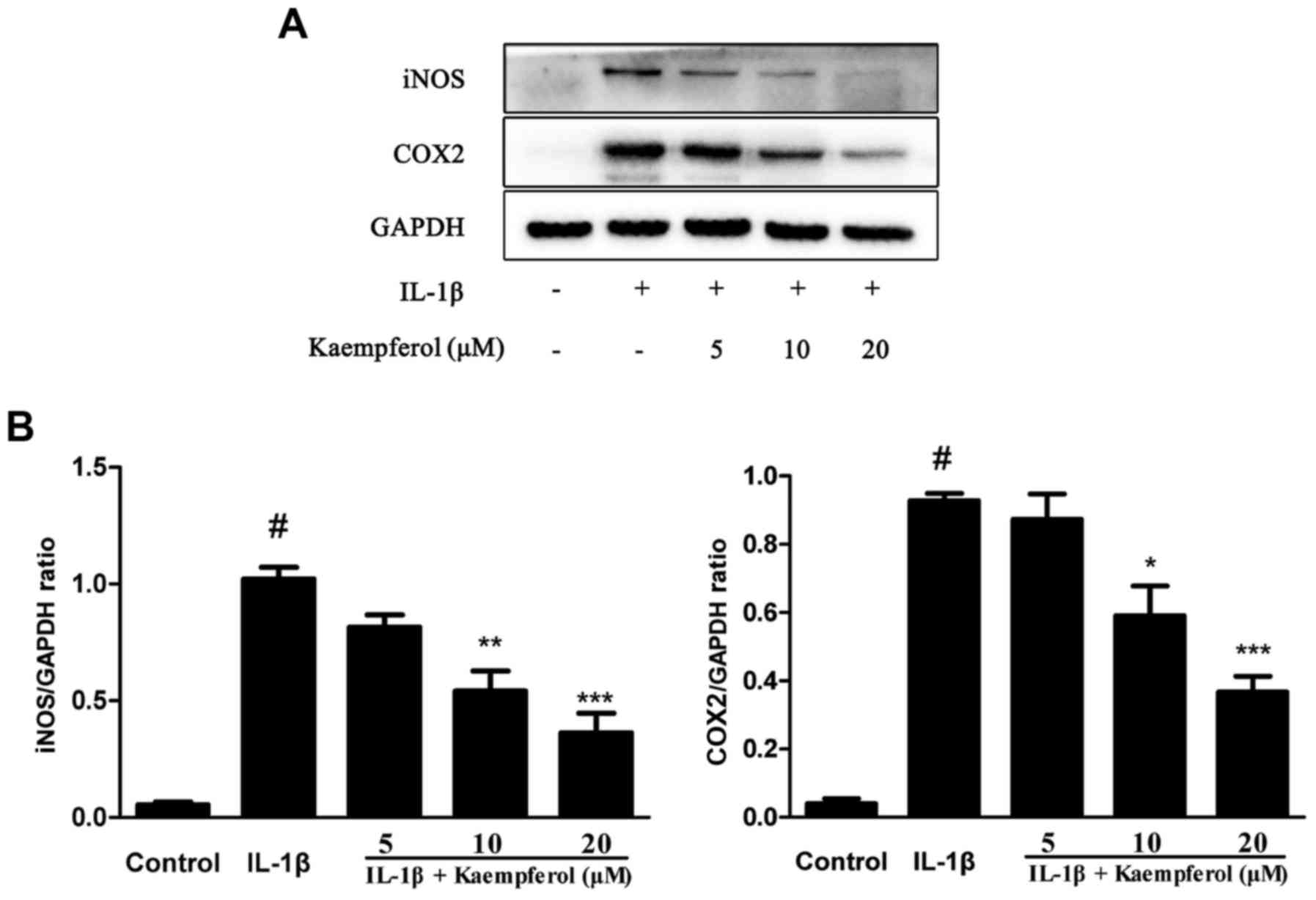
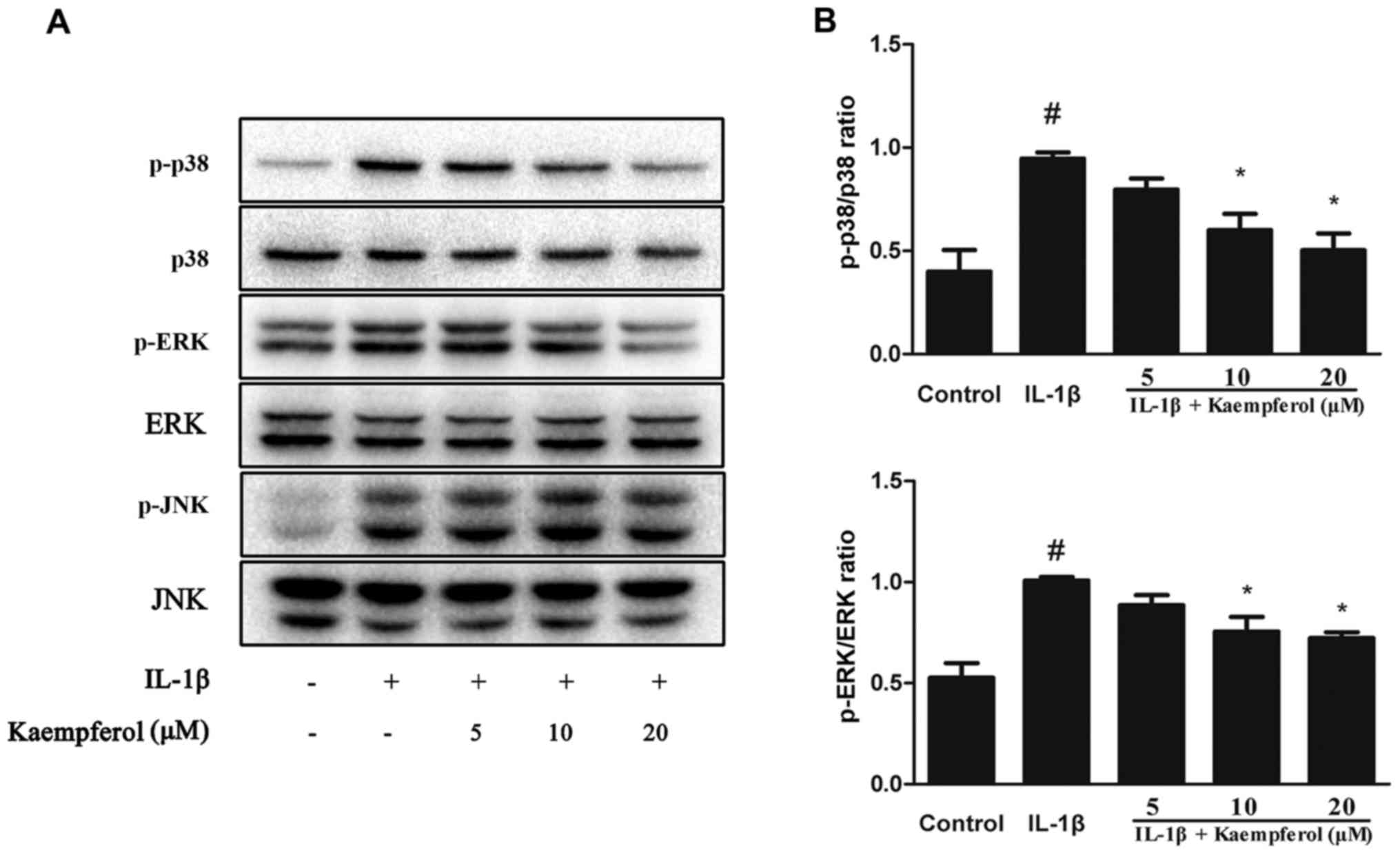
|
1
|
Wieland HA, Michaelis M, Kirschbaum BJ and
Rudolphi KA: Osteoarthritis-an untreatable disease? Nat Rev Drug
Discov. 4:331–344. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Goldring MB and Goldring SR: Articular
cartilage and subchondral bone in the pathogenesis of
osteoarthritis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1192:230–237. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Felson DT: Developments in the clinical
understanding of osteoarthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 11:2032009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wallace IJ, Worthington S, Felson DT,
Jurmain RD, Wren KT, Maijanen H, Woods RJ and Lieberman DE: Knee
osteoarthritis has doubled in prevalence since the mid-20th
century. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 114:9332–9336. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Filardo G, Kon E, Longo UG, Madry H,
Marchettini P, Marmotti A, Van Assche D, Zanon G and Peretti GM:
Non-surgical treatments for the management of early osteoarthritis.
Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 24:1775–1785. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Heinegård D and Saxne T: The role of the
cartilage matrix in osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 7:50–56.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Goldring MB, Otero M, Plumb DA, Dragomir
C, Favero M, El Hachem K, Hashimoto K, Roach HI, Olivotto E, Borzì
RM and Marcu KB: Roles of inflammatory and anabolic cytokines in
cartilage metabolism: Signals and multiple effectors converge upon
MMP-13 regulation in osteoarthritis. Eur Cell Mater. 21:202–220.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Mitchell PG, Magna HA, Reeves LM,
Lopresti-Morrow LL, Yocum SA, Rosner PJ, Geoghegan KF and Hambor
JE: Cloning, expression, and type II collagenolytic activity of
matrix metalloproteinase-13 from human osteoarthritic cartilage. J
Clin Invest. 97:761–768. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kobayashi M, Squires GR, Mousa A, Tanzer
M, Zukor DJ, Antoniou J, Feige U and Poole AR: Role of
interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor alpha in matrix degradation
of human osteoarthritic cartilage. Arthritis Rheum. 52:128–135.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Fermor B, Christensen SE, Youn I, Cernanec
JM, Davies CM and Weinberg JB: Oxygen, nitric oxide and articular
cartilage. Eur Cell Mater. 13:56–65. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Abramson SB, Attur M, Amin AR and Clancy
R: Nitric oxide and inflammatory mediators in the perpetuation of
osteoarthritis. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 3:535–541. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Henrotin Y, Lambert C, Couchourel D,
Ripoll C and Chiotelli E: Nutraceuticals: Do they represent a new
era in the management of osteoarthritis?-a narrative review from
the lessons taken with five products. Osteoarthritis Cartilage.
19:1–21. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Calderón-Montaño JM, Burgos-Morón E,
Pérez-Guerrero C and López-Lázaro M: A review on the dietary
flavonoid kaempferol. Mini Rev Med Chem. 11:298–344. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chen AY and Chen YC: A review of the
dietary flavonoid, kaempferol on human health and cancer
chemoprevention. Food Chem. 138:2099–2107. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Panahi Y, Alishiri GH, Bayat N, Hosseini
SM and Sahebkar A: Efficacy of Elaeagnus Angustifolia
extract in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis: A randomized
controlled trial. EXCLI J. 15:203–210. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhou Y, Zhou Y, Tao H, Li Y, Deng M, He B,
Xia S, Zhang C and Liu S: Berberine promotes proliferation of
sodium nitroprusside-stimulated rat chondrocytes and osteoarthritic
rat cartilage via Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Eur J Pharmacol.
789:109–118. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Rahmati M, Mobasheri A and Mozafari M:
Inflammatory mediators in osteoarthritis: A critical review of the
state-of-the-art, current prospects, and future challenges. Bone.
85:81–90. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Dieppe PA and Lohmander LS: Pathogenesis
and management of pain in osteoarthritis. Lancet. 365:965–973.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wojdasiewicz P, Poniatowski ŁA and
Szukiewicz D: The role of inflammatory and anti-inflammatory
cytokines in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Mediators Inflamm.
2014:5614592014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Goldring MB and Otero M: Inflammation in
osteoarthritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 23:471–478. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Berenbaum F: Osteoarthritis as an
inflammatory disease (osteoarthritis is not osteoarthrosis!).
Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 21:16–21. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Stöve J, Huch K, Günther KP and Scharf HP:
Interleukin-1beta induces different gene expression of stromelysin,
aggrecan and tumor-necrosis-factor-stimulated gene 6 in human
osteoarthritic chondrocytes in vitro. Pathobiology. 68:144–149.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Gu H, Jiao Y, Yu X, Li X, Wang W, Ding L
and Liu L: Resveratrol inhibits the IL-1β-induced expression of
MMP-13 and IL-6 in human articular chondrocytes via
TLR4/MyD88-dependent and -independent signaling cascades. Int J Mol
Med. 39:734–740. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lei M, Wang JG, Xiao DM, Fan M, Wang DP,
Xiong JY, Chen Y, Ding Y and Liu SL: Resveratrol inhibits
interleukin 1β-mediated inducible nitric oxide synthase expression
in articular chondrocytes by activating SIRT1 and thereby
suppressing nuclear factor-κB activity. Eur J Pharmacol. 674:73–79.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Saklatvala J: Inflammatory signaling in
cartilage: MAPK and NF-kappaB pathways in chondrocytes and the use
of inhibitors for research into pathogenesis and therapy of
osteoarthritis. Curr Drug Targets. 8:305–313. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zeng L, Rong XF, Li RH and Wu XY: Icariin
inhibits MMP-1, MMP-3 and MMP-13 expression through MAPK pathways
in IL-1β-stimulated SW1353 chondrosarcoma cells. Mol Med Rep.
15:2853–2858. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Jeong JW, Lee HH, Lee KW, Kim KY, Kim SG,
Hong SH, Kim GY, Park C, Kim HK, Choi YW and Choi YH: Mori folium
inhibits interleukin-1β-induced expression of matrix
metalloproteinases and inflammatory mediators by suppressing the
activation of NF-κB and p38 MAPK in SW1353 human chondrocytes. Int
J Mol Med. 37:452–460. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kim SK, Kim HJ, Choi SE, Park KH, Choi HK
and Lee MW: Anti-oxidative and inhibitory activities on nitric
oxide (NO) and prostaglandin E2 (COX-2) production of flavonoids
from seeds of Prunus tomentosa Thunberg. Arch Pharm Res.
31:424–428. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hämäläinen M, Nieminen R, Vuorela P,
Heinonen M and Moilanen E: Anti-inflammatory effects of flavonoids:
genistein, kaempferol, quercetin, and daidzein inhibit STAT-1 and
NF-kappaB activations, whereas flavone, isorhamnetin, naringenin,
and pelargonidin inhibit only NF-kappaB activation along with their
inhibitory effect on iNOS expression and NO production in activated
macrophages. Mediators Inflamm. 2007:456732007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yoon HY, Lee EG, Lee H, Cho IJ, Choi YJ,
Sung MS, Yoo HG and Yoo WH: Kaempferol inhibits IL-1β-induced
proliferation of rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts and the
production of COX-2, PGE2 and MMPs. Int J Mol Med. 32:971–977.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lim H, Park H and Kim HP: Effects of
flavonoids on matrix metalloproteinase-13 expression of
interleukin-1β-treated articular chondrocytes and their cellular
mechanisms: Inhibition of c-Fos/AP-1 and JAK/STAT signaling
pathways. J Pharmacol Sci. 116:221–231. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Chang CC, Hsieh MS, Liao ST, Chen YH,
Cheng CW, Huang PT, Lin YF and Chen CH: Hyaluronan regulates PPARγ
and inflammatory responses in IL-1β-stimulated human chondrosarcoma
cells, a model for osteoarthritis. Carbohydr Polym. 90:1168–1175.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Gebauer M, Saas J, Sohler F, Haag J, Söder
S, Pieper M, Bartnik E, Beninga J, Zimmer R and Aigner T:
Comparison of the chondrosarcoma cell line SW1353 with primary
human adult articular chondrocytes with regard to their gene
expression profile and reactivity to IL-1beta. Osteoarthritis
Cartilage. 13:697–708. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zhuang Z, Zhuang Z, Ye G and Huang B:
Kaempferol alleviates the interleukin-1β-induced inflammation in
rat osteoarthritis chondrocytes via suppression of NF-κB. Med Sci
Monit. 23:3925–3931. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|