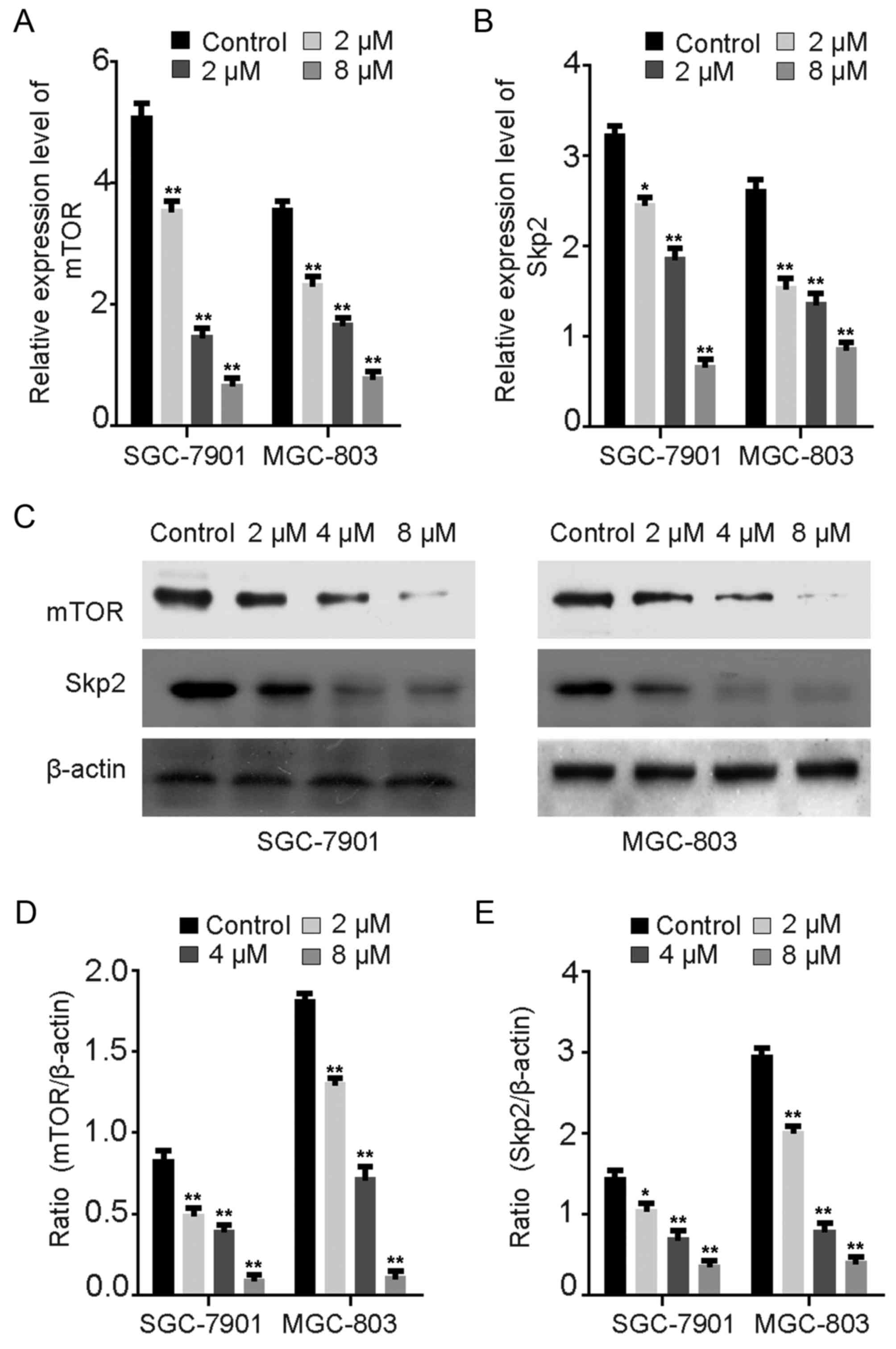
|
1
|
Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 64:9–29. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zeng YJ, Zhang CD and Dai DQ: Impact of
lymph node micrometastasis on gastric carcinoma prognosis: A
meta-analysis. World J Gastroenterol. 21:1628–1635. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Deng JY and Liang H: Clinical significance
of lymph node metastasis in gastric cancer. World J Gastroenterol.
20:3967–3975. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Russo GL: Ins and outs of dietary
phytochemicals in cancer chemoprevention. Biochem Pharmacol.
74:533–544. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Orlikova B and Diederich M: Power from the
garden: Plant compounds as inhibitors of the hallmarks of cancer.
Curr Med Chem. 19:2061–2087. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ji S, Orlikova B and Diederich M:
Non-edible plants as an attractive source of compounds with
chemopreventive potential. J Cancer Prev. 19:1–6. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Gschwendt M, Müller HJ, Kielbassa K, Zang
R, Kittstein W, Rincke G and Marks F: Rottlerin, a novel protein
kinase inhibitor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 199:93–98. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Maioli E, Torricelli C and Valacchi G:
Rottlerin and cancer: Novel evidence and mechanisms.
ScientificWorldJournal. 2012:3508262012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Nguyen BT, Park M, Pyun JC, Yoo YS and
Kang MJ: Efficient PKC inhibitor screening achieved using a
quantitative CE-LIF assay. Electrophoresis. 37:3146–3153. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang X, Tan C, Wang G, Cai JJ, Wang LP,
Imperato-McGinley J and Zhu YS: Dual action of NSC606985 on cell
growth and apoptosis mediated through PKCδ in prostatic cancer
cells. Int J Oncol. 51:1601–1610. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yin X, Zhang Y, Su J, Hou Y, Wang L, Ye X,
Zhao Z, Zhou X, Li Y and Wang Z: Rottlerin exerts its anti-tumor
activity through inhibition of Skp2 in breast cancer cells.
Oncotarget. 7:66512–66524. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lin CJ, Lin CY, Chen Y, Huang SH and Wang
SM: Rottlerin inhibits migration of follicular thyroid carcinoma
cells by PKCdelta-independent destabilization of the focal adhesion
complex. J Cell Biochem. 110:428–437. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Su J, Wang L, Yin X, Zhao Z, Hou Y, Ye X,
Zhou X and Wang Z: Rottlerin exhibits anti-cancer effect through
inactivation of S phase kinase-associated protein 2 in pancreatic
cancer cells. Am J Cancer Res. 6:2178–2191. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Mizushima N and Klionsky DJ: Protein
turnover via autophagy: Implications for metabolism. Annu Rev Nutr.
27:19–40. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Choi KS: Autophagy and cancer. Exp Mol
Med. 44:109–120. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Choi AM, Ryter SW and Levine B: Autophagy
in human health and disease. N Engl J Med. 368:651–662. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Morselli E, Galluzzi L, Kepp O, Vicencio
JM, Criollo A, Maiuri MC and Kroemer G: Anti- and pro-tumor
functions of autophagy. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1793:1524–1532. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Brech A, Ahlquist T, Lothe RA and Stenmark
H: Autophagy in tumour suppression and promotion. Mol Oncol.
3:366–375. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Moretti L, Yang ES, Kim KW and Lu B:
Autophagy signaling in cancer and its potential as novel target to
improve anticancer therapy. Drug Resist Updat. 10:135–143. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kumar D, Shankar S and Srivastava RK:
Rottlerin induces autophagy and apoptosis in prostate cancer stem
cells via PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. Cancer Lett.
343:179–189. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Song KS, Kim JS, Yun EJ, Kim YR, Seo KS,
Park JH, Jung YJ, Park JI, Kweon GR, Yoon WH, et al: Rottlerin
induces autophagy and apoptotic cell death through a
PKC-delta-independent pathway in HT1080 human fibrosarcoma cells:
The protective role of autophagy in apoptosis. Autophagy.
4:650–658. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Torricelli C, Daveri E, Salvadori S,
Valacchi G, Ietta F, Muscettola M, Carlucci F and Maioli E:
Phosphorylation-independent mTORC1 inhibition by the autophagy
inducer Rottlerin. Cancer Lett. 360:17–27. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Parmer TG, Ward MD and Hait WN: Effects of
rottlerin, an inhibitor of calmodulin-dependent protein kinase III,
on cellular proliferation, viability, and cell cycle distribution
in malignant glioma cells. Cell Growth Differ. 8:327–334.
1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Deretic V, Delgado M, Vergne I, Master S,
De Haro S, Ponpuak M and Singh S: Autophagy in immunity against
mycobacterium tuberculosis: A model system to dissect immunological
roles of autophagy. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 335:169–188.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ohno I, Eibl G, Odinokova I, Edderkaoui M,
Damoiseaux RD, Yazbec M, Abrol R, Goddard WA III, Yokosuka O,
Pandol SJ and Gukovskaya AS: Rottlerin stimulates apoptosis in
pancreatic cancer cells through interactions with proteins of the
Bcl-2 family. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 298:G63–G73.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Matsui N, Yoshioka R, Nozawa A, Kobayashi
N, Shichijo Y, Yoshikawa T and Akagi M: Caspase-independent
apoptosis induced by reperfusion following ischemia without bile
duct occlusion in rat liver. Biol Pharm Bull. 40:104–107. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhang M, Harashima N, Moritani T, Huang W
and Harada M: The roles of ROS and caspases in TRAIL-induced
apoptosis and necroptosis in human pancreatic cancer cells. PLoS
One. 10:e01273862015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Torricelli C, Salvadori S, Valacchi G,
Souček K, Slabáková E, Muscettola M, Volpi N and Maioli E:
Alternative pathways of cancer cell death by rottlerin: Apoptosis
versus autophagy. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.
2012:9806582012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wu H, Wang Y, Wang X, Li R and Yin D:
MicroRNA-365 accelerates cardiac hypertrophy by inhibiting
autophagy via the modulation of Skp2 expression. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 484:304–310. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chang HM, Okwuosa TM, Scarabelli T,
Moudgil R and Yeh ETH: Cardiovascular complications of cancer
therapy: Best practices in diagnosis, prevention, and management:
Part 2. J Am Coll Cardiol. 70:2552–2565. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kidane B, Sulman J, Xu W, Kong QQ, Wong R,
Knox JJ and Darling GE: Baseline measure of health-related quality
of life (Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy-Esophagus) is
associated with overall survival in patients with esophageal
cancer. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 151:1571–1580. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ngo D, Jia JB, Green CS, Gulati AT and
Lall C: Cancer therapy related complications in the liver,
pancreas, and biliary system: An imaging perspective. Insights
Imaging. 6:665–677. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Tuorkey MJ: Cancer therapy with
phytochemicals: Present and future perspectives. Biomed Environ
Sci. 28:808–819. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Rao CV, Wang CX, Simi B, Lubet R, Kelloff
G, Steele V and Reddy BS: Enhancement of experimental colon cancer
by genistein. Cancer Res. 57:3717–3722. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Siddique YH, Ara G, Beg T, Gupta J and
Afzal M: Assessment of cell viability, lipid peroxidation and
quantification of DNA fragmentation after the treatment of
anticancerous drug mitomycin C and curcumin in cultured human blood
lymphocytes. Exp Toxicol Pathol. 62:503–508. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Basu A, Adkins B and Basu C:
Down-regulation of caspase-2 by rottlerin via protein kinase
C-delta-independent pathway. Cancer Res. 68:2795–2802. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zhao Z, Zheng N, Wang L, Hou Y, Zhou X and
Wang Z: Rottlerin exhibits antitumor activity via down-regulation
of TAZ in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncotarget. 8:7827–7838.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ashkenazi A and Dixit VM: Death receptors:
Signaling and modulation. Science. 281:1305–1308. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Parrish AB, Freel CD and Kornbluth S:
Cellular mechanisms controlling caspase activation and function.
Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 5:a0086722013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Shukla S, Fu P and Gupta S: Apigenin
induces apoptosis by targeting inhibitor of apoptosis proteins and
Ku70-Bax interaction in prostate cancer. Apoptosis. 19:883–894.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Podmirseg SR, Jakel H, Ranches GD,
Kullmann MK, Sohm B, Villunger A, Lindner H and Hengst L: Caspases
uncouple p27(Kip1) from cell cycle regulated degradation and
abolish its ability to stimulate cell migration and invasion.
Oncogene. 35:4580–4590. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Yoneyama M, Shiba T, Yamaguchi T and Ogita
K: Possible involvement of caspases in proliferation of neocortical
neural stem/progenitor cells in the developing mouse brain. Biol
Pharm Bull. 37:1699–1703. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Frejlich E, Rudno-Rudzińska J, Janiszewski
K, Salomon L, Kotulski K, Pelzer O, Grzebieniak Z, Tarnawa R and
Kielan W: Caspases and their role in gastric cancer. Adv Clin Exp
Med. 22:593–602. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Singh BN, Kumar D, Shankar S and
Srivastava RK: Rottlerin induces autophagy which leads to apoptotic
cell death through inhibition of PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in human
pancreatic cancer stem cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 84:1154–1163.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Ouyang L, Zhang L, Fu L and Liu B: A
small-molecule activator induces ULK1-modulating
autophagy-associated cell death in triple negative breast cancer.
Autophagy. 13:777–778. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Sun L, Hu L, Cogdell D, Lu L, Gao C, Tian
W, Zhang Z, Kang Y, Fleming JB and Zhang W: MIR506 induces
autophagy-related cell death in pancreatic cancer cells by
targeting the STAT3 pathway. Autophagy. 13:703–714. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Parzych KR and Klionsky DJ: An overview of
autophagy: Morphology, mechanism, and regulation. Antioxid Redox
Signal. 20:460–473. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Yu T, Guo F, Yu Y, Sun T, Ma D, Han J,
Qian Y, Kryczek I, Sun D, Nagarsheth N, et al: Fusobacterium
nucleatum promotes chemoresistance to colorectal cancer by
modulating autophagy. Cell. 170(548–563): e5162017.
|
|
50
|
Panneerdoss S, Viswanadhapalli S,
Abdelfattah N, Onyeagucha BC, Timilsina S, Mohammad TA, Chen Y,
Drake M, Vuori K, Kumar TR and Rao MK: Cross-talk between
miR-471-5p and autophagy component proteins regulates
LC3-associated phagocytosis (LAP) of apoptotic germ cells. Nat
Commun. 8:5982017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Vargas Rivera T, Cai Z, Shen Y, Dosset M,
Benoit-Lizon I, Martin T, Roussey A, Flavell RA, Ghiringhelli F and
Apetoh L: Selective degradation of PU.1 during autophagy represses
the differentiation and antitumour activity of TH9
cells. Nat Commun. 8:5592017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Levy JMM, Towers CG and Thorburn A:
Targeting autophagy in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 17:528–542. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Goldsmith J, Levine B and Debnath J:
Autophagy and cancer metabolism. Methods Enzymol. 542:25–57. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Edinger AL and Thompson CB: Death by
design: Apoptosis, necrosis and autophagy. Curr Opin Cell Biol.
16:663–669. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Mills KR, Reginato M, Debnath J, Queenan B
and Brugge JS: Tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing
ligand (TRAIL) is required for induction of autophagy during lumen
formation in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:3438–3443. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|