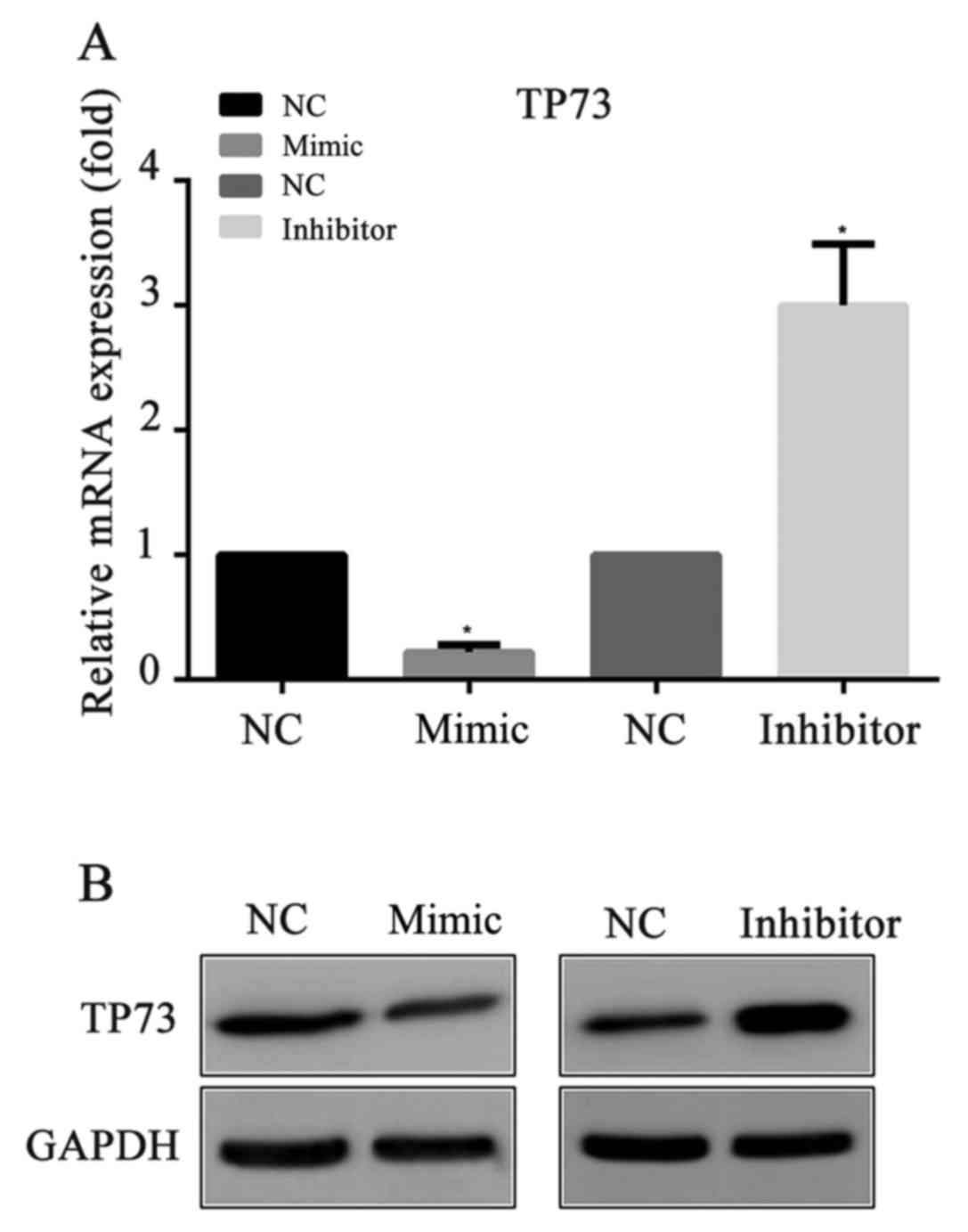
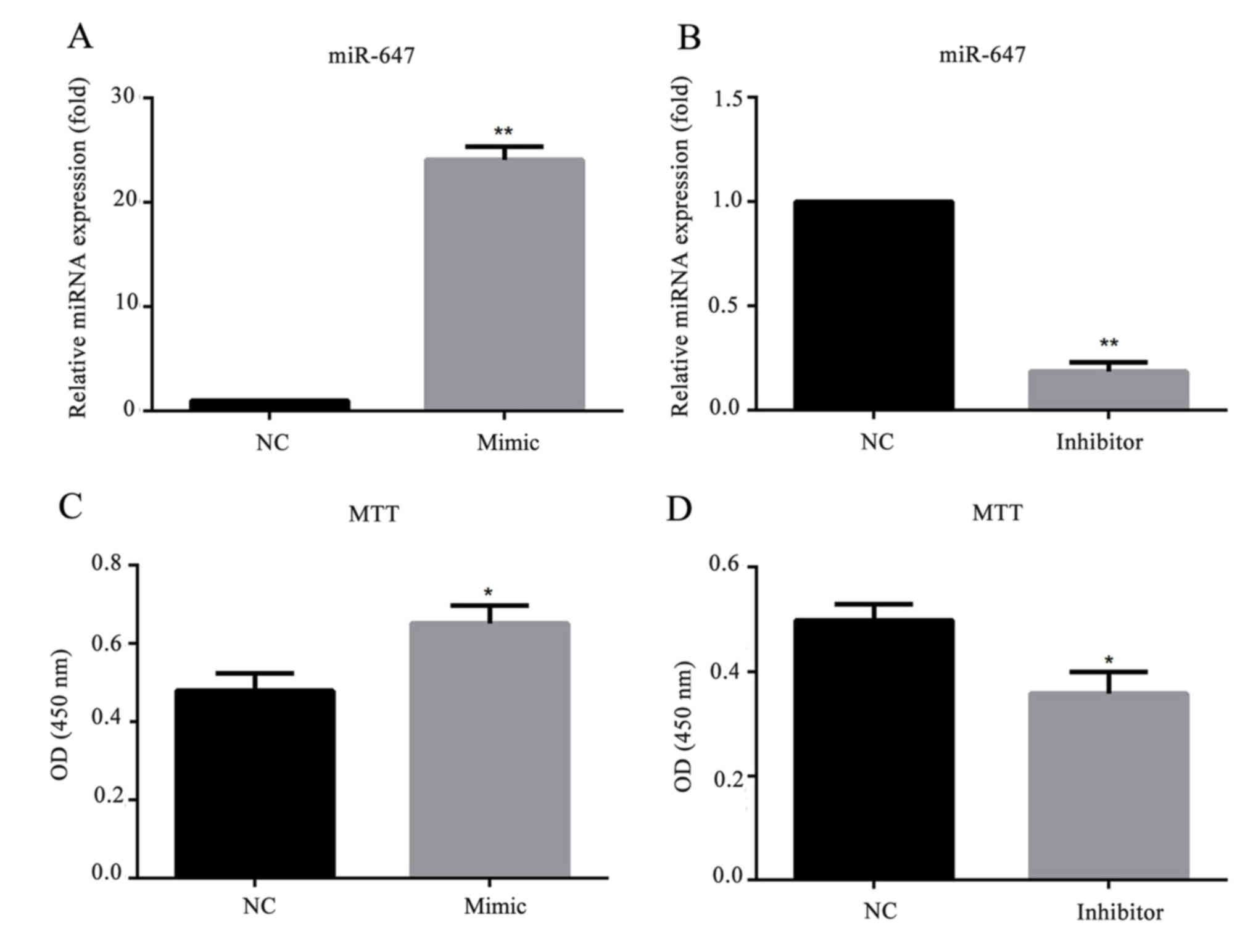
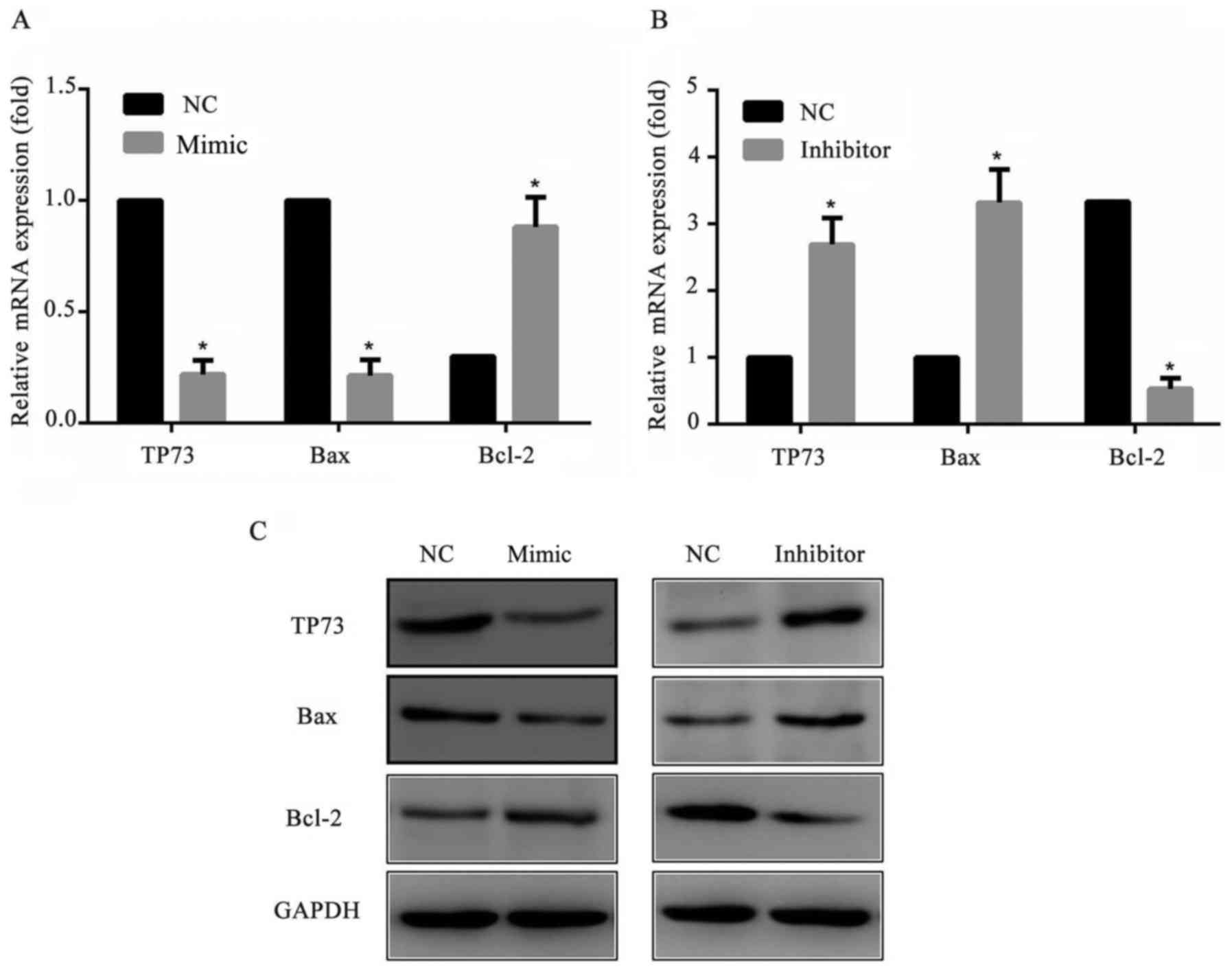
|
1
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Zhang S, Zhao P, Zeng H,
Zou X and He J: Annual report on status of cancer in China, 2010.
Chin J Cancer Res. 26:48–58. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Eichelberger L, Murphy G, Etemadi A, Abnet
CC, Islami F, Shakeri R, Malekzadeh R and Dawsey SM: Risk of
gastric cancer by water source: Evidence from the golestan
case-control study. PLoS One. 10:e01284912015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hamashima C, Shabana M, Okamoto M, Osaki Y
and Kishimoto T: Survival analysis of patients with interval cancer
undergoing gastric cancer screening by endoscopy. PLoS One.
10:e01267962015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Stratilatovas E, Baušys A, Baušys R and
Sangaila E: Mortality after gastrectomy: A 10 year single
institution experience. Acta Chir Belg. 115:123–130. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Li Y, Zhou Y, Zheng J, Niu C, Liu B, Wang
M, Fang H and Hou C: Downregulation of survivin inhibits
proliferation and migration of human gastric carcinoma cells. Int J
Clin Exp Pathol. 8:1731–1736. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wu WK, Lee CW, Cho CH, Fan D, Wu K, Yu J
and Sung JJ: MicroRNA dysregulation in gastric cancer: A new player
enters the game. Oncogene. 29:5761–5771. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Katada T, Ishiguro H, Kuwabara Y, Kimura
M, Mitui A, Mori Y, Ogawa R, Harata K and Fujii Y: microRNA
expression profile in undifferentiated gastric cancer. Int J Oncol.
34:537–542. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bou Kheir T, Futoma-Kazmierczak E,
Jacobsen A, Krogh A, Bardram L, Hother C, Grønbæk K, Federspiel B,
Lund AH and Friis-Hansen L: miR-449 inhibits cell proliferation and
is down-regulated in gastric cancer. Mol Cancer. 10:292011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chiang Y, Zhou X, Wang Z, Song Y, Liu Z,
Zhao F, Zhu J and Xu H: Expression levels of microRNA-192 and −215
in gastric carcinoma. Pathol Oncol Res. 18:585–591. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhang H, Cheng Y, Jia C, Yu S, Xiao Y and
Chen J: MicroRNA-29s could target AKT2 to inhibit gastric cancer
cells invasion ability. Med Oncol. 32:3422015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhang R, Li F, Wang W, Wang X, Li S and
Liu J: The effect of antisense inhibitor of miRNA 106b~25 on the
proliferation, invasion, migration, and apoptosis of gastric cancer
cell. Tumor Biol. 37:10507–10515. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Xiang XJ, Deng J, Liu YW, Wan LY, Feng M,
Chen J and Xiong JP: MiR-1271 inhibits cell proliferation, invasion
and EMT in gastric cancer by targeting FOXQ1. Cell Physiol Biochem.
36:1382–1394. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Long Q, Johnson BA, Osunkoya AO, Lai YH,
Zhou W, Abramovitz M, Xia M, Bouzyk MB, Nam RK, Sugar L, et al:
Protein-coding and microRNA biomarkers of recurrence of prostate
cancer following radical prostatectomy. Am J Pathol. 179:46–54.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kim YW, Kim EY, Jeon D, Liu JL, Kim HS,
Choi JW and Ahn WS: Differential microRNA expression signatures and
cell type-specific association with Taxol resistance in ovarian
cancer cells. Drug Des Devel Ther. 8:293–314. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Rawlings-Goss RA, Campbell MC and Tishkoff
SA: Global population-specific variation in miRNA associated with
cancer risk and clinical biomarkers. BMC Med Genomics. 7:532014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Cao W, Wei W, Zhan Z, Xie D, Xie Y and
Xiao Q: The role of miR-647 in human gastric cancer suppression.
Oncol Rep. 37:1401–1411. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yang B, Jing C, Wang J, Guo X, Chen Y, Xu
R, Peng L, Liu J and Li L: Identification of microRNAs associated
with lymphangiogenesis in human gastric cancer. Clin Transl Oncol.
16:374–379. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Esquela-Kerscher A and Slack FJ:
Oncomirs-microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer.
6:259–269. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Cho WC: OncomiRs: The discovery and
progress of microRNAs in cancers. Mol Cancer. 6:602007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Othman N and Nagoor NH: The role of
microRNAs in the regulation of apoptosis in lung cancer and its
application in cancer treatment. Biomed Res Int2014.
3180302014.
|
|
23
|
Xia H, Sun S, Wang B, Wang T, Liang C, Li
G, Huang C, Qi D and Chu X: miR-143 inhibits NSCLC cell growth and
metastasis by targeting Limk1. Int J Mol Sci. 15:1–11983. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Casciano I, Mazzocco K, Boni L, Pagnan G,
Banelli B, Allemanni G, Ponzoni M, Tonini GP and Romani M:
Expression of DeltaNp73 is a molecular marker for adverse outcome
in neuroblastoma patients. Cell Death Differ. 9:1–251. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Jost CA, Marin MC and Kaelin WG Jr: p73 is
a simian [correction of human] p53-related protein that can induce
apoptosis. Nature. 389:191–194. 1997. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Miyashita T and Reed JC: Tumor suppressor
p53 is a direct transcriptional activator of the human bax gene.
Cell. 80:293–299. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yoon MK, Ha JH, Lee MS and Chi SW:
Structure and apoptotic function of p73. BMB Rep. 48:81–90. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Miramar MD, Costantini P, Ravagnan L,
Saraiva LM, Haouzi D, Brothers G, Penninger JM, Peleato ML, Kroemer
G and Susin SA: NADH oxidase activity of mitochondrial
apoptosis-inducing factor. J Biol Chem. 276:16391–16398. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|