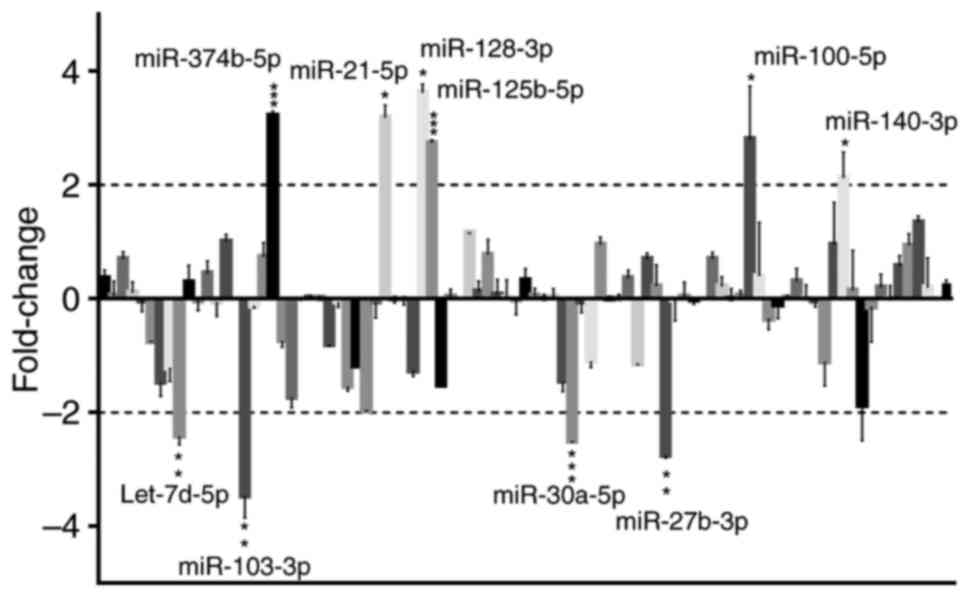
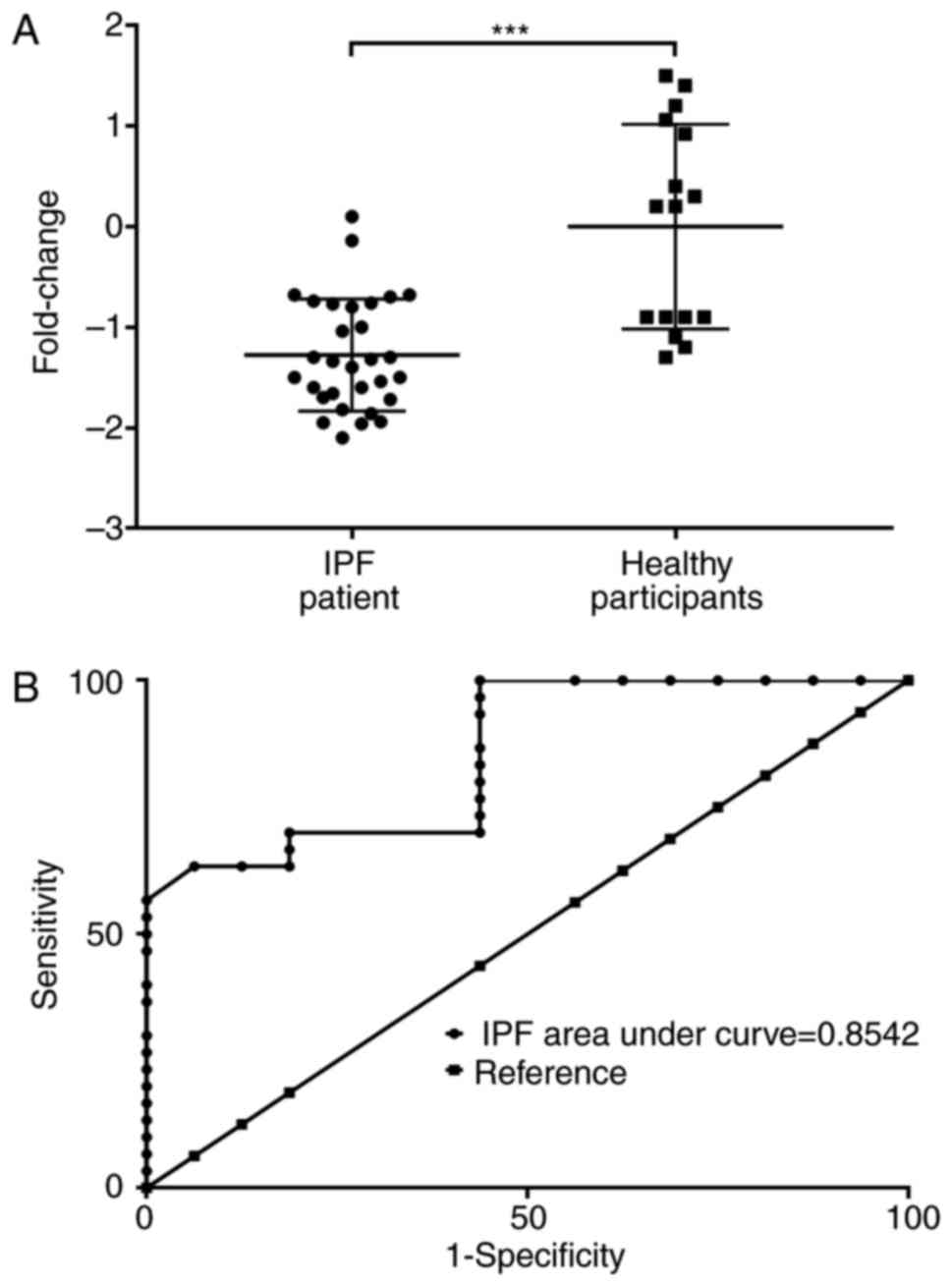
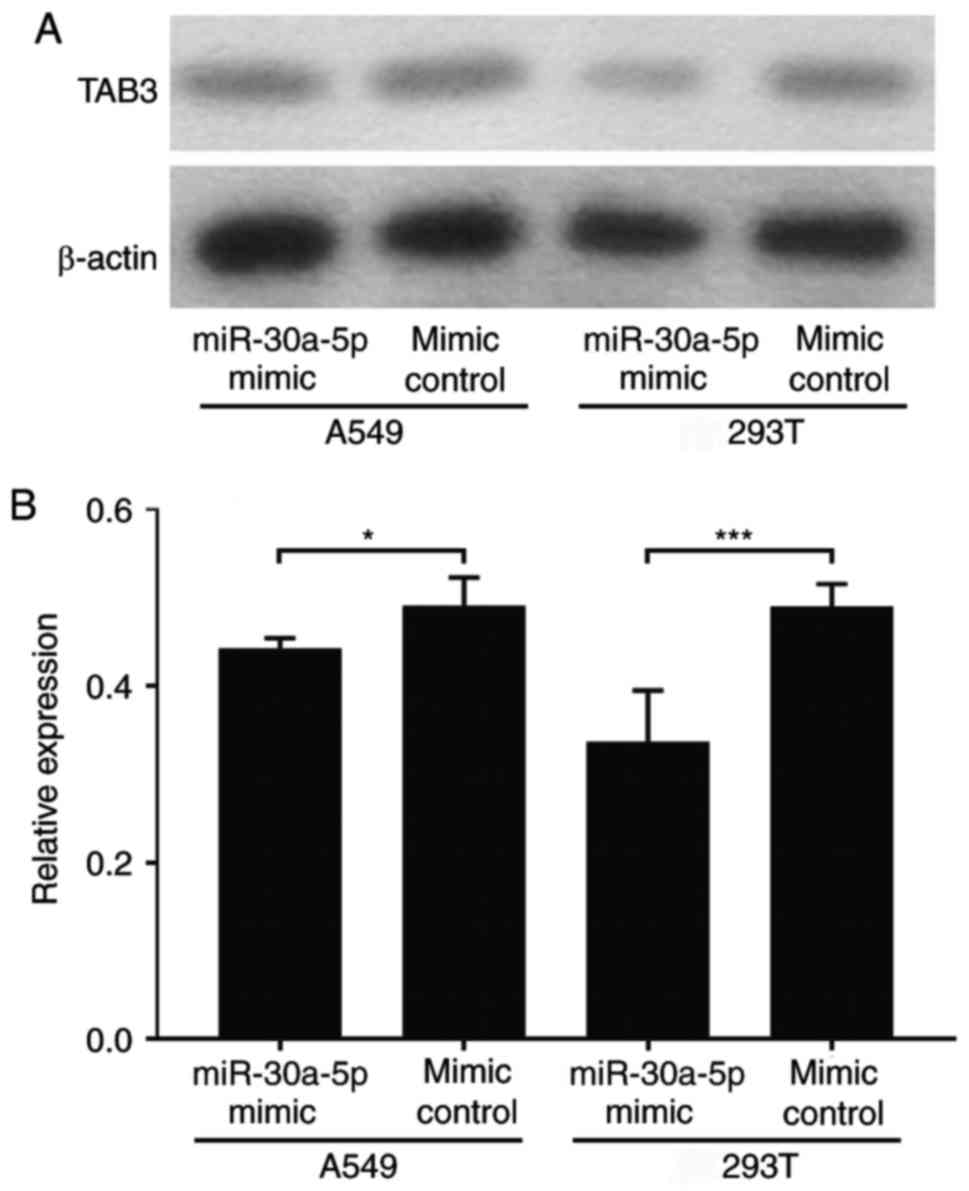
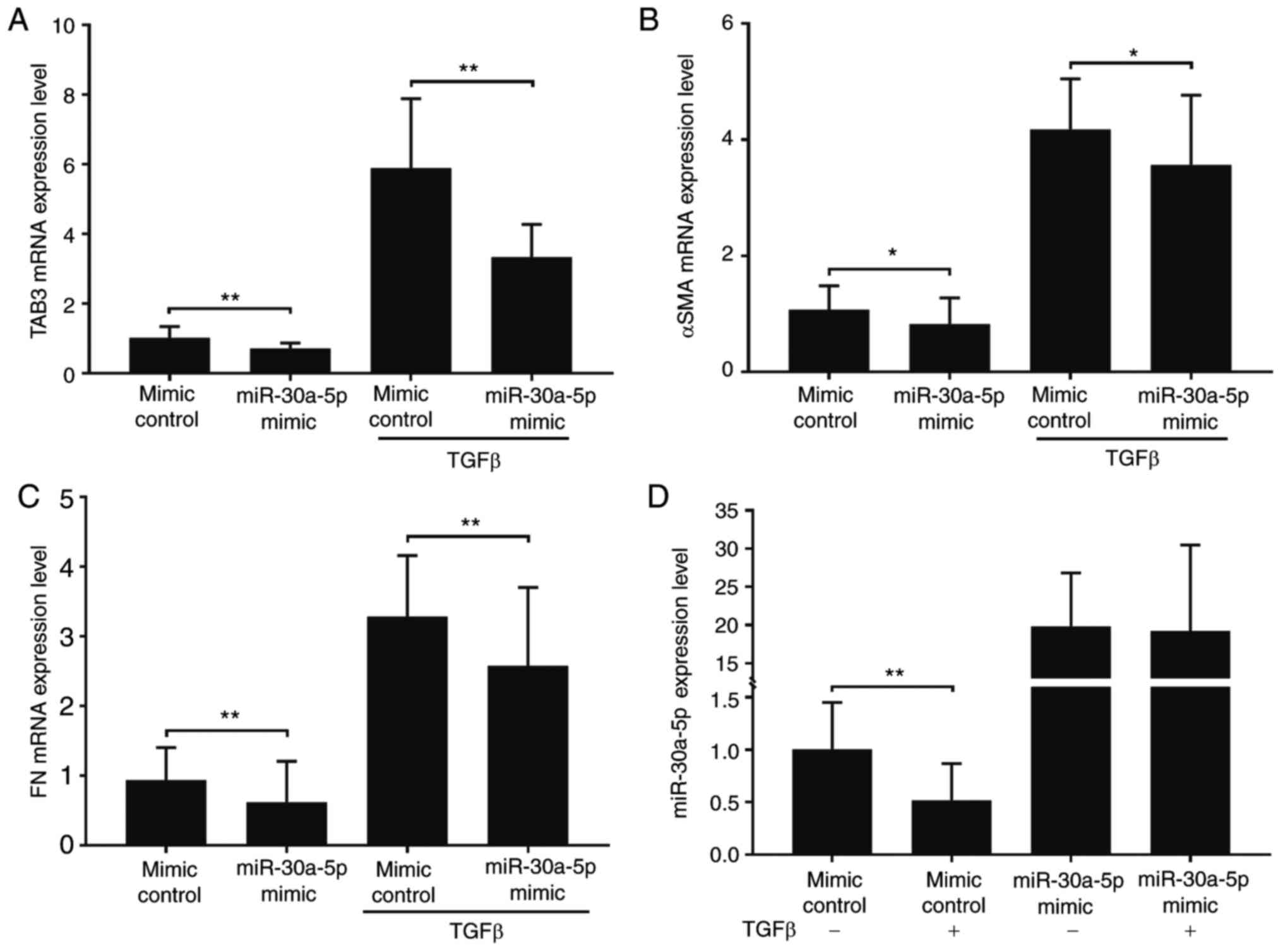
|
1
|
Zibrak JD and Price D: Interstitial lung
disease: Raising the index of suspicion in primary care. NPJ Prim
Care Respir Med. 24:140542014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Matsumoto A and Azuma A: Idiopathic
pulmonary fibrosis (IPF). Nihon Rinsho. 64:1354–1360. 2006.(In
Japanese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Tzouvelekis A, Tzilas V, Papiris S,
Aidinis V and Bouros D: Diagnostic and prognostic challenges in
idiopathic pulmonary Fibrosis: A patient's ‘Q and A’ approach. Pulm
Pharmacol Ther. 42:21–24. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Selman M, King JTE and Pardo A: American
Thoracic Society; European Respiratory Society; American College of
Chest Physicians: Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Prevailing and
evolving hypotheses about its pathogenesis and implications for
therapy. Ann Intern Med. 134:136–151. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Xaubet A, Ancochea J and Molina-Molina M:
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Med Clin (Barc). 148:170–175.
2017.(In English, Spanish). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hostettler K: Idiopathic pulmonary
fibrosis-Pathogenesis and therapeutic concepts. Ther Umsch.
73:19–24. 2016.(In German). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bargagli E, Lavorini F, Pistolesi M, Rosi
E, Prasse A, Rota E and Voltolini L: Trace metals in fluids lining
the respiratory system of patients with idiopathic pulmonary
fibrosis and diffuse lung diseases. J Trace Elem Med Biol.
42:39–44. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Levänen B, Bhakta NR, Paredes Torregrosa
P, Barbeau R, Hiltbrunner S, Pollack JL, Sköld CM, Svartengren M,
Grunewald J, Gabrielsson S, et al: Altered microRNA profiles in
bronchoalveolar lavage fluid exosomes in asthmatic patients. J
Allergy Clin Immunol. 131:894–903. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Michael A, Bajracharya SD, Yuen PS, Zhou
H, Star RA, Illei GG and Alevizos I: Exosomes from human saliva as
a source of microRNA biomarkers. Oral Dis. 16:34–38. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Gallo A, Tandon M, Alevizos I and Illei
GG: The majority of microRNAs detectable in serum and saliva is
concentrated in exosomes. PLoS One. 7:e306792012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Javeed N and Mukhopadhyay D: Exosomes and
their role in the micro-/macro-environment: A comprehensive review.
J Biomed Res. 31:386–394. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chinese Medical Association Respiratory
Diseases Branch: Chinese expert consensus on detection of pathogens
in bronchoalveolar lavage of pulmonary infectious diseases. Chin J
Tuberc Respir Dis. 40:578–583. 2017.
|
|
13
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Raghu G, Collard HR, Egan JJ, Martinez FJ,
Behr J, Brown KK, Colby TV, Cordier JF, Flaherty KR, Lasky JA, et
al: An official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT statement: Idiopathic pulmonary
fibrosis: Evidence-based guidelines for diagnosis and management.
Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 183:788–824. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wells AU, Desai SR, Rubens MB, Goh NS,
Cramer D, Nicholson AG, Colby TV, du Bois RM and Hansell DM:
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: A composite physiologic index
derived from disease extent observed by computed tomography. Am J
Respir Crit Care Med. 167:962–969. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sun X, Zhang S and Ma X: Prognostic value
of MicroRNA-125 in various human malignant Neoplasms: A
meta-analysis. Clin Lab. 61:1667–1674. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hu J, Cheng Y, Li Y, Jin Z, Pan Y, Liu G,
Fu S, Zhang Y, Feng K and Feng Y: microRNA-128 plays a critical
role in human non-small cell lung cancer tumourigenesis,
angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis by directly targeting vascular
endothelial growth factor-C. Eur J Cancer. 50:2336–2350. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lin L, Tu HB, Wu L, Liu M and Jiang GN:
MicroRNA-21 regulates non-small cell lung cancer cell invasion and
chemo-sensitivity through SMAD7. Cell Physiol Biochem.
38:2152–2162. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Jeon YJ, Middleton J, Kim T, Laganà A,
Piovan C, Secchiero P, Nuovo GJ, Cui R, Joshi P, Romano G, et al: A
set of NF-kappaB-regulated microRNAs induces acquired TRAIL
resistance in lung cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 112:E3355–E3364.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Pandit KV, Corcoran D, Yousef H,
Yarlagadda M, Tzouvelekis A, Gibson KF, Konishi K, Yousem SA, Singh
M, Handley D, et al: Inhibition and role of let-7d in idiopathic
pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 182:220–229. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yang D, Wang JJ, Li JS and Xu QY: miR-103
functions as a tumor suppressor by directly targeting programmed
cell death 10 in NSCLC. Oncol Res. 2017.
|
|
22
|
Zhang S, Liu H, Liu Y, Zhang J, Li H, Liu
W, Cao G, Xv P, Zhang J, Lv C and Song X: miR-30a as potential
therapeutics by targeting TET1 through regulation of Drp-1 promoter
hydroxymethylation in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Int J Mol Sci.
18:E6332017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhou H, Liu Y, Xiao L, Hu Z and Xia K:
Overexpression of MicroRNA-27b inhibits proliferation, migration,
and invasion via suppression of MET expression. Oncol Res.
25:147–154. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Rajasekaran S, Rajaguru P and Gandhi
Sudhakar PS: MicroRNAs as potential targets for progressive
pulmonary fibrosis. Front Pharmacol. 6:2542015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Willis BC and Borok Z: TGF-beta-induced
EMT: Mechanisms and implications for fibrotic lung disease. Am J
Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 293:L525–L534. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kis K, Liu X and Hagood JS: Myofibroblast
differentiation and survival in fibrotic disease. Expert Rev Mol
Med. 13:e272011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Choi ME, Ding Y and Kim SI: TGF-β
signaling via TAK1 pathway: Role in kidney fibrosis. Semin Nephrol.
244–252. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Usuki J, Matsuda K, Azuma A, Kudoh S and
Gemma A: Sequential analysis of myofibroblast differentiation and
transforming growth factor-β1/Smad pathway activation in murine
pulmonary fibrosis. J Nippon Med Sch. 79:46–59. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Crosby LM and Waters CM: Epithelial repair
mechanisms in the lung. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol.
298:L715–L731. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hsu E, Yasuoka H and Feghali-Bostwick CA:
Gene expression in pulmonary fibrosis. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr.
18:47–56. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Xu W, Wang Z and Liu Y: The
characterization of microRNA-mediated gene regulation as impacted
by both target site location and seed match type. PLoS One.
9:e1082602014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Oglesby I, McElvaney N and Greene C:
MicroRNAs in inflammatory lung disease-master regulators or target
practice? Respir Res. 11:1482010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Barh D, Malhotra R, Ravi B and Sindhurani
P: Microrna let-7: An emerging next-generation cancer therapeutic.
Curr Oncol. 17:70–80. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Vannella KM and Wynn TA: Mechanisms of
organ injury and repair by macrophages. Annu Rev Physiol.
79:593–617. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Han ZC, Zhang HN, Wang YZ, Lv CY and Xu
ZY: Effect of the human insulin-like growth factor 1 gene
transfection to human umbilical cord blood mesenchymal stem cells.
Saudi Med J. 35:435–441. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Pandit KV, Milosevic J and Kaminski N:
MicroRNAs in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Transl Res.
157:191–199. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Du C, Ren Y, Yao F, Duan J, Zhao H, Du Y,
Xiao X, Duan H and Shi Y: Sphingosine kinase 1 protects renal
tubular epithelial cells from renal fibrosis via induction of
autophagy. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 90:17–28. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ozcan C, Battaglia E, Young R and Suzuki
G: LKB1 knockout mouse develops spontaneous atrial fibrillation and
provides mechanistic insights into human disease process. J Am
Heart Assoc. 4:e0017332015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Wang J, Lesko M, Badri MH, Kapoor BC, Wu
BG, Li Y, Smaldone GC, Bonneau R, Kurtz ZD, Condos R and Segal LN:
Lung microbiome and host immune tone in subjects with idiopathic
pulmonary fibrosis treated with inhaled interferon-gamma. ERJ Open
Res. 3:00008–2017. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zhong M, Bian Z and Wu Z: miR-30a
Suppresses cell migration and invasion through downregulation of
PIK3CD in colorectal carcinoma. Cell Physiol Biochem. 31:209–218.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Jin Y, Chen Z, Liu X and Zhou X:
Evaluating the microRNA targeting sites by luciferase reporter gene
assay. Methods Mol Biol. 936:117–127. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Clarke DL, Murray LA, Crestani B and
Sleeman MA: Is personalised medicine the key to heterogeneity in
idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis? Pharmacol Ther. 169:35–46. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Wolters PJ, Collard HR and Jones KD:
Pathogenesis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Ann Rev Pathol.
9:157–179. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Zhou B, Liu Y, Kahn M, Ann DK, Han A, Wang
H, Nguyen C, Flodby P, Zhong Q, Krishnaveni MS, et al: Interactions
between β-catenin and transforming growth factor-β signaling
pathways mediate epithelial-mesenchymal transition and are
dependent on the transcriptional co-activator cAMP-response
element-binding protein (CREB)-binding protein (CBP). J Biol Chem.
287:7026–7038. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Marmai C, Sutherland RE, Kim KK, Dolganov
GM, Fang X, Kim SS, Jiang S, Golden JA, Hoopes CW, Matthay MA, et
al: Alveolar epithelial cells express mesenchymal proteins in
patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Physiol Lung Cell
Mol Physiol. 301:L71–L78. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Kasai H, Allen J, Mason R, Kamimura T and
Zhang Z: TGF-beta1 induces human alveolar epithelial to mesenchymal
cell transition (EMT). Respir Res. 6:562005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Pardo A, Gibson K, Cisneros J, Richards
TJ, Yang Y, Becerril C, Yousem S, Herrera I, Ruiz V, Selman M and
Kaminski N: Up-regulation and profibrotic role of osteopontin in
human idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. PLoS Med. 2:e2512005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|