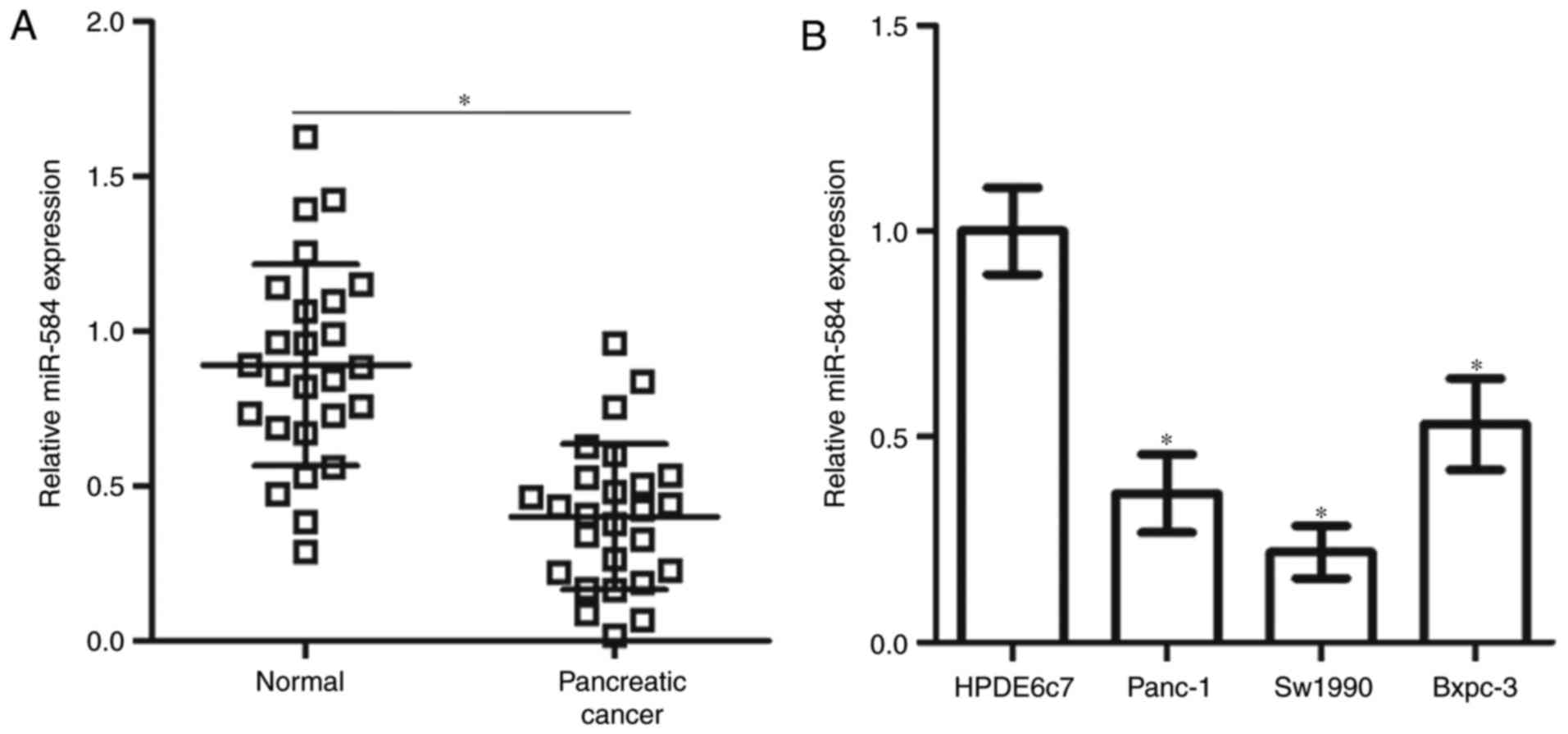
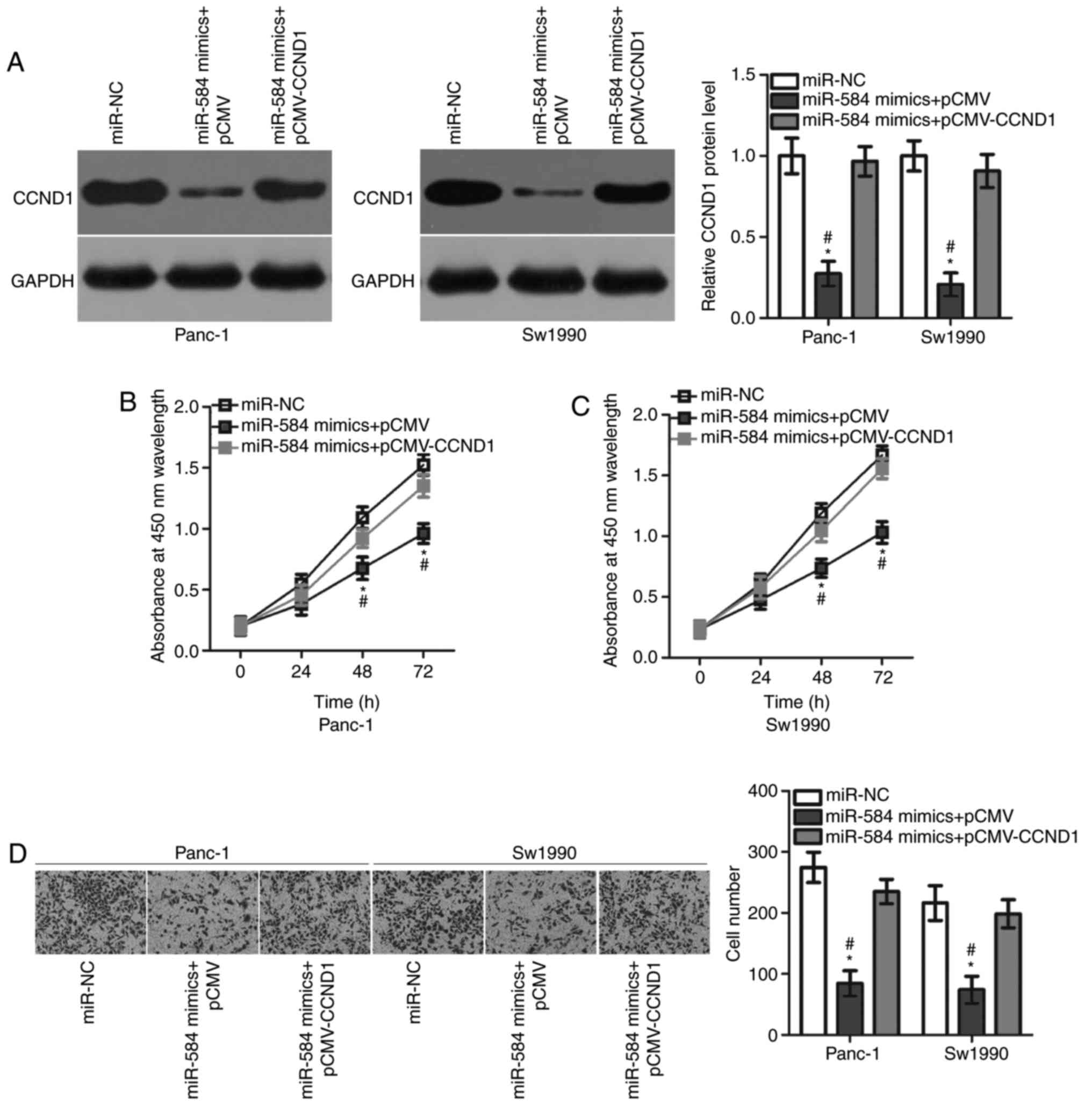
|
1
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Zhang S, Zhao P, Li G, Wu
L and He J: Report of incidence and mortality in China cancer
registries, 2009. Chin J Cancer Res. 25:10–21. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kamisawa T, Wood LD, Itoi T and Takaori K:
Pancreatic cancer. Lancet. 388:73–85. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Cameron JL, Riall TS, Coleman J and
Belcher KA: One thousand consecutive pancreaticoduodenectomies. Ann
Surg. 244:10–15. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Niedergethmann M, Alves F, Neff JK,
Heidrich B, Aramin N, Li L, Pilarsky C, Grützmann R, Allgayer H,
Post S and Gretz N: Gene expression profiling of liver metastases
and tumour invasion in pancreatic cancer using an orthotopic SCID
mouse model. Br J Cancer. 97:1432–1440. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Feng H, Wang Y, Su J, Liang H, Zhang CY,
Chen X and Yao W: MicroRNA-148a suppresses the proliferation and
migration of pancreatic cancer cells by down-regulating ErbB3.
Pancreas. 45:1263–1271. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lewis BP, Burge CB and Bartel DP:
Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that
thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell. 120:15–20.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Galasso M, Sandhu SK and Volinia S:
MicroRNA expression signatures in solid malignancies. Cancer J.
18:238–243. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wald P, Liu XS, Pettit C, Dillhoff M,
Manilchuk A, Schmidt C, Wuthrick E, Chen W and Williams TM:
Prognostic value of microRNA expression levels in pancreatic
adenocarcinoma: A review of the literature. Oncotarget.
8:73345–73361. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sekar D, Krishnan R, Thirugnanasambantham
K, Rajasekaran B, Islam VI and Sekar P: Significance of microRNA 21
in gastric cancer. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 40:538–545.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Celano M, Rosignolo F, Maggisano V, Pecce
V, Iannone M, Russo D and Bulotta S: MicroRNAs as biomarkers in
thyroid carcinoma. Int J Genomics. 2017:64965702017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Fadejeva I, Olschewski H and Hrzenjak A:
MicroRNAs as regulators of cisplatin-resistance in non-small cell
lung carcinomas. Oncotarget. 8:115754–115773. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ebert MS and Sharp PA: Roles for microRNAs
in conferring robustness to biological processes. Cell.
149:515–524. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang Z, Tan Y, Yu W, Zheng S, Zhang S, Sun
L and Ding K: Small role with big impact: MiRNAs as communicators
in the cross-talk between cancer-associated fibroblasts and cancer
cells. Int J Biol Sci. 13:339–348. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kim YK, Yu J, Han TS, Park SY, Namkoong B,
Kim DH, Hur K, Yoo MW, Lee HJ, Yang HK and Kim VN: Functional links
between clustered microRNAs: Suppression of cell-cycle inhibitors
by microRNA clusters in gastric cancer. Nucleic Acids Res.
37:1672–1681. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Fu F, Wan X, Wang D, Kong Z, Zhang Y,
Huang W, Wang C, Wu H and Li Y: MicroRNA-19a acts as a prognostic
marker and promotes prostate cancer progression via inhibiting
VPS37A expression. Oncotarget. 9:1931–1943. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhang Y, Wang Y and Wang J: MicroRNA-584
inhibits cell proliferation and invasion in non-small cell lung
cancer by directly targeting MTDH. Exp Ther Med. 15:2203–2211.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Xiang X, Mei H, Qu H, Zhao X, Li D, Song
H, Jiao W, Pu J, Huang K, Zheng L and Tong Q: miRNA-584-5p exerts
tumor suppressive functions in human neuroblastoma through
repressing transcription of matrix metalloproteinase 14. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1852:1743–1754. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Li Q, Li Z, Wei S, Wang W, Chen Z, Zhang
L, Chen L, Li B, Sun G, Xu J, et al: Overexpression of miR-584-5p
inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis by targeting WW
domain-containing E3 ubiquitin protein ligase 1 in gastric cancer.
J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 36:592017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C (T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Gansauge S, Gansauge F, Ramadani M, Stobbe
H, Rau B, Harada N and Beger HG: Overexpression of cyclin D1 in
human pancreatic carcinoma is associated with poor prognosis.
Cancer Res. 57:1634–1637. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Li YJ and Ji XR: Relationship between the
expression of beta-cat, cyclin D1 and c-myc and the occurance and
biological behavior of pancreatic cancer. Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za
Zhi. 32:238–241. 2003.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Xu Y, Liu T and Gao J: Effects of
antisense cyclin D1 expressing vector on the cell growth and
apoptosis of pancreatic carcinoma. Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi.
27:348–351. 1998.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yan L, Wang Y, Wang ZZ, Rong YT, Chen LL,
Li Q, Liu T, Chen YH, Li YD, Huang ZH and Peng J: Cell motility and
spreading promoted by CEACAM6 through cyclin D1/CDK4 in human
pancreatic carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 35:418–426. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lee Y, Ko D, Min HJ, Kim SB, Ahn HM, Lee Y
and Kim S: TMPRSS4 induces invasion and proliferation of prostate
cancer cells through induction of Slug and cyclin D1. Oncotarget.
7:50315–50332. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhang Y, Su Y, Zhao Y, Lv G and Luo Y:
MicroRNA720 inhibits pancreatic cancer cell proliferation and
invasion by directly targeting cyclin D1. Mol Med Rep.
16:9256–9262. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Cao W, Jin H, Zhang L, Chen X and Qian H:
Identification of miR-601 as a novel regulator in the development
of pancreatic cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 483:638–644.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Le Large TY, Meijer LL, Prado MM, Kazemier
G, Frampton AE and Giovannetti E: Circulating microRNAs as
diagnostic biomarkers for pancreatic cancer. Expert Rev Mol Diagn.
15:1525–1529. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Takikawa T, Masamune A, Yoshida N, Hamada
S, Kogure T and Shimosegawa T: Exosomes derived from pancreatic
stellate cells: MicroRNA signature and effects on pancreatic cancer
cells. Pancreas. 46:19–27. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wang XP, Deng XL and Li LY: MicroRNA-584
functions as a tumor suppressor and targets PTTG1IP in glioma. Int
J Clin Exp Pathol. 7:8573–8582. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ueno K, Hirata H, Shahryari V, Chen Y,
Zaman MS, Singh K, Tabatabai ZL, Hinoda Y and Dahiya R: Tumour
suppressor microRNA-584 directly targets oncogene Rock-1 and
decreases invasion ability in human clear cell renal cell
carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 104:308–315. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Li Y, Wei J, Xu C, Zhao Z and You T:
Prognostic significance of cyclin D1 expression in colorectal
cancer: A meta-analysis of observational studies. PLoS One.
9:e945082014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Li X, Huo X, Li W, Yang Q, Wang Y and Kang
X: Genetic association between cyclin D1 polymorphism and breast
cancer susceptibility. Tumour Biol. 35:11959–11965. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Betticher DC, Heighway J, Hasleton PS,
Altermatt HJ, Ryder WD, Cerny T and Thatcher N: Prognostic
significance of CCND1 (cyclin D1) overexpression in primary
resected non-small-cell lung cancer. Br J Cancer. 73:294–300. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Lu JW, Lin YM, Chang JG, Yeh KT, Chen RM,
Tsai JJ, Su WW and Hu RM: Clinical implications of deregulated CDK4
and Cyclin D1 expression in patients with human hepatocellular
carcinoma. Med Oncol. 30:3792013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Xu Z, Zeng X, Tian D, Xu H, Cai Q, Wang J
and Chen Q: MicroRNA-383 inhibits anchorage-independent growth and
induces cell cycle arrest of glioma cells by targeting CCND1.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 453:833–838. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|