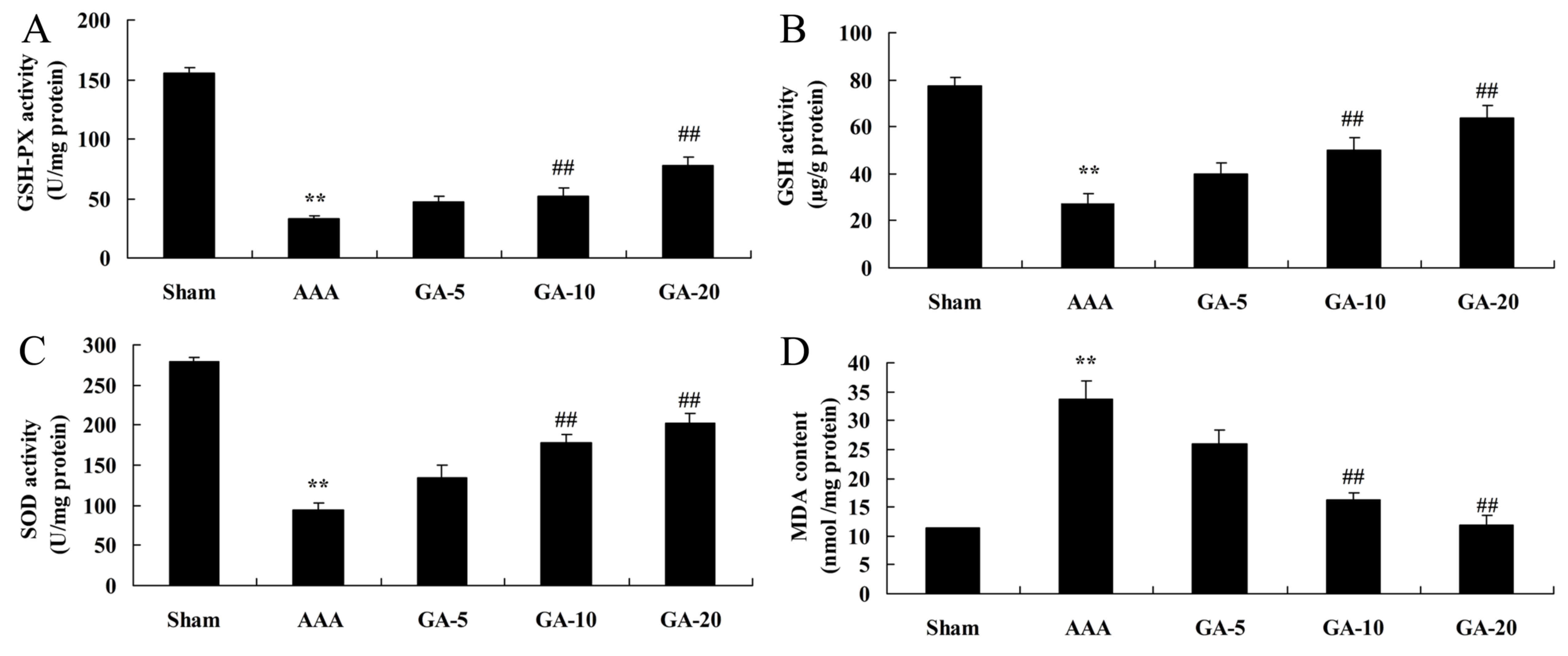
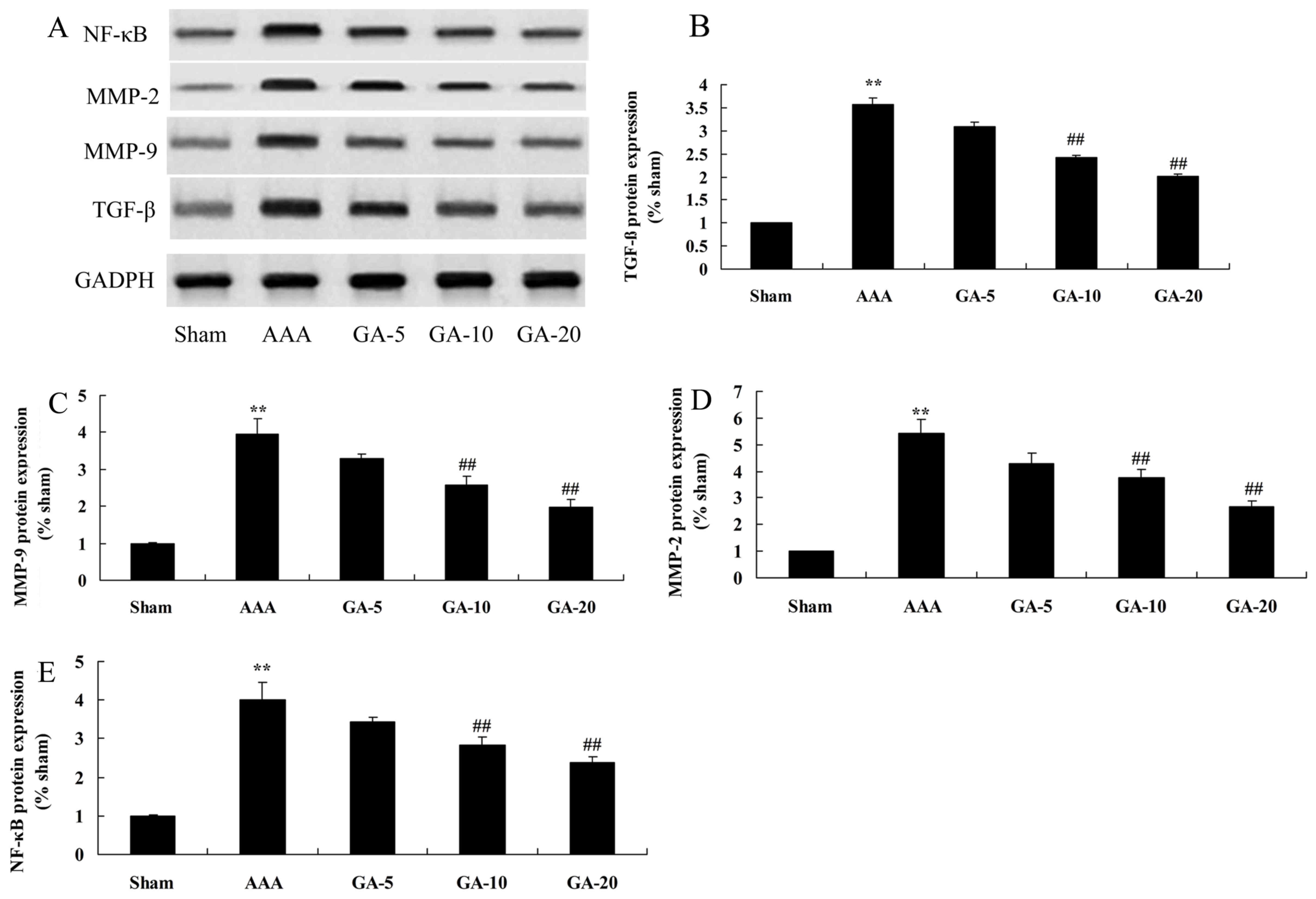
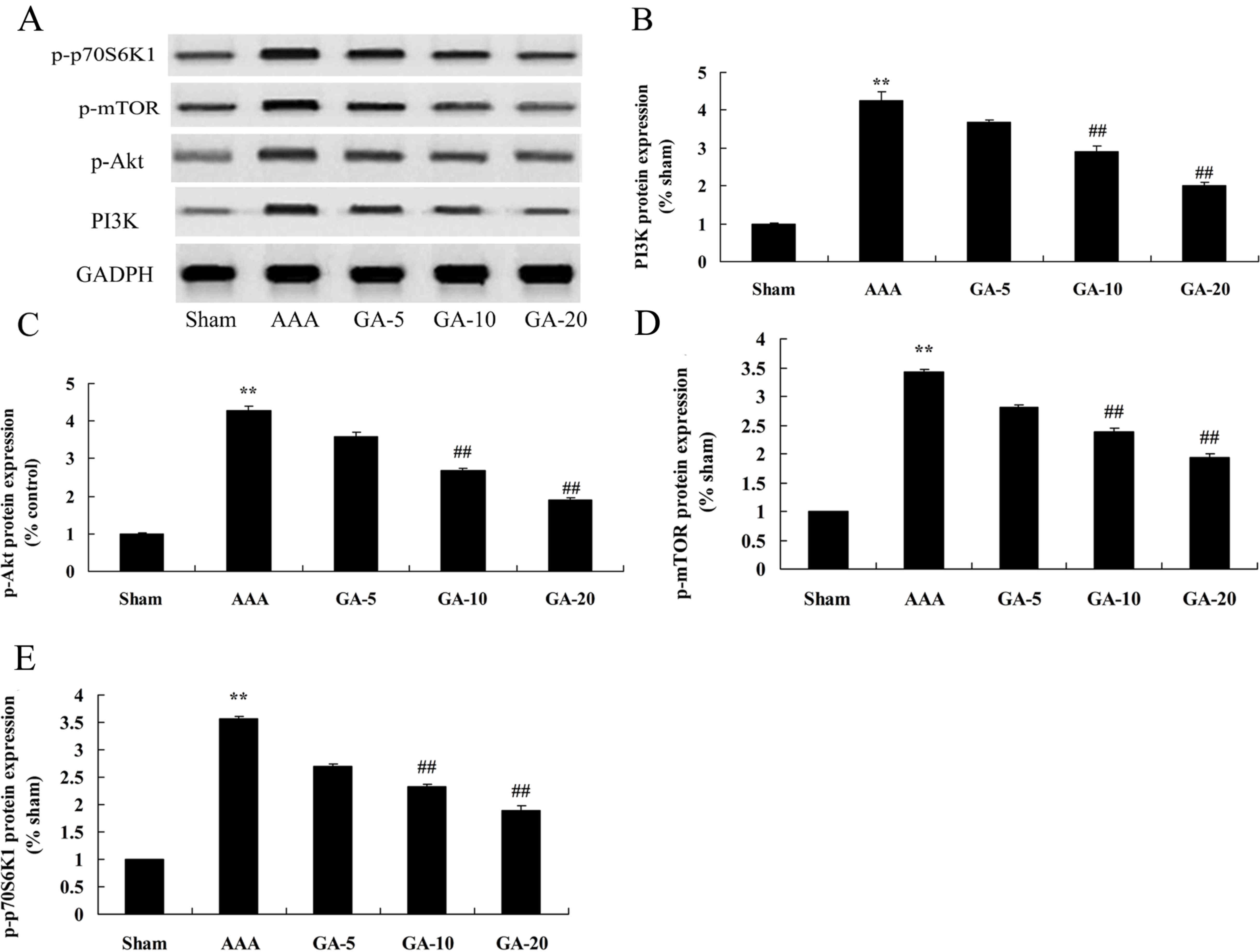
|
1
|
Zhang Y, Zhang D, Wang F, Xu D, Guo Y and
Cui W: Serum miRNAs panel (miR-16-2*, miR-195, miR-2861, miR-497)
as novel non-invasive biomarkers for detection of cervical cancer.
Sci Rep. 5:179422015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Peng S, Gao D, Gao C, Wei P, Niu M and
Shuai C: MicroRNAs regulate signaling pathways in osteogenic
differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells (review). Mol Med Rep.
14:623–629. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wang M, Liang L, Li L, Han K, Li Q, Peng
Y, Peng X and Zeng K: Increased miR-424-5p expression in peripheral
blood mononuclear cells from patients with pemphigus. Mol Med Rep.
15:3479–3484. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Svoboda M, Riha J, Wlcek K, Jaeger W and
Thalhammer T: Organic anion transporting polypeptides (OATPs):
Regulation of expression and function. Curr Drug Metab. 12:139–153.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Meyer Zu, Schwabedissen HE, Böttcher K,
Chaudhry A, Kroemer HK, Schuetz EG and Kim RB: Liver X receptor α
and farnesoid X receptor are major transcriptional regulators of
OATP1B1. Hepatology. 52:1797–1807. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Liao R, Yan F, Zeng Z, Farhan M, Little P,
Quirion R, Srivastava LK and Zheng W: Amiodarone-induced retinal
neuronal cell apoptosis attenuated by IGF-1 via counter regulation
of the PI3k/Akt/FoxO3a pathway. Mol Neurobiol. 54:6931–6943. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhu W, Bijur GN, Styles NA and Li X:
Regulation of FOXO3a by brain-derived neurotrophic factor in
differentiated human SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells. Brain Res Mol
Brain Res. 126:45–56. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Liu MH, Yuan C, He J, Tan TP, Wu SJ, Fu
HY, Liu J, Yu S, Chen YD, Le QF, et al: Resveratrol protects PC12
cells from high glucose-induced neurotoxicity via PI3K/Akt/FoxO3a
pathway. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 35:513–522. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yoo HI, Kim BK and Yoon SK:
MicroRNA-330-5p negatively regulates ITGA5 expression in human
colorectal cancer. Oncol Rep. 36:3023–3029. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Tian Y, Guo S, Wu X, Ma L and Zhao X:
Minocycline alleviates sevoflurane-induced cognitive impairment in
aged rats. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 35:585–594. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yang ZJ, Wang YW, Li CL, Ma LQ and Zhao X:
Pre-treatment with a Xingnaojing preparation ameliorates
sevoflurane-induced neuroapoptosis in the infant rat striatum. Mol
Med Rep. 11:1615–1622. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chmielarz P, Konovalova J, Najam SS, Alter
H, Piepponen TP, Erfle H, Sonntag KC, Schütz G, Vinnikov IA and
Domanskyi A: Dicer and microRNAs protect adult dopamine neurons.
Cell Death Dis. 8:e28132017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zeng Z, Wang X, Bhardwaj SK, Zhou X,
Little PJ, Quirion R, Srivastava LK and Zheng W: The atypical
antipsychotic agent, clozapine, protects against
corticosterone-induced death of PC12 cells by regulating the
Akt/FoxO3a signaling pathway. Mol Neurobiol. 54:3395–3406. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kim HY, Kwon HY, Ha Thi HT, Lee HJ, Kim
GI, Hahm KB and Hong S: MicroRNA-132 and microRNA-223 control
positive feedback circuit by regulating FOXO3a in inflammatory
bowel disease. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 31:1727–1735. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lian R, Lu B, Jiao L, Li S, Wang H, Miao W
and Yu W: MiR-132 plays an oncogenic role in laryngeal squamous
cell carcinoma by targeting FOXO1 and activating the PI3K/AKT
pathway. Eur J Pharmacol. 792:1–6. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Breitkopf K, Nagy LE, Beier JI, Mueller S,
Weng H and Dooley S: Current experimental perspectives on the
clinical progression of alcoholic liver disease. Alcohol Clin Exp
Res. 33:1647–1655. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zubillaga-Guerrero MI, Alarcón-Romero Ldel
C, Illades-Aguiar B, Flores-Alfaro E, Bermúdez-Morales VH, Deas J
and Peralta-Zaragoza O: MicroRNA miR-16-1 regulates CCNE1 (cyclin
E1) gene expression in human cervical cancer cells. Int J Clin Exp
Med. 8:15999–16006. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ziaei S and Halaby R: Immunosuppressive,
anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer properties of triptolide: A mini
review. Avicenna J Phytomed. 6:149–164. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang F, Yin J, Lu Z, Zhang G, Li J, Xing
T, Zhuang S and Wang N: Limb ischemic preconditioning protects
against contrast-induced nephropathy via renalase. EBioMedicine.
9:356–365. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Liu SJ, Yin CX, Ding MC, Xia SY, Shen QM
and Wu JD: Berberine suppresses in vitro migration of human aortic
smooth muscle cells through the inhibitions of MMP-2/9, u-PA, AP-1,
and NF-κB. BMB Rep. 47:388–392. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang F, Zhang G, Lu Z, Geurts AM, Usa K,
Jacob HJ, Cowley AW, Wang N and Liang M: Antithrombin III/SerpinC1
insufficiency exacerbates renal ischemia/reperfusion injury. Kidney
Int. 88:796–803. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yang X, Li CJ, Wan Y, Smith P, Shang G and
Cui Q: Antioxidative fullerol promotes osteogenesis of human
adipose-derived stem cells. Int J Nanomedicine. 9:4023–4031. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
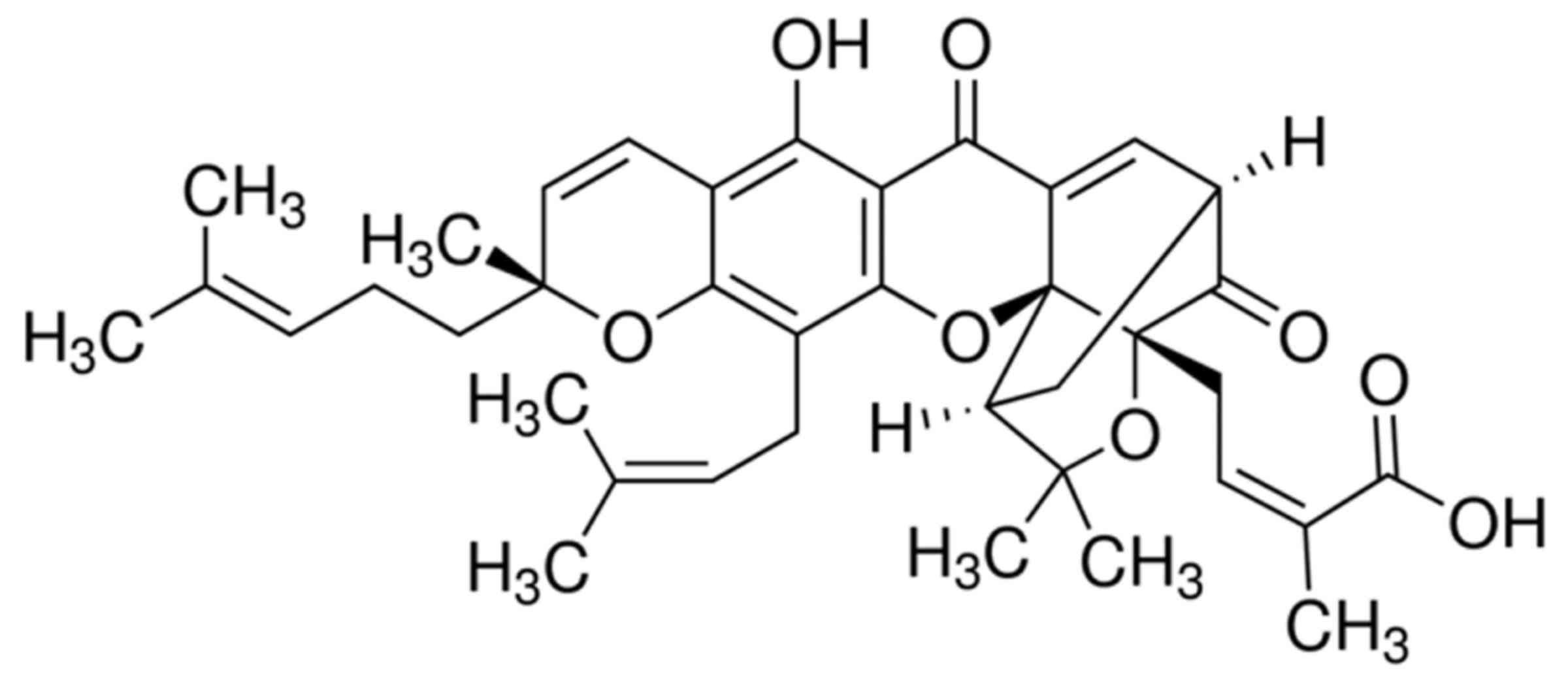
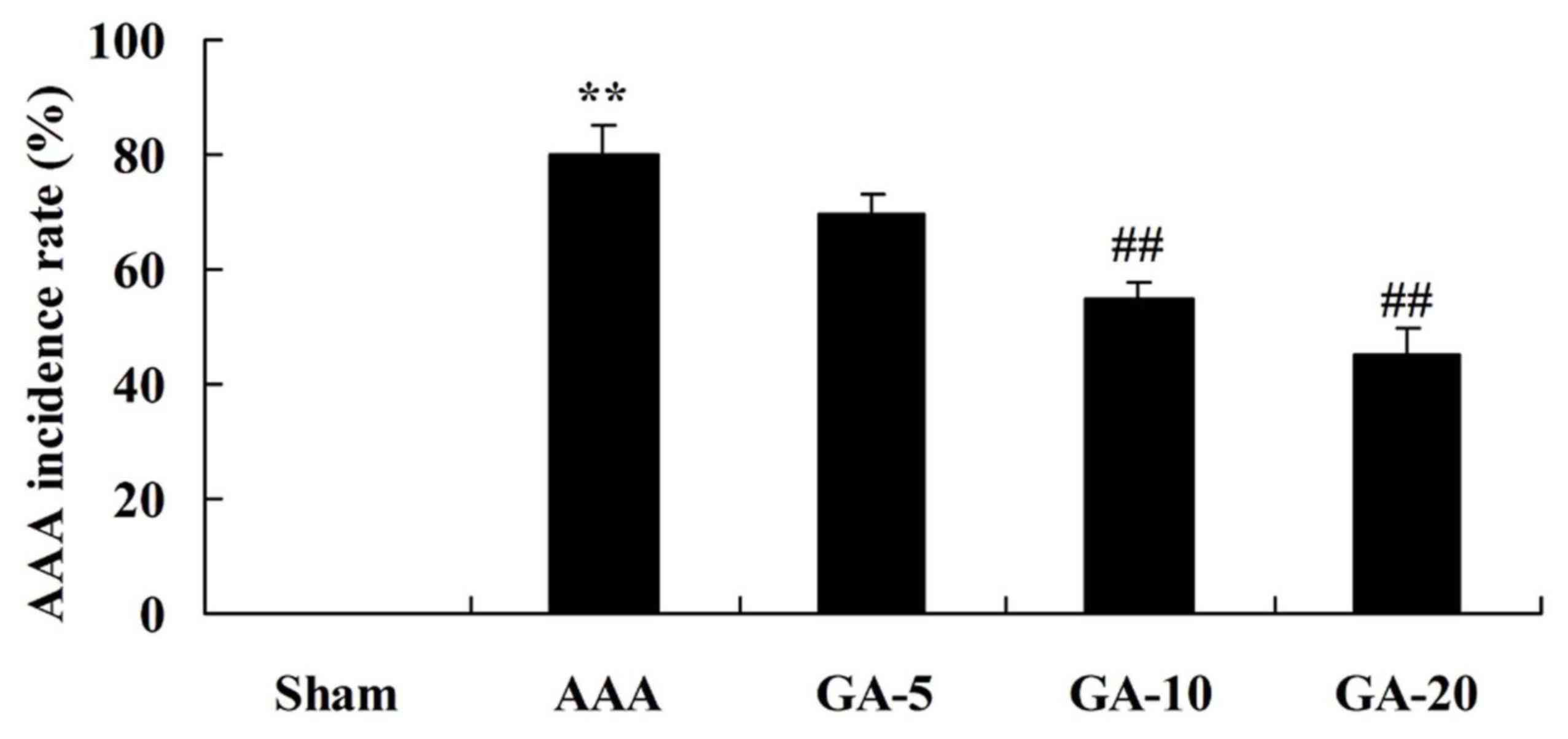
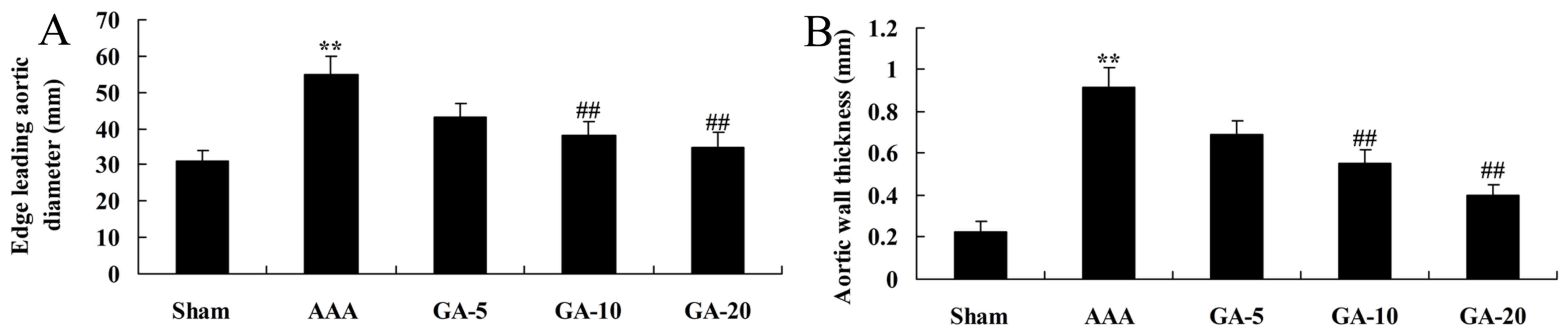
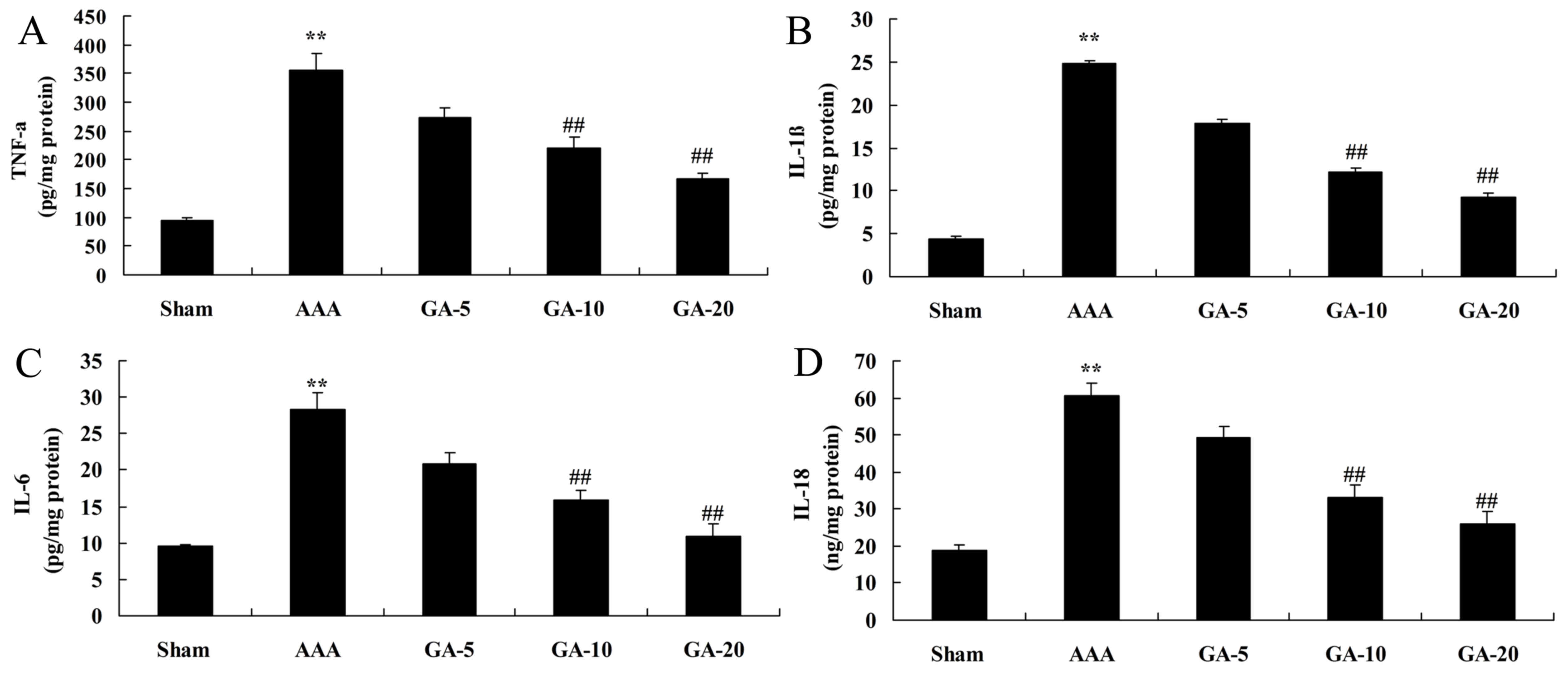
Wen J, Pei H, Wang X, et al: Gambogic acid
exhibits anti-psoriatic efficacy through inhibition of angiogenesis
and inflammation. J Dermatol Sci. 74:242–250. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Tian Y, Wu X, Guo S, Ma L, Huang W and
Zhao X: Minocycline attenuates sevoflurane-induced cell injury via
activation of Nrf2. Int J Mol Med. 39:869–878. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhou ZB, Yang XY, Tang Y, Zhou X, Zhou LH
and Feng X: Subclinical concentrations of sevoflurane reduce
oxidative stress but do not prevent hippocampal apoptosis. Mol Med
Rep. 14:721–727. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Qu Y, Zhang G, Ji Y, Zhua H, Lv C and
Jiang W: Protective role of gambogic acid in experimental pulmonary
fibrosis in vitro and in vivo. Phytomedicine. 23:350–358. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhu G, Wang X, Wu S and Li Q: Involvement
of activation of PI3K/Akt pathway in the protective effects of
puerarin against MPP+-induced human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cell
death. Neurochem Int. 60:400–408. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Xiang J, Pan J, Chen F, Zheng L, Chen Y,
Zhang S and Feng W: L-3-n-butylphthalide improves cognitive
impairment of APP/PS1 mice by BDNF/TrkB/PI3K/AKT pathway. Int J
Clin Exp Med. 7:1706–1713. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hossini AM, Quast AS, Plötz M, Grauel K,
Exner T, Küchler J, Stachelscheid H, Eberle J, Rabien A,
Makrantonaki E and Zouboulis CC: PI3K/AKT signaling pathway is
essential for survival of induced pluripotent stem cells. PLoS One.
11:e01547702016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Qi Q, Gu H, Yang Y, et al: Involvement of
matrix metalloproteinase 2 and 9 in gambogic acid induced
suppression of MDA-MB-435 human breast carcinoma cell lung
metastasis. J Mol Med (Berl). 86:1367–1377. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Luo T, Liu G, Ma H, Lu B, Xu H, Wang Y, Wu
J, Ge P and Liang J: Inhibition of autophagy via activation of
PI3K/Akt pathway contributes to the protection of ginsenoside Rb1
against neuronal death caused by ischemic insults. Int J Mol Sci.
15:15426–15442. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Meng Y, Wang W, Kang J, Wang X and Sun L:
Role of the PI3K/AKT signalling pathway in apoptotic cell death in
the cerebral cortex of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Exp
Ther Med. 13:2417–2422. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wang F, Zhang W, Guo L, Bao W, Jin N, Liu
R, Liu P, Wang Y, Guo Q and Chen B: Gambogic acid suppresses
hypoxia-induced hypoxia-inducible factor-1α/vascular endothelial
growth factor expression via inhibiting phosphatidylinositol
3-kinase/Akt/mammalian target protein of rapamycin pathway in
multiple myeloma cells. Cancer Sci. 105:1063–1070. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yufune S, Satoh Y, Akai R, Yoshinaga Y,
Kobayashi Y, Endo S and Kazama T: Suppression of ERK
phosphorylation through oxidative stress is involved in the
mechanism underlying sevoflurane-induced toxicity in the developing
brain. Sci Rep. 6:218592016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Guo XQ, Cao YL, Hao F, Yan ZR, Wang ML and
Liu XW: Tangeretin alters neuronal apoptosis and ameliorates the
severity of seizures in experimental epilepsy-induced rats by
modulating apoptotic protein expressions, regulating matrix
metalloproteinases, and activating the PI3K/Akt cell survival
pathway. Adv Med Sci. 62:246–253. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Liu WY, Wu XU, Liao CQ, Shen J and Li J:
Apoptotic effect of gambogic acid in esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma cells via suppression of the NF-kappaB pathway. Oncol
Lett. 11:3681–3685. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|