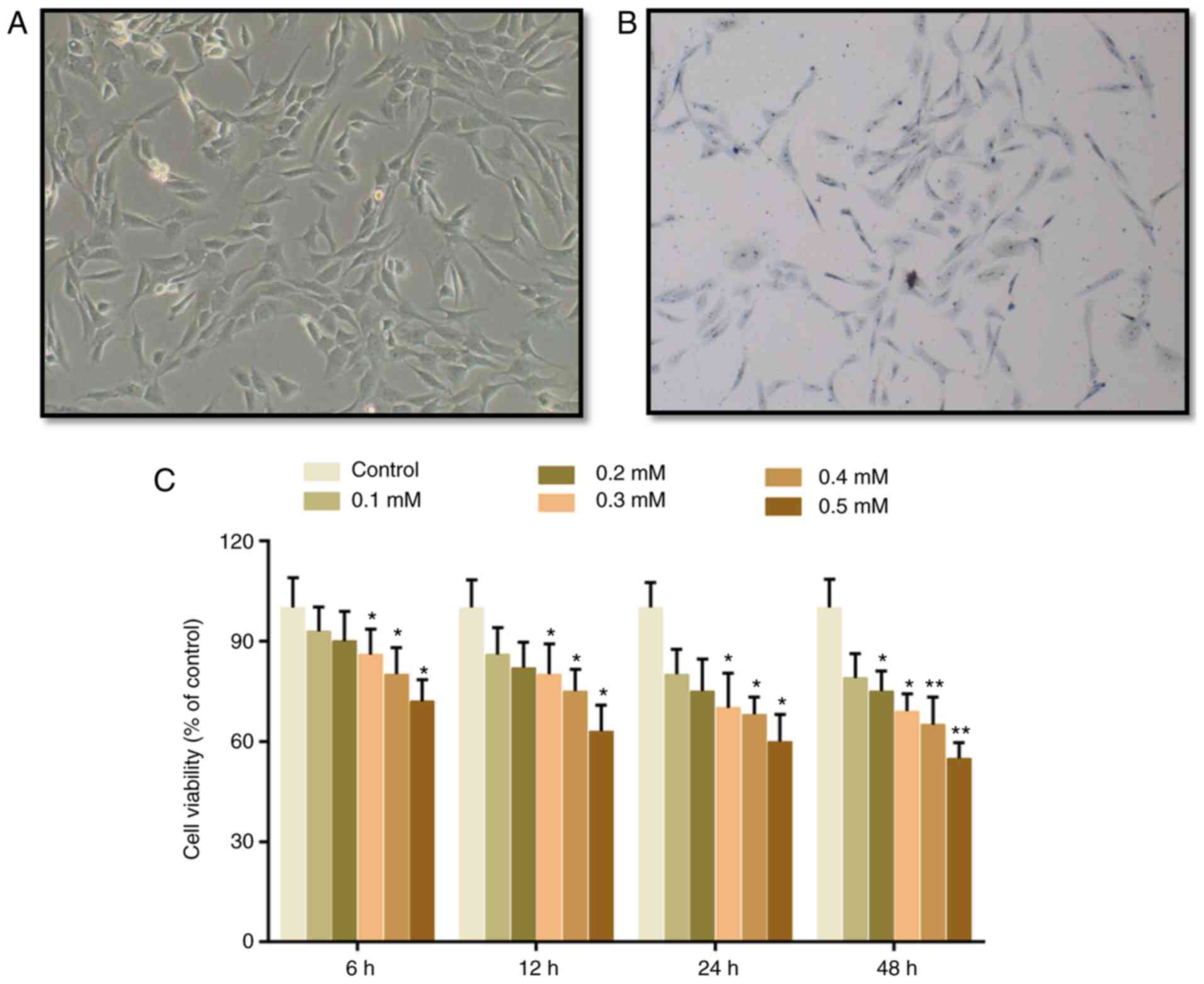
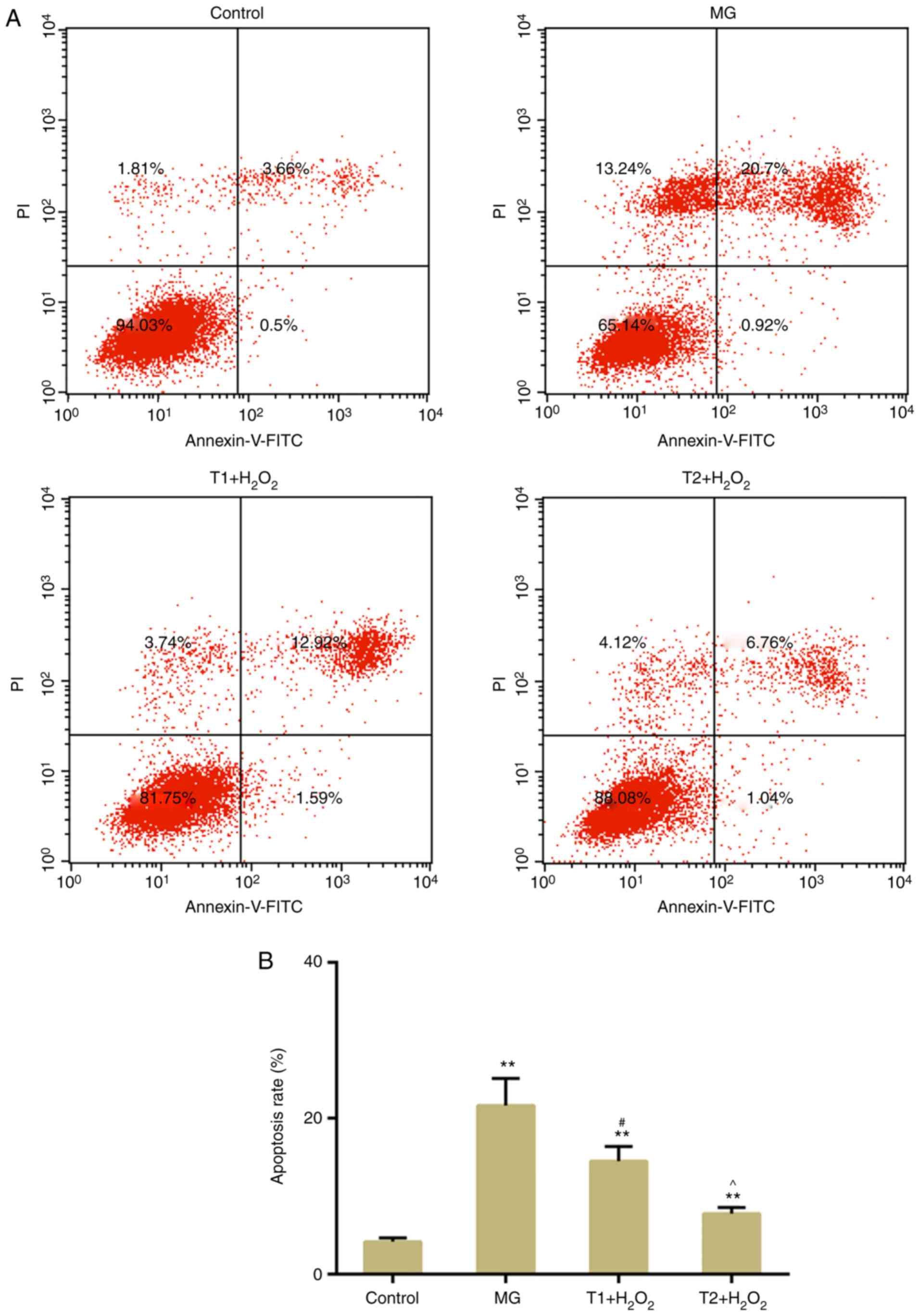
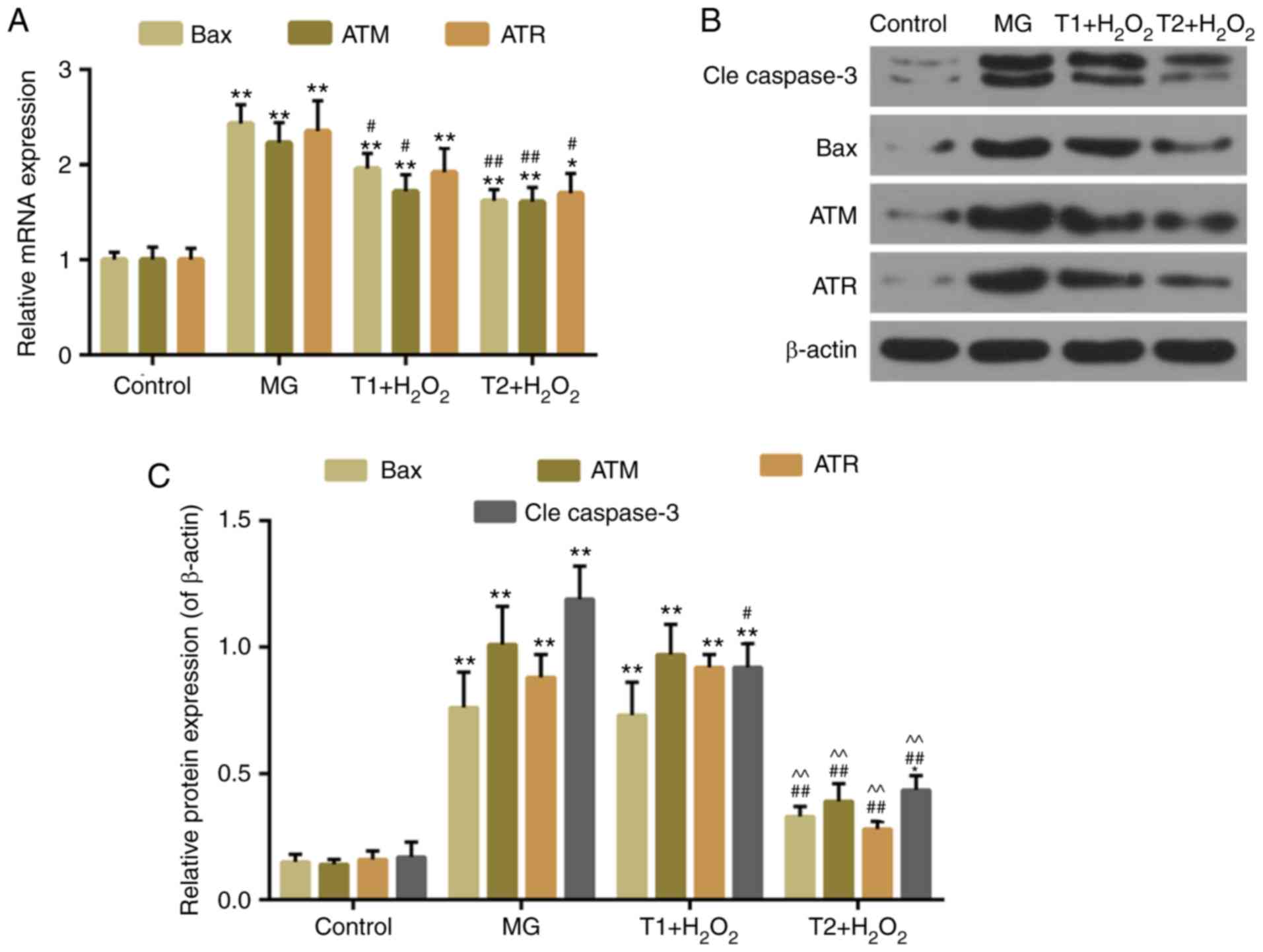
|
1
|
Graham HN: Tea: The plant and its
manufacture; chemistry and consumption of the beverage. Prog Clin
Biol Res. 158:29–74. 1984.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Oka Y, Iwai S, Amano H, Irie Y, Yatomi K,
Ryu K, Yamada S, Inagaki K and Oguchi K: Tea polyphenols inhibit
rat osteoclast formation and differentiation. J Pharm Sci.
118:55–64. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Liu S, Lu H, Zhao Q, He Y, Niu J, Debnath
AK, Wu S and Jiang S: Theaflavin derivatives in black tea and
catechin derivatives in green tea inhibit HIV-1 entry by targeting
gp41. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1723:270–281. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Maron DJ, Lu GP, Cai NS, Wu ZG, Li YH,
Chen H, Zhu JQ, Jin XJ, Wouters BC and Zhao J: Cholesterol-lowering
effect of a theaflavin-enriched green tea extract: A randomized
controlled trial. Arch Intern Med. 163:1448–1453. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lin JK, Chen PC, Ho CT and Lin-Shiau SY:
Inhibition of xanthine oxidase and suppression of intracellular
reactive oxygen species in HL-60 cells by
theaflavin-3,3′-digallate, (−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate, and
propyl gallate. J Agric Food Chem. 48:2736–2743. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Pap T and Korb-Pap A: Cartilage damage in
osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis-two unequal siblings. Nat
Rev Rheumatol. 11:606–615. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hosseinzadeh A, Kamrava SK, Joghataei MT,
Darabi R, Shakeri-Zadeh A, Shahriari M, Reiter RJ, Ghaznavi H and
Mehrzadi S: Apoptosis signaling pathways in osteoarthritis and
possible protective role of melatonin. J Pineal Res. 61:411–425.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lepetsos P and Papavassiliou AG:
ROS/oxidative stress signaling in osteoarthritis. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1862:576–591. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yu SM and Kim SJ: Withaferin A-caused
production of intracellular reactive oxygen species modulates
apoptosis via PI3K/Akt and JNKinase in rabbit articular
chondrocytes. J Korean Med Sci. 29:1042–1053. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chen AF, Davies CM, De Lin M and Fermor B:
Oxidative DNA damage in osteoarthritic porcine articular cartilage.
J Cell Physiol. 217:828–833. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Davies CM, Guilak F, Weinberg JB and
Fermor B: Reactive nitrogen and oxygen species in
interleukin-1-mediated DNA damage associated with osteoarthritis.
Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 16:624–630. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hashimoto S, Ochs RL, Komiya S and Lotz M:
Linkage of chondrocyte apoptosis and cartilage degradation in human
osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 41:1632–1638. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kim HA and Blanco FJ: Cell death and
apoptosis in osteoarthritic cartilage. Curr Drug Targets.
8:333–345. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Calnan DR and Brunet A: The FoxO code.
Oncogene. 27:2276–2288. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
van der Horst A and Burgering BMT:
Stressing the role of FoxO proteins in lifespan and disease. Nat
Rev Mol Cell Biol. 8:440–450. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Brigelius-Flohé R and Maiorino M:
Glutathione peroxidases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1830:3289–3303.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
García Z, Kumar A, Marqués M, Cortés I and
Carrera AC: Phosphoinositide 3-kinase controls early and late
events in mammalian cell division. EMBO J. 25:655–661. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang W, Sun Y, Liu J, Wang J, Li Y, Li H
and Zhang W: Protective effect of theaflavins on
homocysteine-induced injury in HUVEC cells in vitro. J Cardiovasc
Pharmacol. 59:434–440. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lahiry L, Saha B, Chakraborty J,
Bhattacharyya S, Chattopadhyay S, Banerjee S, Choudhuri T, Mandal
D, Bhattacharyya A, Sa G and Das T: Contribution of p53-mediated
Bax transactivation in theaflavin-induced mammary epithelial
carcinoma cell apoptosis. Apoptosis. 13:771–781. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wu CJ, O'Rourke DM, Feng GS, Johnson GR,
Wang Q and Greene MI: The tyrosine phosphatase SHP-2 is required
for mediating phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt activation by
growth factors. Oncogene. 20:6018–6025. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yamada T, Takeuchi S, Fujita N, Nakamura
A, Wang W, Li Q, Oda M, Mitsudomi T, Yatabe Y, Sekido Y, et al: Akt
kinase-interacting protein1, a novel therapeutic target for lung
cancer with EGFR-activating and gatekeeper mutations. Oncogene.
32:4427–4435. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Fani S, Kamalidehghan B, Lo KM, Nigjeh SE,
Keong YS, Dehghan F, Soori R, Abdulla MA, Chow KM, Ali HM, et al:
Anticancer activity of a monobenzyltin complex C1 against
MDA-MB-231 cells through induction of Apoptosis and inhibition of
breast cancer stem cells. Sci Rep. 6:389922016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Li J, Guo YY, Wu W, Bai JL, Xuan ZQ, Yang
J and Wang J: Detecting DNA damage of human lymphocytes exposed to
1,2-DCE with γH2AX identified antibody using flow cytometer assay.
Zhonghua Lao Dong Wei Sheng Zhi Ye Bing Za Zhi. 29:16–19. 2011.(In
Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yu YK, Lu Y, Yu Y and Yang J: γH2AX: A
biomarker for DNA double-stranded breaks. Chin J Pharm Tox.
19:237–240. 2005.
|
|
26
|
Wang D, Gao Q, Wang T, Qian F and Wang Y:
Theanine: the unique amino acid in the tea plant as an oral
hepatoprotective agent. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr. 26:384–391.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Schneider C and Segre T: Green tea:
Potential health benefits. Am Fam Physician. 79:591–594.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Tipoe GL, Leung TM, Hung MW and Fung ML:
Green tea polyphenols as an anti-oxidant and anti-inflammatory
agent for cardiovascular protection. Cardiovasc Hematol Disord Drug
Targets. 7:135–144. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Li YS, Xiao WF and Luo W: Cellular aging
towards osteoarthritis. Mech Ageing Dev. 162:80–84. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Morinobu A, Biao W, Tanaka S, Horiuchi M,
Jun L, Tsuji G, Sakai Y, Kurosaka M and Kumagai S:
(−)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate suppresses osteoclast
differentiation and ameliorates experimental arthritis in mice.
Arthritis Rheum. 58:2012–2018. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Bruyere O, Collette JH, Ethgen O, Rovati
LC, Giacovelli G, Henrotin YE, Seidel L and Reginster JY:
Biochemical markers of bone and cartilage remodeling in prediction
of longterm progression of knee osteoarthritis. J Rheumatol.
30:1043–1050. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Attur M, Yang Q, Kirsch T and Abramson SB:
Role of periostin and discoidin domain receptor-1 (DDR1) in the
regulation of cartilage degeneration and expression of MMP-13.
Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 24:S1562016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Goldring SR: Pathogenesis of bone and
cartilage destruction in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology
(Oxford). 42 Suppl 2:ii11–ii16. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zivanović S, Rackov LP, Vojvodić D and
Vucetić D: Human cartilage glycoprotein 39-biomarker of joint
damage in knee osteoarthritis. Int Orthop. 33:1165–1170. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Oltvai ZN, Milliman CL and Korsmeyer SJ:
Bcl-2 heterodimerizes in vivo with a conserved homolog, Bax, that
accelerates programmed cell death. Cell. 74:609–619. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Porter AG and Jänicke RU: Emerging roles
of caspase-3 in apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 6:99–104. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Lee JH and Paull TT: Activation and
regulation of ATM kinase activity in response to DNA double-strand
breaks. Oncogene. 26:7741–7748. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Sancar A, Lindsey-Boltz LA, Unsal-Kaçmaz K
and Linn S: Molecular mechanisms of mammalian DNA repair and the
DNA damage checkpoints. Annu Rev Biochem. 73:39–85. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zhang J, Cai S, Li J, Xiong L, Tian L, Liu
J, Huang J and Liu Z: Neuroprotective effects of theaflavins
against oxidative stress-induced apoptosis in PC12 cells. Neurochem
Res. 41:3364–3372. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Alotaibi A, Bhatnagar P, Najafzadeh M,
Gupta KC and Anderson D: Tea phenols in bulk and nanoparticle form
modify DNA damage in human lymphocytes from colon cancer patients
and healthy individuals treated in vitro with platinum-based
chemotherapeutic drugs. Nanomedicine (Lond). 8:389–401. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Adhikary A, Mohanty S, Lahiry L, Hossain
DM, Chakraborty S and Das T: Theaflavins retard human breast cancer
cell migration by inhibiting NF-kappaB via p53-ROS cross-talk. FEBS
Lett. 584:7–14. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Bhattacharya U, Halder B, Mukhopadhyay S
and Giri AK: Role of oxidation-triggered activation of JNK and p38
MAPK in black tea polyphenols induced apoptotic death of A375
cells. Cancer Sci. 100:1971–1978. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Schuck AG, Ausubel MB, Zuckerbraun HL and
Babich H: Theaflavin-3,3′-digallate, a component of black tea: An
inducer of oxidative stress and apoptosis. Toxicol In Vitro.
22:598–609. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Kato M, Yuan H, Xu ZG, Lanting L, Li SL,
Wang M, Hu MC, Reddy MA and Natarajan R: Role of the Akt/FoxO3a
pathway in TGF-beta1-mediated mesangial cell dysfunction: A novel
mechanism related to diabetic kidney disease. J Am Soci Nephrol.
17:3325–3335. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Zhao Y, Wang Y and Zhu WG: Applications of
post-translational modifications of FoxO family proteins in
biological functions. J Mol Cell Biol. 3:276–282. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Wilk A, Urbanska K, Yang S, Wang JY, Amini
S, Del Valle L, Peruzzi F, Meggs L and Reiss K: Insulin-like growth
factor-I-forkhead box O transcription factor 3a counteracts high
glucose/tumor necrosis factor-α-mediated neuronal damage:
Implications for human immunodeficiency virus encephalitis. J
Neurosci Res. 89:183–198. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|