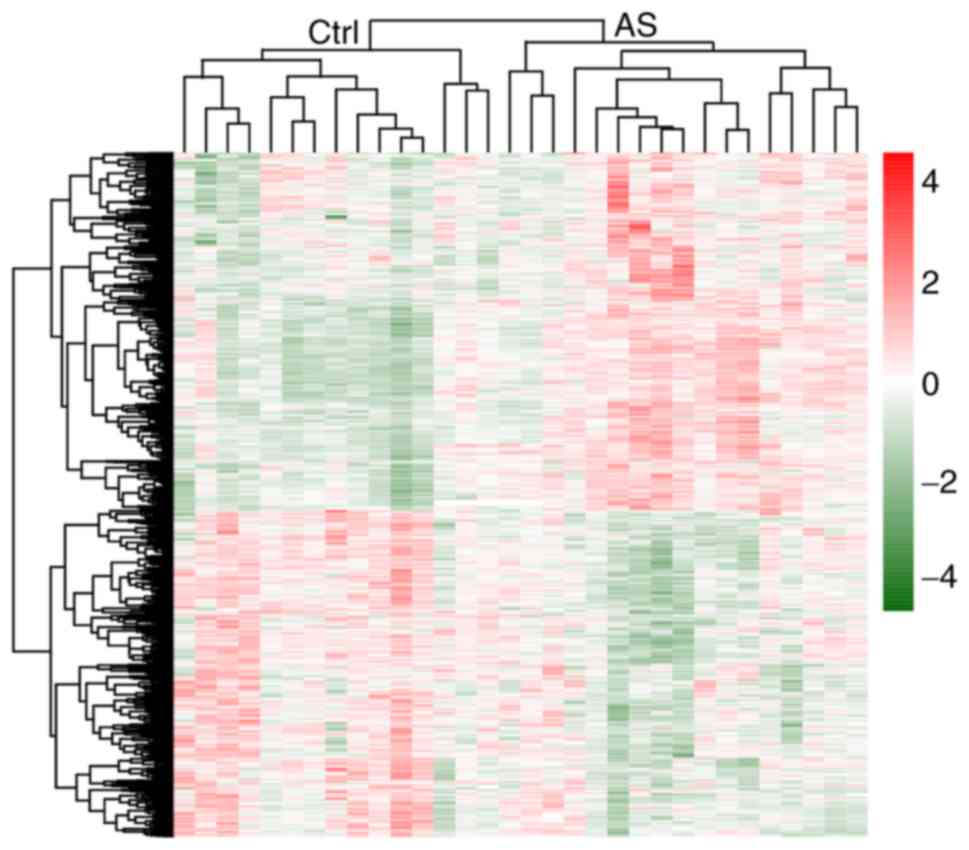
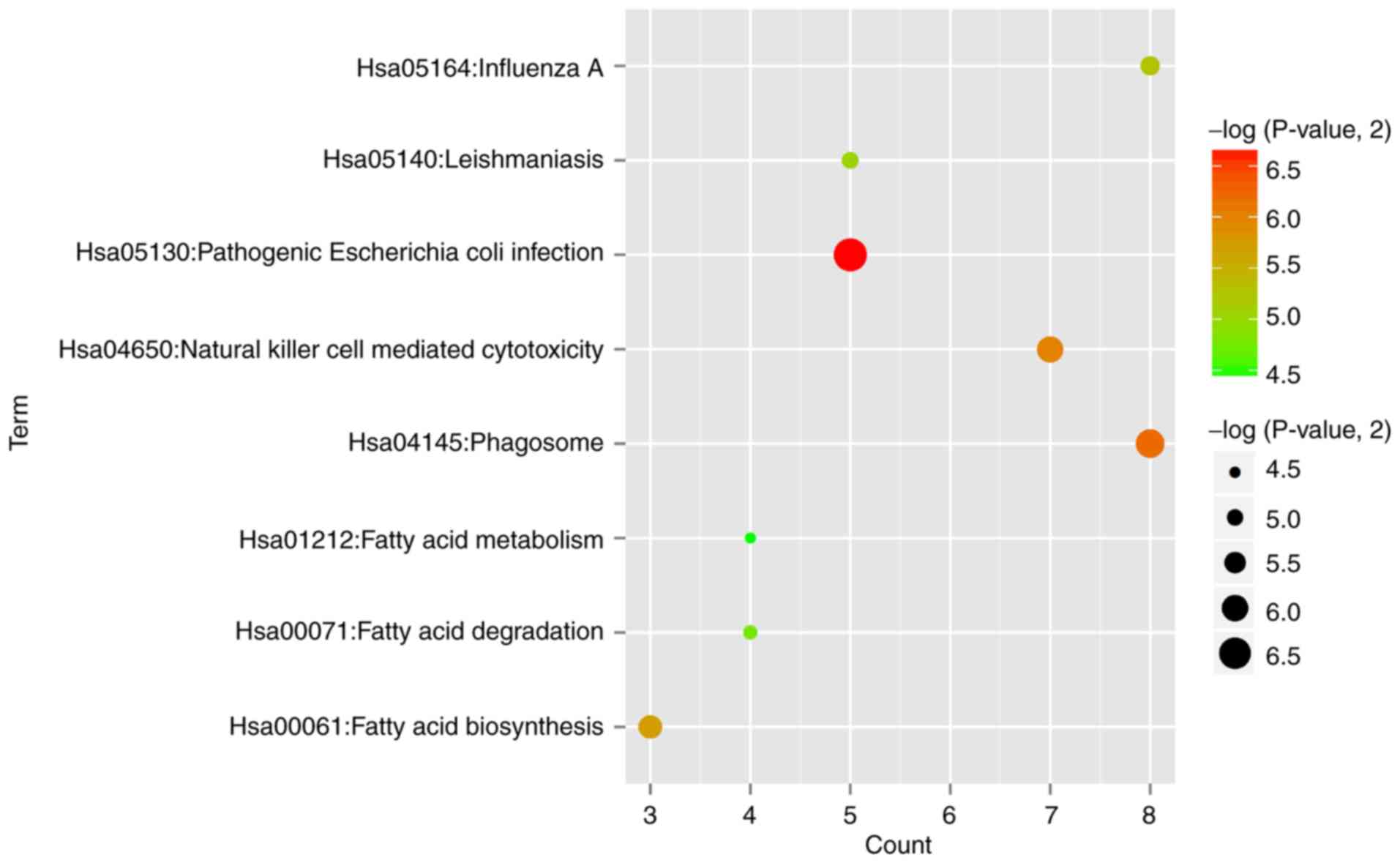
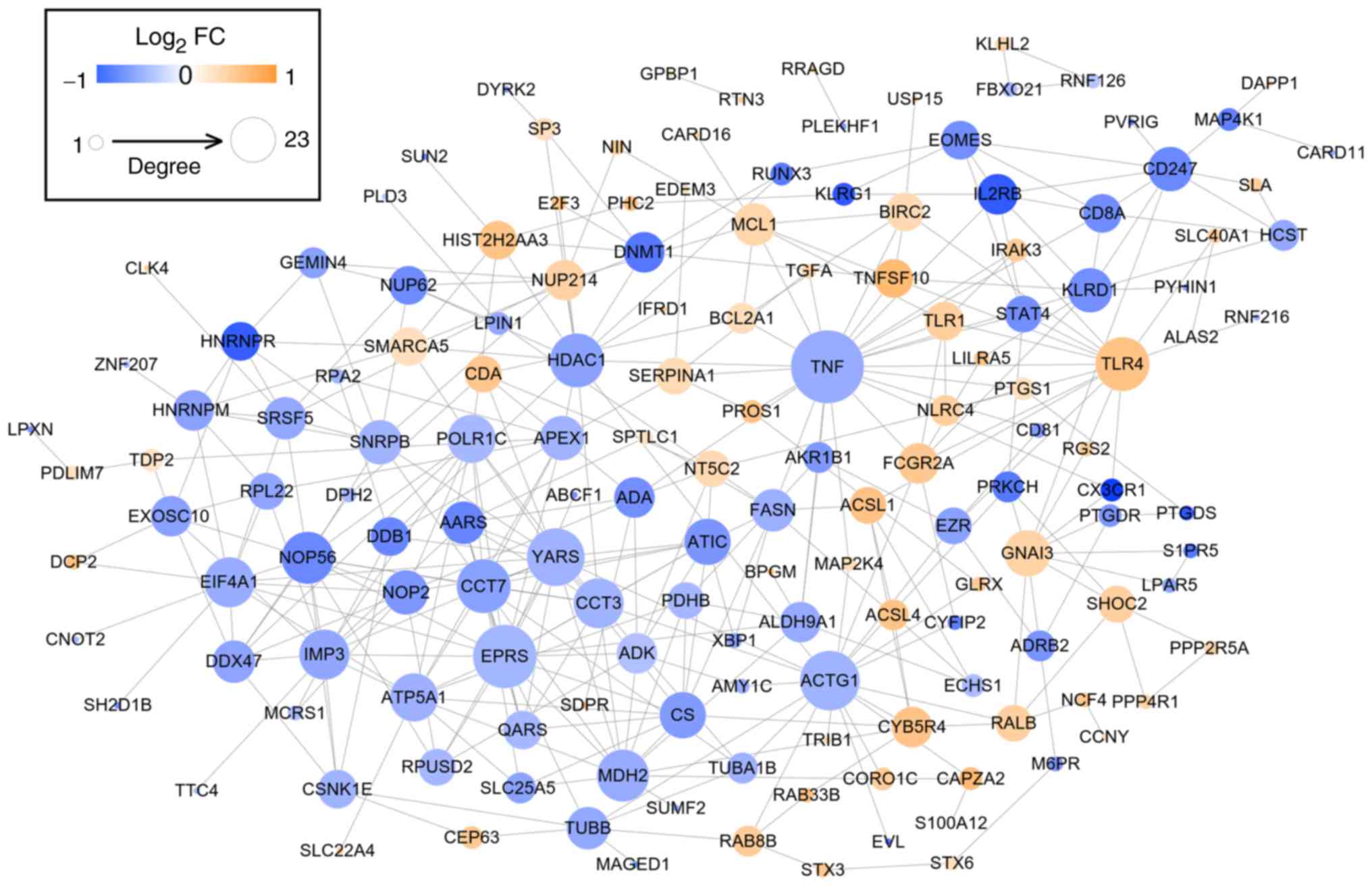
|
1
|
Dean LE, Jones GT, MacDonald AG, Downham
C, Sturrock RD and Macfarlane GJ: Global prevalence of ankylosing
spondylitis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 53:650–657. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Healey EL, Haywood KL, Jordan KP, Garratt
AM and Packham JC: Patients with well-established ankylosing
spondylitis show limited deterioration in a ten-year prospective
cohort study. Clin Rheumatol. 32:67–72. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chen B, Li J, He C, Li D, Tong W, Zou Y
and Xu W: Role of HLA-B27 in the pathogenesis of ankylosing
spondylitis. Mol Med Rep. 15:1943–1951. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Fernández-Sueiro JL, Alonso C, Blanco FJ,
Rodríguez-Gómez M, Galdo F and González-Gay MA: Prevalence of
HLA-B27 and subtypes of HLA-B27 associated with ankylosing
spondylitis in Galicia, Spain. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 22:465–468.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Cauli A, Dessole G, Fiorillo MT, Vacca A,
Mameli A, Bitti P, Passiu G, Sorrentino R and Mathieu A: Increased
level of HLA-B27 expression in ankylosing spondylitis patients
compared with healthy HLA-B27-positive subjects: A possible further
susceptibility factor for the development of disease. Rheumatology
(Oxford) 41(12). 1375–1379. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Yang T, Duan Z, Wu S, Liu S, Zeng Z, Li G,
Wang S, Fan D, Ye D, Xu S, et al: Association of HLA-B27 genetic
polymorphisms with ankylosing spondylitis susceptibility worldwide:
A meta-analysis. Mod Rheumatol. 24:150–161. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lin H and Gong YZ: Association of HLA-B27
with ankylosing spondylitis and clinical features of the
HLA-B27-associated ankylosing spondylitis: A meta-analysis.
Rheumatol Int. 37:1267–1280. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kim TJ, Na KS, Lee HJ, Lee B and Kim TH:
HLA-B27 homozygosity has no influence on clinical manifestations
and functional disability in ankylosing spondylitis. Clin Exp
Rheumatol. 27:574–579. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhang L, Zhang YJ, Chen J, Huang XL, Fang
GS, Yang LJ, Duan Y and Wang J: The association of HLA-B27 and
Klebsiella pneumoniae in ankylosing spondylitis: A systematic
review. Microb Pathog. 117:49–54. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Brown MA, Kennedy LG, Macgregor AJ, Darke
C, Duncan E, Shatford JL, Taylor A, Calin A and Wordsworth P:
Susceptibility to ankylosing spondylitis in twins: The role of
genes, HLA, and the environment. Arthritis Rheum. 40:1823–1828.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Brophy S, Hickey S, Menon A, Taylor G,
Bradbury L, Hamersma J and Calin A: Concordance of disease severity
among family members with ankylosing spondylitis? J Rheumatol.
31:1775–1778. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Azevedo VF, Faria-Neto JR, Stinghen A,
Lorencetti PG, Miller WP, Gonçalves BP, Szyhta CC and Pecoits-Filho
R: IL-8 but not other biomarkers of endothelial damage is
associated with disease activity in patients with ankylosing
spondylitis without treatment with anti-TNF agents. Rheumatol Int.
33:1779–1783. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Gonza-Lezlopez L, Fajardo-Robledo NS,
Saldaña-Cruz AM, Moreno-Sandoval IV, Bonilla-Lara D, Zavaleta-Muñiz
S, Nava-Zavala AH, Hernandez-Cuervo P, Rocha-Muñoz A,
Rodriguez-Jimenez NA, et al: Association of adipokines,
interleukin-6, and tumor necrosis factor-α concentrations with
clinical characteristics and presence of spinal syndesmophytes in
patients with ankylosing spondylitis: A cross-sectional study. J
Int Med Res. 45:1024–1035. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sundström B, Ljung L and Wållberg-Jonsson
S: Exercise habits and C-reactive protein may predict development
of spinal immobility in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Clin
Rheumatol. 37:2881–2885. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sohn DH, Jeong H, Roh JS, Lee HN, Kim E,
Koh JH and Lee SG: Serum CCL11 level is associated with
radiographic spinal damage in patients with ankylosing spondylitis.
Rheumatol Int. 38:1455–1464. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ruan WF, Xie JT, Jin Q, Wang WD and Ping
AS: The diagnostic and prognostic role of interleukin 12B and
interleukin 6R gene polymorphism in patients with ankylosing
spondylitis. J Clin Rheumatol. 24:18–24. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ma HJ, Yin QF, Wu Y and Guo MH: TNF-α-308
polymorphism determines clinical manifestations and therapeutic
response of ankylosing spondylitis in Han chinese. Med Clin (Barc).
149:517–522. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Gracey E, Yao Y, Green B, Qaiyum Z,
Baglaenko Y, Lin A, Anton A, Ayearst R, Yip P and Inman RD: Sexual
dimorphism in the Th17 signature of ankylosing spondylitis.
Arthritis Rheumatol. 68:679–689. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Pimentel-Santos FM, Ligeiro D, Matos M,
Mourão AF, Costa J, Santos H, Barcelos A, Godinho F, Pinto P, Cruz
M, et al: Whole blood transcriptional profiling in ankylosing
spondylitis identifies novel candidate genes that might contribute
to the inflammatory and tissue-destructive disease aspects.
Arthritis Res Ther. 13:R572011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chang X, Xu B, Wang L, Wang Y, Wang Y and
Yan S: Investigating a pathogenic role for TXNDC5 in tumors. Int J
Oncol. 43:1871–1884. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chang X, Zheng Y, Yang Q, Wang L, Pan J,
Xia Y, Yan X and Han J: Carbonic anhydrase I (CA1) is involved in
the process of bone formation and is susceptible to ankylosing
spondylitis. Arthritis Res Ther. 14:R1762012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ritchie ME, Phipson B, Wu D, Hu Y, Law CW,
Shi W and Smyth GK: limma powers differential expression analyses
for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res.
43:e472015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang K, Li M, Hadley D, Liu R, Glessner J,
Grant SFA, Hakonarson H and Bucan M: PennCNV: An integrated hidden
Markov model designed for high-resolution copy number variation
detection in whole-genome SNP genotyping data. Genome Res.
17:1665–1674. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Benjamini Y, Drai D, Elmer G, Kafkafi N
and Golani I: Controlling the false discovery rate in behavior
genetics research. Behav Brain Res. 125:279–284. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Szklarczyk D, Franceschini A, Wyder S,
Forslund K, Heller D, Huerta-Cepas J, Simonovic M, Roth A, Santos
A, Tsafou KP, et al: STRING v10: Protein-protein interaction
networks, integrated over the tree of life. Nucleic Acids Res
43(Database Issue). D447–D452. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Kohl M, Wiese S and Warscheid B:
Cytoscape: Software for visualization and analysis of biological
networks. Methods Mol Biol. 696:291–303. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Tang Y, Li M, Wang J, Pan Y and Wu FX:
CytoNCA: A cytoscape plugin for centrality analysis and evaluation
of protein interaction networks. Biosystems. 127:67–72. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Bader GD and Hogue CW: An automated method
for finding molecular complexes in large protein interaction
networks. BMC Bioinformatics. 4:22003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ku MJ and Lee SY: Contributions of
aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase-interacting multifunctional protein-3 to
mammalian translation initiation. Amino Acids. 44:1241–1245. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kang T, Kwon NH, Lee JY, Park MC, Kang E,
Kim HH, Kang TJ and Kim S: AIMP3/p18 controls translational
initiation by mediating the delivery of charged initiator tRNA to
initiation complex. J Mol Biol. 423:475–481. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hassan MK, Kumar D, Naik M and Dixit M:
The expression profile and prognostic significance of eukaryotic
translation elongation factors in different cancers. PLoS One.
13:e01913772018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yu X, Zheng H, Chan MT and Wu WK: HULC: An
oncogenic long non-coding RNA in human cancer. J Cell Mol Med.
21:410–417. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kim SS, Hur SY, Kim YR, Yoo NJ and Lee SH:
Expression of AIMP1, 2 and 3, the scaffolds for the multi-tRNA
synthetase complex, is downregulated in gastric and colorectal
cancer. Tumori. 97:380–385. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Park BJ, Oh YS, Park SY, Choi SJ, Rudolph
C, Schlegelberger B and Kim S: AIMP3 haploinsufficiency disrupts
oncogene-induced p53 activation and genomic stability. Cancer Res.
66:6913–6918. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Han JM, Park BJ, Sang GP, Oh YS, Choi SJ,
Sang WL, Hwang SK, Chang SH, Cho MH and Kim S: AIMP2/p38, the
scaffold for the multi-tRNA synthetase complex, responds to
genotoxic stresses via p53. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
105:11206–11211. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Gurung PM, Veerakumarasivam A, Williamson
M, Counsell N, Douglas J, Tan WS, Feber A, Crabb SJ, Short SC,
Freeman A, et al: Loss of expression of the tumour suppressor gene
AIMP3 predicts survival following radiotherapy in muscle-invasive
bladder cancer. Int J Cancer. 136:709–720. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Lee S, Yu KR, Ryu YS, Oh YS, Hong IS, Kim
HS, Lee JY, Kim S, Seo KW and Kang KS: miR-543 and miR-590-3p
regulate human mesenchymal stem cell aging via direct targeting of
AIMP3/p18. Age (Dordr). 36:97242014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Abou-Shousha SA, Salah E and Wagdy E:
Study of P53 in peripheral blood and synovial mononuclear cells of
rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis patients and its relation
to the degree of disease activity. Egypt J Immunol. 12:61–70.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Chou CT, Yang JS and Lee MR: Apoptosis in
rheumatoid arthritis-expression of Fas, Fas-L, p53, and Bcl-2 in
rheumatoid synovial tissues. J Pathol. 193:110–116. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Liang D, Halpert MM, Konduri V and Decker
WK: Stepping out of the cytosol: AIMp1/p43 potentiates the link
between innate and adaptive immunity. Int Rev Immunol. 34:367–381.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Choi JW, Kim DG, Park MC, Um JY, Han JM,
Park SG, Choi EC and Kim S: AIMP2 promotes TNFalpha-dependent
apoptosis via ubiquitin-mediated degradation of TRAF2. J Cell Sci.
122:2710–2715. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Hong SH, Cho JG, Yoon KJ, Lim DS, Kim CH,
Lee SW and Park SG: The antibody atliximab attenuates
collagen-induced arthritis by neutralizing AIMP1, an inflammatory
cytokine that enhances osteoclastogenesis. Biomaterials. 44:45–54.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Liu J, Zhu M, Chen W, Xie K, Shen W, Yuan
J, Cheng Y, Geng L, Wang Y, Jin G, et al: Genetic variants in
multisynthetase complex genes are associated with DNA damage levels
in chinese populations. Mutat Res. 786:8–13. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Ozgocmen S, Godekmerdan A and
Ozkurt-Zengin F: Acute-phase response, clinical measures and
disease activity in ankylosing spondylitis. Joint Bone Spine.
74:249–253. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Janciauskiene S, Moraga F and Lindgren S:
C-terminal fragment of alpha1-antitrypsin activates human monocytes
to a pro-inflammatory state through interactions with the CD36
scavenger receptor and LDL receptor. Atherosclerosis. 158:41–51.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Cardenas EI, Breaux K, Da Q, Flores JR,
Ramos MA, Tuvim MJ, Burns AR, Rumbaut RE and Adachi R: Platelet
Munc13-4 regulates hemostasis, thrombosis and airway inflammation.
Haematologica. 103:1235–1244. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Sun S, Fang K, Zhao Y, Yan X and Chang X:
Increased expression of alpha 1-anti-trypsin in the synovial
tissues of patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Clin Exp
Rheumatol. 30:39–44. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|