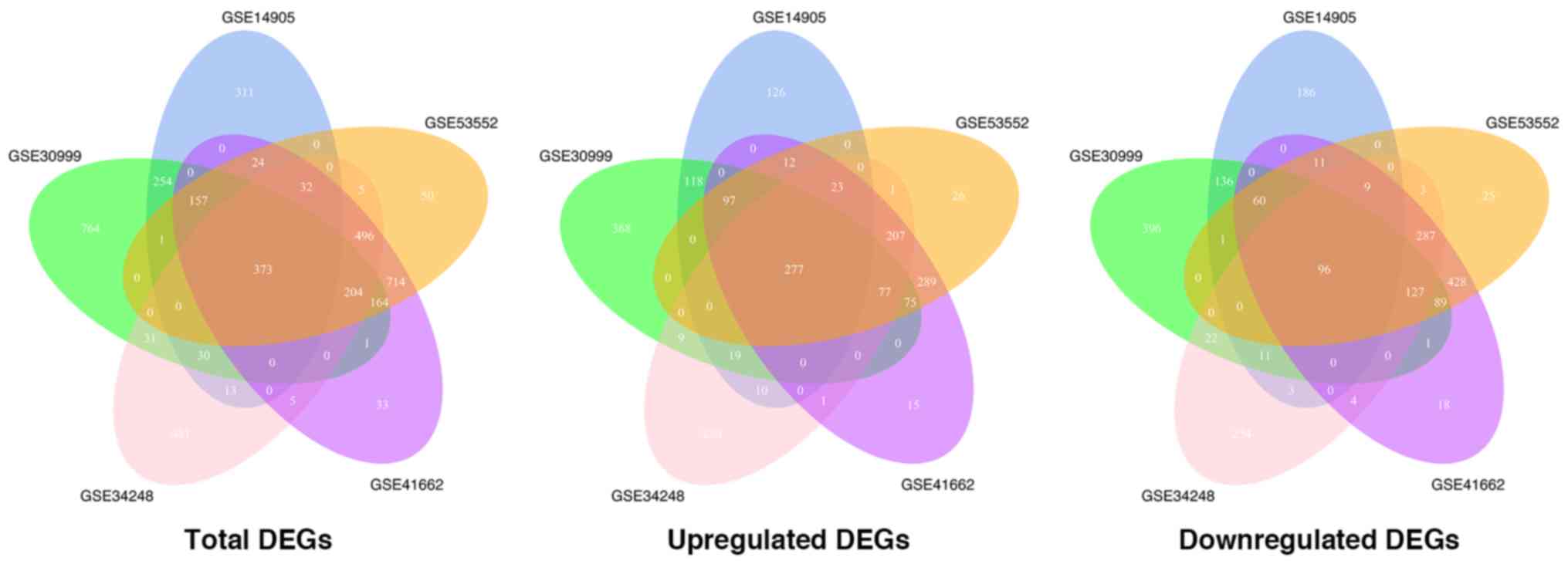
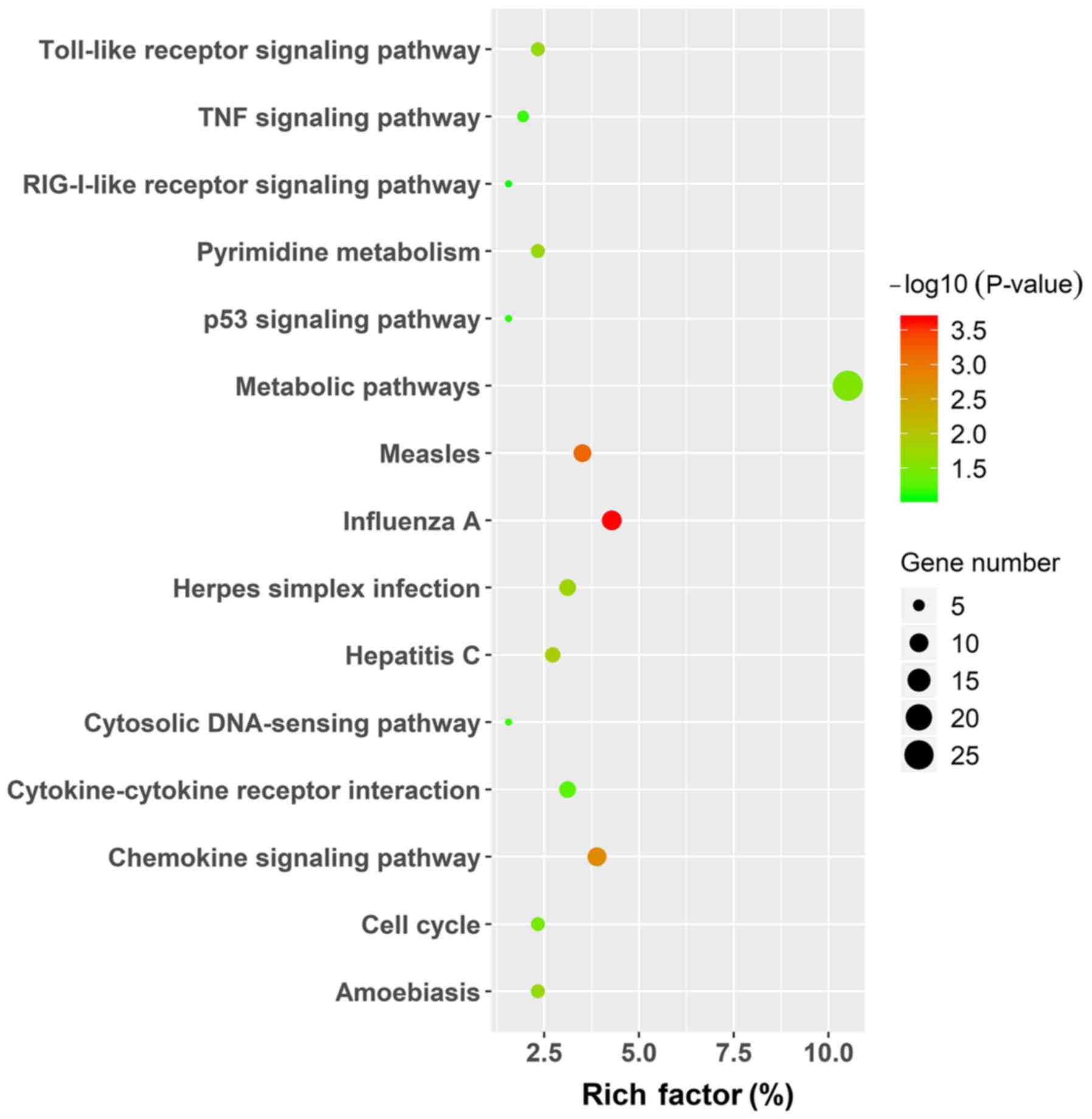
|
1
|
Greb JE, Goldminz AM, Elder JT, Lebwohl
MG, Gladman DD, Wu JJ, Mehta NN, Finlay AY and Gottlieb AB:
Psoriasis. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2:160822016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Parisi R, Symmons DP, Griffiths CE and
Ashcroft DM; Identification Management of Psoriasis, Associated
ComorbidiTy (IMPACT) project team, : Global epidemiology of
psoriasis: A systematic review of incidence and prevalence. J
Invest Dermatol. 133:377–385. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Martinez-Garcia E, Arias-Santiago S,
Valenzuela-Salas I, Garrido-Colmenero C, Garcia-Mellado V and
Buendia-Eisman A: Quality of life in persons living with psoriasis
patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 71:302–307. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Egeberg A, Thyssen JP, Wu JJ and Skov L:
Risk of first-time and recurrent depression in patients with
psoriasis: A population-based cohort study. Br J Dermatol.
180:116–121. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ainali C, Valeyev N, Perera G, Williams A,
Gudjonsson JE, Ouzounis CA, Nestle FO and Tsoka S: Transcriptome
classification reveals molecular subtypes in psoriasis. BMC
genomics. 13:4722012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Mei R and Mei X: Screening of skin
lesion-associated genes in patients with psoriasis by
meta-integration analysis. Dermatology. 233:277–288. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sevimoglu T and Arga KY: Computational
systems biology of psoriasis: Are we ready for the age of omics and
systems biomarkers? OMICS. 19:669–687. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yao Y, Richman L, Morehouse C, de los
Reyes M, Higgs BW, Boutrin A, White B, Coyle A, Krueger J, Kiener
PA and Jallal B: Type I interferon: Potential therapeutic target
for psoriasis? PLoS One. 3:e27372008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Suárez-Fariñas M, Li K, Fuentes-Duculan J,
Hayden K, Brodmerkel C and Krueger JG: Expanding the psoriasis
disease profile: Interrogation of the skin and serum of patients
with moderate-to-severe psoriasis. J Invest Dermatol.
132:2552–2564. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Correa da Rosa J, Kim J, Tian S, Tomalin
LE, Krueger JG and Suárez-Fariñas M: Shrinking the psoriasis
assessment gap: Early gene-expression profiling accurately predicts
response to long-term treatment. J Invest Dermato. 137:305–312.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Bigler J, Rand HA, Kerkof K, Timour M and
Russell CB: Cross-study homogeneity of psoriasis gene expression in
skin across a large expression range. PLoS One. 8:e522422013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Russell CB, Rand H, Bigler J, Kerkof K,
Timour M, Bautista E, Krueger JG, Salinger DH, Welcher AA and
Martin DA: Gene expression profiles normalized in psoriatic skin by
treatment with brodalumab, a human anti-IL-17 receptor monoclonal
antibody. J Immunol. 192:3828–3836. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ruano J, Suárez-Fariñas M, Shemer A, Oliva
M, Guttman-Yassky E and Krueger JG: Molecular and cellular
profiling of scalp psoriasis reveals differences and similarities
compared to skin psoriasis. PLoS One. 11:e01484502016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sherman BT, Huang da W, Tan Q, Guo Y, Bour
S, Liu D, Stephens R, Baseler MW, Lane HC and Lempicki RA: DAVID
Knowledgebase: A gene-centered database integrating heterogeneous
gene annotation resources to facilitate high-throughput gene
functional analysis. BMC Bioinformatics. 8:4262007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Szklarczyk D, Morris JH, Cook H, Kuhn M,
Wyder S, Simonovic M, Santos A, Doncheva NT, Roth A, Bork P, et al:
The STRING database in 2017: Quality-controlled protein-protein
association networks, made broadly accessible. Nucleic Acids Res.
45:D362–D368. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chin CH, Chen SH, Wu HH, Ho CW, Ko MT and
Lin CY: cytoHubba: Identifying hub objects and sub-networks from
complex interactome. BMC Syst Biol. 8 (Suppl 4):S112014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ishida-Yamamoto A and Iizuka H: Structural
organization of cornified cell envelopes and alterations in
inherited skin disorders. Exp Dermatol. 7:1–10. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Telfer NR, Chalmers RJ, Whale K and Colman
G: The role of streptococcal infection in the initiation of guttate
psoriasis. Arch Dermatol. 128:39–42. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Morhenn VB: The relationship of wound
healing with psoriasis and multiple sclerosis. Adv Wound Care (New
Rochelle). 7:185–188. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sweeney CM, Tobin AM and Kirby B: Innate
immunity in the pathogenesis of psoriasis. Arch Dermatol Res.
303:691–705. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Armstrong AW, Harskamp CT, Dhillon JS and
Armstrong EJ: Psoriasis and smoking: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. Br J Dermatol. 170:304–314. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Qureshi AA, Dominguez PL, Choi HK, Han J
and Curhan G: Alcohol intake and risk of incident psoriasis in US
women: A prospective study. Arch Dermatol. 146:1364–1369. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Jensen P and Skov L: Psoriasis and
obesity. Dermatology. 232:633–639. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Frantz C, Stewart KM and Weaver VM: The
extracellular matrix at a glance. J Cell Sci. 123:4195–4200. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Theocharis AD, Skandalis SS, Gialeli C and
Karamanos NK: Extracellular matrix structure. Adv Drug Deliv Rev.
97:4–27. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
McFadden J, Fry L, Powles AV and Kimber I:
Concepts in psoriasis: Psoriasis and the extracellular matrix. Br J
Dermatol. 167:980–986. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Brinkmann V, Reichard U, Goosmann C,
Fauler B, Uhlemann Y, Weiss DS, Weinrauch Y and Zychlinsky A:
Neutrophil extracellular traps kill bacteria. Science.
303:1532–1535. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Brinkmann V and Zychlinsky A: Neutrophil
extracellular traps: Is immunity the second function of chromatin?
J Cell Biol. 198:773–783. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kessenbrock K, Krumbholz M, Schönermarck
U, Back W, Gross WL, Werb Z, Gröne HJ, Brinkmann V and Jenne DE:
Netting neutrophils in autoimmune small-vessel vasculitis. Nat Med.
15:623–625. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Garcia-Romo GS, Caielli S, Vega B,
Connolly J, Allantaz F, Xu Z, Punaro M, Baisch J, Guiducci C,
Coffman RL, et al: Netting neutrophils are major inducers of type I
IFN production in pediatric systemic lupus erythematosus. Sci
Transl Med. 3:73ra202011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lin AM, Rubin CJ, Khandpur R, Wang JY,
Riblett M, Yalavarthi S, Villanueva EC, Shah P, Kaplan MJ and Bruce
AT: Mast cells and neutrophils release IL-17 through extracellular
trap formation in psoriasis. J Immunol. 187:490–500. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Law RH, Zhang Q, McGowan S, Buckle AM,
Silverman GA, Wong W, Rosado CJ, Langendorf CG, Pike RN, Bird PI
and Whisstock JC: An overview of the serpin superfamily. Genome
Biol. 7:2162006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Johnston A, Xing X, Wolterink L, Barnes
DH, Yin Z, Reingold L, Kahlenberg JM, Harms PW and Gudjonsson JE:
IL-1 and IL-36 are dominant cytokines in generalized pustular
psoriasis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 140:109–120. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Krieg P and Fürstenberger G: The role of
lipoxygenases in epidermis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1841:390–400.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chiba H, Michibata H, Wakimoto K, Seishima
M, Kawasaki S, Okubo K, Mitsui H, Torii H and Imai Y: Cloning of a
gene for a novel epithelium-specific cytosolic phospholipase A2,
cPLA2delta, induced in psoriatic skin. J Biol Chem.
279:12890–12897. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kudalkar EM, Scarborough EA, Umbreit NT,
Zelter A, Gestaut DR, Riffle M, Johnson RS, MacCoss MJ, Asbury CL
and Davis TN: Regulation of outer kinetochore Ndc80 complex-based
microtubule attachments by the central kinetochore Mis12/MIND
complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 112:E5583–E5589. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Santaguida S and Musacchio A: The life and
miracles of kinetochores. EMBO J. 28:2511–2531. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
DeLuca KF, Meppelink A, Broad AJ, Mick JE,
Peersen OB, Pektas S, Lens SMA and DeLuca JG: Aurora A kinase
phosphorylates Hec1 to regulate metaphase kinetochore-microtubule
dynamics. J Cell Bio. 217:163–177. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Mills GB, Schmandt R, McGill M, Amendola
A, Hill M, Jacobs K, May C, Rodricks AM, Campbell S and Hogg D:
Expression of TTK, a novel human protein kinase, is associated with
cell proliferation. J Biol Chem. 267:16000–16006. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
George SM, Taylor MR and Farrant PB:
Psoriatic alopecia. Clin Exp Dermatol. 40:717–721. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|