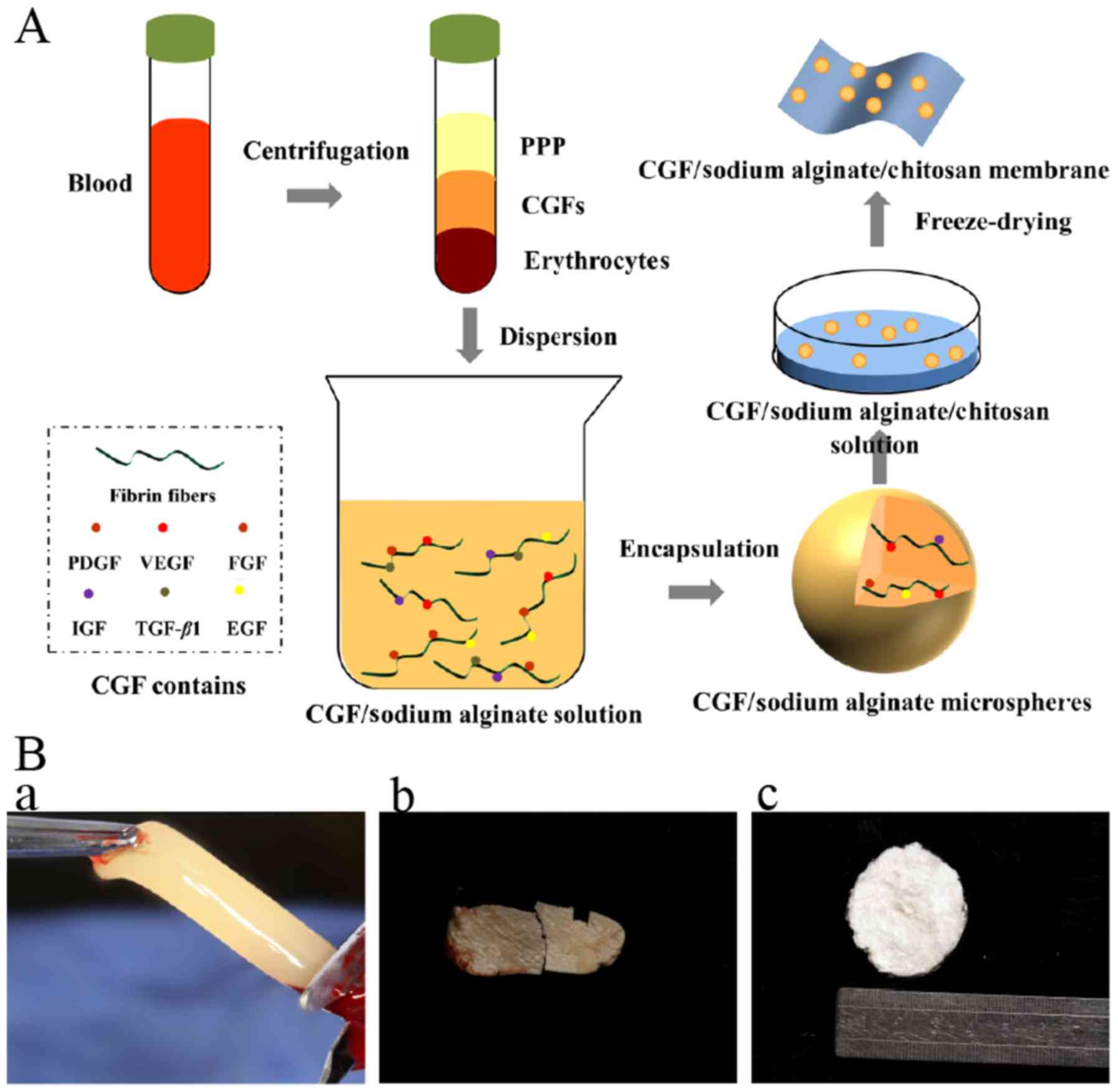
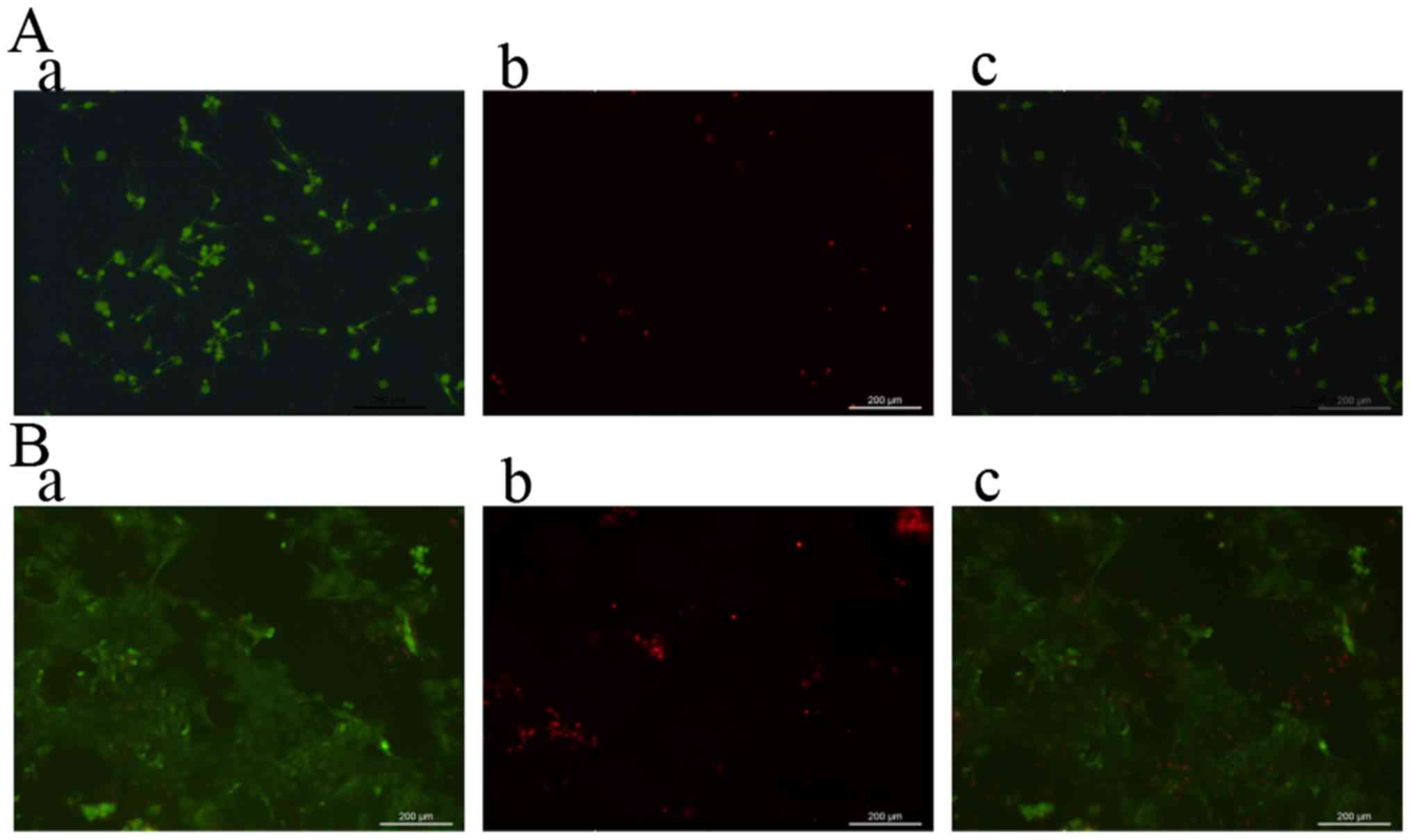
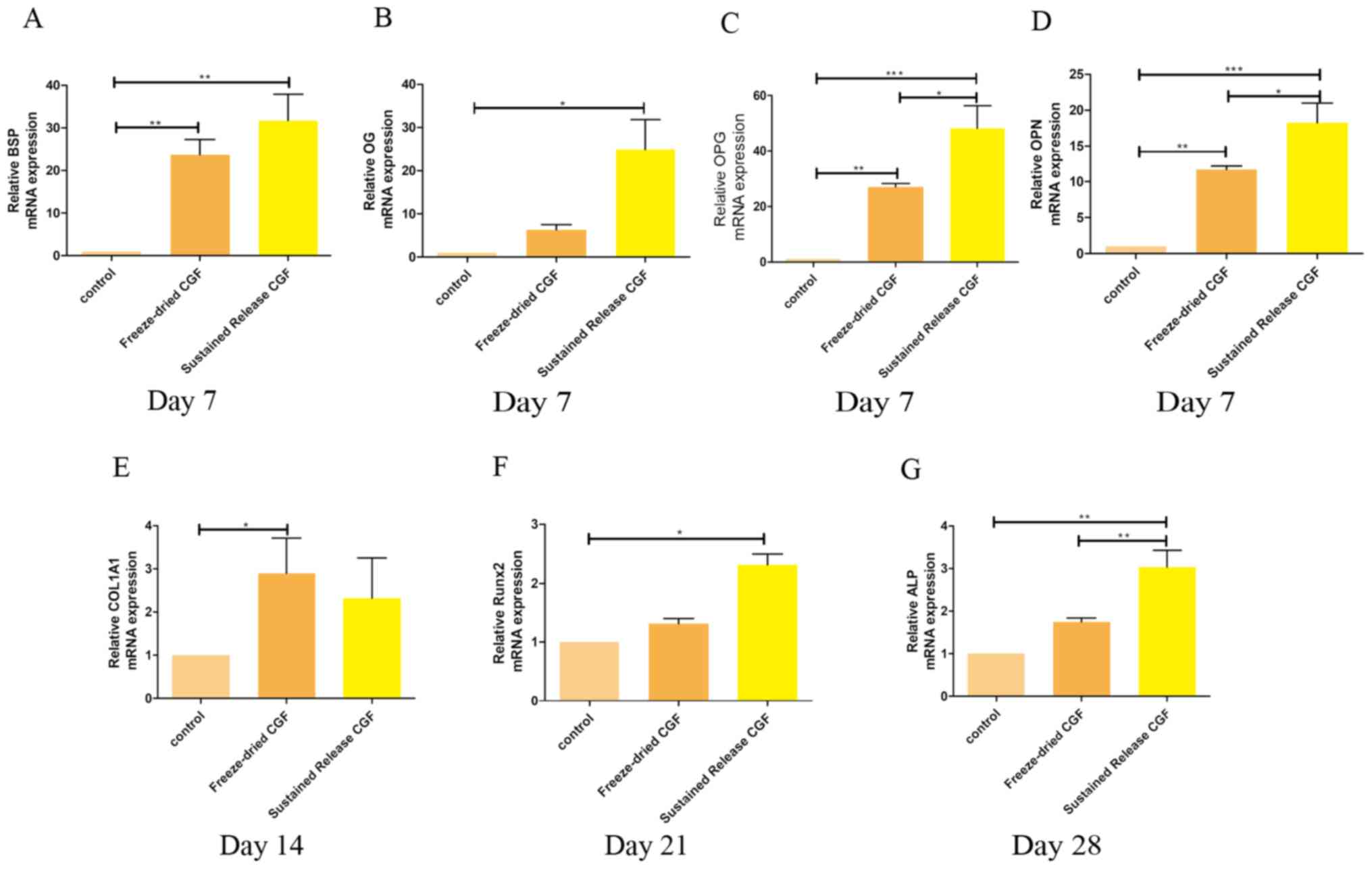
|
1
|
Whitman DH, Berry RL and Green DM:
Platelet gel: An autologous alternative to fibrin glue with
applications in oral and maxillofacial surgery. J Oral Maxillofac
Surg. 55:1294–1299. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
de Vos RJ, Weir A, van Schie HT,
Bierma-Zeinstra SM, Verhaar JA, Weinans H and Tol JL: Platelet-rich
plasma injection for chronic Achilles tendinopathy: A randomized
controlled trial. JAMA. 303:144–149. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Dohan DM, Choukroun J, Diss A, Dohan SL,
Dohan AJJ, Mouhyi J and Gogly B: Platelet-rich fibrin (PRF): A
second-generation platelet concentrate. Part III: Leucocyte
activation: A new feature for platelet concentrates? Oral Surg Oral
Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 101:e51–e55. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Anitua E, Aguirre JJ, Algorta J, Ayerdi E,
Cabezas AI, Orive G and Andia I: Effectiveness of autologous
preparation rich in growth factors for the treatment of chronic
cutaneous ulcers. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 84:415–421.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Rodella LF, Favero G, Boninsegna R,
Buffoli B, Labanca M, Scarì G, Sacco L, Batani T and Rezzani R:
Growth factors, CD34 positive cells, and fibrin network analysis in
concentrated growth factors fraction. Microsc Res Tech. 74:772–777.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kawase T and Tanaka T: An updated proposal
for terminology and classification of platelet-rich fibrin. Regen
Ther. 7:80–81. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sohn DS, Moon JW, Moon YS, Park JS and
Jung HS: The use of concentrated growth factor (CGF) for sinus
augmentation. J Oral Implant. 38:25–38. 2009.
|
|
8
|
Sohn DS, Heo JU, Kwak DH, Kim DE, Kim JM,
Moon JW, Lee JH and Park IS: Bone regeneration in the maxillary
sinus using an autologous fibrin-rich block with concentrated
growth factors alone. Implant Dent. 20:389–395. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yu B and Wang Z: Effect of concentrated
growth factors on beagle periodontal ligament stem cells in vitro.
Mol Med Rep. 9:235–242. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
He L, Lin Y, Hu X, Zhang Y and Wu H: A
comparative study of platelet-rich fibrin (PRF) and platelet-rich
plasma (PRP) on the effect of proliferation and differentiation of
rat osteoblasts in vitro. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral
Radiol Endod. 108:707–713. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bhattarai N, Gunn J and Zhang M:
Chitosan-based hydrogels for controlled, localized drug delivery.
Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 62:83–99. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Riva R, Ragelle H, des Rieux A, Duhem N,
Jérôme C and Préat V: Chitosan and chitosan derivatives in drug
delivery and tissue engineering. Adv Polym Sci. 244:19–44. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Sonia TA and Sharma CP: Chitosan and its
derivatives for drug delivery perspective. Adv Polym Sci.
243:23–53. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Mengatto LN, Helbling IM and Luna JA:
Recent advances in chitosan films for controlled release of drugs.
Recent Pat Drug Deliv Formul. 6:156–170. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kumar AS and Ramaswamy NM: Chitosan
microspheres as potential vaccine delivery systems. Int J Drug
Deliv. 3:43–50. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Taşkın AK, Yaşar M, Ozaydın I, Kaya B, Bat
O, Ankaralı S, Yıldırım U and Aydın M: The hemostatic effect of
calcium alginate in experimental splenic injury model. Ulusal
Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg. 19:195–199. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Pinkas O and Zilberman M: Effect of
hemostatic agents on properties of gelatin-alginate soft tissue
adhesives. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 25:555–573. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
He Q, Gong K, Ao Q, Ma T, Yan Y, Gong Y
and Zhang X: Positive charge of chitosan retards blood coagulation
on chitosan films. J Biomater Appl. 27:1032–1045. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lam PL, Lee KK, Wong RS, Cheng GY, Cheng
SY, Yuen MC, Lam KH, Gambari R, Kok SH and Chui CH: Development of
hydrocortisone succinic acid/and 5-fluorouracil/chitosan
microcapsules for oral and topical drug deliveries. Bioorg Med Chem
Lett. 22:3213–3218. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Prins HJ, Braat AK, Gawlitta D, Dhert WJ,
Egan DA, Tijssen-Slump E, Yuan H, Coffer PJ, Rozemuller H and
Martens AC: In vitro induction of alkaline phosphatase levels
predicts in vivo bone forming capacity of human bone marrow stromal
cells. Stem Cell Res. 12:428–440. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Casati MZ, de Vasconcelos Gurgel BC,
Gonçalves PF, Pimentel SP, da Rocha Nogueira Filho G, Nociti FH Jr
and Sallum EA: Platelet-rich plasma does not improve bone
regeneration around peri-implant bone defects - a pilot study in
dogs. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 36:132–136. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Schaaf H, Streckbein P, Lendeckel S,
Heidinger KS, Rehmann P, Boedeker RH and Howaldt HP: Sinus lift
augmentation using autogenous bone grafts and platelet-rich plasma:
Radiographic results. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol
Endod. 106:673–678. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Dohan Ehrenfest DM, de Peppo GM, Doglioli
P and Sammartino G: Slow release of growth factors and
thrombospondin-1 in Choukroun's platelet-rich fibrin (PRF): A gold
standard to achieve for all surgical platelet concentrates
technologies. Growth Factors. 27:63–69. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Marx RE: Platelet-rich plasma (PRP): What
is PRP and what is not PRP? Implant Dent. 10:225–228. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Park HC, Kim SG, Oh JS, You JS, Kim JS,
Lim SC, Jeong MA, Kim JS, Jung C, Kwon YS and Ji H: Early bone
formation at a femur defect using CGF and PRF grafts in adult dogs:
A comparative study. Implant Dent. 25:387–393. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lu Z and Kipnis J: Thrombospondin 1-a key
astrocyte-derived neurogenic factor. FASEB J. 24:1925–1934. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhao C, Isenberg JS and Popel AS: Human
expression patterns: Qualitative and quantitative analysis of
thrombospondin-1 under physiological and pathological conditions. J
Cell Mol Med. 22:2086–2097. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Murphy-Ullrich JE and Suto MJ:
Thrombospondin-1 regulation of latent TGF-β activation: A
therapeutic target for fibrotic disease. Matrix Biol. 68-69:28–43.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ghadami M, Makita Y, Yoshida K, Nishimura
G, Fukushima Y, Wakui K, Ikegawa S, Yamada K, Kondo S, Niikawa N
and Tomita Ha: Genetic mapping of the Camurati-Engelmann disease
locus to chromosome 19q13.1-q13.3. Am J Hum Genet. 66:143–147.
2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Le Bousse-Kerdilès MC and Martyré MC: Dual
implication of fibrogenic cytokines in the pathogenesis of fibrosis
and myeloproliferation in myeloid metaplasia with myelofibrosis.
Ann Hematol. 78:437–444. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wang CY, Li XD, Hao ZH and Xu D:
Insulin-like growth factor-1 improves diabetic cardiomyopathy
through antioxidative and anti-inflammatory processes along with
modulation of Akt/GSK-3β signaling in rats. Korean J Physiol
Pharmacol. 20:613–619. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Pierce GF, Tarpley JE, Yanagihara D,
Mustoe TA, Fox GM and Thomason A: Platelet-derived growth factor
(BB homodimer), transforming growth factor-beta 1, and basic
fibroblast growth factor in dermal wound healing. Neovessel and
matrix formation and cessation of repair. Am J Pathol.
140:1375–1388. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Hu K and Olsen BR: The roles of vascular
endothelial growth factor in bone repair and regeneration. Bone.
91:30–38. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Liu Y, Chen L, Zhou C, Yang J, Hou Y and
Wang W: Development and evaluation of alginate-chitosan gastric
floating beads loading with oxymatrine solid dispersion. Drug Dev
Ind Pharm. 42:456–463. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
He M, Zhang X, Yao W, Wang C, Shi L and
Zhou P: Construction of alternate layered chitosan/alginate
composite hydrogels and their properties. Mater Lett. 200:43–46.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Coppi G and Iannuccelli V:
Alginate/chitosan microparticles for tamoxifen delivery to the
lymphatic system. Int J Pharm. 367:127–132. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|