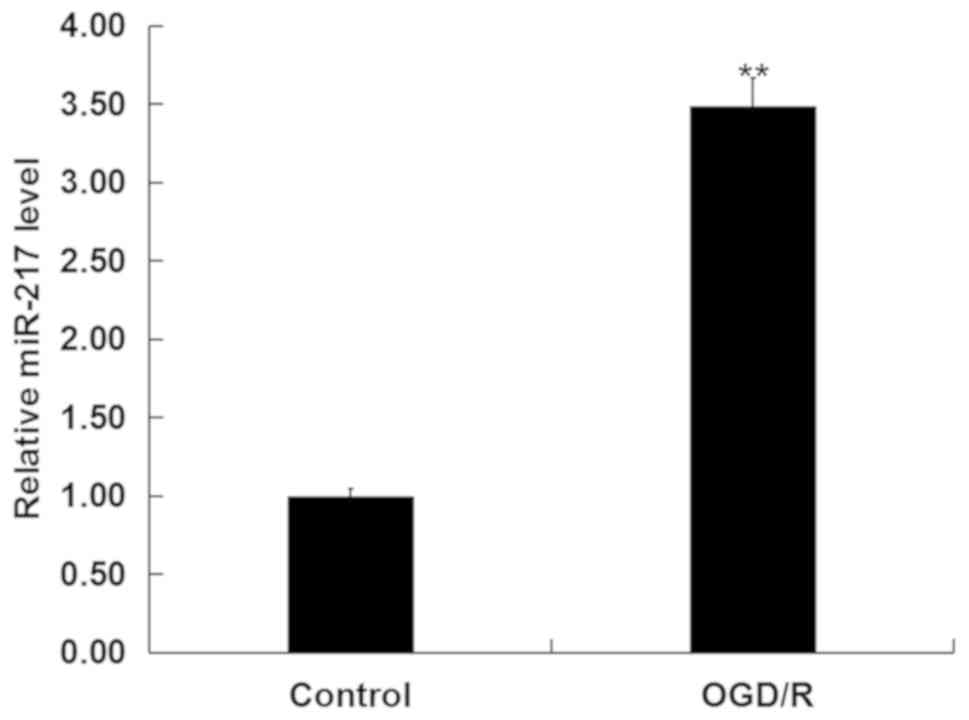
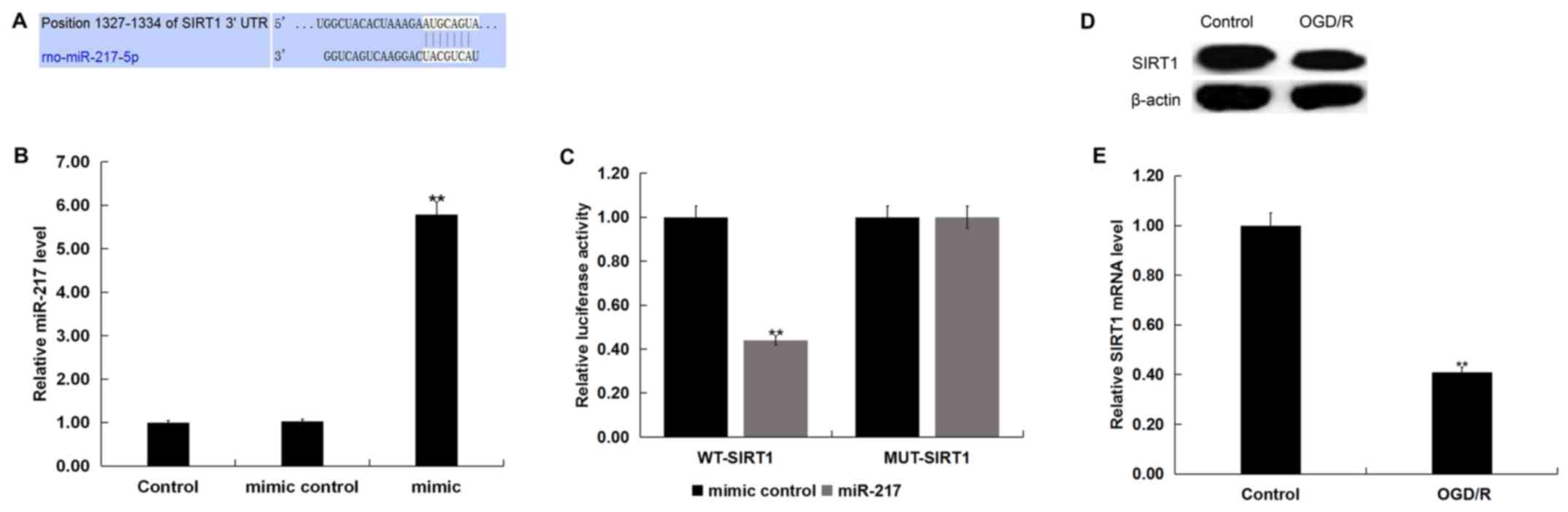
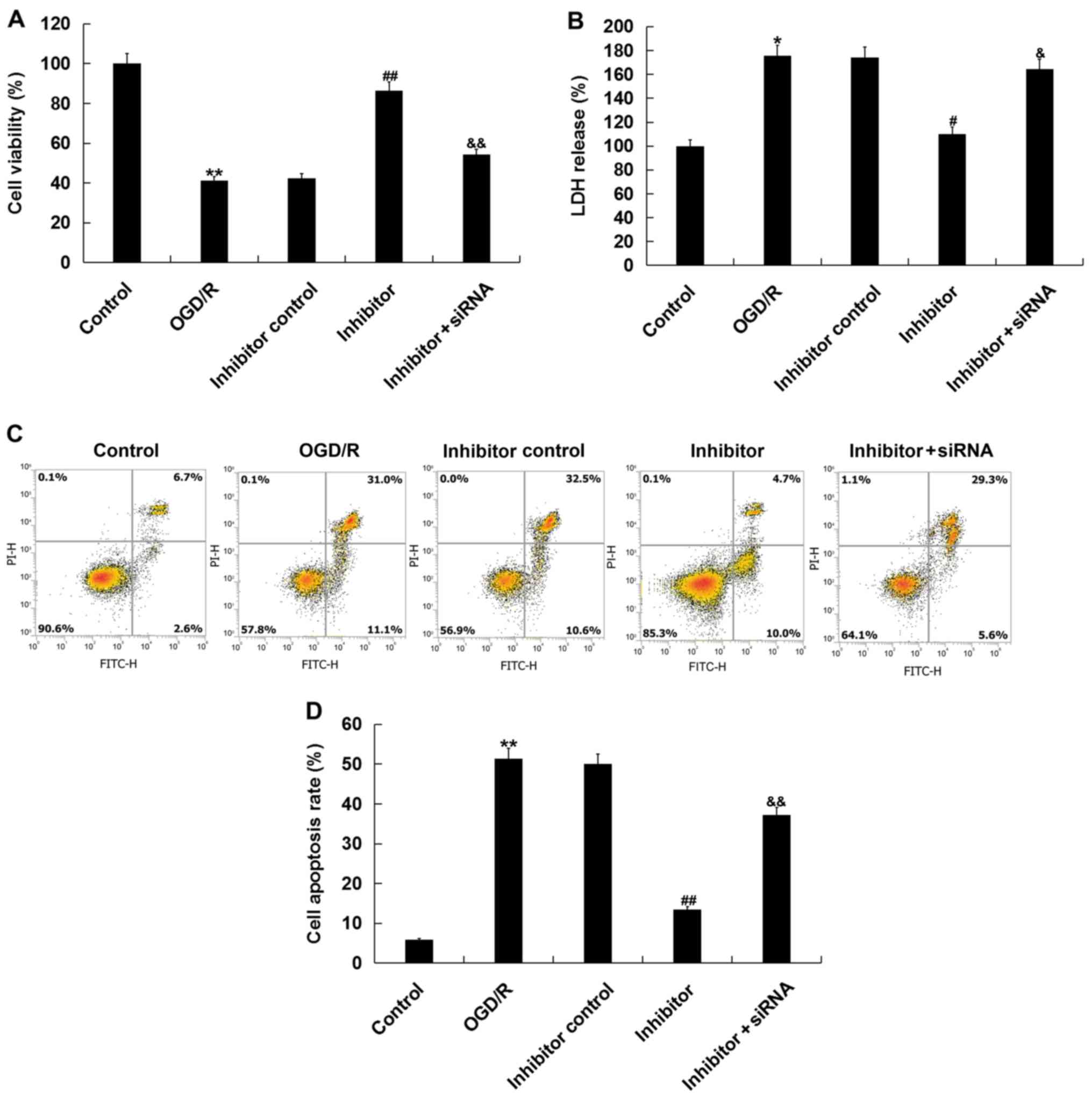
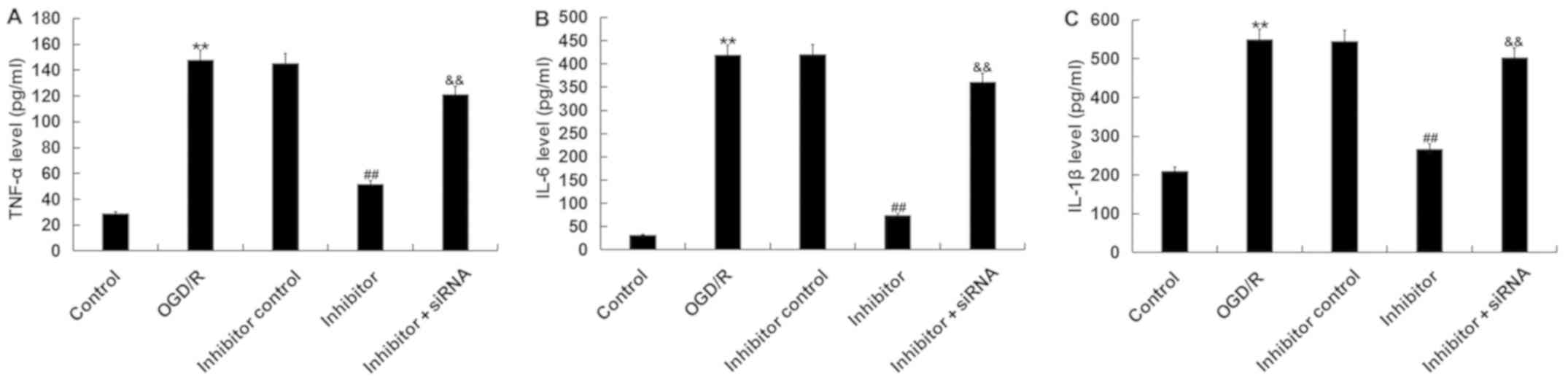
|
1
|
Feigin VL: Stroke epidemiology in the
developing world. Lancet. 365:2160–2161. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Goldstein LB, Adams R, Becker K, Furberg
CD, Gorelick PB, Hademenos G, Hill M, Howard G, Howard VJ, Jacobs
B, et al: Primary prevention of ischemic stroke A statement for
healthcare professionals from the stroke council of the American
heart association. Circulation. 103:163–182. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Jean WC, Spellman SR, Nussbaum ES and Low
WC: Reperfusion injury after focal cerebral ischemia: The role of
inflammation and the therapeutic horizon. Neurosurgery.
43:1382–1397. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Schrepfer E and Scorrano L: Mitofusins,
from mitochondria to metabolism. Mol Cell. 61:683–694. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bhaskar S, Stanwell P, Cordato D, Attia J
and Levi C: Reperfusion therapy in acute ischemic stroke: Dawn of a
new era? BMC Neurol. 18:82018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hammond SM: An overview of microRNAs. Adv
Drug Deliv Rev. 87:3–14. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ghildiyal M and Zamore PD: Small silencing
RNAs: An expanding universe. Nat Rev Genet. 10:94–108. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Soifer HS, Rossi JJ and Saetrom P:
MicroRNAs in disease and potential therapeutic applications. Mol
Ther. 15:2070–2079. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Krol J, Loedige I and Filipowicz W: The
widespread regulation of microRNA biogenesis, function and decay.
Nat Rev Genet. 11:597–610. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
O'Connell RM, Rao DS, Chaudhuri AA and
Baltimore D: Physiological and pathological roles for microRNAs in
the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol. 10:111–122. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Mendell JT and Olson EN: MicroRNAs in
stress signaling and human disease. Cell. 148:1172–1187. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Di Y, Lei Y, Yu F, Changfeng F, Song W and
Xuming M: MicroRNAs expression and function in cerebral ischemia
reperfusion injury. J Mol Neurosci. 53:242–250. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hu Y, Deng H, Xu S and Zhang J: MicroRNAs
regulate mitochondrial function in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion
injury. Int J Mol Sci. 16:24895–24917. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang P, Liang X, Lu Y, Zhao X and Liang J:
MicroRNA-93 downregulation ameliorates cerebral ischemic injury
through the Nrf2/HO-1 defense pathway. Neurochem Res. 41:2627–2635.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang N, Zhang L, Lu Y, Zhang M, Zhang Z,
Wang K and Lv J: Down-regulation of microRNA-142-5p attenuates
oxygen-glucose deprivation and reoxygenation-induced neuron injury
through up-regulating Nrf2/ARE signaling pathway. Biomed
Pharmacother. 89:1187–1195. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Shi F, Dong Z, Li H, Liu X, Liu H and Dong
R: MicroRNA-137 protects neurons against ischemia/reperfusion
injury through regulation of the notch signaling pathway. Exp Cell
Res. 352:1–8. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Liu AN, Qu HJ, Yu CY and Sun P: Knockdown
of LINC01614 inhibits lung adenocarcinoma cell progression by
up-regulating miR-217 and down-regulating FOXP1. J Cell Mol Med.
22:4034–4044. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang LP, Wang JP and Wang XP: HOTAIR
contributes to the growth of liver cancer via targeting miR-217.
Oncol Lett. 15:7963–7972. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yan J, Wu G, Chen J, Xiong L, Chen G and
Li P: Downregulated miR-217 expression predicts a poor outcome in
acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer Biomark. 22:73–78. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Safaralizadeh R, Ajami N, Nemati M,
Hosseinpourfeizi M, Azimzadeh Isfanjani A and Moaddab SY:
Disregulation of miR-216a and miR-217 in gastric cancer and their
clinical significance. J Gastrointest Cancer. 50:78–83. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yu B, Du Q, Li H, Liu HY, Ye X, Zhu B,
Zhai Q and Li XX: Diagnostic potential of serum exosomal colorectal
neoplasia differentially expressed long non-coding RNA (CRNDE-p)
and microRNA-217 expression in colorectal carcinoma. Oncotarget.
8:83745–83753. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zheng J, Liu X, Xue Y, Gong W, Ma J, Xi Z,
Que Z and Liu Y: TTBK2 circular RNA promotes glioma malignancy by
regulating miR-217/HNF1β/Derlin-1 pathway. J Hematol Oncol.
10:522017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Sahu S, Nag DS, Swain A and Samaddar DP:
Biochemical changes in the injured brain. World J Biol Chem.
8:21–31. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhang J, Zhao F, Zhao Y, Wang J, Pei L,
Sun N and Shi J: Hypoxia induces an increase in intracellular
magnesium via transient receptor potential melastatin 7 (TRPM7)
channels in rat hippocampal neurons in vitro. J Biol Chem.
286:20194–20207. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Liu X, Li M, Hou M, Huang W and Song J:
MicroRNA-135a alleviates oxygen-glucose deprivation and
reoxygenation-induced injury in neurons through regulation of
GSK-3β/Nrf2 signaling. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2:e221592018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Bayne K: Revised guide for the care and
use of laboratory animals available. American physiological
society. Physiologist. 39:199208–199211. 1996.
|
|
28
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Li J, Liu B, Xue H, Zhou QQ and Peng L:
miR-217 Is a useful diagnostic biomarker and regulates human
podocyte cells apoptosis via targeting TNFSF11 in membranous
nephropathy. Biomed Res Int. 2017:21687672017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wang B, Du R, Xiao X, Deng ZL, Jian D, Xie
HF and Li J: Microrna-217 modulates human skin fibroblast
senescence by directly targeting DNA methyltransferase 1.
Oncotarget. 8:33475–33486. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yin H, Liang X, Jogasuria A, Davidson NO
and You M: miR-217 regulates ethanol-induced hepatic inflammation
by disrupting sirtuin 1-lipin-1 signaling. Am J Pathol.
185:1286–1296. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Xin L, Junhua W, Long L, Jun Y and Yang X:
Exogenous hydrogen sulfide protects SH-SY5Y cells from OGD/rinduced
injury. Curr Mol Med. 17:563–567. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Nogueiras R, Habegger KM, Chaudhary N,
Finan B, Banks AS, Dietrich MO, Horvath TL, Sinclair DA, Pfluger PT
and Tschöp MH: Sirtuin 1 and sirtuin 3: Physiological modulators of
metabolism. Physiol Rev. 92:1479–1514. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
da Cunha MSB and Arruda SF:
Tucum-do-cerrado (Bactris setosa Mart.) may promote anti-aging
effect by Upregulating SIRT1-Nrf2 pathway and attenuating oxidative
stress and inflammation. Nutrients. 9:E12432017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Rada P, Pardo V, Mobasher MA,
García-Martínez I, Ruiz L, González-Rodríguez Á, Sanchez-Ramos C,
Muntané J, Alemany S, James LP, et al: SIRT1 controls acetaminophen
hepatotoxicity by modulating inflammation and oxidative stress.
Antioxid Redox Signal. 28:1187–1208. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Chan SH, Hung CH, Shih JY, Chu PM, Cheng
YH, Lin HC and Tsai KL: SIRT1 inhibition causes oxidative stress
and inflammation in patients with coronary artery disease. Redox
Biol. 13:301–309. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Cheng YY, Kao CL, Ma HI, Hung CH, Wang CT,
Liu DH, Chen PY and Tsai KL: SIRT1-related inhibition of
pro-inflammatory responses and oxidative stress are involved in the
mechanism of nonspecific low back pain relief after exercise
through modulation of Toll-like receptor 4. J Biochem. 158:299–308.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Tian Y, Ma J, Wang W, Zhang L, Xu J, Wang
K and Li D: Resveratrol supplement inhibited the NF-κB inflammation
pathway through activating AMPKα-SIRT1 pathway in mice with fatty
liver. Mol Cell Biochem. 422:75–84. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Wang XH, Zhu L, Hong X, Wang YT, Wang F,
Bao JP, Xie XH, Liu L and Wu XT: Resveratrol attenuated
TNF-α-induced MMP-3 expression in humannucleus pulposus cells by
activating autophagy via AMPK/SIRT1 signaling pathway. Exp Biol Med
(Maywood). 241:848–853. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Ferreira RS, Dos Santos NAG, Bernardes CP,
Sisti FM, Amaral L, Fontana ACK and Dos Santos AC: Caffeic acid
phenethyl ester (CAPE) protects PC12 cells against
cisplatin-induced neurotoxicity by activating the AMPK/SIRT1,
MAPK/Erk, and PI3k/Akt signaling pathways. Neurotox Res. Apr
23–2019.(Epub ahead of print). doi: 10.1007/s12640-019-00042-w.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Zhao D, Sun X, Lv S, Sun M, Guo H, Zhai Y,
Wang Z, Dai P, Zheng L, Ye M and Wang X: Salidroside attenuates
oxidized low-density lipoprotein-induced endothelial cell injury
via promotion of the AMPK/SIRT1 pathway. Int J Mol Med.
43:2279–2290. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Yin WL, Yin WG, Huang BS and Wu LX: LncRNA
SNHG12 inhibits miR-199a to upregulate SIRT1 to attenuate cerebral
ischemia/reperfusion injury through activating AMPK signaling
pathway. Neurosci Lett. 690:188–195. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|