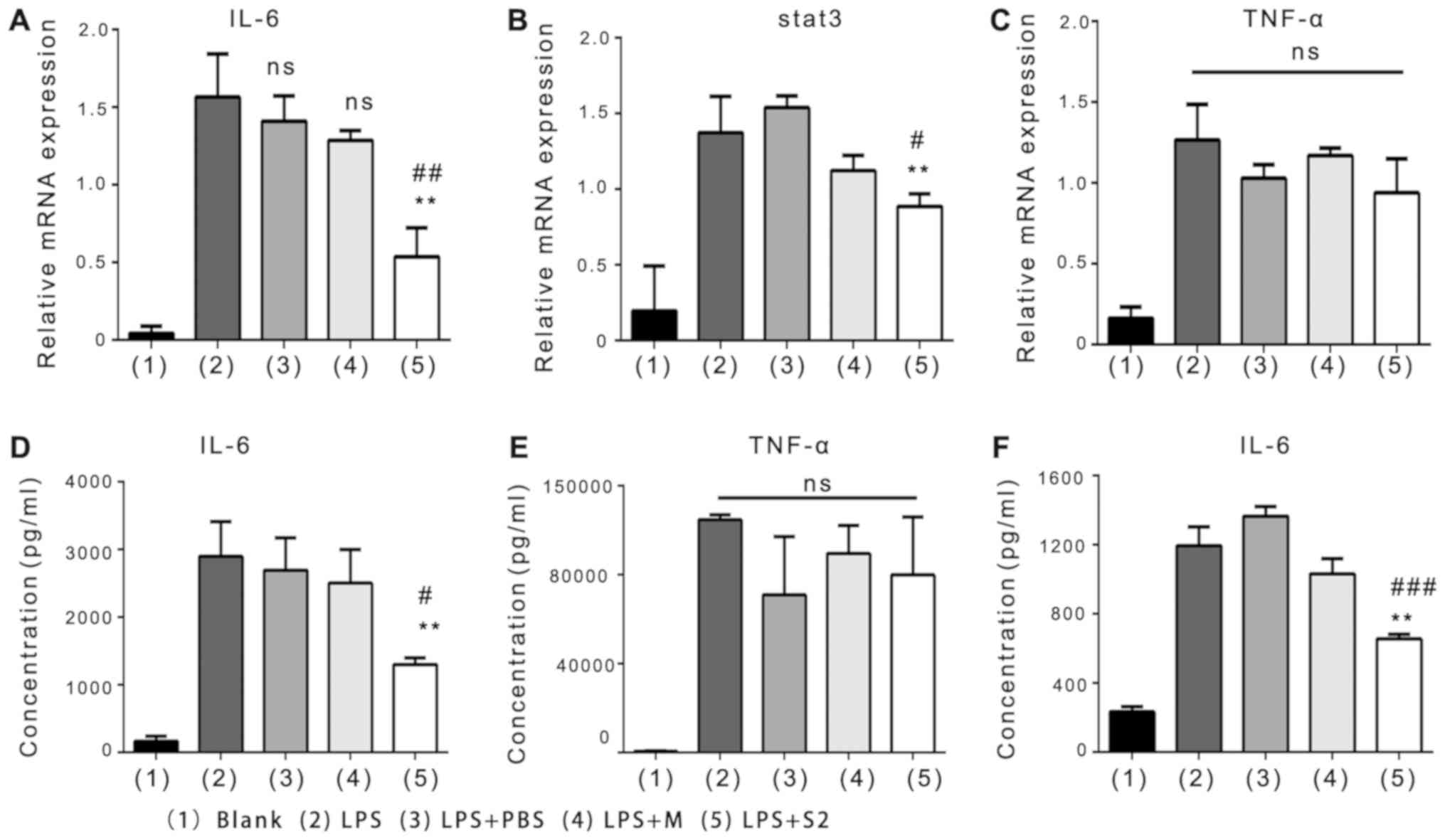
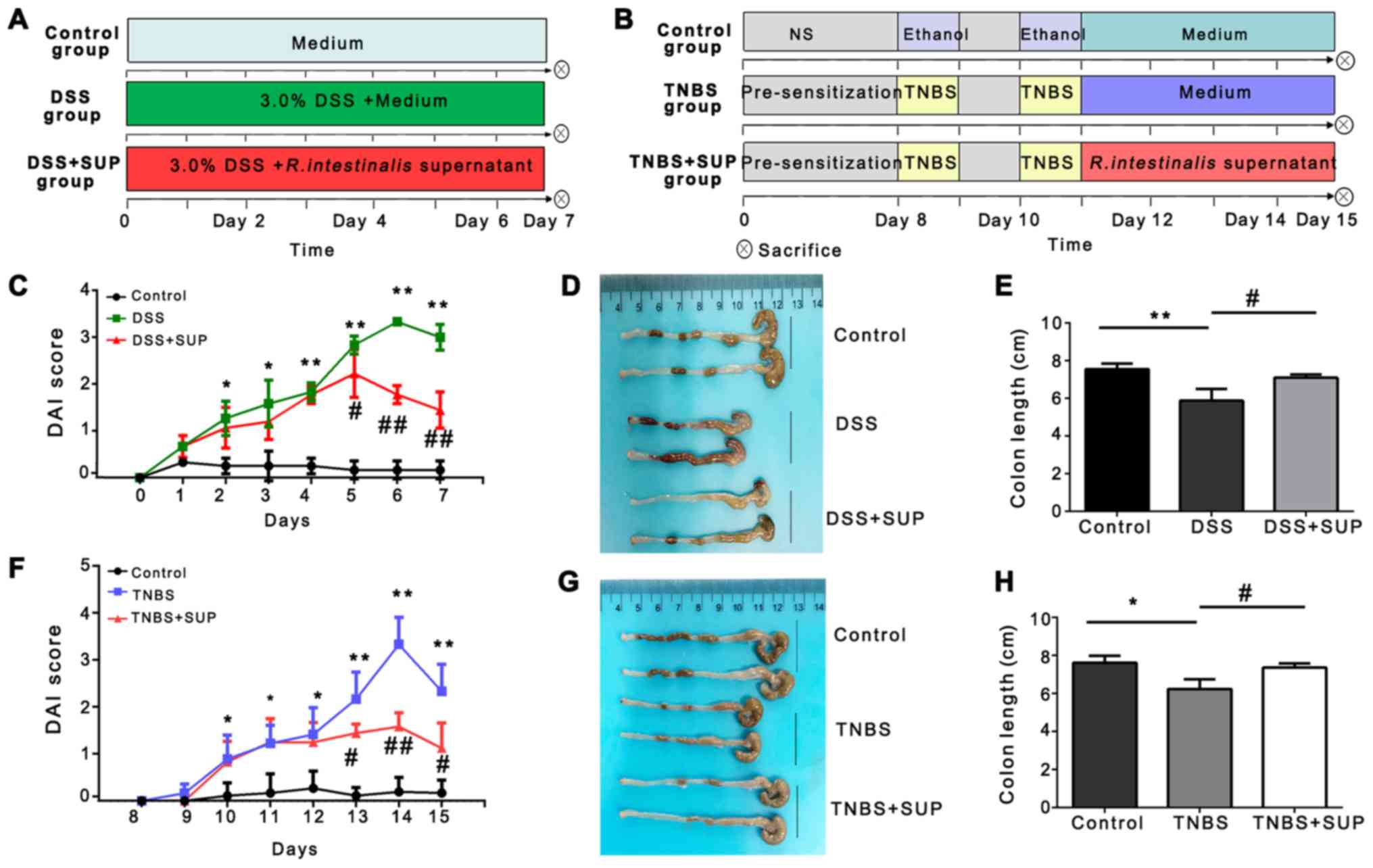
|
1
|
Torres J, Mehandru S, Colombel JF and
Peyrin-Biroulet L: Crohn's disease. Lancet. 389:1741–1755. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ungaro R, Mehandru S, Allen PB,
Peyrin-Biroulet L and Colombel JF: Ulcerative colitis. Lancet.
389:1756–1770. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
de Souza HSP, Fiocchi C and Iliopoulos D:
The IBD interactome: An integrated view of aetiology, pathogenesis
and therapy. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 14:739–749. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Shen Z, Zhu C, Quan Y, Yang J, Yuan W,
Yang Z, Wu S, Luo W, Tan B and Wang X: Insights into Roseburia
intestinalis which alleviates experimental colitis pathology by
inducing anti-inflammatory responses. J Gastroenterol Hepatol.
33:1751–1760. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zhu C, Song K, Shen Z, Quan Y, Tan B, Luo
W, Wu S, Tang K, Yang Z and Wang X: Roseburia intestinalis inhibits
Interleukin17 Excretion and promotes regulatory T cells
differentiation in colitis. Mol Med Rep. 17:7567–7574.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Duncan SH, Hold GL, Barcenilla A, Stewart
CS and Flint HJ: Roseburia intestinalis sp. nov., a novel
saccharolytic, butyrate-producing bacterium from human faeces. Int
J Syst Evol Microbiol. 52:1615–1620. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Cani PD: Human gut microbiome: Hopes,
threats and promises. Gut. 67:1716–1725. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Goncalves P, Araujo JR and Di Santo JP: A
Cross-talk between Microbiota-derived short-chain fatty acids and
the host mucosal immune system regulates intestinal homeostasis and
inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 24:558–572. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Arpaia N, Campbell C, Fan X, Dikiy S, van
der Veeken J, deRoos P, Liu H, Cross JR, Pfeffer K, Coffer PJ and
Rudensky AY: Metabolites produced by commensal bacteria promote
peripheral regulatory T-cell generation. Nature. 504:451–455. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Singh N, Gurav A, Sivaprakasam S, Brady E,
Padia R, Shi H, Thangaraju M, Prasad PD, Manicassamy S, Munn DH, et
al: Activation of Gpr109a, receptor for niacin and the commensal
metabolite butyrate, suppresses colonic inflammation and
carcinogenesis. Immunity. 40:128–139. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhou L, Zhang M, Wang Y, Dorfman RG, Liu
H, Yu T, Chen X, Tang D, Xu L, Yin Y, et al: Faecalibacterium
prausnitzii produces butyrate to maintain Th17/Treg balance and to
ameliorate colorectal colitis by inhibiting histone deacetylase 1.
Inflamm Bowel Dis. May 23–2018.(Epub ahead of print). doi:
10.1093/ibd/izy182. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
12
|
National Research Council (US) Committee
for the Update of the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory A, .
The National Academies Collection: Reports funded by National
Institutes of Health. Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory
Animals. 8th. National Academies Press (US); Washington, DC: 2011,
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Murray PJ, Allen JE, Biswas SK, Fisher EA,
Gilroy DW, Goerdt S, Gordon S, Hamilton JA, Ivashkiv LB, Lawrence
T, et al: Macrophage activation and polarization: Nomenclature and
experimental guidelines. Immunity. 41:14–20. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chang PV, Hao L, Offermanns S and
Medzhitov R: The microbial metabolite butyrate regulates intestinal
macrophage function via histone deacetylase inhibition. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 111:2247–2252. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Turnbaugh PJ, Ley RE, Mahowald MA, Magrini
V, Mardis ER and Gordon JI: An obesity-associated gut microbiome
with increased capacity for energy harvest. Nature. 444:1027–1031.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Samuel BS and Gordon JI: A humanized
gnotobiotic mouse model of host-archaeal-bacterial mutualism. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:10011–10016. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wirtz S, Popp V, Kindermann M, Gerlach K,
Weigmann B, Fichtner-Feigl S and Neurath MF: Chemically induced
mouse models of acute and chronic intestinal inflammation. Nat
Protoc. 12:1295–1309. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Dale DC, Boxer L and Liles WC: The
phagocytes: Neutrophils and monocytes. Blood. 112:935–945. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sica A and Mantovani A: Macrophage
plasticity and polarization: In vivo veritas. J Clin Invest.
122:787–795. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Gren ST and Grip O: Role of monocytes and
intestinal macrophages in crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis.
Inflamm Bowel Dis. 22:1992–1998. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhou B, Xia X, Wang P, Chen S, Yu C, Huang
R, Zhang R, Wang Y, Lu L, Yuan F, et al: Induction and amelioration
of methotrexate-induced gastrointestinal toxicity are related to
immune response and gut microbiota. EBioMedicine. 33:122–133. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Mitsuyama K, Matsumoto S, Masuda J,
Yamasakii H, Kuwaki K, Takedatsu H and Sata M: Therapeutic
strategies for targeting the IL-6/STAT3 cytokine signaling pathway
in inflammatory bowel disease. Anticancer Res. 27:3749–3756.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Imam T, Park S, Kaplan MH and Olson MR:
Effector T helper cell subsets in inflammatory bowel diseases.
Front Immunol. 9:12122018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chen ML and Sundrud MS: Cytokine networks
and T-Cell subsets in inflammatory bowel diseases. Inflamm Bowel
Dis. 22:1157–1167. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Nagashima H, Ishii N and So T: Regulation
of interleukin-6 receptor signaling by TNF receptor-associated
factor 2 and 5 during differentiation of inflammatory CD4(+) T
cells. Front Immunol. 9:19862018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chen G, Ran X, Li B, Li Y, He D, Huang B,
Fu S, Liu J and Wang W: Sodium butyrate inhibits inflammation and
maintains epithelium barrier integrity in a TNBS-induced
inflammatory bowel disease mice model. EBioMedicine. 30:317–325.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhang Y, Brenner M, Yang WL and Wang P:
Recombinant human MFG-E8 ameliorates colon damage in DSS- and
TNBS-induced colitis in mice. Lab Invest. 95:480–490. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Gordon S: Alternative activation of
macrophages. Nat Rev Immunol. 3:23–35. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Mosser DM and Edwards JP: Exploring the
full spectrum of macrophage activation. Nat Rev Immunol. 8:958–969.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Rhee L, Murphy SF, Kolodziej LE, Grimm WA,
Weber CR, Lodolce JP, Chang JE, Bartulis SJ, Messer JS, Schneider
JR, et al: Expression of TNFAIP3 in intestinal epithelial cells
protects from DSS-but not TNBS-induced colitis. Am J Physiol
Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 303:G220–G227. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wang W, XY L, Zheng D, Zhang D, Huang S,
Zhang X, Ai F, Wang X, Ma J, Xiong W, et al: Dynamic changes of
peritoneal macrophages and subpopulations during ulcerative colitis
to metastasis of colorectal carcinoma in a mouse model. Inflamm
Res. 62:669–680. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Bettelli E, Carrier Y, Gao W, Korn T,
Strom TB, Oukka M, Weiner HL and Kuchroo VK: Reciprocal
developmental pathways for the generation of pathogenic effector
TH17 and regulatory T cells. Nature. 441:235–238. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hodge DR, Hurt EM and Farrar WL: The role
of IL-6 and STAT3 in inflammation and cancer. Eur J Cancer.
41:2502–2512. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Quan Y, Song K, Zhang Y, Zhu C, Shen Z, Wu
S, Luo W, Tan B, Yang Z and Wang X: Roseburia intestinalis-derived
flagellin is a negative regulator of intestinal inflammation.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 501:791–799. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Vieira RS, Castoldi A, Basso PJ, Hiyane
MI, Câmara NOS and Almeida RR: Butyrate attenuates lung
inflammation by negatively modulating Th9 cells. Front Immunol.
10:672019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zhong X, Zhang Z, Wang S, Cao L, Zhou L,
Sun A, Zhong Z and Nabben M: Microbial-Driven butyrate regulates
Jejunal homeostasis in piglets during the weaning stage. Front
Microbiol. 9:33352019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Chakravortty D, Koide N, Kato Y, Sugiyama
T, Mu MM, Yoshida T and Yokochi T: The inhibitory action of
butyrate on lipopolysaccharide-induced nitric oxide production in
RAW 264.7 murine macrophage cells. J Endotoxin Res. 6:243–247.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Martin R, Chain F, Miquel S, Lu J,
Gratadoux JJ, Sokol H, Verdu EF, Bercik P, Bermudez-Humaran LG and
Langella P: The commensal bacterium Faecalibacterium prausnitzii is
protective in DNBS-induced chronic moderate and severe colitis
models. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 20:417–430. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|