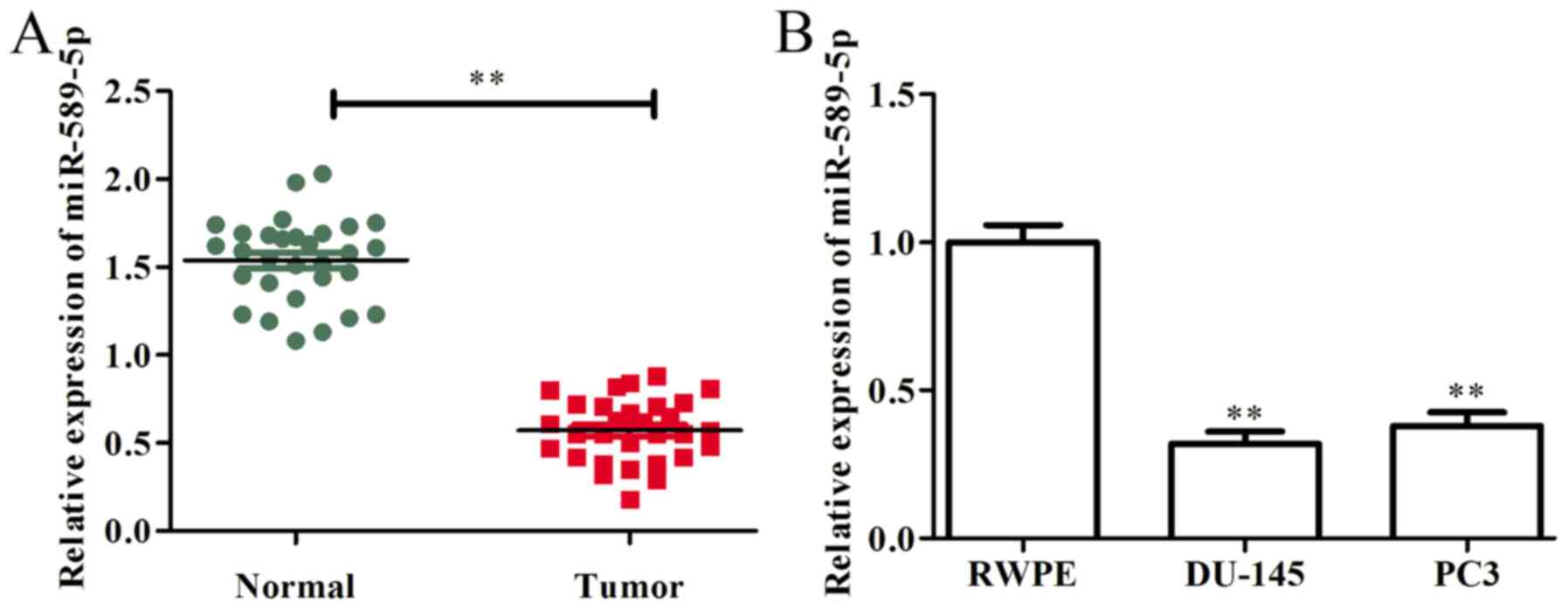
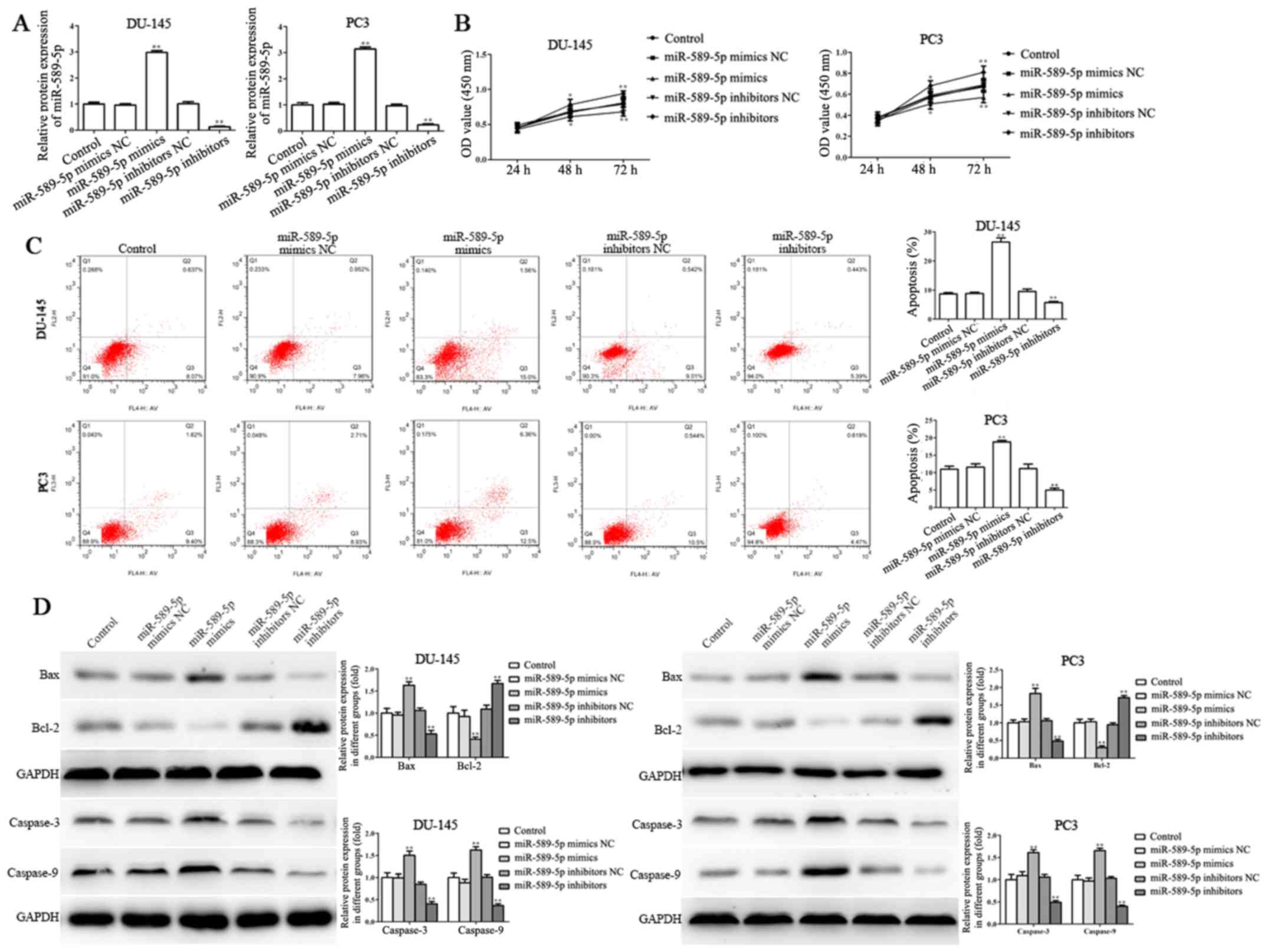
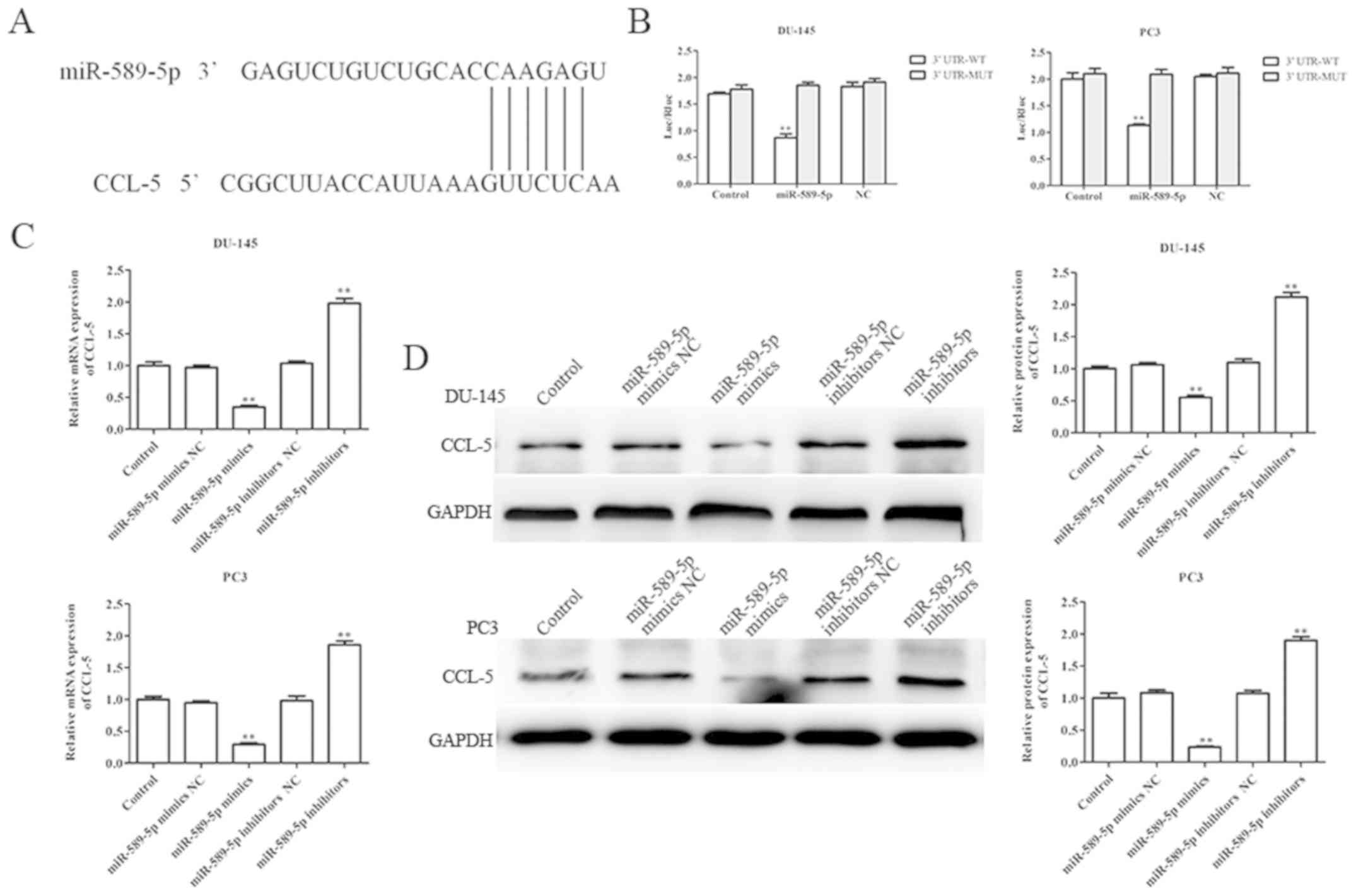
|
1
|
Kojima K, Fujita Y, Nozawa Y, Deguchi T
and Ito M: miR-34a attenuates paclitaxel-resistance of
hormone-refractory prostate cancer PC3 cells through direct and
indirect mechanisms. Prostate. 70:1501–1512. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Viticchiè G, Lena AM, Latina A, Formosa A,
Gregersen LH, Lund AH, Bernardini S, Mauriello A, Miano R, Spagnoli
LG, et al: miR-203 controls proliferation, migration and invasive
potential of prostate cancer cell lines. Cell Cycle. 10:1121–1131.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Guan H, You Z, Wang C, Fang F, Peng R, Mao
L, Xu B and Chen M: MicroRNA-200a suppresses prostate cancer
progression through BRD4/AR signaling pathway. Cancer Med.
8:1474–1485. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Fan H and Zhang YS: miR-490-3p modulates
the progression of prostate cancer through regulating histone
deacetylase 2. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 23:539–546.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zhang FB, Du Y, Tian Y, Ji ZG and Yang PQ:
miR-1299 functions as a tumor suppressor to inhibit the
proliferation and metastasis of prostate cancer by targeting NEK2.
Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 23:530–538. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ota A, Tagawa H, Karnan S, Tsuzuki S,
Karpas A, Kira S, Yoshida Y and Seto M: Identification and
characterization of a novel gene, C13orf25, as a target for
13q31-q32 amplification in malignant lymphoma. Cancer Res.
64:3087–3095. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Doehn C, Böhmer T, Kausch I, Sommerauer M
and Jocham D: Prostate cancer vaccines: Current status and future
potential. BioDrugs. 22:71–84. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Oesterling JE: Prostate specific antigen:
A critical assessment of the most useful tumor marker for
adenocarcinoma of the prostate. J Urol. 145:907–923. 1991.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Moyer VA and U.S. Preventive Services Task
Force: Screening for prostate cancer: U.S. Preventive Services Task
Force recommendation statement. Ann Intern Med. 157:120–134. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Tadayon F, Arezegar HR, Khorrami MH,
Hashemi Juzdani R, Shahdoost AA and Mellat M: Evaluation of
prostatic cancer prevalence in patients with prostatic-specific
antigen between 4 and 10 and normal digital rectal examination. Adv
Biomed Res. 5:1122016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zugor V, Kühn R, Engelhard K, Poth S,
Bernat MM, Porres D and Labanaris AP: The value of endorectal
magnetic resonance imaging of the prostate in improving the
detection of anterior prostate cancer. Anticancer Res.
36:4279–4283. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Choi SK, Shim M, Kim M, Park M, Lee S,
Song C, Lee HL and Ahn H: Heterogeneous oncologic outcomes
according to surgical pathology in high-risk prostate cancer:
Implications for better risk stratification and preoperative
prediction of oncologic outcomes. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol.
143:1871–1878. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Murphy DG and Zargar H: Words of Wisdom.
Re: Chemohormonal therapy in metastatic hormone-sensitive prostate
cancer. Eur Urol. 69:5402016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Langius-Eklöf A, Christiansen M, Lindström
V, Blomberg K, Hälleberg Nyman M, Wengström Y and Sundberg K:
Adherence to report and patient perception of an interactive app
for managing symptoms during radiotherapy for prostate cancer:
Descriptive study of logged and interview data. JMIR Cancer.
3:e182017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Cheng AM, Byrom MW, Shelton J and Ford LP:
Antisense inhibition of human miRNA and indications for an
involvement of miRNA in cell growth and apoptosis. Nucleic Acids
Res. 33:1290–1297. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wu W, Sun M, Zou GM and Chen J: MicroRNA
and cancer: Current status and prospective. Int J Cancer.
120:953–960. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Iorio MV and Croce CM: MicroRNA
dysregulation in cancer: Diagnostics, monitoring and therapeutics.
A comprehensive review. EMBO Mol Med. 4:143–159. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Eulalio A, Huntzinger E and Izaurralde E:
Getting to the root of miRNA-mediated gene silencing. Cell.
132:9–14. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Bhayani MK, Calin GA and Lai SY:
Functional relevance of miRNA sequences in human disease. Mutat
Res. 731:14–19. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Guan B, Wu K, Zeng J, Xu S, Mu L, Gao Y,
Wang K, Ma Z, Tian J, Shi Q, et al: Tumor-suppressive microRNA-218
inhibits tumor angiogenesis via targeting the mTOR component RICTOR
in prostate cancer. Oncotarget. 8:8162–8172. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Mao A, Liu Y, Wang Y, Zhao Q, Zhou X, Sun
C, Di C, Si J, Gan L and Zhang H: miR-449a enhances
radiosensitivity through modulating pRb/E2F1 in prostate cancer
cells. Tumour Biol. 37:4831–4840. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Liu C, Lv D, Li M, Zhang X, Sun G, Bai Y
and Chang D: Hypermethylation of miRNA-589 promoter leads to
upregulation of HDAC5 which promotes malignancy in non-small cell
lung cancer. Int J Oncol. 50:2079–2090. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhu Q, Luo Z, Lu G, Gui F, Wu J, Li F and
Ni Y: LncRNA FABP5P3/miR-589-5p/ZMYND19 axis contributes to
hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation, migration and
invasion. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 498:551–558. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lin YC, Lin JF, Tsai TF, Chou KY, Chen HE
and Hwang TI: Tumor suppressor miRNA-204-5p promotes apoptosis by
targeting BCL2 in prostate cancer cells. Asian J Surg. 40:396–406.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wang X, Yi Y, Lv Q, Zhang J, Wu K, Wu W
and Zhang W: Novel 1,3,5-triazine derivatives exert potent
anti-cervical cancer effects by modulating Bax, Bcl2 and caspases
expression. Chem Biol Drug Des. 91:728–734. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Powell WC, Knox JD, Navre M, Grogan TM,
Kittelson J, Nagle RB and Bowden GT: Expression of the
metalloproteinase matrilysin in DU-145 cells increases their
invasive potential in severe combined immunodeficient mice. Cancer
Res. 53:417–422. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Heidenreich A, Bastian PJ, Bellmunt J,
Bolla M, Joniau S, van der Kwast T, Mason M, Matveev V, Wiegel T,
Zattoni F, et al: EAU guidelines on prostate cancer. Part 1:
Screening, diagnosis, and local treatment with curative
intent-update 2013. Eur Urol. 65:124–137. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Veltri RW and Christudass CS: Nuclear
morphometry, epigenetic changes, and clinical relevance in prostate
cancer. Adv Exp Med Biol. 773:77–99. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
He H, Jazdzewski K, Li W, Liyanarachchi S,
Nagy R, Volinia S, Calin GA, Liu CG, Franssila K, Suster S, et al:
The role of microRNA genes in papillary thyoid carcinoma. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 102:19075–19080. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wu M, Jolicoeur N, Li Z, Zhang L, Fortin
Y, L'Abbe D, Yu Z and Shen SH: Genetic variations of microRNAs in
human cancer and their effects on the expression of miRNAs.
Carcinogenesis. 29:1710–1716. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhang X, Jiang P, Shuai L, Chen K, Li Z,
Zhang Y, Jiang Y and Li X: miR-589-5p inhibits MAP3K8 and
suppresses CD90+ cancer stem cells in hepatocellular
carcinoma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 35:1762016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Monteiro HP, Silva EF and Stern A: Nitric
oxide: A potential inducer of adhesion-related apoptosis-anoikis.
Nitric Oxide. 10:1–10. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Green DR and Reed JC: Mitochondria and
apoptosis. Science. 281:1309–1312. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Deveraux QL, Schendel SL and Reed JC:
Antiapoptotic proteins. The bcl-2 and inhibitor of apoptosis
protein families. Cardiol Clin. 19:57–74. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wang H, Liu G, Shen D, Ye H, Huang J, Jiao
L and Sun Y: HOXA1 enhances the cell proliferation, invasion and
metastasis of prostate cancer cells. Oncol Rep. 34:1203–1210. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wang WJ, Yang W, Ouyang ZH, Xue JB, Li XL,
Zhang J, He WS, Chen WK, Yan YG and Wang C: miR-21 promotes ECM
degradation through inhibiting autophagy via the PTEN/akt/mTOR
signaling pathway in human degenerated NP cells. Biomed
Pharmacother. 99:725–734. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Cui Z, Tang J, Chen J and Wang Z:
Hsa-miR-574-5p negatively regulates MACC-1 expression to suppress
colorectal cancer liver metastasis. Cancer Cell Int. 14:472014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Bar-Or A, Nuttall RK, Duddy M, Alter A,
Kim HJ, Ifergan I, Pennington CJ, Bourgoin P, Edwards DR and Yong
VW: Analyses of all matrix metalloproteinase members in leukocytes
emphasize monocytes as major inflammatory mediators in multiple
sclerosis. Brain. 126:2738–2749. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Westermarck J and Kähäri VM: Regulation of
matrix metalloproteinase expression in tumor invasion. FASEB J.
13:781–792. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Kraiem Z and Korem S: Matrix
metalloproteinases and the thyroid. Thyroid. 10:1061–1069. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Ventura A and Jacks T: MicroRNAs and
cancer: Short RNAs go a long way. Cell. 136:586–591. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Azenshtein E, Luboshits G, Shina S,
Neumark E, Shahbazian D, Weil M, Wigler N, Keydar I and Ben-Baruch
A: The CC chemokine RANTES in breast carcinoma progression:
Regulation of expression and potential mechanisms of promalignant
activity. Cancer Res. 62:1093–1102. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Yaal-Hahoshen N, Shina S, Leider-Trejo L,
Barnea I, Shabtai EL, Azenshtein E, Greenberg I, Keydar I and
Ben-Baruch A: The chemokine CCL5 as a potential prognostic factor
predicting disease progression in stage II breast cancer patients.
Clin Cancer Res. 12:4474–4478. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Kwon KH, Lee YC, Chung JH and Eun YG:
Association study of chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 5 gene
polymorphism and papillary thyroid cancer. J Invest Surg.
26:319–324. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Kuo CH, Liu CJ, Lu CY, Hu HM, Kuo FC, Liou
YS, Yang YC, Hsieh MC, Lee OK, Wu DC, et al: 17β-estradiol inhibits
mesenchymal stem cells-induced human AGS gastric cancer cell
mobility via suppression of CCL5-Src/Cas/Paxillin signaling
pathway. Int J Med Sci. 11:7–16. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Swamydas M, Ricci K, Rego SL and Dréau D:
Mesenchymal stem cell-derived CCL-9 and CCL-5 promote mammary tumor
cell invasion and the activation of matrix metalloproteinases. Cell
Adh Migr. 7:315–324. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|