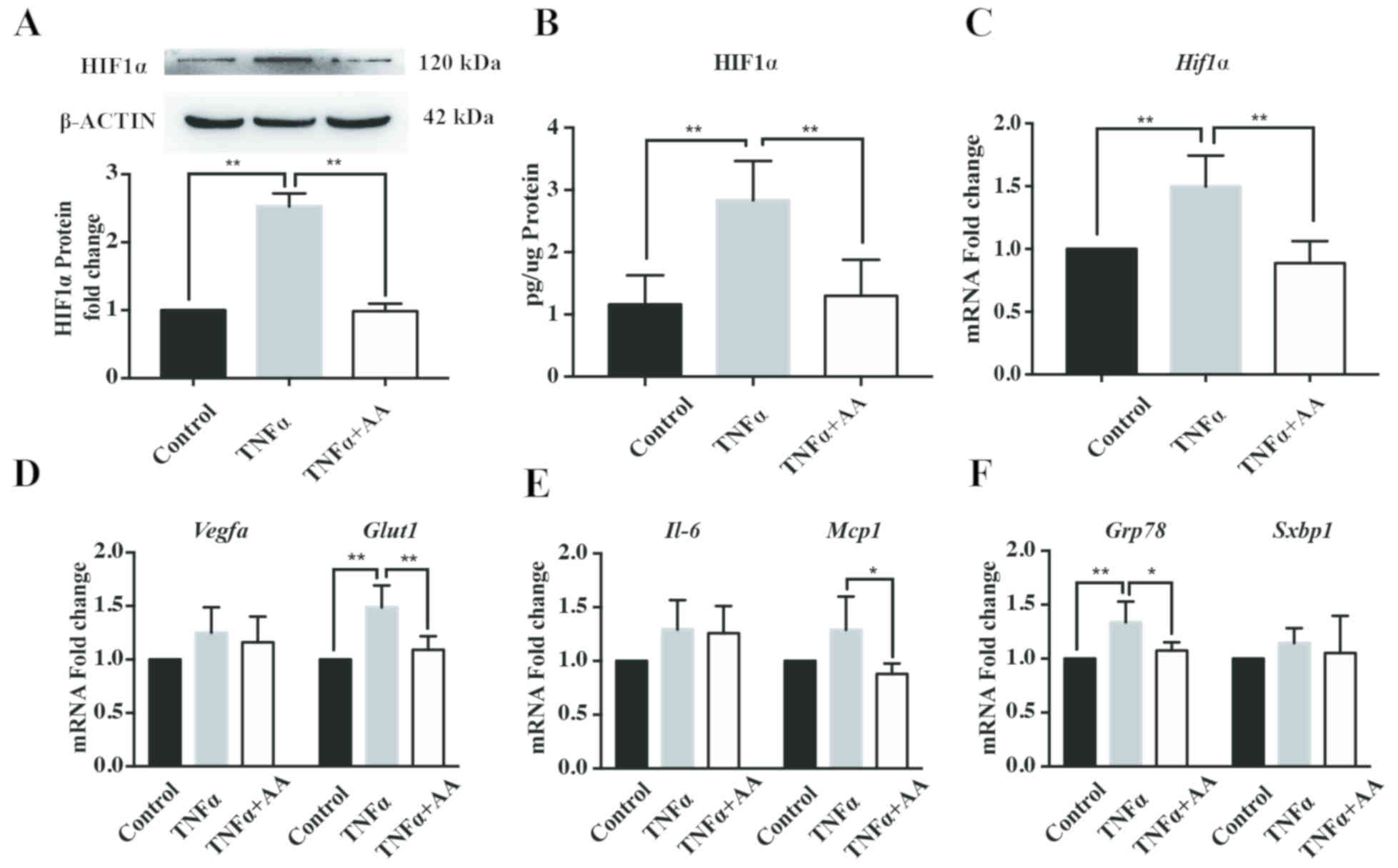
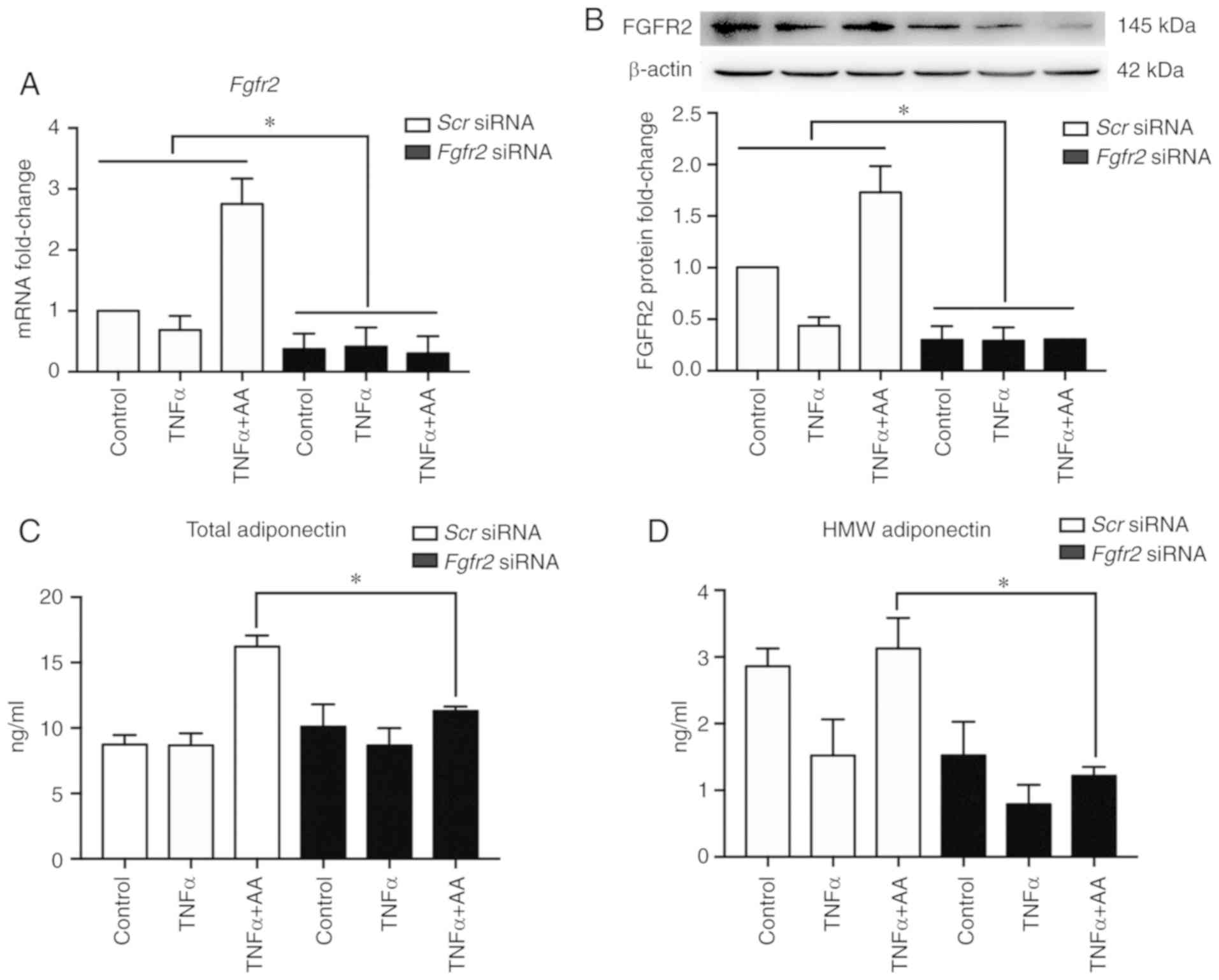
|
1
|
Younossi ZM, Koenig AB, Abdelatif D, Fazel
Y, Henry L and Wymer M: Global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty
liver disease-Meta-analytic assessment of prevalence, incidence,
and outcomes. Hepatology. 64:73–84. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Castera L, Vilgrain V and Angulo P:
Noninvasive evaluation of NAFLD. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol.
10:666–675. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ahmed A, Wong RJ and Harrison SA:
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease review: Diagnosis, treatment, and
outcomes. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 13:2062–2070. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Fabbrini E, Sullivan S and Klein S:
Obesity and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Biochemical,
metabolic, and clinical implications. Hepatology. 51:679–689. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Handa P, Vemulakonda AL, Maliken BD,
Morgan-Stevenson V, Nelson JE, Dhillon BK, Hennessey KA, Gupta R,
Yeh MM and Kowdley KV: Differences in hepatic expression of iron,
inflammation and stress-related genes in patients with nonalcoholic
steatohepatitis. Ann Hepatol. 16:77–85. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Trujillo ME and Scherer PE:
Adiponectin-journey from an adipocyte secretory protein to
biomarker of the metabolic syndrome. J Intern Med. 257:167–175.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Kawano J and Arora R: The role of
adiponectin in obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular disease. J
Cardiometab Syndr. 4:44–49. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hebbard L and George J: Animal models of
nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol.
8:35–44. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Mandal P, Park PH, McMullen MR, Pratt BT
and Nagy LE: The anti-inflammatory effects of adiponectin are
mediated via a heme oxygenase-1-dependent pathway in rat Kupffer
cells. Hepatology. 51:1420–1429. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lee UE and Friedman SL: Mechanisms of
hepatic fibrogenesis. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol.
25:195–206. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Polyzos SA, Kountouras J, Zavos C and
Tsiaousi E: Role of adiponectin in the pathogenesis and treatment
of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Diabetes Obes Metab.
12:365–383. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Finelli C and Tarantino G: What is the
role of adiponectin in obesity related non-alcoholic fatty liver
disease? World J Gastroenterol. 19:802–812. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Phillips LK, Peake JM, Zhang X, Hickman
IJ, Briskey DR, Huang BE, Simpson P, Li SH, Whitehead JP, Martin JH
and Prins JB: Postprandial total and HMW adiponectin following a
high-fat meal in lean, obese and diabetic men. Eur J Clin Nutr.
67:377–384. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Liu X, Tong W, Zhao X, Zhang H, Tang Y and
Deng X: Chinese herb extract improves liver steatosis by promoting
the expression of high molecular weight adiponectin in NAFLD rats.
Mol Med Rep. 16:5580–5586. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhang X, Sun LR, Li MZ, et al: The changes
of serum high molecular weight adiponectin levels in T2DM with
nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Medical Innovation of China.
9:5–7. 2013.
|
|
16
|
Gimeno RE and Moller DE: FGF21-based
pharmacotherapy-potential utility for metabolic disorders. Trends
Endocrinol Metab. 25:303–311. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lee JH, Kang YE, Chang JY, Park KC, Kim
HW, Kim JT, Kim HJ, Yi HS, Shong M, Chung HK and Kim KS: An
engineered FGF21 variant, LY2405319, can prevent non-alcoholic
steatohepatitis by enhancing hepatic mitochondrial function. Am J
Transl Res. 8:4750–4763. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Fisher FM, Chui PC, Nasser IA, Popov Y,
Cunniff JC, Lundasen T, Kharitonenkov A, Schuppan D, Flier JS and
Maratos-Flier E: Fibroblast growth factor 21 limits lipotoxicity by
promoting hepatic fatty acid activation in mice on methionine and
choline-deficient diets. Gastroenterology. 147:1073–1083.e6. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Fisher FM and Maratos-Flier E:
Understanding the physiology of FGF21. Annu Rev Physiol.
78:223–241. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Inagaki T: Research perspectives on the
regulation and physiological functions of FGF21 and its association
with NAFLD. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 6:1472015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Musso G, Cassader M and Gambino R:
Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: Emerging molecular targets and
therapeutic strategies. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 15:249–274. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Vernia S, Cavanagh-Kyros J, Garcia-Haro L,
Sabio G, Barrett T, Jung DY, Kim JK, Xu J, Shulha HP, Garber M, et
al: The PPARα-FGF21 hormone axis contributes to metabolic
regulation by the hepatic JNK signaling pathway. Cell Metab.
20:512–525. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Piccinin E and Moschetta A:
Hepatic-specific PPARα-FGF21 action in NAFLD. Gut. 65:1075–1076.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Bao L, Yin J, Gao W, Wang Q, Yao W and Gao
X: A long-acting FGF21 alleviates hepatic steatosis and
inflammation in NASH mice partly through an FGF21- adiponectin-
IL17A pathway. Br J Pharmacol. 175:3379–3393. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Duerbeck NB, Dowling DD and Duerbeck JM:
Vitamin C: Promises not kept. Obstet Gynecol Surv. 71:187–193.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Oliveira CP, Gayotto LC, Tatai C, Della
Nina BI, Lima ES, Abdalla DS, Lopasso FP, Laurindo FR and Carrilho
FJ: Vitamin C and vitamin E in prevention of nonalcoholic fatty
liver disease (NAFLD) in choline deficient diet fed rats. Nutr J.
2:92003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hadzi-Petrushev N, Dimovska K, Jankulovski
N, Mitrov D and Mladenov M: Supplementation with Alpha-Tocopherol
and ascorbic acid to nonalcoholic fatty liver disease's statin
therapy in men. Adv Pharmacol Sci. 2018:46730612018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Fischer AP and Miles SL: Ascorbic acid,
but not dehydroascorbic acid increases intracellular vitamin C
content to decrease Hypoxia Inducible Factor-1 alpha activity and
reduce malignant potential in human melanoma. Biomed Pharmacother.
86:502–513. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Pires AS, Marques CR, Encarnação JC,
Abrantes AM, Mamede AC, Laranjo M, Gonçalves AC, Sarmento-Ribeiro
AB and Botelho MF: Ascorbic acid and colon cancer: An oxidative
stimulus to cell death depending on cell profile. Eur J Cell Biol.
95:208–218. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Rose FJ, Webster J, Barry JB, Phillips LK,
Richards AA and Whitehead JP: Synergistic effects of ascorbic acid
and thiazolidinedione on secretion of high molecular weight
adiponectin from human adipocytes. Diabetes Obes Metab.
12:1084–1089. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kuiper C, Dachs GU, Currie MJ and Vissers
MC: Intracellular ascorbate enhances hypoxia-inducible factor
(HIF)-hydroxylase activity and preferentially suppresses the HIF-1
transcriptional response. Free Radic Biol Med. 69:308–317. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kanuri G, Spruss A, Wagnerberger S,
Bischoff SC and Bergheim I: Role of tumor necrosis factor α (TNFα)
in the onset of fructose-induced nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
in mice. J Nutr Biochem. 22:527–534. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ajmal MR, Yaccha M, Malik MA, Rabbani MU,
Ahmad I, Isalm N and Abdali N: Prevalence of nonalcoholic fatty
liver disease (NAFLD) in patients of cardiovascular diseases and
its association with hs-CRP and TNF-α. Indian Heart J. 66:574–579.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Mann JP, Raponi M and Nobili V: Clinical
implications of understanding the association between oxidative
stress and pediatric NAFLD. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol.
11:371–382. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Mahesh K, Kumar PP, Ali MS, et al:
Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress in non-alcoholic fatty liver
disease (NAFLD). J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2:S38–S39. 2012.(In Chinese).
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Ao N, Yang J, Wang X and Du J:
Glucagon-like peptide-1 preserves non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
through inhibition of the endoplasmic reticulum stress-associated
pathway. Hepatol Res. 46:343–353. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Block G, Jensen CD, Dalvi TB, Norkus EP,
Hudes M, Crawford PB, Holland N, Fung EB, Schumacher L and Harmatz
P: Vitamin C treatment reduces elevated C-reactive protein. Free
Radic Biol Med. 46:70–77. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Schumacker PT: Hypoxia-inducible factor-1
(HIF-1). Crit Care Med. 33:423–425. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Vissers MC, Gunningham SP, Morrison MJ,
Dachs GU and Currie MJ: Modulation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1
alpha in cultured primary cells by intracellular ascorbate. Free
Radic Biol Med. 42:765–772. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Miyata T, Wada Y, Cai Z, Iida Y, Horie K,
Yasuda Y, Maeda K, Kurokawa K and van Ypersele de Strihou C:
Implication of an increased oxidative stress in the formation of
advanced glycation end products in patients with end-stage renal
failure. Kidney Int. 51:1170–1181. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Li G, Yin J, Fu J, Li L, Grant SFA, Li C,
Li M, Mi J, Li M and Gao S: FGF21 deficiency is associated with
childhood obesity, insulin resistance and hypoadiponectinaemia: The
BCAMS study. Diabetes Metab. 43:253–260. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
McMorrow AM, Connaughton RM, Magalhães TR,
McGillicuddy FC, Hughes MF, Cheishvili D, Morine MJ, Ennis S, Healy
ML, Roche EF, et al: Personalized cardio-metabolic responses to an
anti-inflammatory nutrition intervention in obese adolescents: A
randomized controlled crossover trial. Mol Nutr Food Res.
62:e17010082018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Xu J, Lloyd DJ, Hale C, Stanislaus S, Chen
M, Sivits G, Vonderfecht S, Hecht R, Li YS, Lindberg RA, et al:
Fibroblast growth factor 21 reverses hepatic steatosis, increases
energy expenditure, and improves insulin sensitivity in
diet-induced obese mice. Diabetes. 58:250–259. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Singhal G, Kumar G, Chan S, Fisher FM, Ma
Y, Vardeh HG, Nasser IA, Flier JS and Maratos-Flier E: Deficiency
of fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) promotes hepatocellular
carcinoma (HCC) in mice on a long term obesogenic diet. Mol Metab.
13:56–66. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Samms RJ, Lewis JE, Norton L, Stephens FB,
Gaffney CJ, Butterfield T, Smith DP, Cheng CC, Perfield JW II,
Adams AC, et al: FGF21 is an insulin-dependent postprandial hormone
in adult humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 102:3806–3813. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Zhang J and Li Y: Fibroblast growth factor
21, the endocrine FGF pathway and novel treatments for metabolic
syndrome. Drug Discovery Today. 19:579–589. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Talukdar S, Zhou Y, Li D, Rossulek M, Dong
J, Somayaji V, Weng Y, Clark R, Lanba A, Owen BM, et al: A
long-acting FGF21 molecule, PF-05231023, decreases body weight and
improves lipid profile in non-human primates and type 2 diabetic
subjects. Cell Metab. 23:427–440. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Holland WL, Adams AC, Brozinick JT, Bui
HH, Miyauchi Y, Kusminski CM, Bauer SM, Wade M, Singhal E, Cheng
CC, et al: An FGF21-adiponectin-ceramide axis controls energy
expenditure and insulin action in mice. Cell Metab. 17:790–797.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Lin Z, Tian H, Lam KS, Lin S, Hoo RC,
Konishi M, Itoh N, Wang Y, Bornstein SR, Xu A and Li X: Adiponectin
mediates the metabolic effects of FGF21 on glucose homeostasis and
insulin sensitivity in mice. Cell Metab. 17:779–789. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Song H, Zheng Z, Wu J, Lai J, Chu Q and
Zheng X: White pitaya (Hylocereus undatus) juice attenuates insulin
resistance and hepatic steatosis in diet-induced obese mice. PLoS
One. 11:e01496702016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Berglund ED, Kang L, Lee-Young RS,
Hasenour CM, Lustig DG, Lynes SE, Donahue EP, Swift LL, Charron MJ
and Wasserman DH: Glucagon and lipid interactions in the regulation
of hepatic AMPK signaling and expression of PPARalpha and FGF21
transcripts in vivo. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 299:E607–E614.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Liu X, Wang Y, Hou L, Xiong Y and Zhao S:
Fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) promotes formation of aerobic
myofibers via the FGF21-SIRT1-AMPK-PGC1α pathway. J Cell Physiol.
232:1893–1906. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Salminen A, Kauppinen A and Kaarniranta K:
FGF21 activates AMPK signaling: Impact on metabolic regulation and
the aging process. J Mol Med (Berl). 95:123–131. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Forbes-Hernández TY, Giampieri F,
Gasparrini M, Afrin S, Mazzoni L, Cordero MD, Mezzetti B, Quiles JL
and Battino M: Lipid accumulation in HepG2 cells is attenuated by
strawberry extract through AMPK activation. Nutrients. 9:E6212017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|