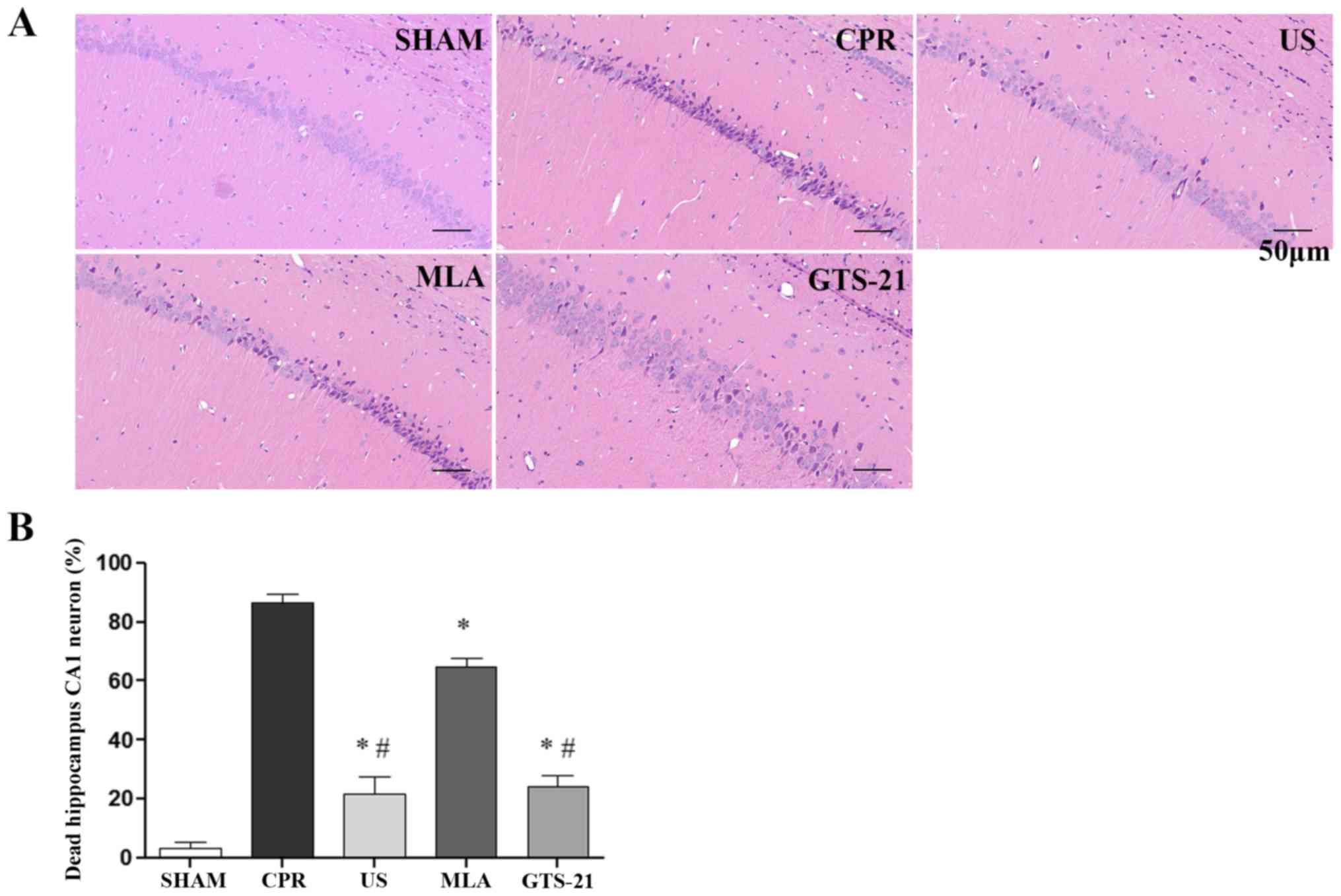
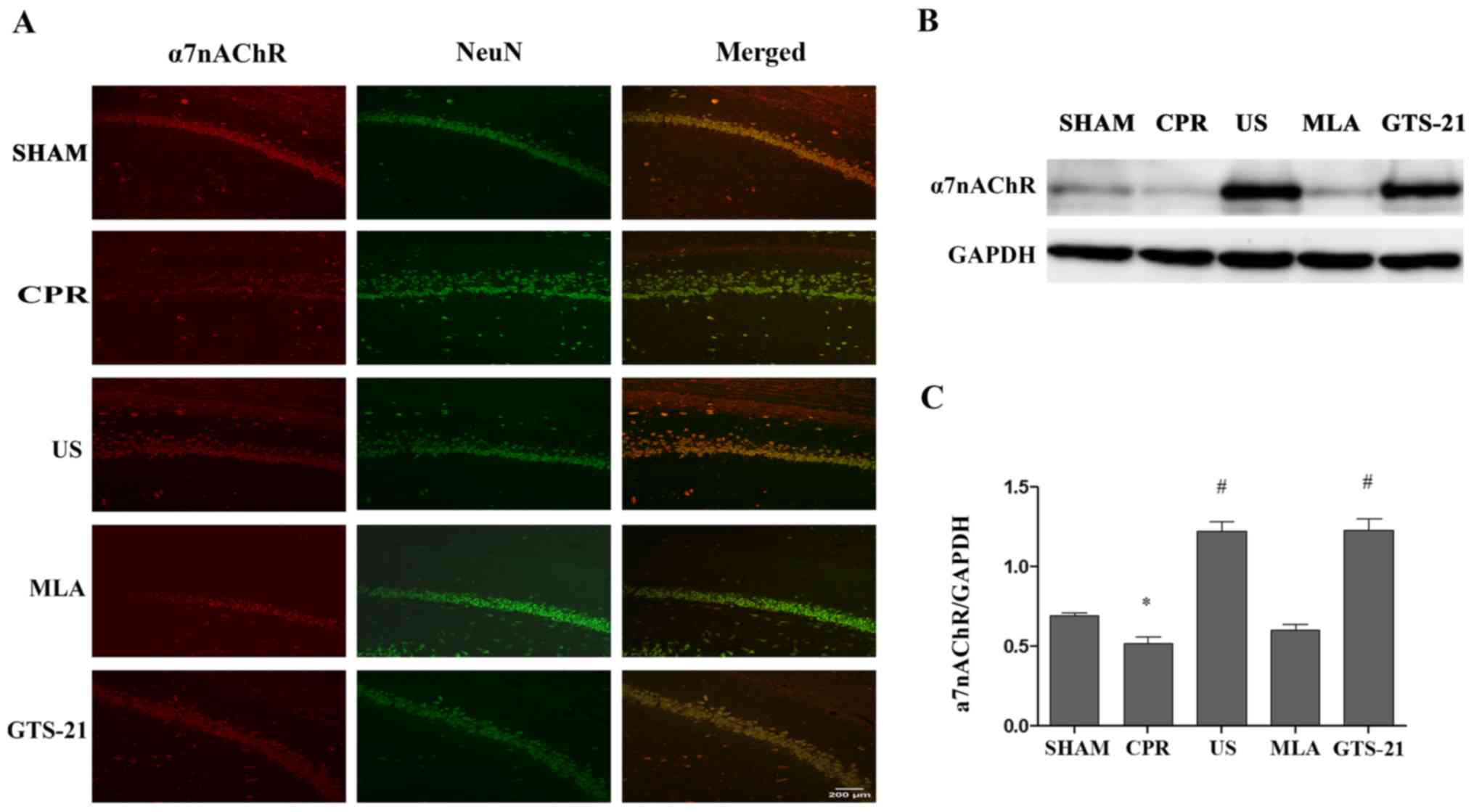
|
1
|
Adrie C, Adib-Conquy M, Laurent I, Monchi
M, Vinsonneau C, Fitting C, Fraisse F, Dinh-Xuan AT, Carli P,
Spaulding C, et al: Successful cardiopulmonary resuscitation after
cardiac arrest as a ‘sepsis-like’ syndrome. Circulation.
106:562–568. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Borovikova LV, Ivanova S, Zhang M, Yang H,
Botchkina GI, Watkins LR, Wang H, Abumrad N, Eaton JW and Tracey
KJ: Vagus nerve stimulation attenuates the systemic inflammatory
response to endotoxin. Nature. 405:458–462. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zhao M, He X, Bi XY, Yu XJ, Gil Wier W and
Zang WJ: Vagal stimulation triggers peripheral vascular protection
through the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway in a rat model of
myocardial ischemia/reperfusion. Basic Res Cardiol. 108:3452013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sun Z, Baker W, Hiraki T and Greenberg JH:
The effect of right vagus nerve stimulation on focal cerebral
ischemia: An experimental study in the rat. Brain Stimul. 5:1–10.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Inoue T, Abe C, Sung SS, Moscalu S,
Jankowski J, Huang L, Ye H, Rosin DL, Guyenet PG and Okusa MD:
Vagus nerve stimulation mediates protection from kidney
ischemia-reperfusion injury through α7nAChR+ plenocytes.
J Clin Invest. 126:1939–1952. 2016. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sun P, Wang J, Zhao S, Yang Z, Tang Z,
Ravindra N, Bradley J, Ornato JP, Peberdy MA and Tang W: Improved
outcomes of cardiopulmonary resuscitation in rats treated with
vagus nerve stimulation and its potential mechanism. Shock.
49:698–703. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hougardy JM, Sadis C and Le Moine A:
Ultrasonic stimulation of the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway
for renal protection. J Am Soc Nephrol. 24:1340–1342. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Gigliotti JC, Huang L, Ye H, Bajwa A,
Chattrabhuti K, Lee S, Klibanov AL, Kalantari K, Rosin DL and Okusa
MD: Ultrasound prevents renal ischemia-reperfusion injury by
stimulating the splenic cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway. J Am
Soc Nephrol. 24:1451–1460. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Research NRCU: Guide for the Care and Use
of Laboratory Animals. National Academies Press; Washington, DC:
1996
|
|
10
|
Lin JY, Liao XX, Li H, Wei HY, Liu R, Hu
CL, Huang GQ, Dai G and Li X: Model of cardiac arrest in rats by
transcutaneous electrical epicardium stimulation. Resuscitation.
81:1197–1204. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gong P, Zhao S, Wang J, Yang Z, Qian J, Wu
X, Cahoon J and Tang W: Mild hypothermia preserves cerebral cortex
microcirculation after resuscitation in a rat model of cardiac
arrest. Resuscitation. 97:109–114. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ye S, Weng Y, Sun S, Chen W, Wu X, Li Z,
Weil MH and Tang W: Comparison of the durations of mild therapeutic
hypothermia on outcome after cardiopulmonary resuscitation in the
rat. Circulation. 125:123–129. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Gigliotti JC, Huang L, Bajwa A, Ye H, Mace
EH, Hossack JA, Kalantari K, Inoue T, Rosin DL and Okusa MD:
Ultrasound modulates the splenic neuroimmune axis in attenuating
AKI. J Am Soc Nephrol. 26:2470–2481. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Niemann JT, Garner D and Lewis RJ: Tumor
necrosis factor-alpha is associated with early postresuscitation
myocardial dysfunction. Crit Care Med. 32:1753–1758. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Niemann JT, Youngquist ST, Shah AP, Thomas
JL and Rosborough JP: TNF-α blockade improves early
post-resuscitation survival and hemodynamics in a swine model of
ischemic ventricular fibrillation. Resuscitation. 84:103–107. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Oda Y, Tsuruta R, Kasaoka S, Inoue T and
Maekawa T: The cutoff values of intrathecal interleukin 8 and 6 for
predicting the neurological outcome in cardiac arrest victims.
Resuscitation. 80:189–193. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Vaahersalo J, Skrifvars MB, Pulkki K,
Stridsberg M, Røsjø H, Hovilehto S, Tiainen M, Varpula T, Pettilä V
and Ruokonen E; FINNRESUSCI Laboratory Study Group, : Admission
interleukin-6 is associated with post resuscitation organ
dysfunction and predicts long-term neurological outcome after
out-of-hospital ventricular fibrillation. Resuscitation.
85:1573–1579. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Van Kempen MJ, Fromaget C, Gros D, Moorman
AF and Lamers WH: Spatial distribution of connexin 43, the major
cardiac gap junction protein, in the developing and adult rat
heart. Circ Res. 68:1638–1651. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Niemann JT, Rosborough J, Youngquist S,
Lewis RJ, Phan QT and Filler S: The proinflammatory cytokine
response following resuscitation in the swine model depends on the
method of ventricular fibrillation induction. Acad Emerg Med.
15:939–944. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Fernandez-Cobo M, Gingalewski C, Drujan D
and De Maio A: Downregulation of connexin 43 gene expression in rat
heart during inflammation. The role of tumour necrosis factor.
Cytokine. 11:216–224. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sims JJ, Schoff KL, Loeb JM and Wiegert
NA: Regional gap junction inhibition increases defibrillation
thresholds. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 285:H10–H16. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Pavlov VA, Ochani M, Yang LH,
Gallowitsch-Puerta M, Ochani K, Lin X, Levi J, Parrish WR,
Rosas-Ballina M, Czura CJ, et al: Selective a7-nicotinic
acetylcholine receptor agonist GTS-21 improves survival in murine
endotoxemia and severe sepsis. Crit Care Med. 35:1139–1144. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Norman GJ, Morris JS, Karelina K, Weil ZM,
Zhang N, Al-Abed Y, Brothers HM, Wenk GL, Pavlov VA, Tracey KJ and
Devries AC: Cardiopulmonary arrest and resuscitation disrupts
cholinergic anti-inflammatory processes: A role for cholinergic a7
nicotinic receptors. J Neurosci. 31:3446–3452. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Khraiche ML, Phillips WB, Jackson N and
Muthuswamy J: Ultrasound induced increase in excitability of single
neurons. Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2008:4246–4249.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Mihran RT, Lineaweaver S, Barnes FS and
Wachtel H: Effects of pulsed acoustic and mechanical stimuli on the
excitability of isolated neuronal and cardiac cells. Appl Occup
Environ. Hyg. 11:271–274. 1996.
|
|
26
|
Lu T, Loh TM, El-Sayed HF and Davies MG:
Single-center retrospective review of ultrasound-accelerated versus
traditional catheter-directed thrombolysis for acute lower
extremity deep venous thrombosis. Vascular. 25:525–532. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Nazer B, Gerstenfeld EP, Hata A, Crum LA
and Matula TJ: Cardiovascular applications of therapeutic
ultrasound. J Interv Card Electrophysiol. 39:287–294. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Miller DL, Smith NB, Bailey MR, Czarnota
GJ, Hynynen K and Makin IR; Bioeffects Committee of the American
Institute of Ultrasound in Medicine, : Overview of therapeutic
ultrasound applications and safety considerations. J Ultrasound
Med. 31:623–634. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|