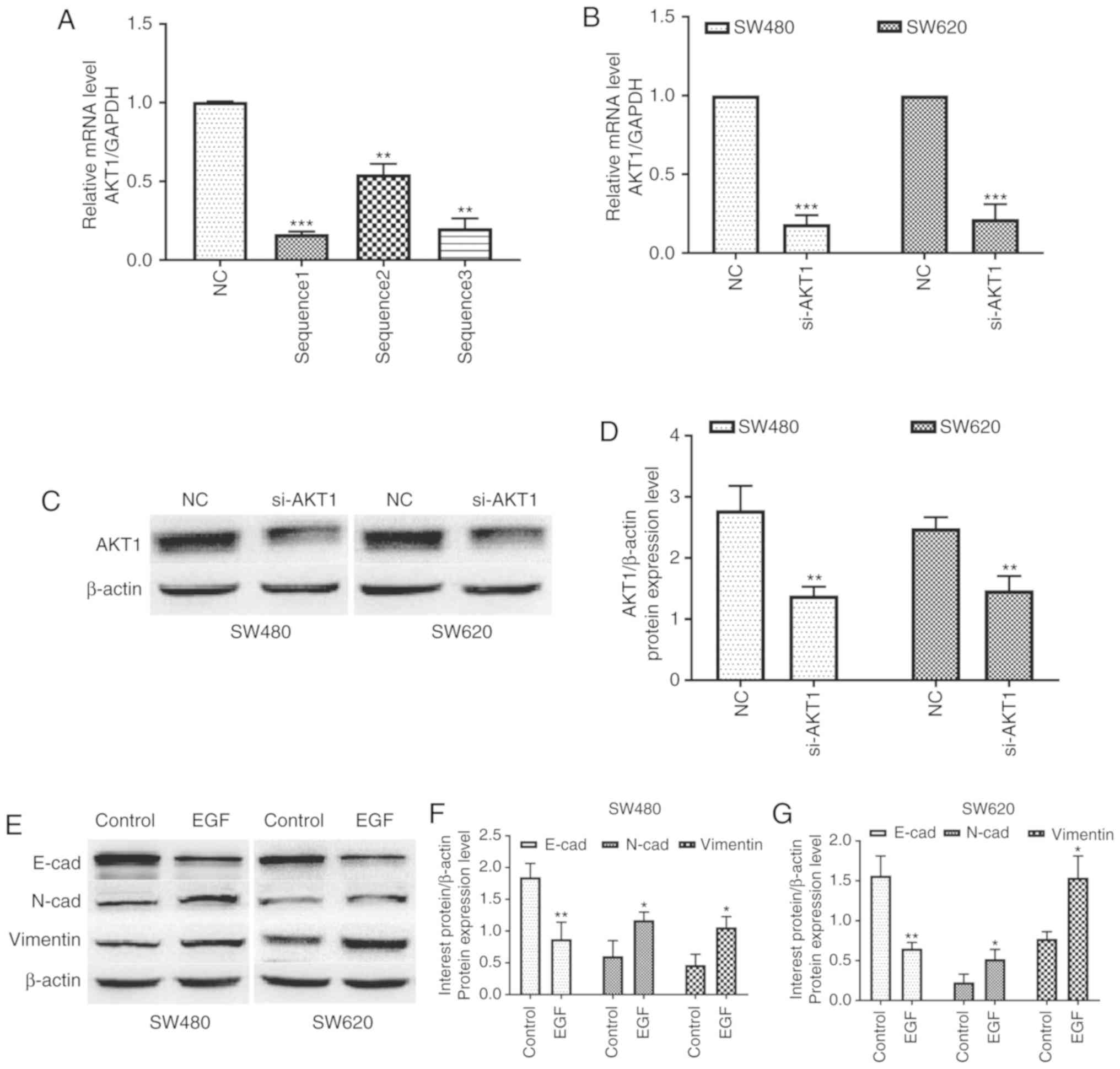
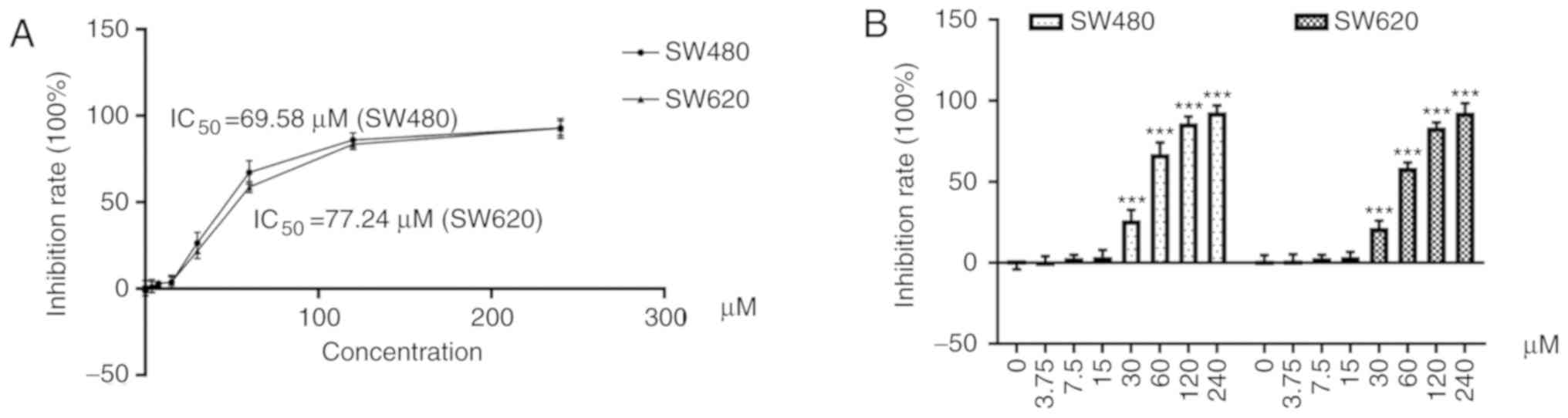
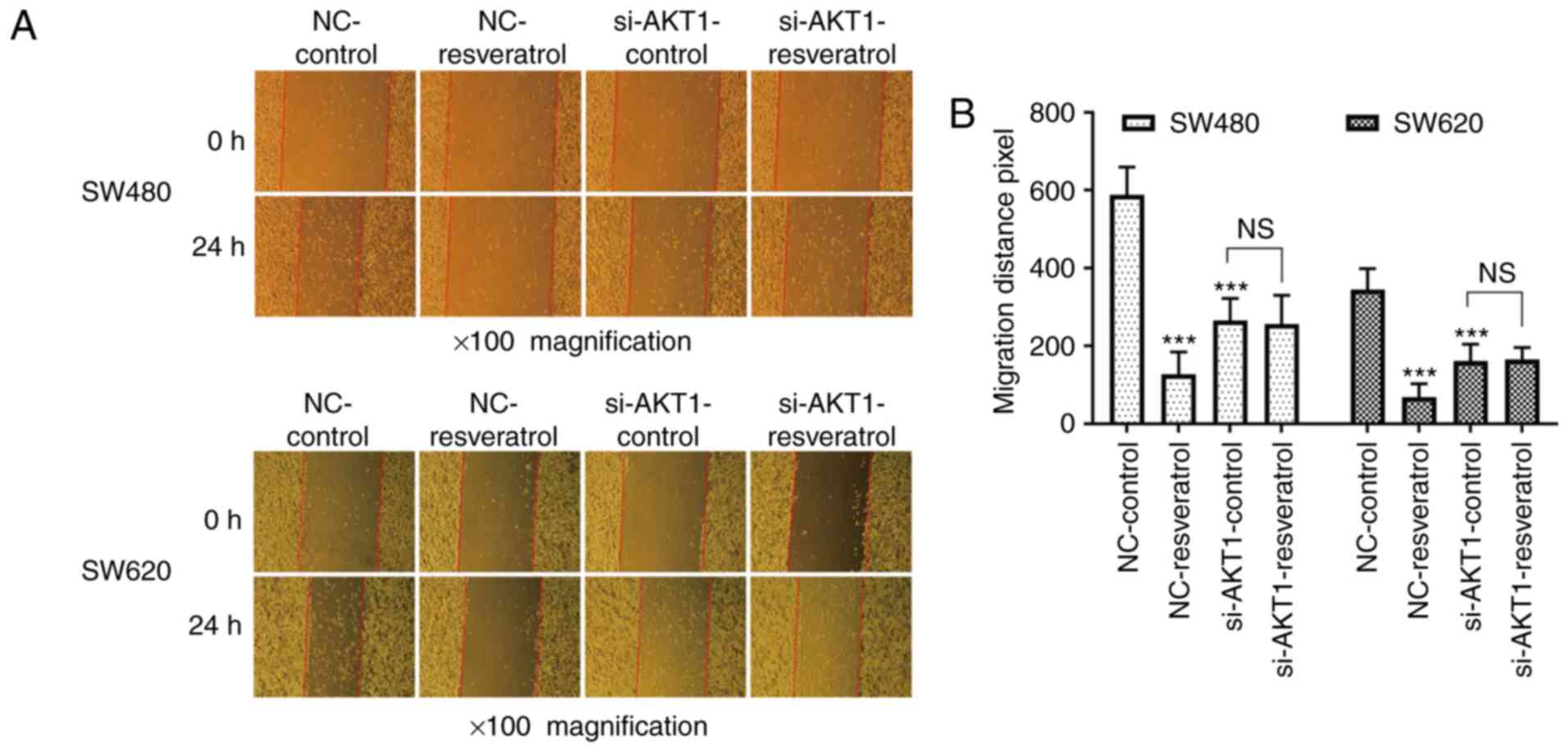
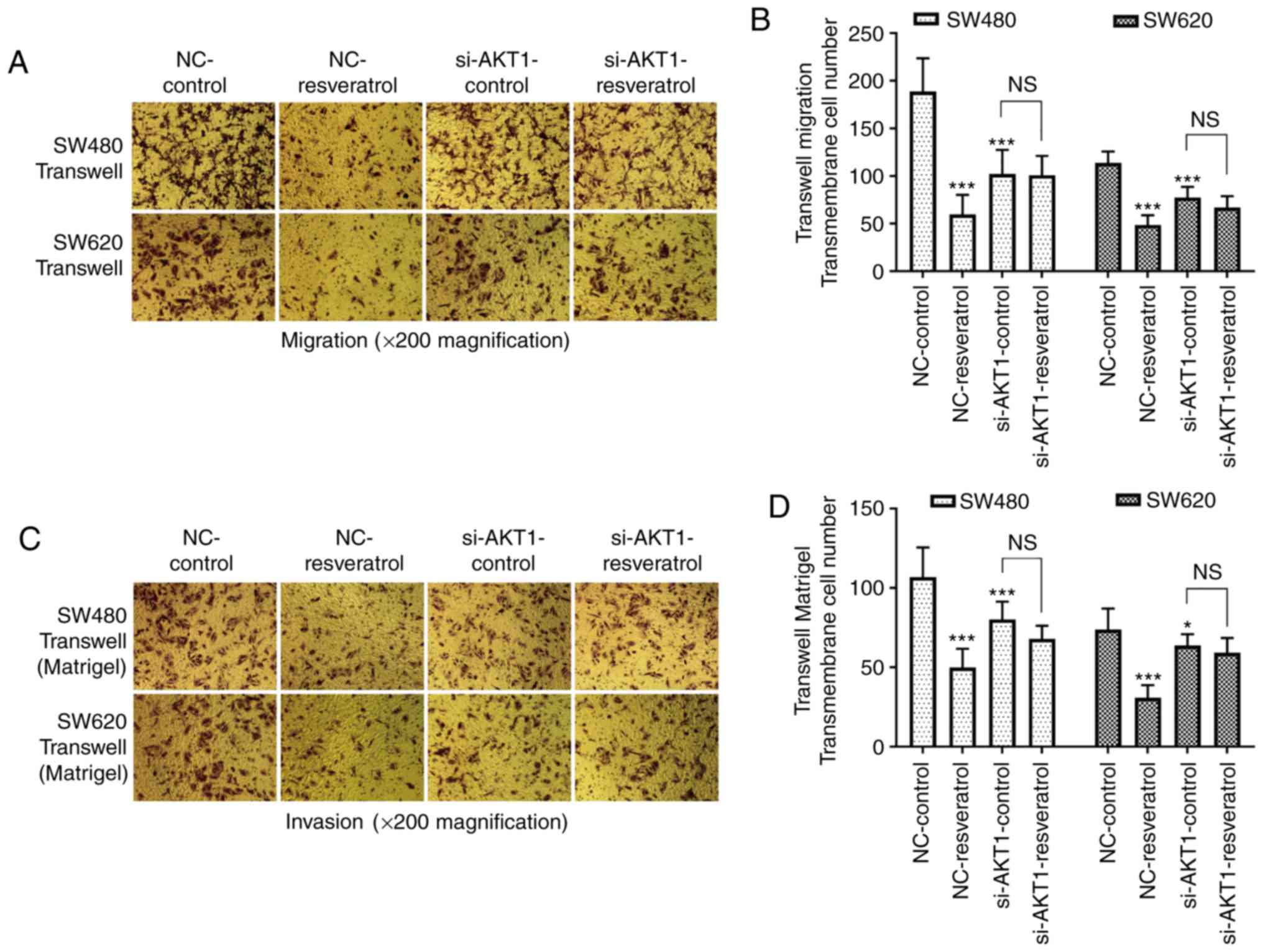
|
1
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin. 67:7–30. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Arnold M, Sierra MS, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global patterns and trends in
colorectal cancer incidence and mortality. Gut. 66:683–691. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fedewa SA, Ahnen DJ,
Meester RGS, Barzi A and Jemal A: Colorectal cancer statistics,
2017. CA Cancer J Clin. 67:177–193. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Liang WC, Fu WM, Wong CW, Wang Y, Wang WM,
Hu GX, Zhang L, Xiao LJ, Wan DC, Zhang JF and Waye MM: The lncRNA
H19 promotes epithelial to mesenchymal transition by functioning as
miRNA sponges in colorectal cancer. Oncotarget. 6:22513–22525.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Edwards BK, Ward E, Kohler BA, Eheman C,
Zauber AG, Anderson RN, Jemal A, Schymura MJ, Lansdorp-Vogelaar I,
Seeff LC, et al: Annual report to the nation on the status of
cancer, 1975–2006, featuring colorectal cancer trends and impact of
interventions (risk factors, screening, and treatment) to reduce
future rates. Cancer. 116:544–573. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Diepenbruck M and Christofori G:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and metastasis: Yes, no,
maybe? Curr Opin Cell Biol. 43:7–13. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Vences-Catalan F and Levy S: Immune
targeting of tetraspanins involved in cell invasion and metastasis.
Front Immunol. 9:12772018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Carter LG, D'Orazio JA and Pearson KJ:
Resveratrol and cancer: Focus on in vivo evidence. Endocr Relat
Cancer. 21:R209–R225. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Borriello A: Resveratrol in cancer
prevention and treatment: Focusing on molecular targets and
mechanism of action. Proceedings. 1:9762017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Kim SE, Shin SH, Lee JY, Kim CH, Chung IK,
Kang HM, Park HR, Park BS and Kim IR: Resveratrol induces
mitochondrial apoptosis and inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal
transition in oral squamous cell carcinoma cells. Nutr Cancer.
70:125–135. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Cilibrasi C, Riva G, Romano G, Cadamuro M,
Bazzoni R, Butta V, Paoletta L, Dalprà L, Strazzabosco M, Lavitrano
M, et al: Resveratrol impairs glioma stem cells proliferation and
motility by modulating the wnt signaling pathway. PLoS One.
12:e01698542017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li W, Ma J, Ma Q, Li B, Han L, Liu J, Xu
Q, Duan W, Yu S, Wang F and Wu E: Resveratrol inhibits the
epithelial-mesenchymal transition of pancreatic cancer cells via
suppression of the PI-3K/Akt/NF-κB pathway. Curr Med Chem.
20:4185–4194. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Aiello NM, Maddipati R, Norgard RJ, Balli
D, Li J, Yuan S, Yamazoe T, Black T, Sahmoud A, Furth EE, et al:
EMT subtype influences epithelial plasticity and mode of cell
migration. Dev Cell. 45:681–695.e684. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhang H, Sun JD, Yan LJ and Zhao XP:
PDGF-D/PDGFRβ promotes tongue squamous carcinoma cell (TSCC)
progression via activating p38/AKT/ERK/EMT signal pathway. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 478:845–851. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Saegusa M, Hashimura M, Kuwata T and
Okayasu I: Requirement of the Akt/beta-catenin pathway for uterine
carcinosarcoma genesis, modulating E-cadherin expression through
the transactivation of slug. Am J Pathol. 174:2107–2115. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tokunaga E, Oki E, Egashira A, Sadanaga N,
Morita M, Kakeji Y and Maehara Y: Deregulation of the Akt pathway
in human cancer. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 8:27–36. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Dou Y, Lei JQ, Guo SL, Zhao D, Yue HM and
Yu Q: The CNPY2 enhances epithelial-mesenchymal transition via
activating the AKT/GSK3β pathway in non-small cell lung cancer.
Cell Biol Int. 42:959–964. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lu LL, Chen XH, Zhang G, Liu ZC, Wu N,
Wang H, Qi YF, Wang HS, Cai SH and Du J: CCL21 facilitates
chemoresistance and cancer stem cell-like properties of colorectal
cancer cells through AKT/GSK-3β/snail signals. Oxid Med Cell
Longev. 2016:58741272016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Jiang H, Zhou Z, Jin S, Xu K, Zhang H and
Xu J, Sun Q, Wang J and Xu J: PRMT9 promotes hepatocellular
carcinoma invasion and metastasis via activating
PI3K/Akt/GSK-3β/Snail signaling. Cancer Sci. 109:1414–1427. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Matsumoto T, Yokoi A, Hashimura M, Oguri
Y, Akiya M and Saegusa M: TGF-β-mediated LEFTY/Akt/GSK-3β/Snail
axis modulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer stem
cell properties in ovarian clear cell carcinomas. Mol Carcinog.
57:957–967. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Li Y, Lin Z, Chen B, Chen S, Jiang Z, Zhou
T, Hou Z and Wang Y: Ezrin/NF-kB activation regulates epithelial-
mesenchymal transition induced by EGF and promotes metastasis of
colorectal cancer. Biomed Pharmacother. 92:140–148. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Liu ZC, Chen XH, Song HX, Wang HS, Zhang
G, Wang H, Chen DY, Fang R, Liu H, Cai SH and Du J: Snail regulated
by PKC/GSK-3β pathway is crucial for EGF-induced
epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) of cancer cells. Cell
Tissue Res. 358:491–502. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Shimaoka H, Takeno S, Maki K, Sasaki T,
Hasegawa S and Yamashita Y: A cytokine signal inhibitor for
rheumatoid arthritis enhances cancer metastasis via depletion of NK
cells in an experimental lung metastasis mouse model of colon
cancer. Oncol Lett. 14:3019–3027. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Mateo-Lozano S, Bazzocco S, Rodrigues P,
Mazzolini R, Andretta E, Dopeso H, Fernández Y, Del Llano E, Bilic
J, Suárez-López L, et al: Loss of the EPH receptor B6 contributes
to colorectal cancer metastasis. Sci Rep. 7:437022017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Liu X, Ji Q, Deng W, Chai N, Feng Y, Zhou
L, Sui H, Li C, Sun X and Li Q: JianPi JieDu recipe inhibits
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in colorectal cancer through
TGF-β/Smad mediated Snail/E-cadherin expression. Biomed Res Int.
2017:26131982017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhang Z, Chen H, Xu C, Song L, Huang L,
Lai Y, Wang Y, Chen H, Gu D, Ren L and Yao Q: Curcumin inhibits
tumor epithelialmesenchymal transition by downregulating the Wnt
signaling pathway and upregulating NKD2 expression in colon cancer
cells. Oncol Rep. 35:2615–2623. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Berman AY, Motechin RA, Wiesenfeld MY and
Holz MK: The therapeutic potential of resveratrol: A review of
clinical trials. NPJ Precis Oncol. 1:352017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Gao Q, Yuan Y, Gan HZ and Peng Q:
Resveratrol inhibits the hedgehog signaling pathway and
epithelial-mesenchymal transition and suppresses gastric cancer
invasion and metastasis. Oncol Lett. 9:2381–2387. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Jiao Y, Li H, Liu Y, Guo A, Xu X, Qu X,
Wang S, Zhao J, Li Y and Cao Y: Resveratrol inhibits the invasion
of glioblastoma-initiating cells via down-regulation of the
PI3K/Akt/NF-κB signaling pathway. Nutrients. 7:4383–4402. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kim YS, Sull JW and Sung HJ: Suppressing
effect of resveratrol on the migration and invasion of human
metastatic lung and cervical cancer cells. Mol Biol Rep.
39:8709–8716. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ji Q, Liu X, Fu X, Zhang L, Sui H, Zhou L,
Sun J, Cai J, Qin J, Ren J and Li Q: Resveratrol inhibits invasion
and metastasis of colorectal cancer cells via MALAT1 mediated
Wnt/β-catenin signal pathway. Plos One. 8:e787002013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ombrato L and Malanchi I: The EMT
universe: Space between cancer cell dissemination and metastasis
initiation. Crit Rev Oncog. 19:349–361. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Karimi Dermani F, Saidijam M, Amini R,
Mahdavinezhad A, Heydari K and Najafi R: Resveratrol inhibits
proliferation, invasion, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition by
increasing miR-200c expression in HCT-116 colorectal cancer cells.
J Cell Biochem. 118:1547–1555. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Buhrmann C, Shayan P, Kraehe P, Popper B,
Goel A and Shakibaei M: Resveratrol induces chemosensitization to
5-fluorouracil through up-regulation of intercellular junctions,
Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and apoptosis in colorectal
cancer. Biochem Pharmacol. 98:51–68. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ye X and Weinberg RA:
Epithelial-mesenchymal plasticity: A central regulator of cancer
progression. Trends Cell Biol. 25:675–686. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zhang X, Jiang G, Sun M, Zhou H, Miao Y,
Liang M, Wang E and Zhang Y: Cytosolic THUMPD1 promotes breast
cancer cells invasion and metastasis via the AKT-GSK3-Snail
pathway. Oncotarget. 8:13357–13366. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zhao J, Ou B, Han D, Wang P, Zong Y, Zhu
C, Liu D, Zheng M, Sun J, Feng H and Lu A: Tumor-derived CXCL5
promotes human colorectal cancer metastasis through activation of
the ERK/Elk-1/Snail and AKT/GSK3β/β-catenin pathways. Mol Cancer.
16:702017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|