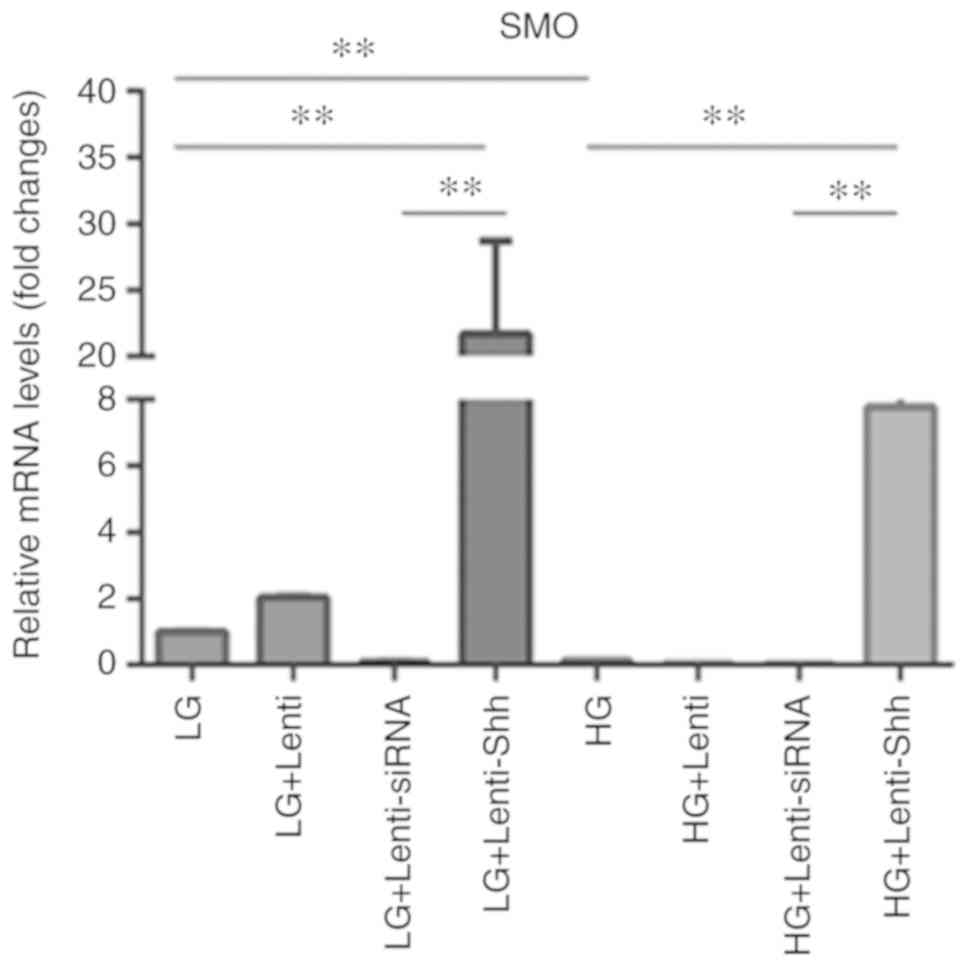
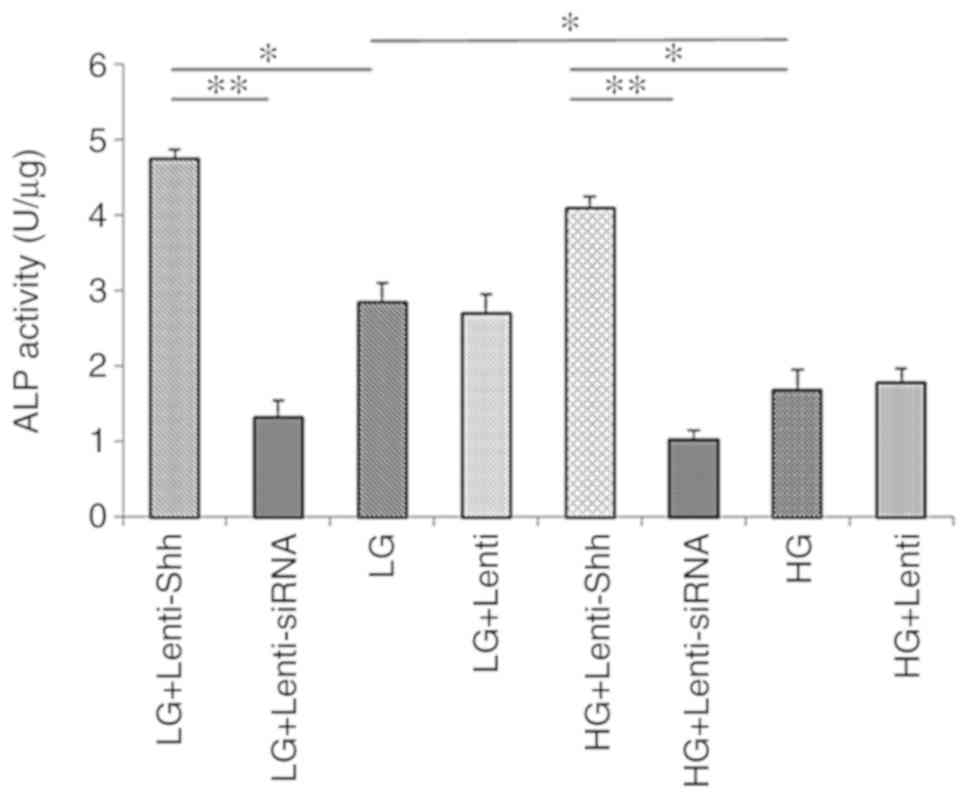
|
1
|
de Carvalho GB, Dias-Vasconcelos NL,
Santos RKF, Brandão-Lima PN, da Silva DG and Pires LV: Effect of
different dietary patterns on glycemic control in individuals with
type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review. Crit Rev Food Sci
Nutr. 1–12. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Marin C, Luyten FP, Van der Schueren B,
Kerckhofs G and Vandamme K: The impact of type 2 diabetes on bone
fracture healing. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 9:62018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ge Z, Liu ZZ, Kan J, Zhang JJ, Li SJ, Tian
NL, Ye F, Qian XS, Yang S, Chen MX, et al: Stent fracture is
associated with a higher mortality in patients with type-2 diabetes
treated by implantation of a second-generation drug-eluting stent.
Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 33:1873–1881. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kayal RA, Siqueira M, Alblowi J, McLean J,
Krothapalli N, Faibish D, Einhorn TA, Gerstenfeld LC and Graves DT:
TNF-alpha mediates diabetes-enhanced chondrocyte apoptosis during
fracture healing and stimulates chondrocyte apoptosis through
FOXO1. J Bone Miner Res. 25:1604–1615. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Liu R, Bal HS, Desta T, Krothapalli N,
Alyassi M, Luan Q and Graves DT: Diabetes enhances periodontal bone
loss through enhanced resorption and diminished bone formation. J
Dent Res. 85:510–514. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Jiang ZL, Cui YQ, Gao R, Li Y, Fu ZC,
Zhang B and Guan CC: Study of TNF-α, IL-1β and LPS levels in the
gingival crevicular fluid of a rat model of diabetes mellitus and
periodontitis. Dis Markers. 34:295–304. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wittrant Y, Gorin Y, Woodruff K, Horn D,
Abboud HE, Mohan S and Abboud-Werner SL: High D(+)glucose
concentration inhibits RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis. Bone.
42:1122–1130. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Serrano S, Mariñoso ML, Nacher M, Torres
A, Cuevas X, Loreta J, Munné A and Diez A: Modulation of osteoblast
activity by serum from diabetic and non-diabetic patients on
hemodialysis: A three-dimensional culture study. J Nephrol.
17:369–376. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Liu C and Jiang D: High glucose-induced
LIF suppresses osteoblast differentiation via regulating
STAT3/SOCS3 signaling. Cytokine. 91:132–139. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Luo J, Sun MH, Kang Q, Peng Y, Jiang W,
Luu HH, Luo Q, Park JY, Li Y, Haydon RC and He TC: Gene therapy for
bone regeneration. Curr Gene Ther. 5:167–179. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Milone MC and O'Doherty U: Clinical use of
lentiviral vectors. Leukemia. 32:1529–1541. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Naldini L, Blömer U, Gallay P, Ory D,
Mulligan R, Gage FH, Verma IM and Trono D: In vivo gene delivery
and stable transduction of nondividing cells by a lentiviral
vector. Science. 272:263–267. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Naldini L, Blömer U, Gage FH, Trono D and
Verma IM: Efficient transfer, integration, and sustained long-term
expression of the transgene in adult rat brains injected with a
lentiviral vector. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 93:11382–11388. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kimura H, Ng JM and Curran T: Transient
inhibition of the Hedgehog pathway in young mice causes permanent
defects in bone structure. Cancer Cell. 13:249–260. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yuan X, Cao J, He X, Serra R, Qu J, Cao X
and Yang S: Ciliary IFT80 balances canonical versus non-canonical
hedgehog signalling for osteoblast differentiation. Nat Commun.
7:11018–11024. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang C, Shan S, Wang C, Wang J, Li J, Hu
G, Dai K, Li Q and Zhang X: Mechanical stimulation promote the
osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow stromal cells through
epigenetic regulation of Sonic Hedgehog. Exp Cell Res. 352:346–356.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kinto N, Iwamoto M, Enomoto-Iwamoto M,
Noji S, Ohuchi H, Yoshioka H, Kataoka H, Wada Y, Yuhao G, Takahashi
HE, et al: Fibroblasts expressing Sonic hedgehog induce osteoblast
differentiation and ectopic bone formation. FEBS Lett. 404:319–323.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ho JE, Chung EH, Wall S, Schaffer DV and
Healy KE: Immobilized sonic hedgehog N-terminal signaling domain
enhances differentiation of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem
cells. J Biomed Mater Res A. 83:1200–1208. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Liao DM, Ng YK, Tay SSW, Ling EA and Dheen
ST: Altered gene expression with abnormal patterning of the
telencephalon in embryos of diabetic Albino Swiss mice.
Diabetologia. 47:523–531. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Dunaeva M, Voo S, van Oosterhoud C and
Waltenberger J: Sonic hedgehog is a potent chemoattractant for
human monocytes: Diabetes mellitus inhibits Sonic hedgehog-induced
monocyte chemotaxis. Basic Res Cardiol. 105:61–71. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Srinivasan K, Viswanad B, Asrat L, Kaul CL
and Ramarao P: Combination of high fat diet-fed and low-dose
streptozotocin-treated rat: A model for type 2 diabetes and
pharmacological screening. Pharmacol Res. 52:313–320. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ti Y, Xie GL, Wang ZH, Bi XL, Ding WY,
Wang J, Jiang GH, Bu PL, Zhang Y, Zhong M and Zhang W: TRB3 gene
silencing alleviates diabetic cardiomyopathy in a type 2 diabetic
rat model. Diabetes. 60:2963–2974. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Li C, Shi C, Kim J, Chen Y, Ni S, Jiang L,
Zheng C, Li D, Hou J, Taichman RS and Sun H: Erythropoietin
promotes bone formation through Ephr inB2/EphB4 signaling. J Dent
Res. 94:455–463. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Elsubeihi ES and Heersche JN: Quantitative
assessment of post-extraction healing and alveolar ridge
remodelling of the mandible in female rats. Arch Oral Biol.
49:401–412. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Arai Y, Aoki K, Shimizu Y, Tabata Y, Ono
T, Murali R, Mise-Omata S and Wakabayashi N: Peptide-induced de
novo bone formation after tooth extraction prevents alveolar bone
loss in a murine tooth extraction model. Eur J Pharmacol.
782:89–97. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Reseland JE, Syversen U, Bakke I, Qvigstad
G, Eide LG, Hjertner O, Gordeladze JO and Drevon CA: Leptin is
expressed in and secreted from primary cultures of human
osteoblasts and promotes bone mineralization. J Bone Miner Res.
16:1426–1433. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ingham PW and McMahon AP: Hedgehog
signaling in animal development: Paradigms and principles. Genes
Dev. 15:3059–3087. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
McMahon AP, Ingham PW and Tabin CJ:
Developmental roles and clinical significance of hedgehog
signaling. Curr Top Dev Biol. 53:1–114. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Oliveira FS, Bellesini LS, Defino HL, da
Silva Herrero CF, Beloti MM and Rosa AL: Hedgehog signaling and
osteoblast gene expression are regulated by purmorphamine in human
mesenchymal stem cells. J Cell Biochem. 113:204–208. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wu X, Walker J, Zhang J, Ding S and
Schultz PG: Purmorphamine induces osteogenesis by activation of the
hedgehog signaling pathway. Chem Biol. 11:1229–1238. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Sinha S and Chen JK: Purmorphamine
activates the hedgehog pathway by targeting smoothened. Nat Chem
Biol. 2:29–30. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kasai T, Bandow K, Suzuki H, Chiba N,
Kakimoto K, Ohnishi T, Kawamoto S, Nagaoka E and Matsuguchi T:
Osteoblast differentiation is functionally associated with
decreased AMP kinase activity. J Cell Physiol. 221:740–749. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Jung WW: Protective effect of apigenin
against oxidative stress-induced damage in osteoblastic cells. Int
J Mol Med. 33:1327–1334. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Suh KS, Rhee SY, Jung WW, Kim NJ, Jang YP,
Kim HJ, Kim MK, Choi YK and Kim YS: Chrysanthemum zawadskii extract
protects osteoblastic cells from highly reducing sugar-induced
oxidative damage. Int J Mol Med. 32:241–250. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kawai S and Sugiura T: Characterization of
human bone morphogenetic protein (BMP)-4 and −7 gene promoters:
Activation of BMP promoters by Gli, a sonic hedgehog mediator.
Bone. 29:54–61. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Courties A, Berenbaum F and Sellam J: The
phenotypic approach to osteoarthritis: A look at metabolic
syndrome-associated osteoarthritis. Joint Bone Spine. Dec
22–2018.doi: 10.1016/j.jbspin.2018.12.005 (Epub ahead of print).
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Tebé C, Martinez-Laguna D, Moreno V,
Cooper C, Diez-Perez A, Collins GS and Prieto-Alhambra D:
Differential mortality and the excess rates of hip fracture
associated with type 2 diabetes: Accounting for competing risks in
fracture prediction matters. J Bone Miner Res. 33:1417–1421. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kim SY, Lee JY, Park YD, Kang KL, Lee JC
and Heo JS: Hesperetin alleviates the inhibitory effects of high
glucose on the osteoblastic differentiation of periodontal ligament
stem cells. PLoS One. 8:e675042013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Balint E, Szabo P, Marshall CF and Sprague
SM: Glucose-induced inhibition of in vitro bone mineralization.
Bone. 28:21–28. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Wang Q, Huang C, Zeng F, Xue M and Zhang
X: Activation of the Hh pathway in periosteum-derived mesenchymal
stem cells induces bone formation in vivo: Implication for
postnatal bone repair. Am J Pathol. 177:3100–3111. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Sugiyama O, An DS, Kung SP, Feeley BT,
Gamradt S, Liu NQ, Chen IS and Lieberman JR: Lentivirus-mediated
gene transfer induces long-term transgene expression of BMP-2 in
vitro and new bone formation in vivo. Mol Ther. 11:390–398. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Guan CC, Yan M, Jiang XQ, Zhang P, Zhang
XL, Li J, Ye DX and Zhang FQ: Sonic hedgehog alleviates the
inhibitory effects of high glucose on the osteoblastic
differentiation of bone marrow stromal cells. Bone. 45:1146–1152.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Mazumdar T, DeVecchio J, Shi T, Jones J,
Agyeman A and Houghton JA: Hedgehog signaling drives cellular
survival in human colon carcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 71:1092–1102.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Pan D, Li Y, Li Z, Wang P and Liang Y: Gli
inhibitor GANT61 causes apoptosis in myeloid leukemia cells and
acts in synergy with rapamycin. Leuk Res. 36:742–748. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Lee SJ: Cytokine delivery and tissue
engineering. Yonsei Med J. 41:704–719. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Marei MK, Nouh SR, Saad MM and Ismail NS:
Preservation and regeneration of alveolar bone by tissue-engineered
implants. Tissue Eng. 11:751–767. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|