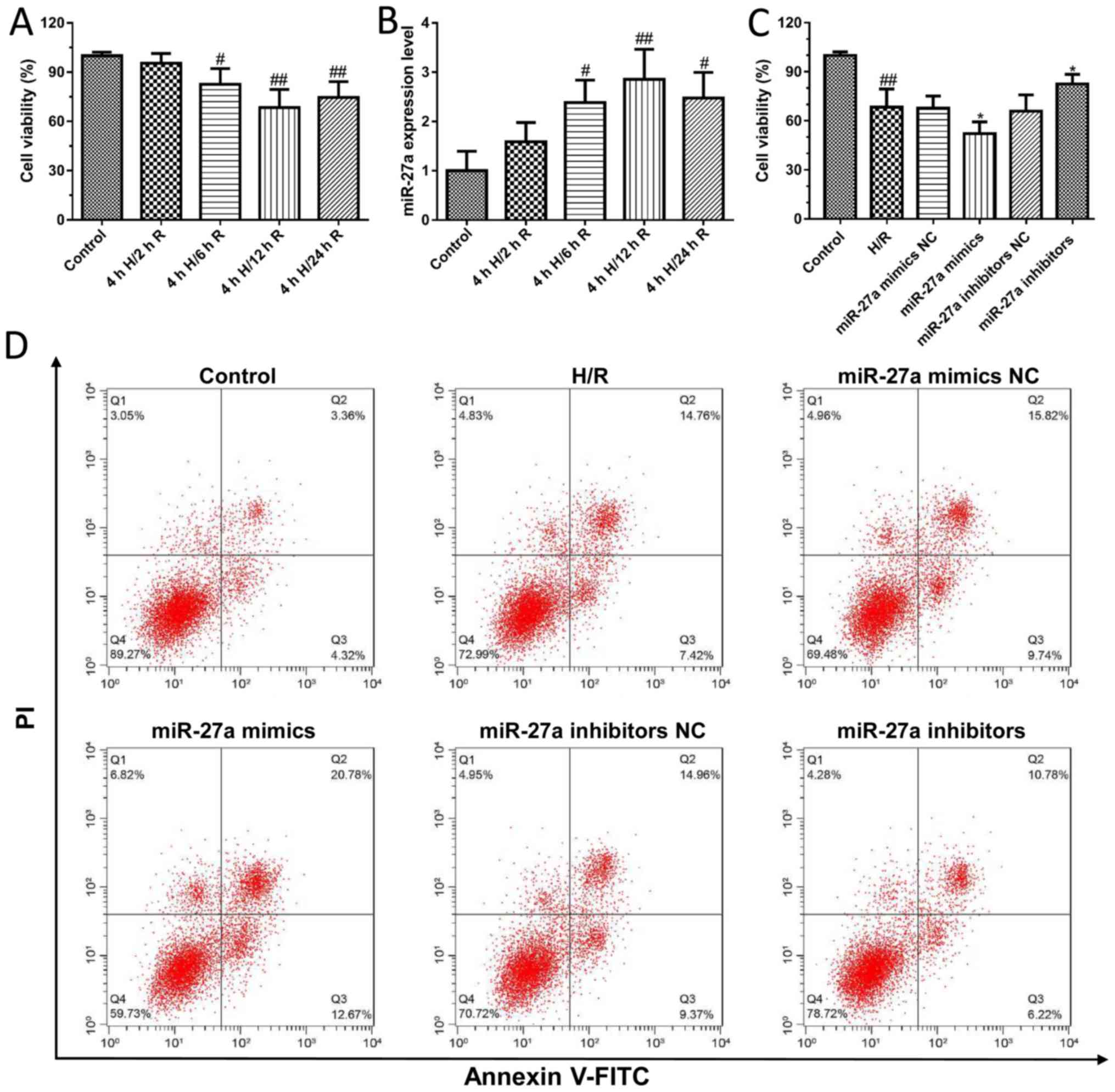
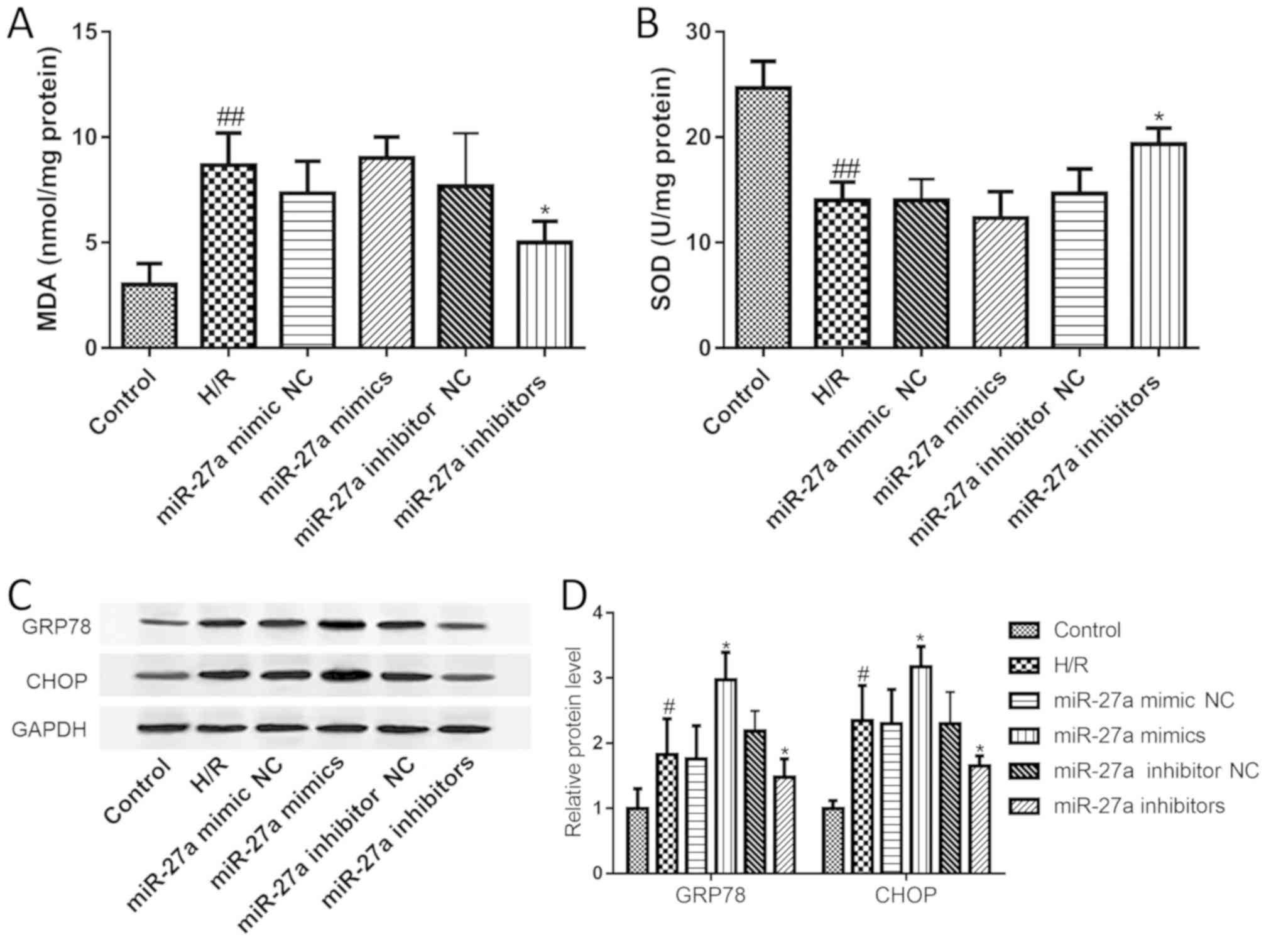
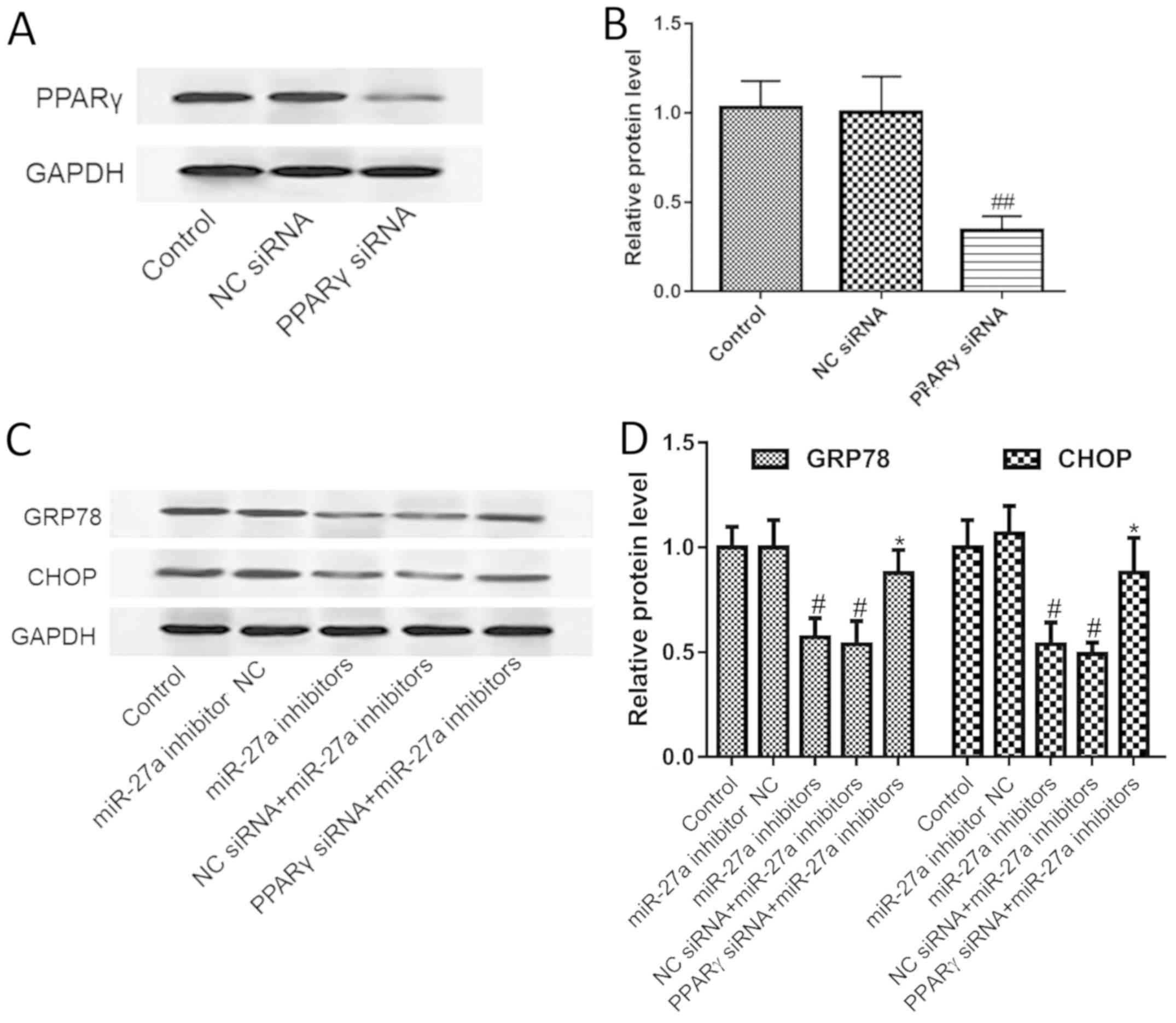
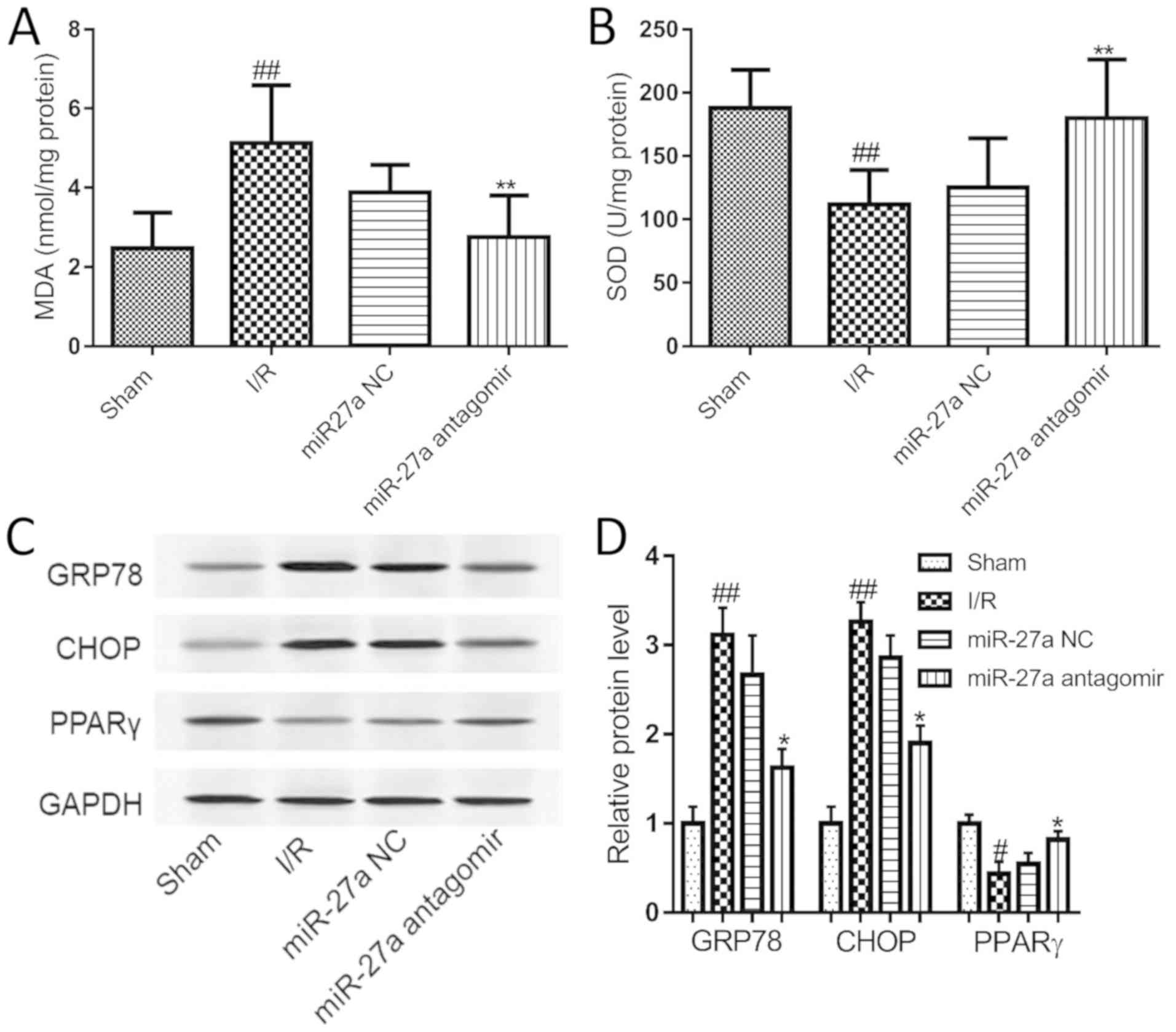
|
1
|
Zhai Y, Petrowsky H, Hong JC, Busuttil RW
and Kupiec-Weglinski JW: Ischaemia-reperfusion injury in liver
transplantation-from bench to bedside. Nat Rev Gastroenterol
Hepatol. 10:79–89. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Irie T, Ito K, Ozasa H, Noda Y, Ikeda S,
Tanaka S, Arii S and Horikawa S: Splenic artery ligation: A
protection against hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury in partially
hepatectomized rats. Hepatol Res. 42:819–827. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zhai Y, Busuttil RW and Kupiec-Weglinski
JW: Liver ischemia and reperfusion injury: New insights into
mechanisms of innate-adaptive immune-mediated tissue inflammation.
Am J Transplant. 11:1563–1569. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lentsch AB, Kato A, Yoshidome H, McMasters
KM and Edwards MJ: Inflammatory mechanisms and therapeutic
strategies for warm hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury.
Hepatology. 32:169–173. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Brenner C, Galluzzi L, Kepp O and Kroemer
G: Decoding cell death signals in liver inflammation. J Hepatol.
59:583–594. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Guo L, Wu X, Zhang Y, Wang F, Li J and Zhu
J: Protective effects of gastrin-releasing peptide receptor
antagonist RC-3095 in an animal model of hepatic
ischemia/reperfusion injury. Hepatol Res. 49:247–255. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kong D, Hua X, Qin T, Zhang J and He K:
Inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase 3β protects liver against
ischemia/reperfusion injury by activating 5′ adenosine
monophosphate-activated protein kinase-mediated autophagy. Hepatol
Res. 49:462–472. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Li J, Wu B, Teng D, Sun X, Li J, Li J,
Zhang G and Cai J: Cobalt-protoporphyrin enhances heme oxygenase 1
expression and attenuates liver ischemia/reperfusion injury by
inhibiting apoptosis. Mol Med Rep. 17:4567–4572. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Suyavaran A and Thirunavukkarasu C:
Preconditioning methods in the management of hepatic ischemia
reperfusion- induced injury: Update on molecular and future
perspectives. Hepatol Res. 47:31–48. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Liu J, Ren F, Cheng Q, Bai L, Shen X, Gao
F, Busuttil RW, Kupiec-Weglinski JW and Zhai Y: Endoplasmic
reticulum stress modulates liver inflammatory immune response in
the pathogenesis of liver ischemia and reperfusion injury.
Transplantation. 94:211–217. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Malhi H and Kaufman RJ: Endoplasmic
reticulum stress in liver disease. J Hepatol. 54:795–809. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Malhotra JD and Kaufman RJ: The
endoplasmic reticulum and the unfolded protein response. Semin Cell
Dev Biol. 18:716–731. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wu J and Kaufman RJ: From acute ER stress
to physiological roles of the unfolded protein response. Cell Death
Differ. 13:374–384. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Folch-Puy E, Panisello A, Oliva J, Lopez
A, Castro Benítez C, Adam R and Roselló-Catafau J: Relevance of
endoplasmic reticulum stress cell signaling in liver cold ischemia
reperfusion injury. Int J Mol Sci. 17(pii): E8072016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hammadi M, Oulidi A, Gackiere F,
Katsogiannou M, Slomianny C, Roudbaraki M, Dewailly E, Delcourt P,
Lepage G, Lotteau S, et al: Modulation of ER stress and apoptosis
by endoplasmic reticulum calcium leak via translocon during
unfolded protein response: Involvement of GRP78. FASEB J.
27:1600–1609. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Cui FF, Pan YY, Xie HH, Wang XH, Shi HX,
Xiao J, Zhang HY, Chang HT and Jiang LP: Pressure combined with
ischemia/reperfusion injury induces deep tissue injury via
endoplasmic reticulum stress in a rat pressure ulcer model. Int J
Mol Sci. 17:2842016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Peralta C and Brenner C: Endoplasmic
reticulum stress inhibition enhances liver tolerance to
ischemia/reperfusion. Curr Med Chem. 18:2016–2024. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kim I, Xu W and Reed JC: Cell death and
endoplasmic reticulum stress: Disease relevance and therapeutic
opportunities. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 7:1013–1030. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Shukla GC, Singh J and Barik S: MicroRNAs:
Processing, maturation, target recognition and regulatory
functions. Mol Cell Pharmacol. 3:83–92. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Target recognition
and regulatory functions. Cell. 136:215–233. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Li S, Ren J and Sun Q: The expression of
microRNA-23a regulates acute myocardial infarction in patients and
in vitro through targeting PTEN. Mol Med Rep. 17:6866–6872.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zheng X, Zhou H, Qiu Z, Gao S, Wang Z and
Xiao L: Gene microarray analysis of expression profiles in liver
ischemia and reperfusion. Mol Med Rep. 16:3299–3307. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zheng W, Men H, Li J, Xing Y, Wu B, Wang
Z, Li J, Teng D, Shi Y, Li J, et al: Global MicroRNA expression
profiling of mouse livers following ischemia-reperfusion injury at
different stages. PLoS One. 11:e01486772016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Xu CF, Yu CH and Li YM: Regulation of
hepatic microRNA expression in response to ischemic preconditioning
following ischemia/reperfusion injury in mice. OMICS. 13:513–520.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Raza A, Dikdan G, Desai KK, Shareef A,
Fernandes H, Aris V, de la Torre AN, Wilson D, Fisher A,
Soteropoulos P and Koneru B: Global gene expression profiles of
ischemic preconditioning in deceased donor liver transplantation.
Liver Transpl. 16:588–599. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chen Q, Xu J, Li L, Li H, Mao S, Zhang F,
Zen K, Zhang CY and Zhang Q: MicroRNA-23a/b and microRNA-27a/b
suppress Apaf-1 protein and alleviate hypoxia-induced neuronal
apoptosis. Cell Death Dis. 5:e11322014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lv X, Yan J, Jiang J, Zhou X, Lu Y and
Jiang H: MicroRNA-27a-3p suppression of peroxisome
Proliferator-Activated receptor-γ contributes to cognitive
impairments resulting from sevoflurane treatment. J Neurochem.
143:306–319. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chhabra R, Dubey R and Saini N:
Cooperative and individualistic functions of the microRNAs in the
miR-23a~27a~24-2 cluster and its implication in human diseases. Mol
Cancer. 9:2322010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhou Z, Wan J, Hou X, Geng J, Li X and Bai
X: MicroRNA-27a promotes podocyte injury via PPARγ-mediated
β-catenin activation in diabetic nephropathy. Cell Death Dis.
8:e26582017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Xiao Y, Li B and Liu J: miRNA27a regulates
arthritis via PPARγ in vivo and in vitro. Mol Med Rep.
17:5454–5462. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Akahori T, Sho M, Hamada K, Suzaki Y,
Kuzumoto Y, Nomi T, Nakamura S, Enomoto K, Kanehiro H and Nakajima
Y: Importance of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma
in hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury in mice. J Hepatol.
47:784–792. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kuboki S, Shin T, Huber N, Eismann T,
Galloway E, Schuster R, Blanchard J, Zingarelli B and Lentsch AB:
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma protects against
hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury in mice. Hepatology.
47:215–224. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Xing Y, Li J, Li SP, Xi J, Ma N, Liu L,
Wang JS and Cai JZ: MiR-27a-5p regulates apoptosis of liver
ischemia-reperfusion injury in mice by targeting Bach1. J Cell
Biochem. 119:10376–10383. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Schmittgen TD and Livak KJ: Analyzing
real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method. Nat Protoc.
3:1101–1108. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Li Y, Ma D, Wang Z and Yang J:
MicroRNA-155 Deficiency in kupffer cells ameliorates liver
Ischemia-Reperfusion injury in mice. Transplantation.
101:1600–1608. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Li L, Li G, Yu C, Shen Z, Xu C, Feng Z,
Zhang X and Li Y: A role of microRNA-370 in hepatic
ischaemia-reperfusion injury by targeting transforming growth
factor-β receptor II. Liver Int. 35:1124–1132. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Jiang W, Liu G and Tang W: MicroRNA-182-5p
Ameliorates Liver Ischemia-Reperfusion injury by suppressing
toll-like receptor 4. Transplant Proc. 48:2809–2814. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Farid WR, Verhoeven CJ, de Jonge J,
Metselaar HJ, Kazemier G and van der Laan LJ: The ins and outs of
microRNAs as biomarkers in liver disease and transplantation.
Transpl Int. 27:1222–1232. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Imarisio C, Alchera E, Bangalore Revanna
C, Valente G, Follenzi A, Trisolini E, Boldorini R and Carini R:
Oxidative and ER stress-dependent ASK1 activation in steatotic
hepatocytes and Kupffer cells sensitizes mice fatty liver to
ischemia/reperfusion injury. Free Radic Biol Med. 112:141–148.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Guo Y, Hu B, Huang H, Tsung A, Gaikwad NW,
Xu M, Jiang M, Ren S, Fan J, Billiar TR, et al: Estrogen
Sulfotransferase is an oxidative stress-responsive gene that
gender-specifically affects liver ischemia/reperfusion injury. J
Biol Chem. 290:14754–14764. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Zhu J, Hua X, Li D, Zhang J and Xia Q:
Rapamycin attenuates mouse liver ischemia and reperfusion injury by
inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress. Transplant Proc.
47:1646–1652. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Hu R, Chen ZF, Yan J, Li QF, Huang Y, Xu
H, Zhang XP and Jiang H: Endoplasmic reticulum stress of
neutrophils is required for Ischemia/Reperfusion-Induced acute lung
injury. J Immunol. 195:4802–4809. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Xia JG, Xu FF, Qu Y, Song DG, Shen H and
Liu XH: Atorvastatin post-conditioning attenuates myocardial
ischemia reperfusion injury via inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum
stress-related apoptosis. Shock. 42:365–371. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Wu L, Wang Q, Guo F, Ma X, Ji H, Liu F,
Zhao Y and Qin G: MicroRNA-27a induces mesangial cell injury by
targeting of PPARγ, and its in vivo knockdown prevents progression
of diabetic nephropathy. Sci Rep. 6:260722016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Zhu B, Ferry CH, Markell LK, Blazanin N,
Glick AB, Gonzalez FJ and Peters JM: The nuclear receptor
peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-β/δ (PPARβ/δ) promotes
oncogene-induced cellular senescence through repression of
endoplasmic reticulum stress. J Biol Chem. 289:20102–20119. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Tang WX, Wang LK, Wang YQ, Zong ZJ, Gao
ZX, Liu XS, Shen YJ, Shen YX and Li YH: Peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor-α activation protects against
endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced HepG2 cell apoptosis. Mol Cell
Biochem. 385:179–190. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Lee CM, Peng HH, Yang P, Liou JT, Liao CC
and Day YJ: C-C Chemokine Ligand-5 is critical for facilitating
macrophage infiltration in the early phase of liver
ischemia/reperfusion injury. Sci Rep. 7:36982017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|