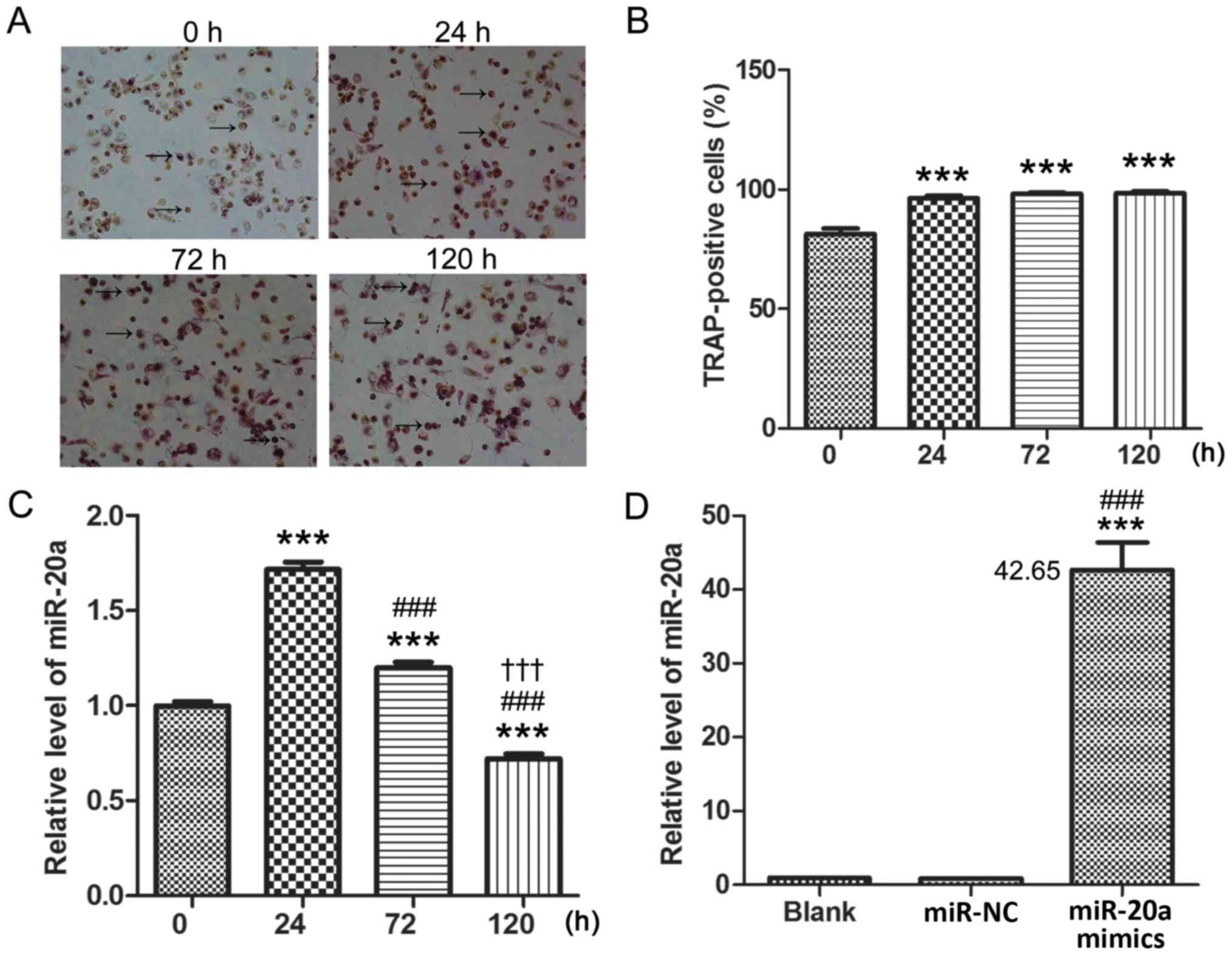
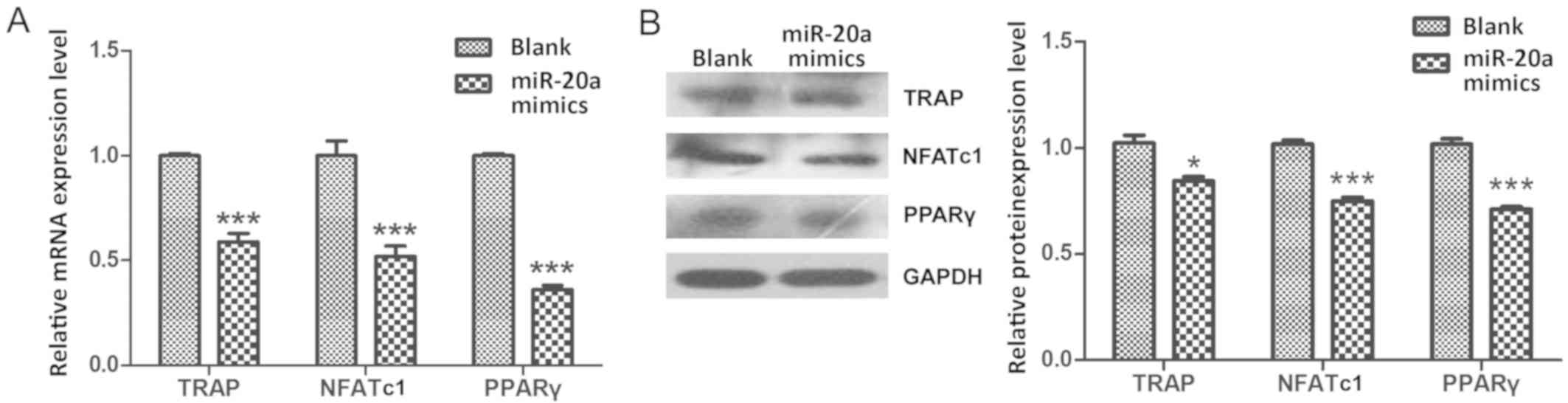
|
1
|
Cheng J, Liang H, Li Q, Peng C, Li Z, Shi
S, Yang L, Tian Z, Tian Y, Zhang Z and Cao W: Hematoporphyrin
monomethyl ether-mediated photodynamic effects on THP-1
cell-derived macrophages. J Photochem Photobiol B. 101:9–15. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sengupta S, Park SH, Seok GE, Patel A,
Numata K, Lu CL and Kaplan DL: Quantifying osteogenic cell
degradation of silk biomaterials. Biomacromolecules. 11:3592–3599.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Geijtenbeek TB, Torensma R, van Vliet SJ,
van Duijnhoven GC, Adema GJ, van Kooyk Y and Figdor CG:
Identification of DC-SIGN, a novel dendritic cell-specific ICAM-3
receptor that supports primary immune responses. Cell. 100:575–585.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Jakob F, Siggelkow H, Homann D, Köhrle J,
Adamski J and Schütze N: Local estradiol metabolism in osteoblast-
and osteoclast-like cells. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 61:167–174.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hattersley G, Owens J, Flanagan AM and
Chambers TJ: Macrophage colony stimulating factor (M-CSF) is
essential for osteoclast formation in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 177:526–531. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Takahashi N, Udagawa N and Suda T: A new
member of tumor necrosis factor ligand family,
ODF/OPGL/TRANCE/RANKL, regulates osteoclast differentiation and
function. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 256:449–455. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Takayanagi H, Kim S, Koga T, Nishina H,
Isshiki M, Yoshida H, Saiura A, Isobe M, Yokochi T, Inoue J, et al:
Induction and activation of the transcription factor NFATc1 (NFAT2)
integrate RANKL signaling in terminal differentiation of
osteoclasts. Dev Cell. 3:889–901. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Matsumoto M, Kogawa M, Wada S, Takayanagi
H, Tsujimoto M, Katayama S, Hisatake K and Nogi Y: Essential role
of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase in cathepsin K gene
expression during osteoclastogenesis through association of NFATc1
and PU.1. J Biol Chem. 279:45969–45979. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Qu B, Xia X, Yan M, Gong K, Deng S, Huang
G, Ma Z and Pan X: miR-218 is involved in the negative regulation
of osteoclastogenesis and bone resorption by partial suppression of
p38MAPK-c-Fos-NFATc1 signaling: Potential role for osteopenic
diseases. Exp Cell Res. 338:89–96. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Esteller M: Non-coding RNAs in human
disease. Nat Rev Genet. 12:861–874. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kapinas K and Delany AM: MicroRNA
biogenesis and regulation of bone remodeling. Arthritis Res Ther.
13:2202011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Fontana L, Pelosi E, Greco P, Racanicchi
S, Testa U, Liuzzi F, Croce CM, Brunetti E, Grignani F and Peschle
C: MicroRNAs 17-5p-20a-106a control monocytopoiesis through AML1
targeting and M-CSF receptor upregulation. Nat Cell Biol.
9:775–787. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sun KT, Chen MY, Tu MG, Wang IK, Chang SS
and Li CY: MicroRNA-20a regulates autophagy related protein-ATG16L1
in hypoxia-induced osteoclast differentiation. Bone. 73:145–153.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Shi C, Qi J, Huang P, Jiang M, Zhou Q,
Zhou H, Kang H, Qian N, Yang Q, Guo L and Deng L: MicroRNA-17/20a
inhibits glucocorticoid-induced osteoclast differentiation and
function through targeting RANKL expression in osteoblast cells.
Bone. 68:67–75. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhou BR, Guo XF, Zhang JA, Xu Y, Li W, Wu
D, Yin ZQ, Permatasari F and Luo D: Elevated miR-34c-5p mediates
dermal fibroblast senescence by ultraviolet irradiation. Int J Biol
Sci. 9:743–752. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kim MH, Ryu SY, Choi JS, Min YK and Kim
SH: Saurolactam inhibits osteoclast differentiation and stimulates
apoptosis of mature osteoclasts. J Cell Physiol. 221:618–628. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
M'Baya-Moutoula E, Louvet L, Metzinger-Le
Meuth V, Massy ZA and Metzinger L: High inorganic phosphate
concentration inhibits osteoclastogenesis by modulating miR-223.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1852:2202–2212. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yuan FL, Xu RS, Jiang DL, He XL, Su Q, Jin
C and Li X: Leonurine hydrochloride inhibits osteoclastogenesis and
prevents osteoporosis associated with estrogen deficiency by
inhibiting the NF-κB and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways. Bone.
75:128–137. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wan Y, Chong LW and Evans RM: PPAR-gamma
regulates osteoclastogenesis in mice. Nat Med. 13:1496–1503. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Li H, Li T, Fan J, Li T, Fan L, Wang S,
Weng X, Han Q and Zhao RC: miR-216a rescues dexamethasone
suppression of osteogenesis, promotes osteoblast differentiation
and enhances bone formation, by regulating c-Cbl-mediated PI3K/AKT
pathway. Cell Death Differ. 22:1935–1945. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Guo DW, Han YX, Cong L, Liang D and Tu GJ:
Resveratrol prevents osteoporosis in ovariectomized rats by
regulating microRNA-338-3p. Mol Med Report. 12:2098–2106. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Sun T, Leung F and Lu WW: miR-9-5p,
miR-675-5p and miR-138-5p damages the strontium and LRP5-mediated
skeletal cell proliferation, differentiation, and adhesion. Int J
Mol Sci. 17:2362016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Tiago DM, Marques CL, Roberto VP, Cancela
ML and Laizé V: Mir-20a regulates in vitro mineralization and BMP
signaling pathway by targeting BMP-2 transcript in fish. Arch
Biochem Biophys. 543:23–30. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhang JF, Fu WM, He ML, Xie WD, Lv Q, Wan
G, Li G, Wang H, Lu G, Hu X, et al: MiRNA-20a promotes osteogenic
differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells by co-regulating
BMP signaling. RNA Biol. 8:829–838. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhou M, Ma J, Chen S, Chen X and Yu X:
MicroRNA-17-92 cluster regulates osteoblast proliferation and
differentiation. Endocrine. 45:302–310. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhou G, Chen T and Raj JU: MicroRNAs in
pulmonary arterial hypertension. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol.
52:139–151. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Krishnan A, Nair SA and Pillai MR: Biology
of PPAR gamma in cancer: A critical review on existing lacunae.
Curr Mol Med. 7:532–540. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhou J, Guo F, Wang G, Wang J, Zheng F,
Guan X, Chang A, Zhang X, Dai C, Li S, et al: miR-20a regulates
adipocyte differentiation by targeting lysine-specific demethylase
6b and transforming growth factor-β signaling. Int J Obes (Lond).
39:1282–1291. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Fan J, Li J and Fan Q: Naringin promotes
differentiation of bone marrow stem cells into osteoblasts by
upregulating the expression levels of microRNA-20a and
downregulating the expression levels of PPARγ. Mol Med Report.
12:4759–4765. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Shao B, Liao L, Yu Y, Shuai Y, Su X, Jing
H, Yang D and Jin Y: Estrogen preserves Fas ligand levels by
inhibiting microRNA-181a in bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem
cells to maintain bone remodeling balance. FASEB J. 29:3935–3944.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Fan MQ, Huang CB, Gu Y, Xiao Y, Sheng JX
and Zhong L: Decrease expression of microRNA-20a promotes cancer
cell proliferation and predicts poor survival of hepatocellular
carcinoma. J Exp Clin Canc Res. 32:212013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Trompeter HI, Abbad H, Iwaniuk KM, Hafner
M, Renwick N, Tuschl T, Schira J, Müller HW and Wernet P: MicroRNAs
MiR-17, MiR-20a, and MiR-106b act in concert to modulate E2F
activity on cell cycle arrest during neuronal lineage
differentiation of USSC. PLoS One. 6:e161382011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|