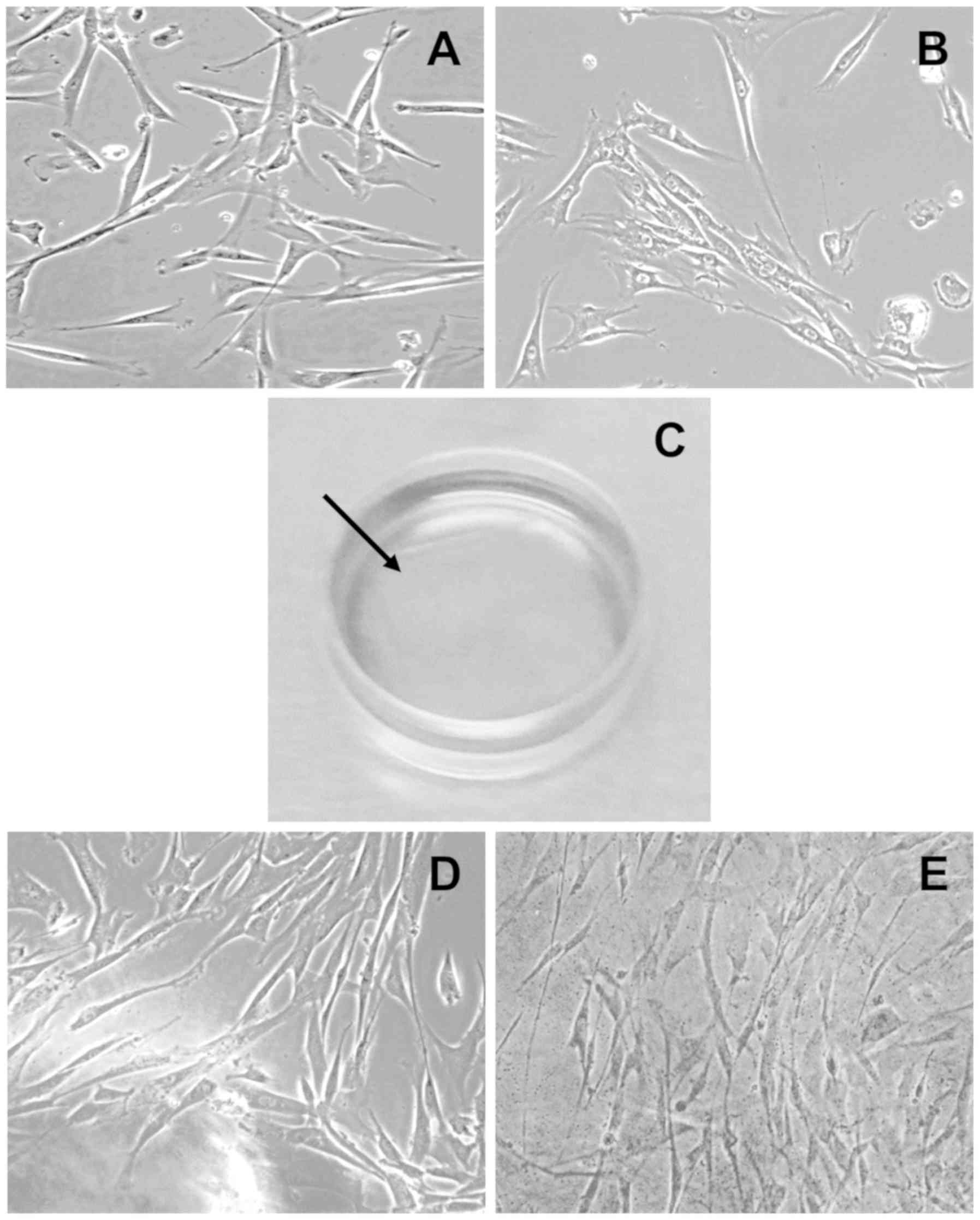
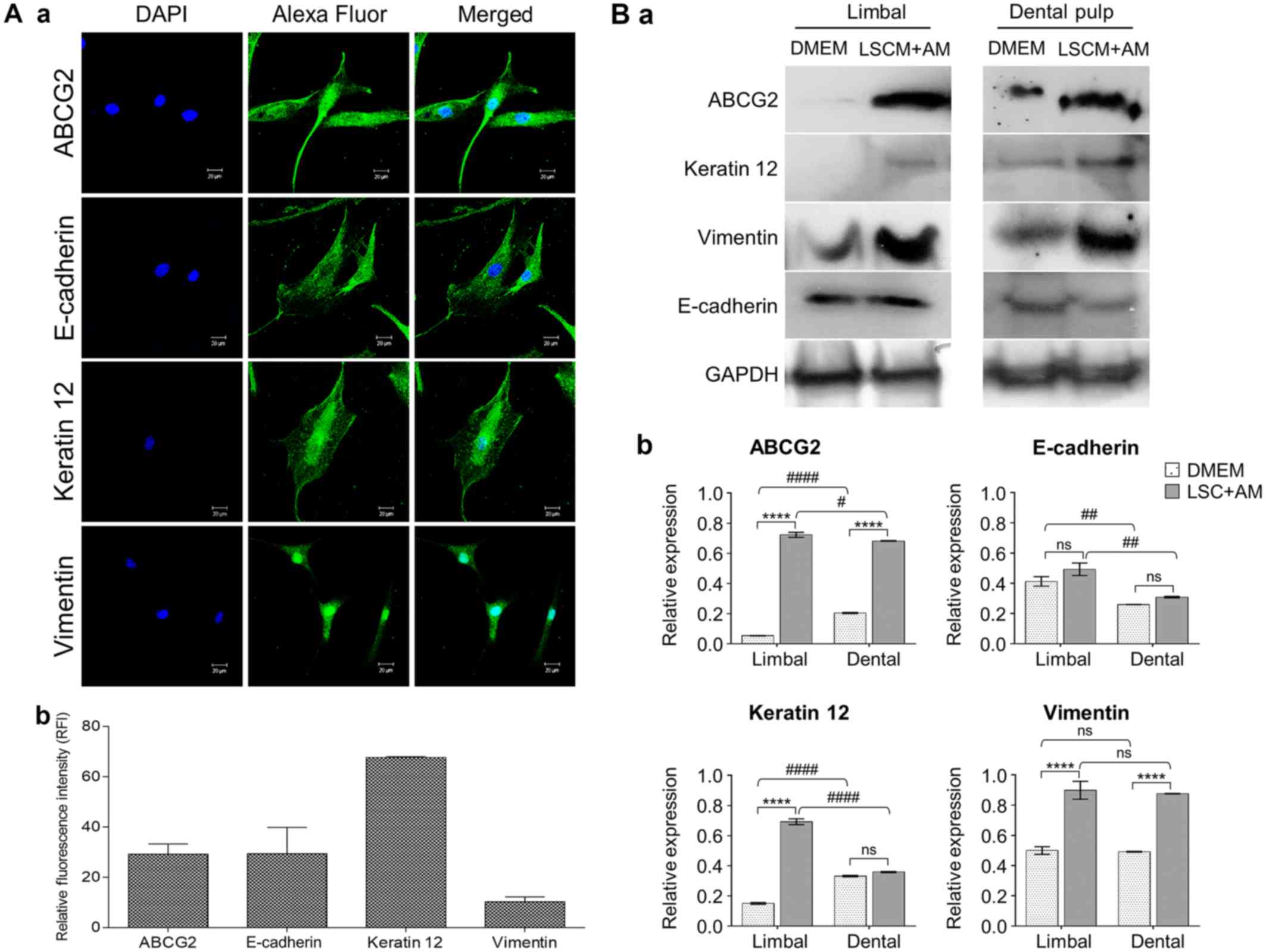
|
1
|
Vashist P, Gupta N, Tandon R, Gupta S and
Sreenivas V: Burden of corneal blindness in India. Indian J
Community Med. 38:198–206. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Oliva MS, Schottman T and Gulati M:
Turning the tide of corneal blindness. Indian J Ophthalmol.
60:423–427. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Le Q, Xu J and Deng SX: The diagnosis of
limbal stem cell deficiency. Ocul Surf. 16:58–69. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Barut Selver Ö, Yağcı A, Eğrilmez S,
Gürdal M, Palamar M, Çavuşoğlu T, Ateş U, Veral A, Güven Ç and
Wolosin JM: Limbal stem cell deficiency and treatment with stem
cell transplantation. Turk J Ophthalmol. 47:285–291. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ahmad S: Concise review: Limbal stem cell
deficiency, dysfunction, and distress. Stem Cells Transl Med.
1:110–115. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ebrahimi M, Taghi-Abadi E and Baharvand H:
Limbal stem cells in review. J Ophthalmic Vis Res. 4:40–58.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lim P, Fuchsluger TA and Jurkunas UV:
Limbal stem cell deficiency and corneal neovascularization. Semin
Ophthalmol. 24:139–148. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Skeens HM, Brooks BP and Holland EJ:
Congenital aniridia variant: Minimally abnormal irides with severe
limbal stem cell deficiency. Ophthalmology. 118:1260–1264.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sejpal K, Bakhtiari P and Deng SX:
Presentation, diagnosis and management of limbal stem cell
deficiency. Middle East Afr J Ophthalmol. 20:5–10. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
White ML, Chodosh J, Jang J and Dohlman C:
Incidence of Stevens-Johnson syndrome and chemical burns to the
eye. Cornea. 34:1527–1533. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Araújo AL, Ricardo JR, Sakai VN, Barros JN
and Gomes JÁ: Impression cytology and in vivo confocal microscopy
in corneas with total limbal stem cell deficiency. Arq Bras
Oftalmol. 76:305–308. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Medical Advisory Secretariat, . Limbal
stem cell transplantation: An evidence-based analysis. Ont Health
Technol Assess Ser. 8:1–58. 2008.
|
|
13
|
Liang L, Sheha H, Li J and Tseng S: Limbal
stem cell transplantation: New progresses and challenges. Eye
(Lond). 23:1946–1953. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Burman S and Sangwan V: Cultivated limbal
stem cell transplantation for ocular surface reconstruction. Clin
Ophthalmol. 2:489–502. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Dua HS and Azuara-Blanco A: Corneal
allograft rejection: Risk factors, diagnosis, prevention, and
treatment. Indian J Ophthalmol. 47:3–9. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Pirjali T, Azarpira N, Ayatollahi M,
Aghdaie MH, Geramizadeh B and Talai T: Isolation and
characterization of human mesenchymal stem cells derived from human
umbilical cord Wharton's Jelly and amniotic membrane. Int J Organ
Transplant Med. 4:111–116. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Haagdorens M, Van Acker SI, Van Gerwen V,
Ní Dhubhghaill S, Koppen C, Tassignon MJ and Zakaria N: Limbal stem
cell deficiency: Current treatment options and emerging therapies.
Stem Cells Int. 2016:97983742016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Dhamodaran K, Subramani M, Ponnalagu M,
Shetty R and Das D: Ocular stem cells: A status update! Stem Cell
Res Ther. 5:562014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
He H and Yiu SC: Stem cell-based therapy
for treating limbal stem cells deficiency: A review of different
strategies. Saudi J Ophthalmol. 28:188–194. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Pisciotta A, Carnevale G, Meloni S, Riccio
M, De Biasi S, Gibellini L, Ferrari A, Bruzzesi G and De Pol A:
Human dental pulp stem cells (hDPSCs): Isolation, enrichment and
comparative differentiation of two sub-populations. BMC Dev Biol.
15:142015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ferro F, Spelat R and Baheney CS: Dental
pulp stem cell (DPSC) isolation, characterization, and
differentiation. Methods Mol Biol. 1210:91–115. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Huang AH, Chen YK, Lin LM, Shieh TY and
Chan AW: Isolation and characterization of dental pulp stem cells
from a supernumerary tooth. J Oral Pathol Med. 37:571–574. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Shetty PK, Thamake SI, Biswas S, Johansson
SL and Vishwanatha JK: Reciprocal regulation of annexin A2 and EGFR
with Her-2 in Her-2 negative and herceptin-resistant breast cancer.
PLoS One. 7:e442992012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Polisetti N, Agarwal P, Khan I, Kondaiah
P, Sangwan VS and Vemuganti GK: Gene expression profile of
epithelial cells and mesenchymal cells derived from limbal explant
culture. Mol Vis. 16:1227–1240. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Greco D, Vellonen KS, Turner HC, Häkli M,
Tervo T, Auvinen P, Wolosin JM and Urtti A: Gene expression
analysis in SV-40 immortalized human corneal epithelial cells
cultured with an air-liquid interface. Mol Vis. 16:2109–2120.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Nam SM, Maeng YS, Kim EK, Seo KY and Lew
H: Ex vivo expansion of human limbal epithelial cells using human
placenta-derived and umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells.
Stem Cells Int. 2017:42061872017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Shi W, Chen M and Xie L: Amniotic membrane
transplantation combined with antiviral and steroid therapy for
herpes necrotizing stromal keratitis. Ophthalmology. 114:1476–1481.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Atallah MR, Palioura S, Perez VL and
Amescua G: Limbal stem cell transplantation: Current perspectives.
Clin Ophthalmol. 10:593–602. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Karaöz E, Demircan PC, Sağlam O, Aksoy A,
Kaymaz F and Duruksu G: Human dental pulp stem cells demonstrate
better neural and epithelial stem cell properties than bone
marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Histochem Cell Biol.
136:455–473. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kushnerev E, Shawcross SG, Sothirachagan
S, Carley F, Brahma A, Yates JM and Hillarby MC: Regeneration of
corneal epithelium with dental pulp stem cells using a contact lens
delivery system. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 57:5192–5199. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Spath L, Rotilio V, Alessandrini M,
Gambara G, De Angelis L, Mancini M, Mitsiadis TA, Vivarelli E, Naro
F, Filippini A and Papaccio G: Explant-derived human dental pulp
stem cells enhance differentiation and proliferation potentials. J
Cell Mol Med. 14:1635–1644. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kerkis I and Caplan AI: Stem cells in
dental pulp of deciduous teeth. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 18:129–138.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhan X, Dravid G, Ye Z, Hammond H,
Shamblott M, Gearhart J and Cheng L: Functional antigen-presenting
leucocytes derived from human embryonic stem cells in vitro.
Lancet. 364:163–171. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Graziano A, d'Aquino R, Laino G and
Papaccio G: Dental pulp stem cells: A promising tool for bone
regeneration. Stem Cell Rev. 4:21–26. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Syed-Picard FN, Du Y, Lathrop KL, Mann MM,
Funderburgh ML and Funderburgh JL: Dental pulp stem cells: A new
cellular resource for corneal stromal regeneration. Stem Cells
Transl Med. 4:276–285. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|