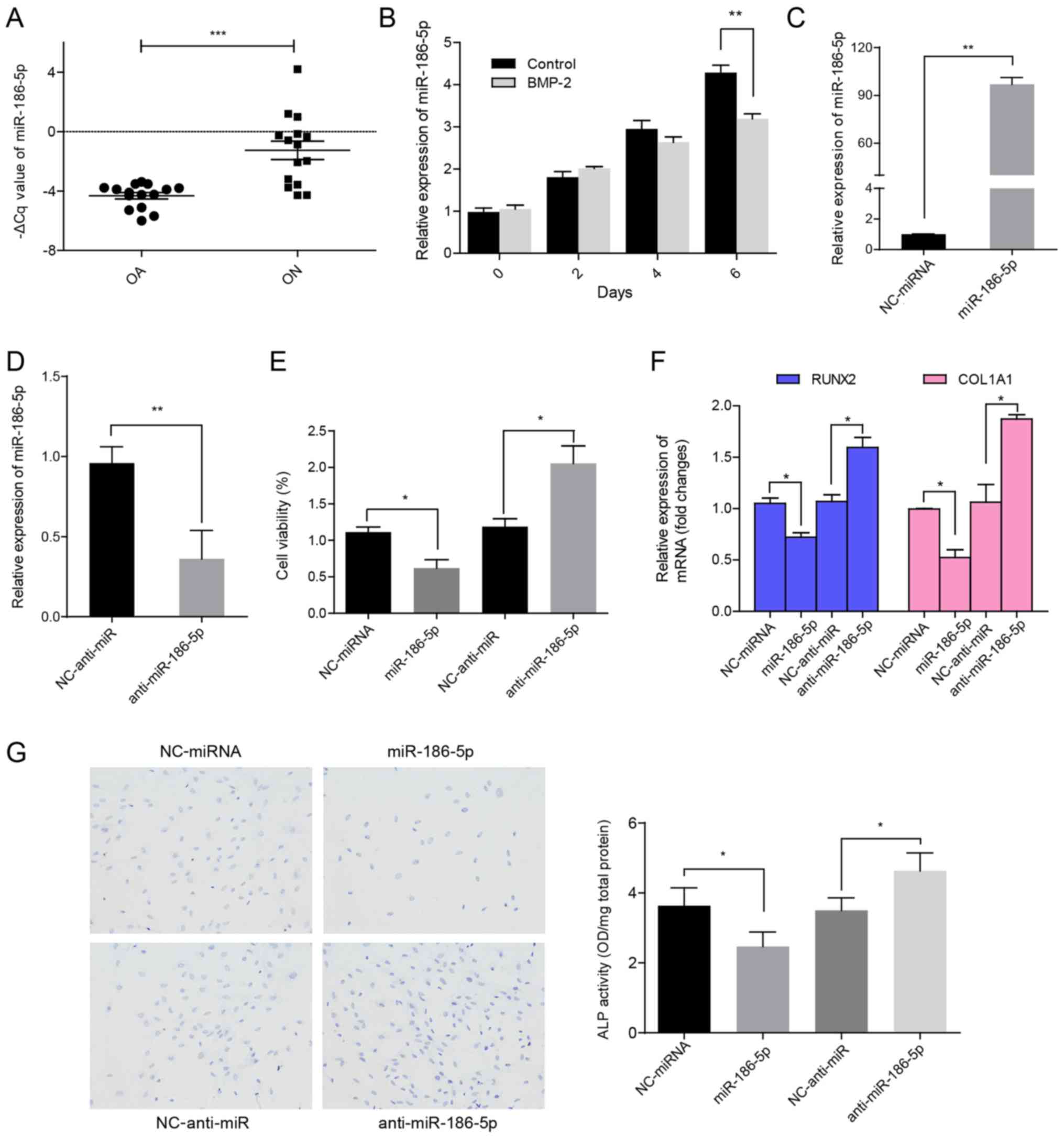
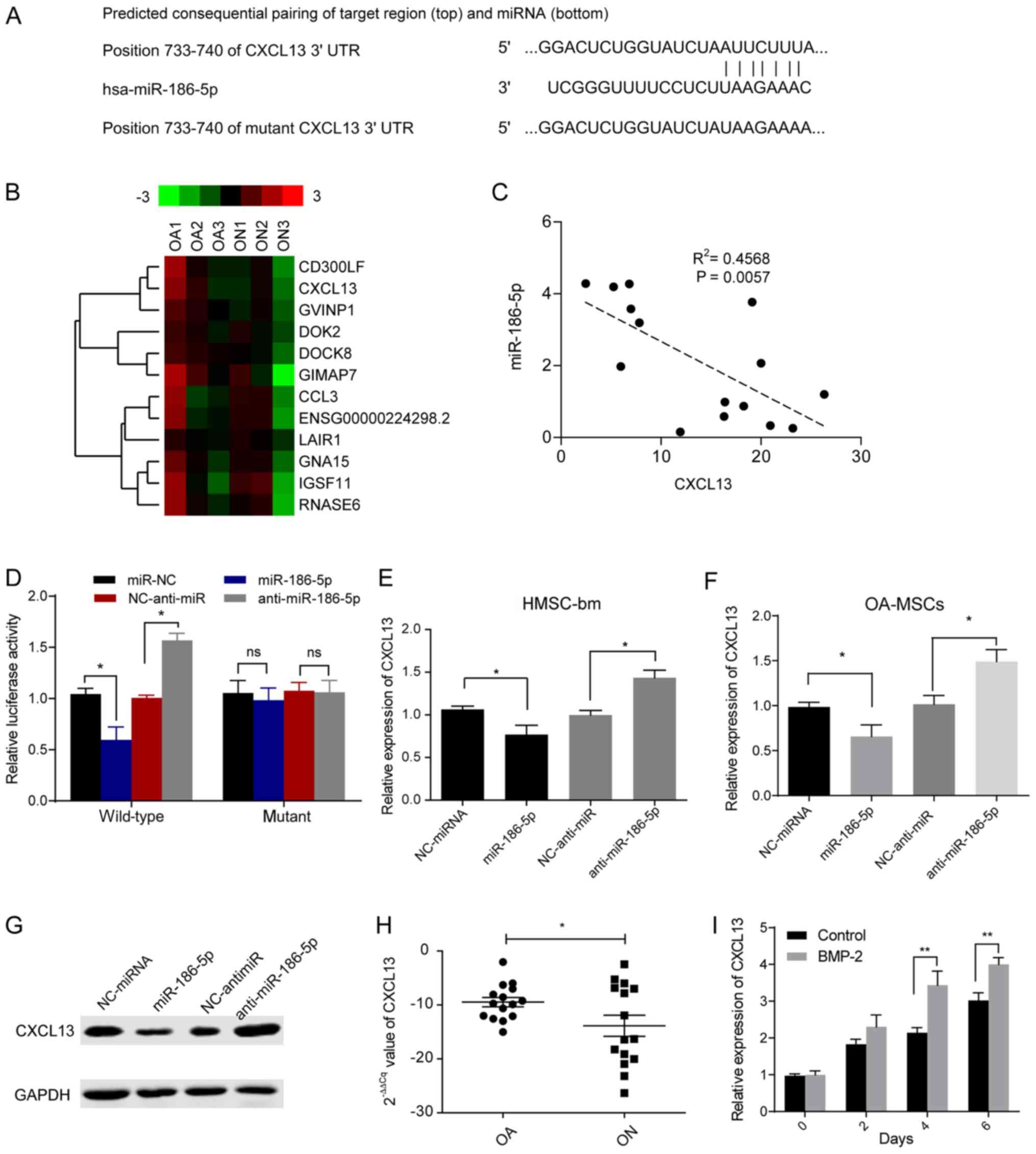
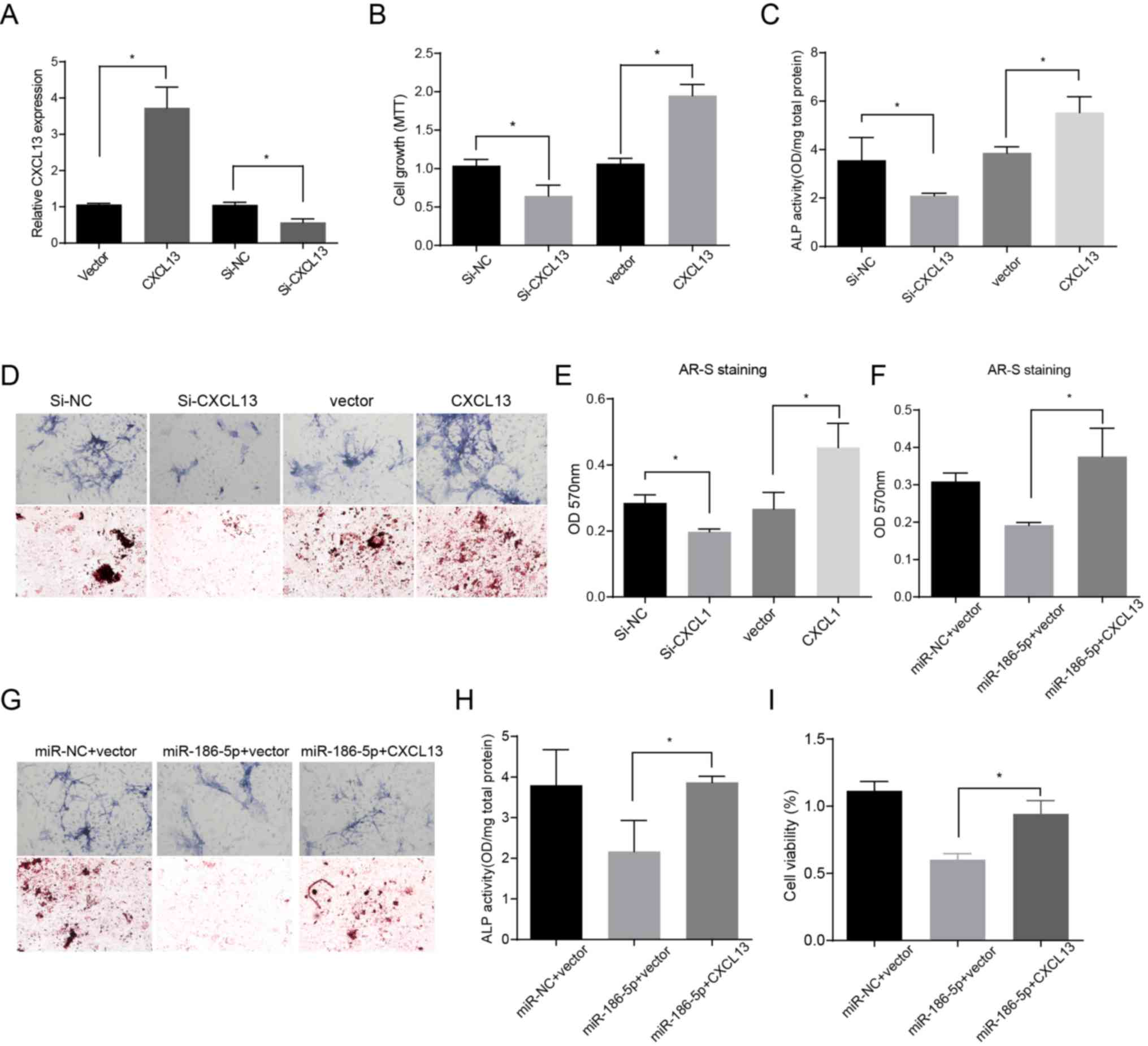
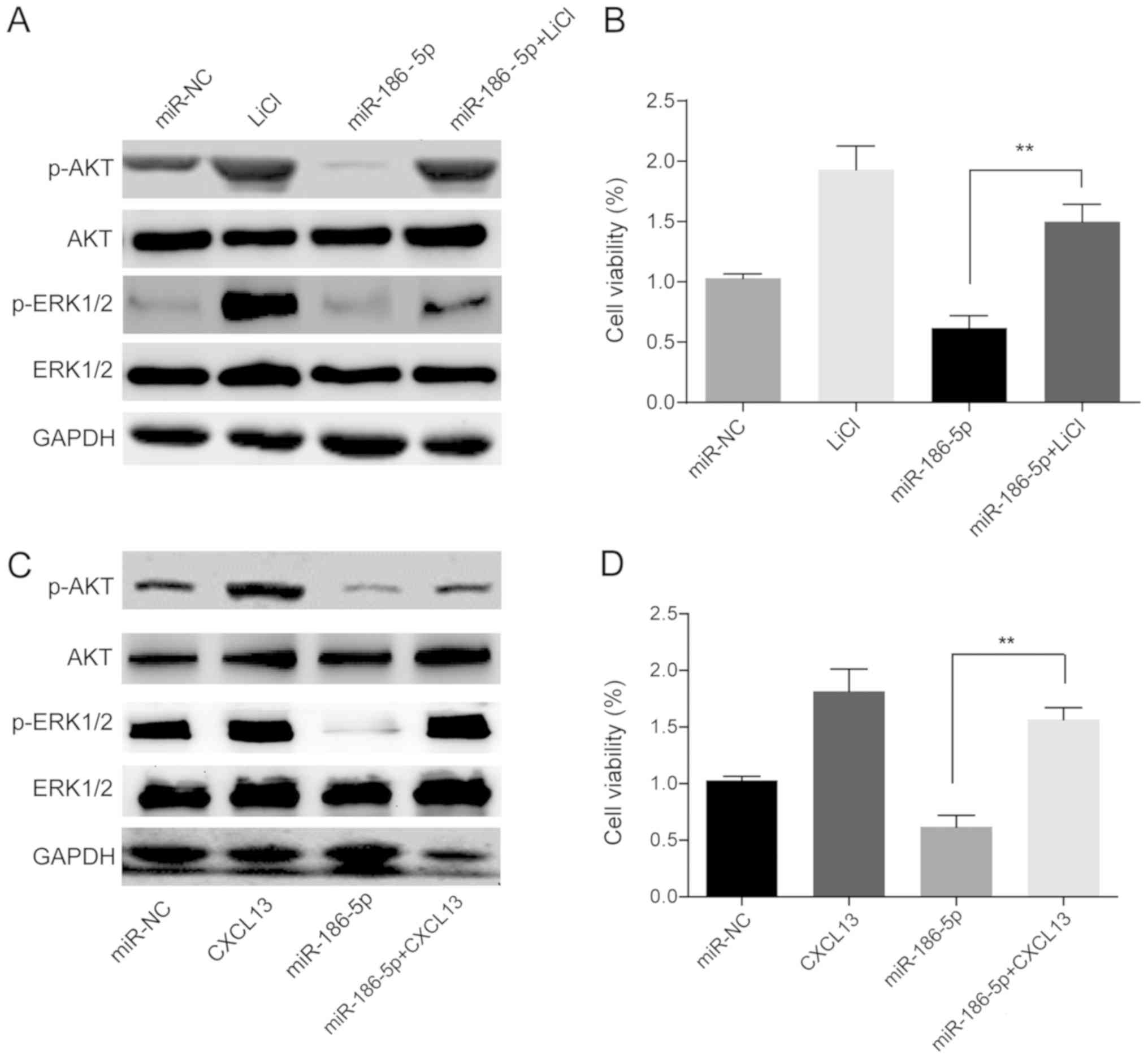
|
1
|
Liu Y, Wu J, Zhu Y and Han J: Therapeutic
application of mesenchymal stem cells in bone and joint diseases.
Clin Exp Med. 14:13–24. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Mont MA, Marulanda GA, Jones LC, Saleh KJ,
Gordon N, Hungerford DS and Steinberg ME: Systematic analysis of
classification systems for osteonecrosis of the femoral head. J
Bone Joint Surg Am. 88 (Suppl 3):S16–S26. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Zhao DW, Yu M, Hu K, Wang W, Yang L, Wang
BJ, Gao XH, Guo YM, Xu YQ, Wei YS, et al: Prevalence of
Nontraumatic osteonecrosis of the femoral head and its associated
risk factors in the Chinese population: Results from a nationally
representative survey. Chin Med J (Engl). 128:2843–2850. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yamamoto T, DiCarlo EF and Bullough PG:
The prevalence and clinicopathological appearance of extension of
osteonecrosis in the femoral head. J Bone Joint Surg Br.
81:328–332. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Tan G, Kang PD and Pei FX: Glucocorticoids
affect the metabolism of bone marrow stromal cells and lead to
osteonecrosis of the femoral head: A review. Chin Med J (Engl).
125:134–139. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Seamon J, Keller T, Saleh J and Cui Q: The
pathogenesis of nontraumatic osteonecrosis. Arthritis.
2012:6017632012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Feng Y, Yang SH, Xiao BJ, Xu WH, Ye SN,
Xia T, Zheng D, Liu XZ and Liao YF: Decreased in the number and
function of circulation endothelial progenitor cells in patients
with avascular necrosis of the femoral head. Bone. 46:32–40. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Li Z, Liao W, Zhao Q, Liu M, Xia W, Yang Y
and Shao N: Angiogenesis and bone regeneration by allogeneic
mesenchymal stem cell intravenous transplantation in rabbit model
of avascular necrotic femoral head. J Surg Res. 183:193–203. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhao D, Cui D, Wang B, Tian F, Guo L, Yang
L, Liu B and Yu X: Treatment of early stage osteonecrosis of the
femoral head with autologous implantation of bone marrow-derived
and cultured mesenchymal stem cells. Bone. 50:325–330. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Gangji V, De Maertelaer V and Hauzeur JP:
Autologous bone marrow cell implantation in the treatment of
non-traumatic osteonecrosis of the femoral head: Five year
follow-up of a prospective controlled study. Bone. 49:1005–1009.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yan Z, Hang D, Guo C and Chen Z: Fate of
mesenchymal stem cells transplanted to osteonecrosis of femoral
head. J Orthop Res. 27:442–446. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Jiang S, Zu Y, Fu Y, Zhang Y and Efferth
T: Activation of the mitochondria-driven pathway of apoptosis in
human PC-3 prostate cancer cells by a novel hydrophilic paclitaxel
derivative, 7-xylosyl-10-deacetylpaclitaxel. Int J Oncol.
33:103–111. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Nishimori S, Tanaka Y, Chiba T, Fujii M,
Imamura T, Miyazono K, Ogasawara T, Kawaguchi H, Igarashi T, Fujita
T, et al: Smad-mediated transcription is required for transforming
growth factor-beta 1-induced p57(Kip2) proteolysis in osteoblastic
cells. J Biol Chem. 276:10700–10705. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Fabian MR, Sonenberg N and Filipowicz W:
Regulation of mRNA translation and stability by microRNAs. Annu Rev
Biochem. 79:351–379. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Guo H, Ingolia NT, Weissman JS and Bartel
DP: Mammalian microRNAs predominantly act to decrease target mRNA
levels. Nature. 466:835–840. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lau NC, Lim LP, Weinstein EG and Bartel
DP: An abundant class of tiny RNAs with probable regulatory roles
in Caenorhabditis elegans. Science. 294:858–862. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lagos-Quintana M, Rauhut R, Lendeckel W
and Tuschl T: Identification of novel genes coding for small
expressed RNAs. Science. 294:853–858. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Gustafson D, Tyryshkin K and Renwick N:
microRNA-guided diagnostics in clinical samples. Best Pract Res
Clin Endocrinol Metab. 30:563–575. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yamasaki K, Nakasa T, Miyaki S, Yamasaki
T, Yasunaga Y and Ochi M: Angiogenic microRNA-210 is present in
cells surrounding osteonecrosis. J Orthop Res. 30:1263–1270. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
van Wijnen AJ, van de Peppel J, van
Leeuwen JP, Lian JB, Stein GS, Westendorf JJ, Oursler MJ, Im HJ,
Taipaleenmäki H, Hesse E, et al: MicroRNA functions in osteogenesis
and dysfunctions in osteoporosis. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 11:72–82.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Cai J, Wu J, Zhang H, Fang L, Huang Y,
Yang Y, Zhu X, Li R and Li M: miR-186 downregulation correlates
with poor survival in lung adenocarcinoma, where it interferes with
cell-cycle regulation. Cancer Res. 73:756–766. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Li H, Yin C, Zhang B, Sun Y, Shi L, Liu N,
Liang S, Lu S, Liu Y, Zhang J, et al: PTTG1 promotes migration and
invasion of human non-small cell lung cancer cells and is modulated
by miR-186. Carcinogenesis. 34:2145–2155. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kim SY, Lee YH and Bae YS: MiR-186,
miR-216b, miR-337-3p, and miR-760 cooperatively induce cellular
senescence by targeting α subunit of protein kinase CKII in human
colorectal cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 429:173–179.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Pike KA, Hutchins AP, Vinette V, Théberge
JF, Sabbagh L, Tremblay ML and Miranda-Saavedra D: Protein tyrosine
phosphatase 1B is a regulator of the interleukin-10-induced
transcriptional program in macrophages. Sci Signal. 7:ra432014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Trapnell C, Williams BA, Pertea G,
Mortazavi A, Kwan G, van Baren MJ, Salzberg SL, Wold BJ and Pachter
L: Transcript assembly and quantification by RNA-Seq reveals
unannotated transcripts and isoform switching during cell
differentiation. Nat Biotechnol. 28:511–515. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Anders S and Huber W: Differential
expression analysis for sequence count data. Genome Biol.
11:R1062010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hutchins AP, Jauch R, Dyla M and
Miranda-Saavedra D: Glbase: A framework for combining, analyzing
and displaying heterogeneous genomic and high-throughput sequencing
data. Cell Regen (Lond). 3:12014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression using real-time quantitative PCR and the
2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hu L, Chen L, Li L, Sun H, Yang G, Chang
Y, Tu Q, Wu M and Wang H: Hepatitis B virus X protein enhances
cisplatin-induced hepatotoxicity via a mechanism involving
degradation of Mcl-1. J Virol. 85:3214–3228. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lu K, Zeng D, Zhang Y, Xia L, Xu L, Kaplan
DL, Jiang X and Zhang F: BMP-2 gene modified canine bMSCs promote
ectopic bone formation mediated by a nonviral PEI derivative. Ann
Biomed Eng. 39:1829–1839. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhu Z, Zhang X, Guo H, Fu L, Pan G and Sun
Y: CXCL13-CXCR5 axis promotes the growth and invasion of colon
cancer cells via PI3K/AKT pathway. Mol Cell Biochem. 400:287–295.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Jia J, Feng X, Xu W, Yang S, Zhang Q, Liu
X, Feng Y and Dai Z: MiR-17-5p modulates osteoblastic
differentiation and cell proliferation by targeting SMAD7 in
non-traumatic osteonecrosis. Exp Mol Med. 46:e1072014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Jing D, Hao J, Shen Y, Tang G, Li ML,
Huang SH and Zhao ZH: The role of microRNAs in bone remodeling. Int
J Oral Sci. 7:131–143. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Rüegg C, Hasmim M, Lejeune FJ and Alghisi
GC: Antiangiogenic peptides and proteins: From experimental tools
to clinical drugs. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1765:155–177.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lisignoli G, Toneguzzi S, Piacentini A,
Cristino S, Grassi F, Cavallo C and Facchini A: CXCL12 (SDF-1) and
CXCL13 (BCA-1) chemokines significantly induce proliferation and
collagen type I expression in osteoblasts from osteoarthritis
patients. J Cell Physiol. 206:78–85. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Cristino S, Piacentini A, Manferdini C,
Codeluppi K, Grassi F, Facchini A and Lisignoli G: Expression of
CXC chemokines and their receptors is modulated during chondrogenic
differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells grown in
three-dimensional scaffold: Evidence in native cartilage. Tissue
Eng Part A. 14:97–105. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Tian F, Ji XL, Xiao WA, Wang B and Wang F:
CXCL13 promotes osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem
cells by inhibiting miR-23a expression. Stem Cells Int.
2015:6323052015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Adapala NS and Kim HW: Comprehensive
genome-wide transcriptomic analysis of immature articular cartilage
following ischemic osteonecrosis of the femoral head in piglets.
PLoS One. 11:e01531742016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Yuan C and Cai J: Time-series expression
profile analysis of fracture healing in young and old mice. Mol Med
Rep. 16:4529–4536. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|