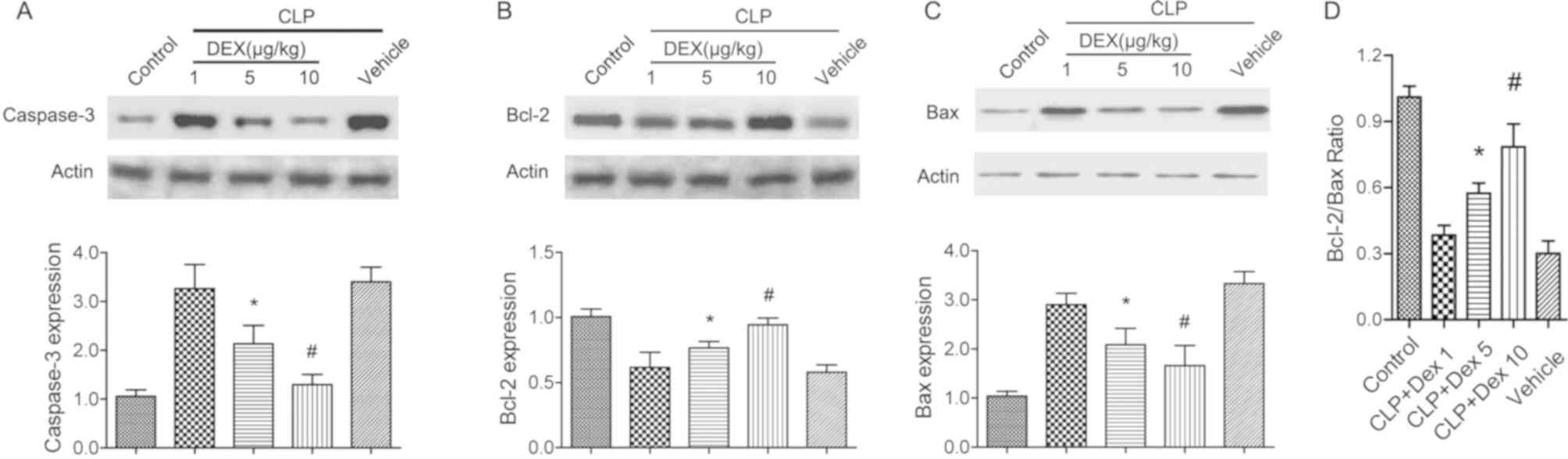
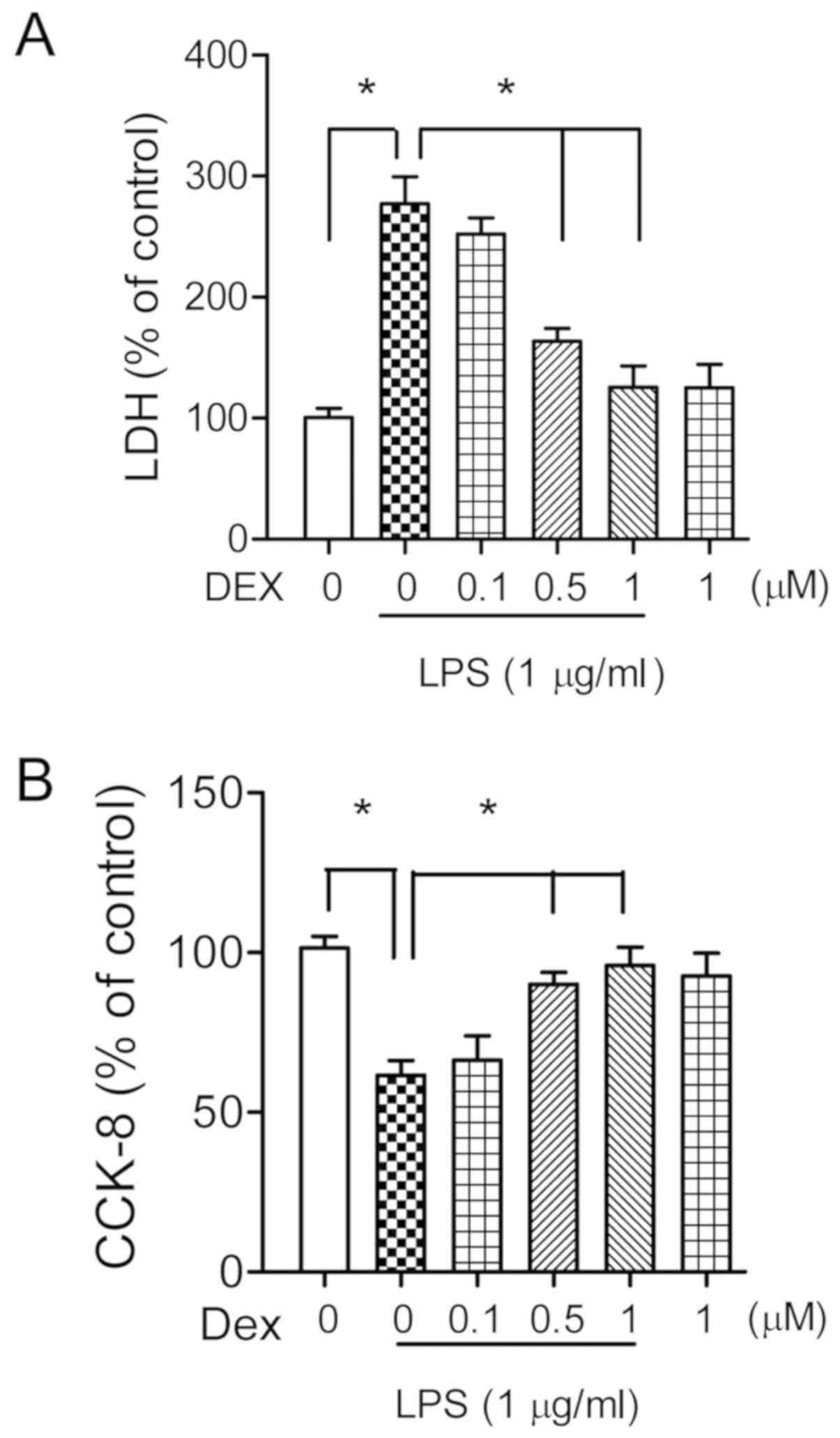
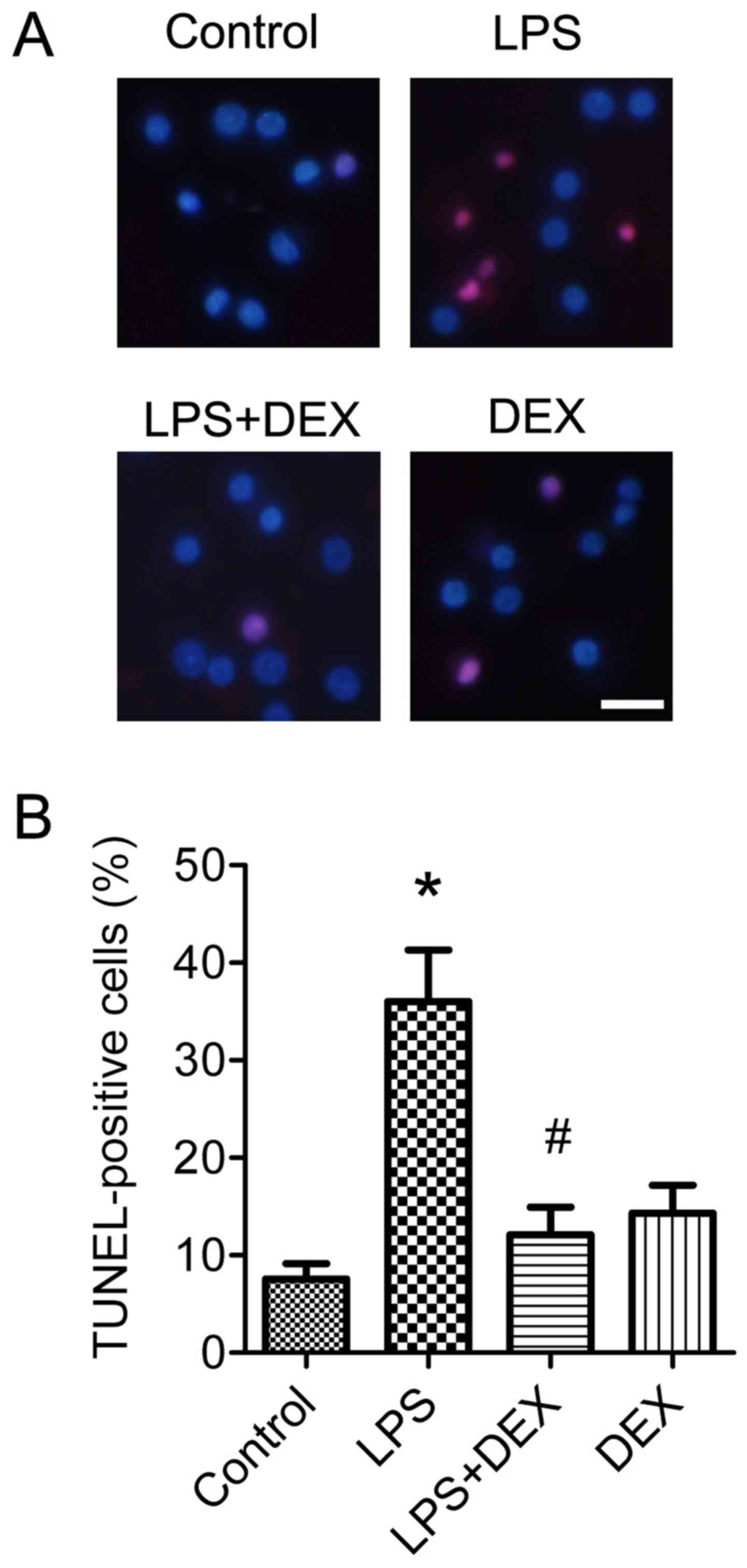
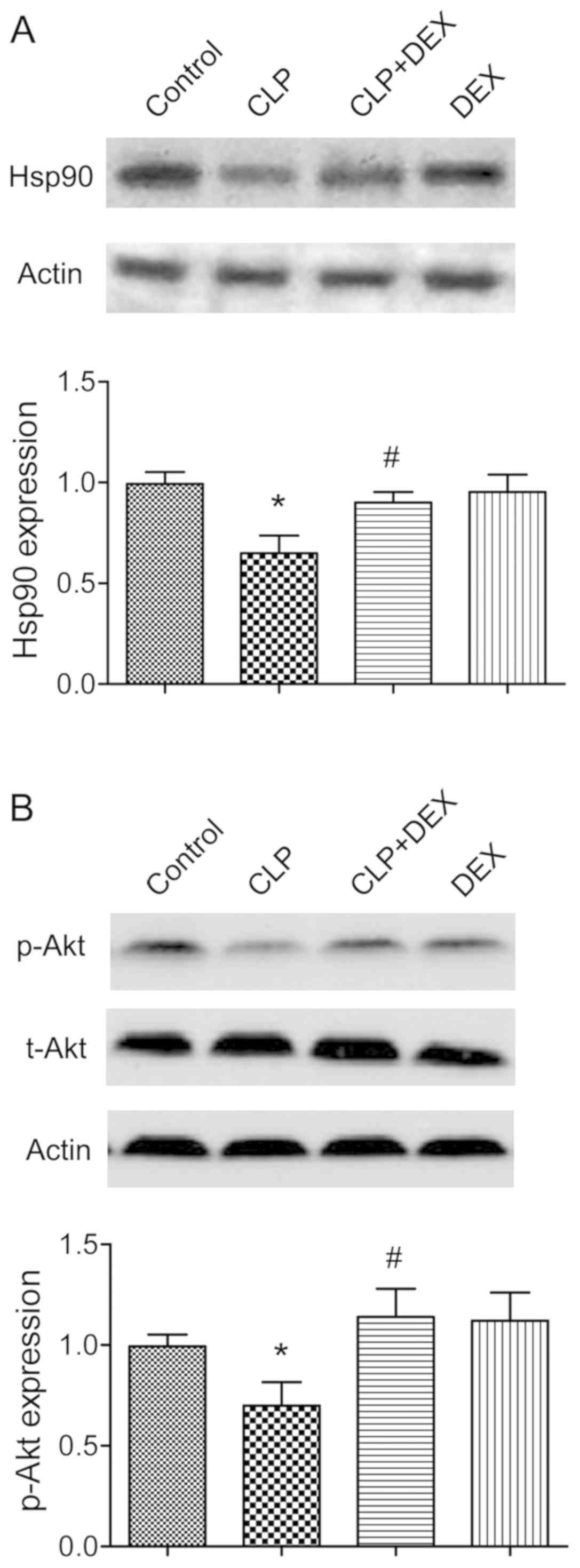
|
1
|
Vincent JL, Sakr Y, Sprung CL, Ranieri VM,
Reinhart K, Gerlach H, Moreno R, Carlet J, Le Gall JR, Payen D, et
al: Sepsis in European intensive care units: Results of the SOAP
study. Crit Care Med. 34:344–353. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Iacobone E, Bailly-Salin J, Polito A,
Friedman D, Stevens RD and Sharshar T: Sepsis-associated
encephalopathy and its differential diagnosis. Crit Care Med. 37
(10 Suppl):S331–S336. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Comim CM, Rezin GT, Scaini G, Di-Pietro
PB, Cardoso MR, Petronilho FC, Ritter C, Streck EL, Quevedo J and
Dal-Pizzol F: Mitochondrial respiratory chain and creatine kinase
activities in rat brain after sepsis induced by cecal ligation and
perforation. Mitochondrion. 8:313–318. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
d'Avila JC, Santiago AP, Amâncio RT,
Galina A, Oliveira MF and Bozza FA: Sepsis induces brain
mitochondrial dysfunction. Crit Care Med. 36:1925–1932. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Weberpals M, Hermes M, Hermann S, Kummer
MP, Terwel D, Semmler A, Berger M, Schäfers M and Heneka MT: NOS2
gene deficiency protects from sepsis-induced long-term cognitive
deficits. J Neurosci. 29:14177–14184. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hall JE, Uhrich TD, Barney JA, Arain SR
and Ebert TJ: Sedative, amnestic, and analgesic properties of
small-dose dexmedetomidine infusions. Anesth Analg. 90:699–705.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Arcangeli A, D'alo C and Gaspari R:
Dexmedetomidine use in general anaesthesia. Current Drug Targets.
10:687–695. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Pandharipande PP, Pun BT, Herr DL, Maze M,
Girard TD, Miller RR, Shintani AK, Thompson JL, Jackson JC, Deppen
SA, et al: Effect of sedation with dexmedetomidine vs lorazepam on
acute brain dysfunction in mechanically ventilated patients: The
MENDS randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 298:2644–2653. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Martin E, Ramsay GJ, Mantz J and Sum-Ping
ST: The role of the alpha2-adrenoceptor agonist dexmedetomidine in
postsurgical sedation in the intensive care unit. J Intensive Care
Med. 18:29–41. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yang CL, Chen CH, Tsai PS, Wang TY and
Huang CJ: Protective effects of dexmedetomidine-ketamine
combination against ventilator-induced lung injury in endotoxemia
rats. J Surg Res. 167:e273–e281. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Okada H, Kurita T, Mochizuki T, Morita K
and Sato S: The cardioprotective effect of dexmedetomidine on
global ischaemia in isolated rat hearts. Resuscitation. 74:538–545.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kocoglu H, Ozturk H, Ozturk H, Yilmaz F
and Gulcu N: Effect of dexmedetomidine on ischemia-reperfusion
injury in rat kidney: A histopathologic study. Ren Fail. 31:70–74.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Engelhard K, Werner C, Eberspacher E,
Bachl M, Blobner M, Hildt E, Hutzler P and Kochs E: The effect of
the alpha2-agonist dexmedetomidine and the N-methyl-D-aspartate
antagonist S(+)-ketamine on the expression of apoptosis-regulating
proteins after incomplete cerebral ischemia and reperfusion in
rats. Anesth Analg. 96:524–531. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hanci V, Erol B, Bektas S, Mungan G,
Yurtlu S, Tokgöz H, Can M and Ozkoçak Turan I: Effect of
dexmedetomidine on testicular torsion/detorsion damage in rats.
Urol Int. 84:105–111. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Downward J: PI 3-kinase, AKT and cell
survival. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 15:177–182. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gass P, Schröder H, Prior P and Kiessling
M: Constitutive expression of heat shock protein 90 (HSP90) in
neurons of the rat brain. Neurosci Lett. 182:188–192. 1194.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Sato S, Fujita N and Tsuruo T: Modulation
of AKT kinase activity by binding to Hsp90. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
97:10832–10837. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Li X, Luo R, Jiang R, Meng X, Wu X, Zhang
S and Hua W: The role of the Hsp90/AKT pathway in myocardial
calpain-induced caspase-3 activation and apoptosis during sepsis.
BMC Cardiovas Dis. 13:82013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Shen E, Fan J and Peng T: Glycogen
synthase kinase-3beta suppresses tumor necrosis factor-alpha
expression in cardiomyocytes during lipopolysaccharide stimulation.
J Cell Biochem. 104:329–338. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Basso AD, Solit DB, Chiosis G, Giri B,
Tsichlis P and Rosen N: AKT forms an intracellular complex with
heat shock protein 90 (Hsp90) and Cdc37 and is destabilized by
inhibitors of Hsp90 function. J Biol Chem. 277:39858–39866. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang R, Luo D, Miao R, Bai L, Ge Q, Sessa
WC and Min W: Hsp90-AKT phosphorylates ASK1 and inhibits
ASK1-mediated apoptosis. Oncogene. 24:3954–3963. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhu YM, Wang CC, Chen L, Qian LB, Ma LL,
Yu J, Zhu MH, Wen CY, Yu LN and Yan M: Both PI3K/AKT and ERK1/2
pathways participate in the protection by dexmedetomidine against
transient focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. Brain
Res. 1494:1–8. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
McGrath JC, Drummond GB, McLachlan EM,
Kilkenny C and Wainwright CL: Guidelines for reporting experiments
involving animals: The ARRIVE guidelines. Br J Pharmacol.
160:1573–1576. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Bayne K: Revised guide for the care and
use of laboratory animals available. American Physiological
Society. Physiologist. 39:199, 208–211. 1996.
|
|
25
|
Kaech S and Banker G: Culturing
hippocampal neurons. Nat Protoc. 1:2406–2415. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Huang X, Venet F, Wang YL, Lepape A, Yuan
Z, Chen Y, Swan R, Kherouf H, Monneret G, Chung CS and Ayala A:
PD-1 expression by macrophages serves a pathologic role in altering
microbial clearance and the innate inflammatory response to sepsis.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:6303–6308. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ritter C, Andrades ME, Reinke A,
Menna-Barreto S, Moreira JC and Dal-Pizzol F: Treatment with
Nacetylcysteine plus deferoxamine protects rats against oxidative
stress and improves survival in sepsis. Crit Care Med. 32:342–249.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Vorhees CV and Williams MT: Morris water
maze: Procedures for assessing spatial and related forms of
learning and memory. Nat Protoc. 1:848–858. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Satomoto M, Satoh Y, Terui K, Miyao H,
Takishima K, Ito M and Imaki J: Neonatal exposure to sevoflurane
induces abnormal social behaviors and deficits in fear conditioning
in mice. Anesthesiology. 110:628–637. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Brealey D, Karyampudi S, Jacques TS,
Novelli M, Stidwill R, Taylor V, Smolenski RT and Singer M:
Mitochondrial dysfunction in a long-term rodent model of sepsis and
organ failure. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol.
286:R491–R497. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kamibayashi T and Maze M: Clinical uses of
alpha2-adrenergic agonists. Anesthesiology. 93:1345–1349. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Siami S, Annane D and Sharshar T: The
encephalopathy in sepsis. Crit Care Clin. 24:67–82. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Pytel P and Alexander JJ: Pathogenesis of
septic encephalopathy. Cur Opin Neurol. 22:283–287. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Semmler A, Hermann S, Mormann F, Weberpals
M, Paxian SA, Okulla T, Schäfers M, Kummer MP, Klockgether T and
Heneka MT: Sepsis causes neuroinflammation and concomitant decrease
of cerebral metabolism. J Neuroinflam. 5:382008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Taccone FS, Su F, Pierrakos C, He X, James
S, Dewitte O, Vincent JL and De Backer D: Cerebral microcirculation
is impaired during sepsis: An experimental study. Crit Care.
14:R1402010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Schoeler M, Loetscher PD, Rossaint R,
Fahlenkamp AV, Eberhardt G, Rex S, Weis J and Coburn M:
Dexmedetomidine is neuroprotective in an in vitro model for
traumatic brain injury. BMC Neurol. 12:202012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Degos V, Charpentier TL, Chhor V, Brissaud
O, Lebon S, Schwendimann L, Bednareck N, Passemard S, Mantz J and
Gressens P: Neuroprotective effects of dexmedetomidine against
glutamate agonist-induced neuronal cell death are related to
increased astrocyte brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression.
Anesthesiology. 118:1123–1132. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
McAdams RM, McPherson RJ, Kapur R,
Phillips B, Shen DD and Juul SE: Dexmedetomidine reduces cranial
temperature in hypothermic neonatal rats. Pediatr Res. 77:772–778.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Park JH, Derry K and Owens R: 896:
Dexmedetomidine as adjunctive sedation in mechanically ventilated
patients. Crit Care Med. 47:4272019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Martini M, De Santis MC, Braccini L,
Gulluni F and Hirsch E: PI3K/AKT signaling pathway and cancer: An
updated review. Ann Med. 46:372–383. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Dudek H, Datta SR, Franke TF, Birnbaum MJ,
Yao R, Cooper GM, Segal RA, Kaplan DR and Greenberg ME: Regulation
of neuronal survival by the serine-threonine protein kinase AKT.
Science. 275:661–665. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Li Y, Zeng M, Chen W, Liu C, Wang F, Han
X, Zuo Z and Peng S: Dexmedetomidine reduces isofluraneinduced
neuroapoptosis partly by preserving PI3K/AKT pathway in the
hippocampus of neonatal rats. PLoS One. 9:e936392014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Farghaly HS, Mahmoud AM and Abdel-Sater
KA: Effect of dexmedetomidine and cold stress in a rat model of
neuropathic pain: Role of interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis
factor-α. Eur J Pharmacol. 776:139–145. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Li J, Chen Q, He X, Alam A, Ning J, Yi B,
Lu K and Gu J: Dexmedetomidine attenuates lung apoptosis induced by
renal ischemia-reperfusion injury through α2AR/PI3K/AKT
pathway. J Transl Med. 16:782018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Ibacache M, Sanchez G, Pedrozo Z, Galvez
F, Humeres C, Echevarria G, Duaso J, Hassi M, Garcia L, Díaz-Araya
G and Lavandero S: Dexmedetomidine preconditioning activates
pro-survival kinases and attenuates regional ischemia/reperfusion
injury in rat heart. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1822:537–545. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Karkoulias G, Mastrogianni O,
Lymperopoulos A, Paris H and Flordellis C: alpha(2)-Adrenergic
receptors activate MAPK and AKT through a pathway involving
arachidonic acid metabolism by cytochrome P450-dependent
epoxygenase, matrix metalloproteinase activation and
subtype-specific transactivation of EGFR. Cell Signal. 18:729–739.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Cai W, Rudolph JL, Harrison SM, Jin L,
Frantz AL, Harrison DA and Andres DA: An evolutionarily conserved
Rit GTPase-p38 MAPK signaling pathway mediates oxidative stress
resistance. Mol Biol Cell. 22:3231–3241. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Koh PO: Nicotinamide attenuates the
ischemic brain injury-induced decrease of AKT activation and Bad
phosphorylation. Neurosci Lett. 498:105–109. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Mendoza MC, Er EE and Blenis J: The
Ras-ERK and PI3K-mTOR pathways: Cross-talk and compensation. Trends
Biochem Sci. 36:320–328. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Parcellier A, Tintignac LA, Zhuravleva E
and Hemmings BA: PKB and the mitochondria: AKTing on apoptosis.
Cell Signal. 20:21–30. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Franke TF: PI3K/Akt: Getting it right
matters. Oncogene. 27:6473–6488. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Horwood JM, Dufour F, Laroche S and Davis
S: Signalling mechanisms mediated by the phosphoinositide
3-kinase/AKT cascade in synaptic plasticity and memory in the rat.
Eur J Neurosci. 23:3375–3384. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Björklund M, Siverina I, Heikkinen T,
Tanila H, Sallinen J, Scheinin M and Riekkinen P Jr: Spatial
working memory improvement by an alpha2-adrenoceptor agonist
dexmedetomidine is not mediated through alpha2C-adrenoceptor. Prog
Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 25:1539–1554. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Ji MH, Jia M, Zhang MQ, Liu WX, Xie ZC,
Wang ZY and Yang JJ: Dexmedetomidine alleviates anxiety-like
behaviors and cognitive impairments in a rat model of
post-traumatic stress disorder. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol
Psychiatry. 54:284–288. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|