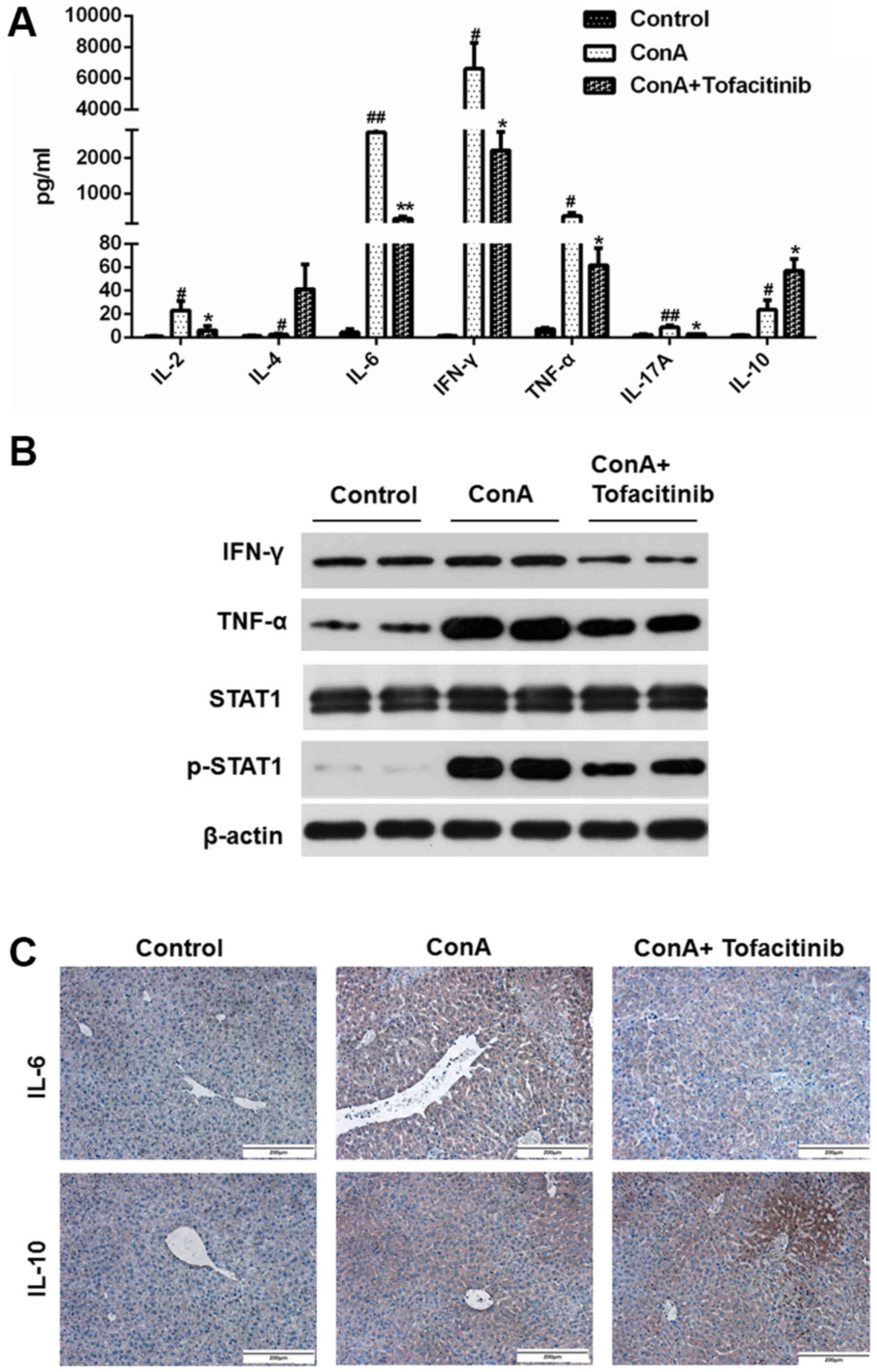
|
1
|
Eksteen B, Afford SC, Wigmore SJ, Holt AP
and Adams DH: Immune-mediated liver injury. Semin Liver Dis.
27:351–366. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Webb GJ, Hirschfield GM, Krawitt EL and
Gershwin ME: Cellular and molecular mechanisms of autoimmune
hepatitis. Annu Rev Pathol. 13:247–292. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Manns MP, Czaja AJ, Gorham JD, Krawitt EL,
Mieli-Vergani G, Vergani D and Vierling JM; American Association
for the Study of Liver Diseases, : Diagnosis and management of
autoimmune hepatitis. Hepatology. 51:2193–2213. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Liberal R, Grant CR, Yuksel M, Graham J,
Kalbasi A, Ma Y, Heneghan MA, Mieli-Vergani G, Vergani D and Longhi
MS: Regulatory T-cell conditioning endows activated effector T
cells with suppressor function in autoimmune hepatitis/autoimmune
sclerosing cholangitis. Hepatology. 66:1570–1584. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Romano M, Fanelli G, Tan N, Nova-Lamperti
E, McGregor R, Lechler RI, Lombardi G and Scottà C: Expanded
regulatory T cells induce alternatively activated monocytes with a
reduced capacity to expand T helper-17 cells. Front Immunol.
9:16252018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Beringer A and Miossec P: IL-17 and
IL-17-producing cells and liver diseases, with focus on autoimmune
liver diseases. Autoimmun Rev. 17:1176–1185. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Longhi MS, Liberal R, Holder B, Robson SC,
Ma Y, Mieli-Vergani G and Vergani D: Inhibition of interleukin-17
promotes differentiation of CD25− cells into stable T
regulatory cells in patients with autoimmune hepatitis.
Gastroenterology. 142:1526–1535.e6. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sun XF, Gu L, Deng WS and Xu Q: Impaired
balance of T helper 17/T regulatory cells in carbon
tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis in mice. World J
Gastroenterol. 20:2062–2070. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Noack M and Miossec P: Th17 and regulatory
T cell balance in autoimmune and inflammatory diseases. Autoimmun
Rev. 13:668–677. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Tiegs G, Hentschel J and Wendel A: A T
cell-dependent experimental liver injury in mice inducible by
concanavalin A. J Clin Invest. 90:196–203. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ji YR, Kim HJ, Bae KB, Lee S, Kim MO and
Ryoo ZY: Hepatic serum amyloid A1 aggravates T cell-mediated
hepatitis by inducing chemokines via Toll-like receptor 2 in mice.
J Biol Chem. 290:12804–12811. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Erhardt A, Biburger M, Papadopoulos T and
Tiegs G: IL-10, regulatory T cells, and Kupffer cells mediate
tolerance in concanavalin A-induced liver injury in mice.
Hepatology. 45:475–485. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Shinohara Y and Tsukimoto M: Adenine
nucleotides attenuate murine T cell activation induced by
concanavalin A or T cell receptor stimulation. Front Pharmacol.
8:9862018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang HX, Liu M, Weng SY, Li JJ, Xie C, He
HL, Guan W, Yuan YS and Gao J: Immune mechanisms of Concanavalin A
model of autoimmune hepatitis. World J Gastroenterol. 18:119–125.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Küsters S, Gantner F, Künstle G and Tiegs
G: Interferon gamma plays a critical role in T cell-dependent liver
injury in mice initiated by concanavalin A. Gastroenterology.
111:462–471. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Saitis A, Gatselis N, Zachou K and Dalekos
GN: Use of TNFα antagonists in refractory AIH: Revealing the
unforeseen. J Hepatol. 59:197–198. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ehser J, Holdener M, Christen S, Bayer M,
Pfeilschifter JM, Hintermann E, Bogdanos D and Christen U:
Molecular mimicry rather than identity breaks T-cell tolerance in
the CYP2D6 mouse model for human autoimmune hepatitis. J Autoimmun.
42:39–49. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hintermann E, Ehser J, Bayer M,
Pfeilschifter JM and Christen U: Mechanism of autoimmune hepatic
fibrogenesis induced by an adenovirus encoding the human liver
autoantigen cytochrome P450 2D6. J Autoimmun. 44:49–60. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hardtke-Wolenski M, Dywicki J, Fischer K,
Hapke M, Sievers M, Schlue J, Anderson MS, Taubert R, Noyan F,
Manns MP and Jaeckel E: The influence of genetic predisposition and
autoimmune hepatitis inducing antigens in disease development. J
Autoimmun. 78:39–45. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Holdener M, Hintermann E, Bayer M, Rhode
A, Rodrigo E, Hintereder G, Johnson EF, Gonzalez FJ, Pfeilschifter
J, Manns MP, et al: Breaking tolerance to the natural human liver
autoantigen cytochrome P450 2D6 by virus infection. J Exp Med.
205:1409–1422. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Christen U, Holdener M and Hintermann E:
Cytochrome P450 2D6 as a model antigen. Dig Dis. 28:80–85. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ghoreschi K, Laurence A and O'Shea JJ:
Janus kinases in immune cell signaling. Immunol Rev. 228:273–287.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Shuai K and Liu B: Regulation of JAK-STAT
signalling in the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol. 3:900–911. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Perner F, Schnoder TM, Ranjan S,
Wolleschak D, Ebert C, Pils MC, Frey S, Polanetzki A, Fahldieck C,
Schönborn U, et al: Specificity of JAK-kinase inhibition determines
impact on human and murine T-cell function. Leukemia. 30:991–995.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Vainchenker W and Constantinescu SN:
JAK/STAT signaling in hematological malignancies. Oncogene.
32:2601–2613. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Dhillon S: Tofacitinib: A review in
rheumatoid arthritis. Drugs. 77:1987–2001. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Boyle DL, Soma K, Hodge J, Kavanaugh A,
Mandel D, Mease P, Shurmur R, Singhal AK, Wei N, Rosengren S, et
al: The JAK inhibitor tofacitinib suppresses synovial JAK1-STAT
signalling in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 74:1311–1316.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Mease P, Hall S, FitzGerald O, van der
Heijde D, Merola JF, Avila-Zapata F, Cieślak D, Graham D, Wang C,
Menon S, et al: Tofacitinib or Adalimumab versus placebo for
psoriatic arthritis. N Engl J Med. 377:1537–1550. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Pouillon L, Bossuyt P and Peyrin-Biroulet
L: Tofacitinib is the right OCTAVE for ulcerative colitis.
Gastroenterology. 153:862–864. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Bayart CB, DeNiro KL, Brichta L, Craiglow
BG and Sidbury R: Topical Janus kinase inhibitors for the treatment
of pediatric alopecia areata. J Am Acad Dermatol. 77:167–170. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ghoreschi K, Jesson MI, Li X, Lee JL,
Ghosh S, Alsup JW, Warner JD, Tanaka M, Steward-Tharp SM, Gadina M,
et al: Modulation of innate and adaptive immune responses by
tofacitinib (CP-690,550). J Immunol. 186:4234–4243. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Nakamura S, Maehara T, Watanabe S,
Ishihara M and Sato M: Improvement of hydrodynamics-based gene
transfer of nonviral DNA targeted to murine hepatocytes. Biomed Res
Int. 2013:9287902013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Vidal B, Cascao R, Finnila MA, Lopes IP,
da Glória VG, Saarakkala S, Zioupos P, Canhão H and Fonseca JE:
Effects of tofacitinib in early arthritis-induced bone loss in an
adjuvant-induced arthritis rat model. Rheumatology (Oxford).
57:1461–1471. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Feng XX, Chi G, Wang H, Gao Y, Chen Q, Ru
YX, Luo ZL, Yan W, Li PY, Liu M, et al: IL-37 suppresses the
sustained hepatic IFN-γ/TNF-α production and T cell-dependent liver
injury. Int Immunopharmacol. 69:184–193. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chi G, Feng XX, Ru YX, Xiong T, Gao Y,
Wang H, Luo ZL, Mo R, Guo F, He YP, et al: TLR2/4 ligand-amplified
liver inflammation promotes initiation of autoimmune hepatitis due
to sustained IL-6/IL-12/IL-4/IL-25 expression. Mol Immunol.
99:171–181. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Chen X, Tan Q, Wang Y, Lv H, Wang Z, Lin
Z, Du Z, Xiong S, Han J, Tian D and Wang B: Overexpression of KLF14
protects against immune-mediated hepatic injury in mice. Lab
Invest. 99:37–47. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ye T, Wang T, Yang X, Fan X, Wen M, Shen
Y, Xi X, Men R and Yang L: Comparison of concanavalin a-induced
murine autoimmune hepatitis models. Cell Physiol Biochem.
46:1241–1251. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Li J, Wang FP, She WM, Yang CQ, Li L, Tu
CT, Wang JY and Jiang W: Enhanced high-mobility group box 1 (HMGB1)
modulates regulatory T cells (Treg)/T helper 17 (Th17) balance via
toll-like receptor (TLR)-4-interleukin (IL)-6 pathway in patients
with chronic hepatitis B. J viral hepatitis. 21:129–140. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Li J, Qiu SJ, She WM, Wang FP, Gao H, Li
L, Tu CT, Wang JY, Shen XZ and Jiang W: Significance of the balance
between regulatory T (Treg) and T helper 17 (Th17) cells during
hepatitis B virus related liver fibrosis. PLoS One. 7:e393072012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Yang F, Wang Q, Bian Z, Ren LL, Jia J and
Ma X: Autoimmune hepatitis: East meets west. J Gastroenterol
Hepatol. 30:1230–1236. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Liberal R, Krawitt EL, Vierling JM, Manns
MP, Mieli-Vergani G and Vergani D: Cutting edge issues in
autoimmune hepatitis. J Autoimmun. 75:6–19. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Czaja AJ: Emerging opportunities for
site-specific molecular and cellular interventions in autoimmune
hepatitis. Dig Dis Sci. 55:2712–2726. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Lopez-Sanz L, Bernal S, Recio C, Lazaro I,
Oguiza A, Melgar A, Jimenez-Castilla L, Egido J and Gomez-Guerrero
C: SOCS1-targeted therapy ameliorates renal and vascular oxidative
stress in diabetes via STAT1 and PI3K inhibition. Lab Invest.
98:1276–1290. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Fleischmann R, Mysler E, Hall S, Kivitz
AJ, Moots RJ, Luo Z, DeMasi R, Soma K, Zhang R, Takiya L, et al:
Efficacy and safety of tofacitinib monotherapy, tofacitinib with
methotrexate, and adalimumab with methotrexate in patients with
rheumatoid arthritis (ORAL Strategy): A phase 3b/4, double-blind,
head-to-head, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 390:457–468.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Uttley L, Bermejo I, Ren S, Martyn-St
James M, Wong R, Scott DL, Young A and Stevenson M: Tofacitinib for
treating rheumatoid arthritis after the failure of
disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs: An evidence review group
perspective of a NICE single technology appraisal.
Pharmacoeconomics. 36:1063–1072. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
White JR, Phillips F, Monaghan T, Fateen
W, Samuel S, Ghosh S and Moran GW: Review article: Novel
oral-targeted therapies in inflammatory bowel disease. Aliment
Pharmacol Ther. 47:1610–1622. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Patel NU, Oussedik E, Grammenos A and
Pichardo-Geisinger R: A case report highlighting the effective
treatment of alopecia universalis with tofacitinib in an adolescent
and adult patient. J Cutan Med Surg. 22:439–442. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Silberstein SD, Yeung PP and Aycardi E:
Preventive therapies for chronic migraine. N Engl J Med.
378:7742018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Longhi MS, Hussain MJ, Mitry RR, Arora SK,
Mieli-Vergani G, Vergani D and Ma Y: Functional study of CD4+CD25+
regulatory T cells in health and autoimmune hepatitis. J Immunol.
176:4484–4491. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Nakaya M, Hashimoto M, Nakagawa R,
Wakabayashi Y, Ishizaki T, Takada I, Komai K, Yoshida H and
Yoshimura A: SOCS3 in T and NKT cells negatively regulates cytokine
production and ameliorates ConA-induced hepatitis. J Immunol.
183:7047–7053. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Kato J, Okamoto T, Motoyama H, Uchiyama R,
Kirchhofer D, Van Rooijen N, Enomoto H, Nishiguchi S, Kawada N,
Fujimoto J and Tsutsui H: Interferon-gamma-mediated tissue factor
expression contributes to T-cell-mediated hepatitis through
induction of hypercoagulation in mice. Hepatology. 57:362–372.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Iwamoto S, Kido M, Aoki N, Nishiura H,
Maruoka R, Ikeda A, Okazaki T, Chiba T and Watanabe N: TNF-α is
essential in the induction of fatal autoimmune hepatitis in mice
through upregulation of hepatic CCL20 expression. Clin Immunol.
146:15–25. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|