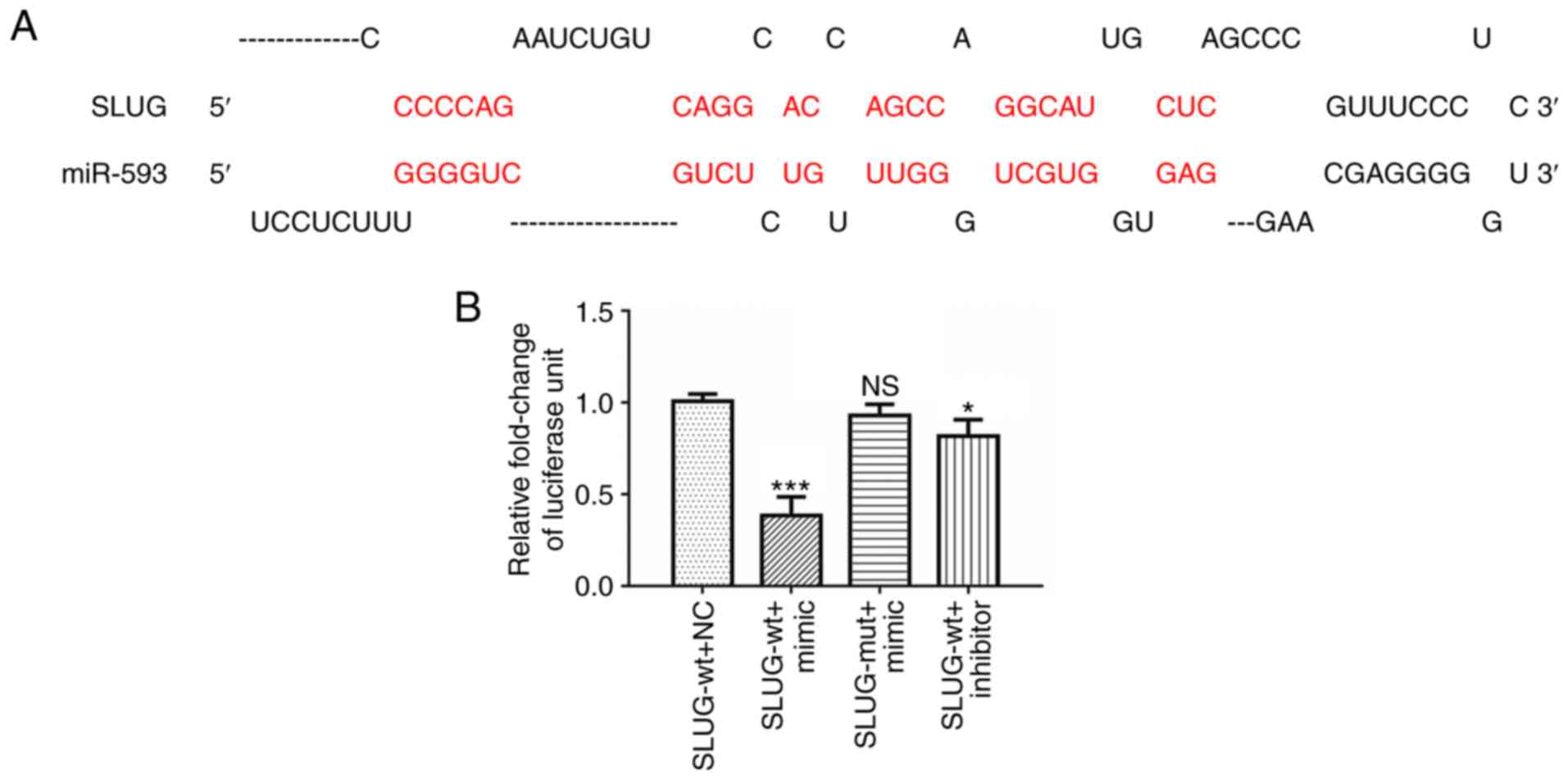
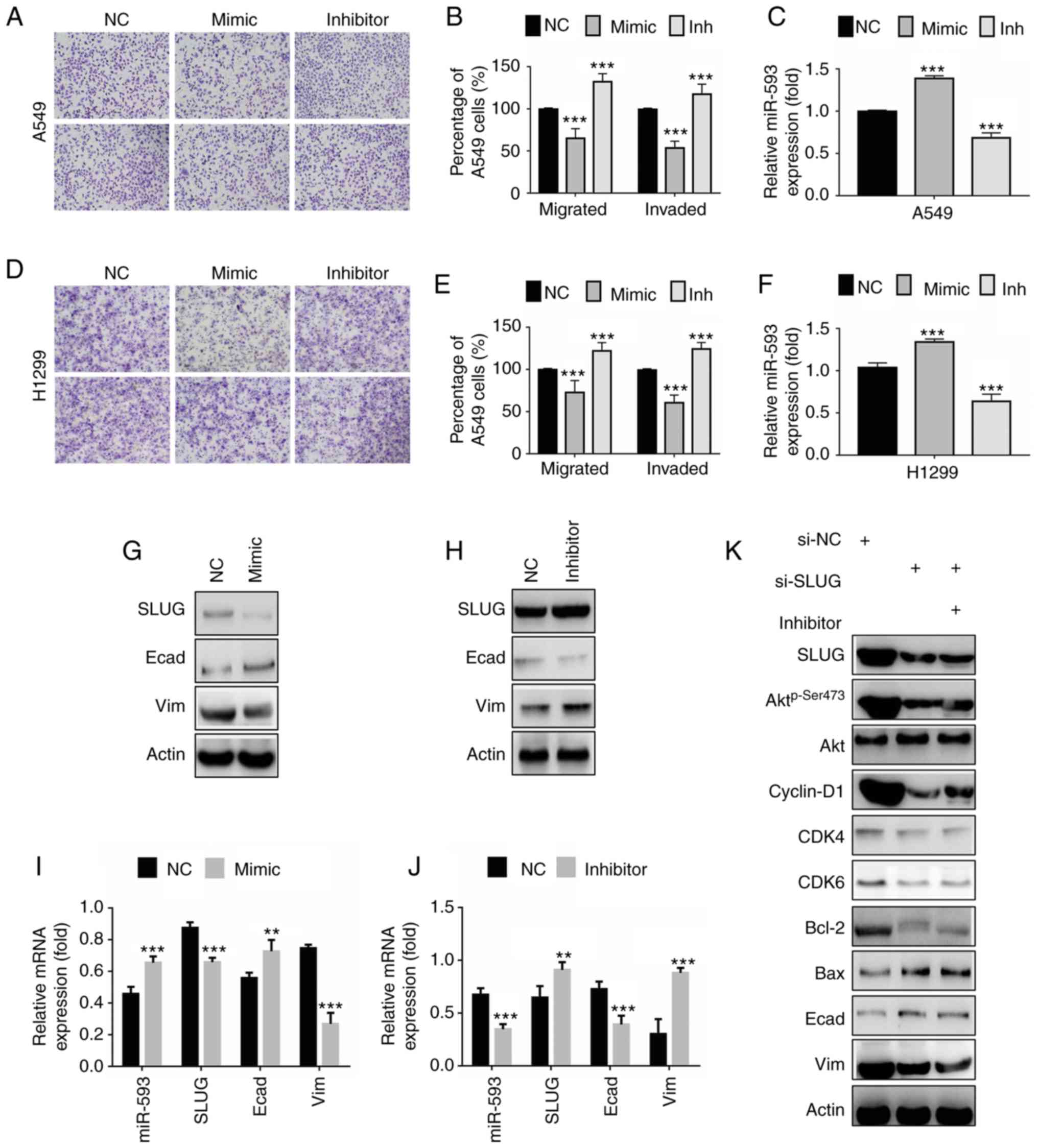
|
1
|
Hellmann MD, Li BT, Chaft JE and Kris MG:
Chemotherapy remains an essential element of personalized care for
persons with lung cancers. Ann Oncol. 27:1829–1835. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Shih JY and Yang PC: The EMT regulator
slug and lung carcinogenesis. Carcinogenesis. 32:1299–1304. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Atmaca A, Wirtz RW, Werner D, Steinmetz K,
Claas S, Brueckl WM, Jäger E and Al-Batran SE: SNAI2/SLUG and
estrogen receptor mRNA expression are inversely correlated and
prognostic of patient outcome in metastatic non-small cell lung
cancer. BMC Cancer. 15:3002015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Merikallio H, T TT, Pääkkö P, Mäkitaro R,
Kaarteenaho R, Lehtonen S, Salo S, Salo T, Harju T and Soini Y:
Slug is associated with poor survival in squamous cell carcinoma of
the lung. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 7:5846–5854. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Tamura D, Arao T, Nagai T, Kaneda H,
Aomatsu K, Fujita Y, Matsumoto K, De Velasco MA, Kato H, Hayashi H,
et al: Slug increases sensitivity to tubulin-binding agents via the
downregulation of βIII and βIVa-tubulin in lung cancer cells.
Cancer Med. 2:144–154. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kuo TC, Tan CT, Chang YW, Hong CC, Lee WJ,
Chen MW, Jeng YM, Chiou J, Yu P, Chen PS, et al: Angiopoietin-like
protein 1 suppresses SLUG to inhibit cancer cell motility. J Clin
Invest. 123:1082–1095. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang SP, Wang WL, Chang YL, Wu CT, Chao
YC, Kao SH, Yuan A, Lin CW, Yang SC, Chan WK, et al: p53 controls
cancer cell invasion by inducing the MDM2-mediated degradation of
Slug. Nat Cell Biol. 11:694–704. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wang YP, Wang MZ, Luo YR, Shen Y and Wei
ZX: Lentivirus-mediated shRNA interference targeting SLUG inhibits
lung cancer growth and metastasis. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev.
13:4947–4951. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tominaga E, Yuasa K, Shimazaki S and
Hijikata T: MicroRNA-1 targets Slug and endows lung cancer A549
cells with epithelial and anti-tumorigenic properties. Exp Cell
Res. 319:77–88. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li W, Jiang G, Zhou J, Wang H, Gong Z,
Zhang Z, Min K, Zhu H and Tan Y: Down-regulation of miR-140 induces
EMT and promotes invasion by targeting Slug in esophageal cancer.
Cell Physiol Biochem. 34:1466–1476. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Liao H, Bai Y, Qiu S, Zheng L, Huang L,
Liu T, Wang X, Liu Y, Xu N, Yan X and Guo H: MiR-203 downregulation
is responsible for chemoresistance in human glioblastoma by
promoting epithelial-mesenchymal transition via SNAI2. Oncotarget.
6:8914–8928. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Fan S, Liu B, Sun L, Lv XB, Lin Z, Chen W,
Chen W, Tang Q, Wang Y, Su Y, et al: Mitochondrial fission
determines cisplatin sensitivity in tongue squamous cell carcinoma
through the BRCA1-miR-593-5p-MFF axis. Oncotarget. 6:14885–14904.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ito T, Sato F, Kan T, Cheng Y, David S,
Agarwal R, Paun BC, Jin Z, Olaru AV, Hamilton JP, et al: Polo-like
kinase 1 regulates cell proliferation and is targeted by miR-593*
in esophageal cancer. Int J Cancer. 129:2134–2146. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
General Assembly of the World medical
association, . World medical association declaration of helsinki:
Ethical principles for medical research involving human subjects. J
Am Coll Dent. 81:14–18. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Liu W and Wang X: Prediction of functional
microRNA targets by integrative modeling of microRNA binding and
target expression data. Genome Biol. 20:182019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wong N and Wang X: miRDB: An online
resource for microRNA target prediction and functional annotations.
Nucleic Acids Res. 43((Database Issue)): D146–D152. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang X: Improving microRNA target
prediction by modeling with unambiguously identified
microRNA-target pairs from CLIP-ligation studies. Bioinformatics.
32:1316–1322. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Tang S, Hou Y, Zhang H, Tu G, Yang L, Sun
Y, Lang L, Tang X, Du YE, Zhou M, et al: Oxidized ATM promotes
abnormal proliferation of breast CAFs through maintaining
intracellular redox homeostasis and activating the PI3K-AKT,
MEK-ERK, and Wnt-β-catenin signaling pathways. Cell Cycle.
14:1908–1924. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ananda Sadagopan SK, Mohebali N, Looi CY,
Hasanpourghadi M, Pandurangan AK, Arya A, Karimian H and Mustafa
MR: Forkhead box transcription factor (FOXO3a) mediates the
cytotoxic effect of vernodalin in vitro and inhibits the breast
tumor growth in vivo. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 34:1472015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chandra V, Fatima I, Manohar M, Popli P,
Sirohi VK, Hussain MK, Hajela K, Sankhwar P and Dwivedi A:
Inhibitory effect of
2-(piperidinoethoxyphenyl)-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-2H-benzo(b)pyran
(K-1) on human primary endometrial hyperplasial cells mediated via
combined suppression of Wnt/β-catenin signaling and PI3K/Akt
survival pathway. Cell Death Dis. 5:e13802014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Singh A and Settleman J: EMT, cancer stem
cells and drug resistance: An emerging axis of evil in the war on
cancer. Oncogene. 29:4741–4751. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Mallini P, Lennard T, Kirby J and Meeson
A: Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition: What is the impact on
breast cancer stem cells and drug resistance. Cancer Treat Rev.
40:341–348. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kahlert UD, Nikkhah G and Maciaczyk J:
Epithelial-to-mesenchymal(-like) transition as a relevant molecular
event in malignant gliomas. Cancer Lett. 331:131–138. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lee KH, Ahn EJ, Oh SJ, Kim O, Joo YE, Bae
JA, Yoon S, Ryu HH, Jung S, Kim KK, et al: KITENIN promotes glioma
invasiveness and progression, associated with the induction of EMT
and stemness markers. Oncotarget. 6:3240–3253. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yu M, Zhang C, Li L, Dong S, Zhang N and
Tong X: Cx43 reverses the resistance of A549 lung adenocarcinoma
cells to cisplatin by inhibiting EMT. Oncol Rep. 31:2751–2758.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Mizuno K, Mataki H, Seki N, Kumamoto T,
Kamikawaji K and Inoue H: MicroRNAs in non-small cell lung cancer
and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. J Hum Genet. 62:57–65. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Fan H, Shao M, Huang S, Liu Y, Liu J, Wang
Z, Diao J, Liu Y, Tong LI and Fan Q: MiR-593 mediates
curcumin-induced radiosensitization of nasopharyngeal carcinoma
cells via MDR1. Oncol Lett. 11:3729–3734. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Song J, Feng L, Zhong R, Xia Z, Zhang L,
Cui L, Yan H, Jia X and Zhang Z: Icariside II inhibits the EMT of
NSCLC cells in inflammatory microenvironment via down-regulation of
Akt/NF-κB signaling pathway. Mol Carcinog. 56:36–48. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Sivakumar R, Koga H, Selvendiran K,
Maeyama M, Ueno T and Sata M: Autocrine loop for IGF-I receptor
signaling in SLUG-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Int J
Oncol. 34:329–338. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Phuchareon J, McCormick F, Eisele DW and
Tetsu O: EGFR inhibition evokes innate drug resistance in lung
cancer cells by preventing Akt activity and thus inactivating Ets-1
function. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 112:E3855–E3863. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|