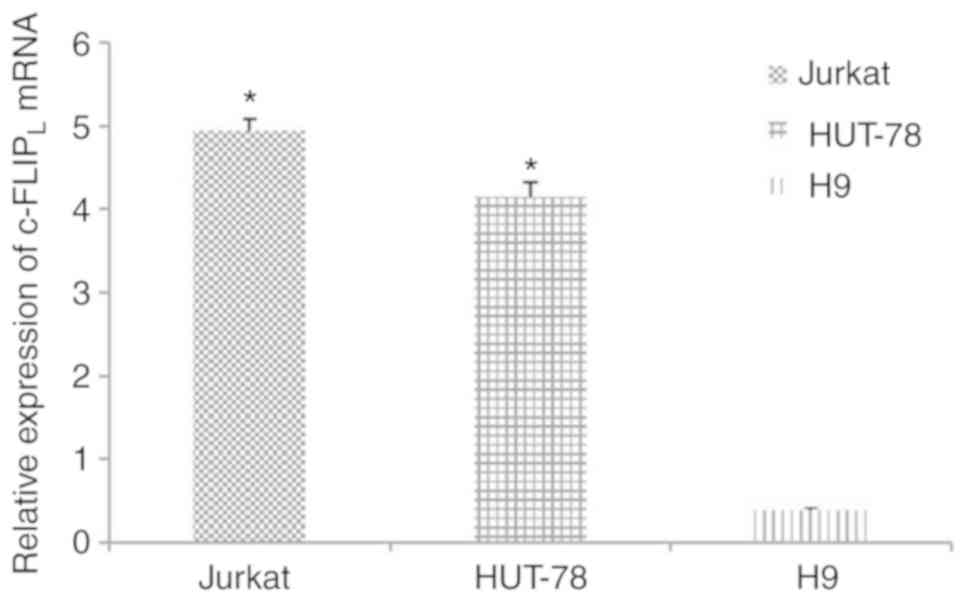
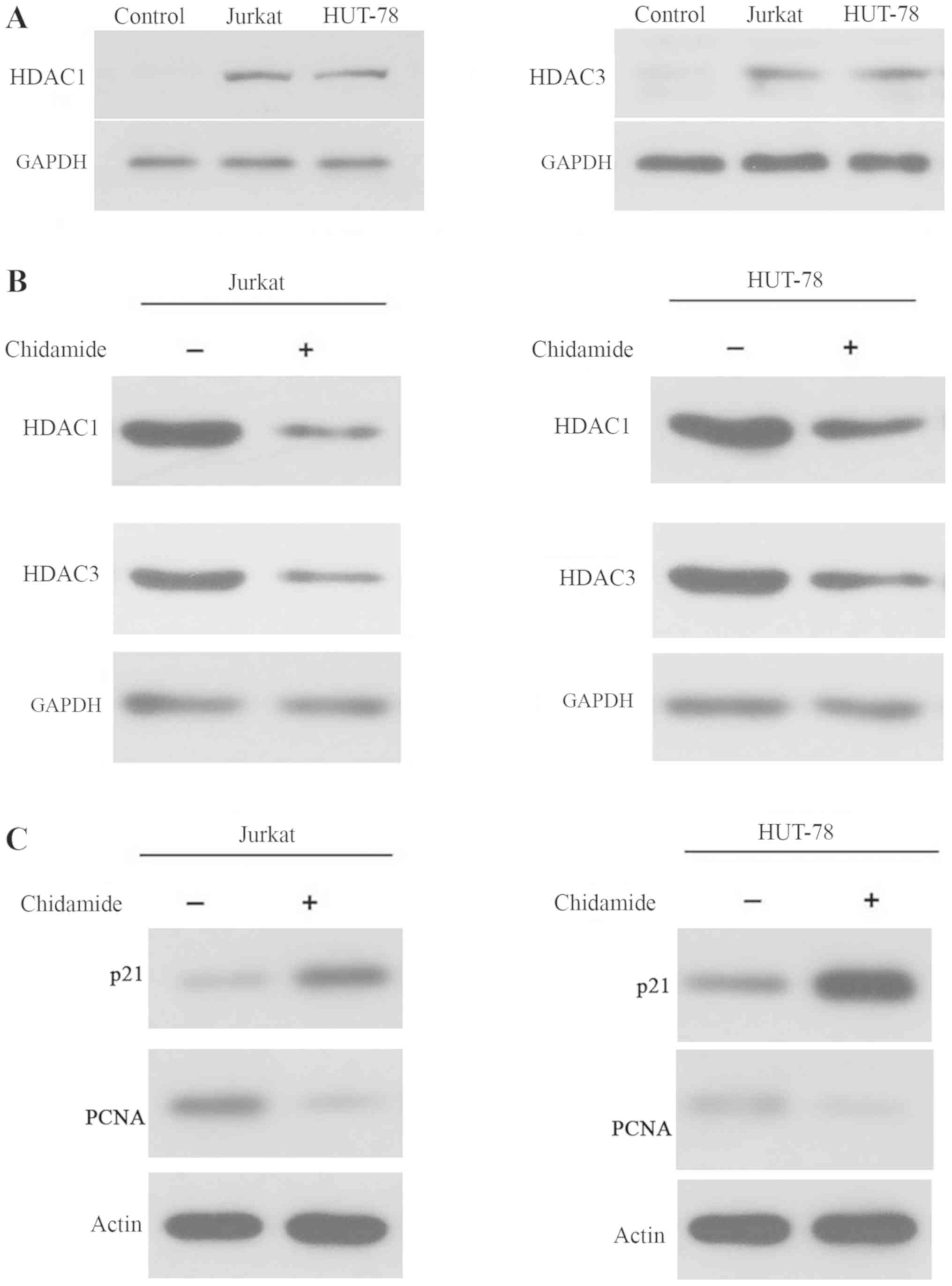
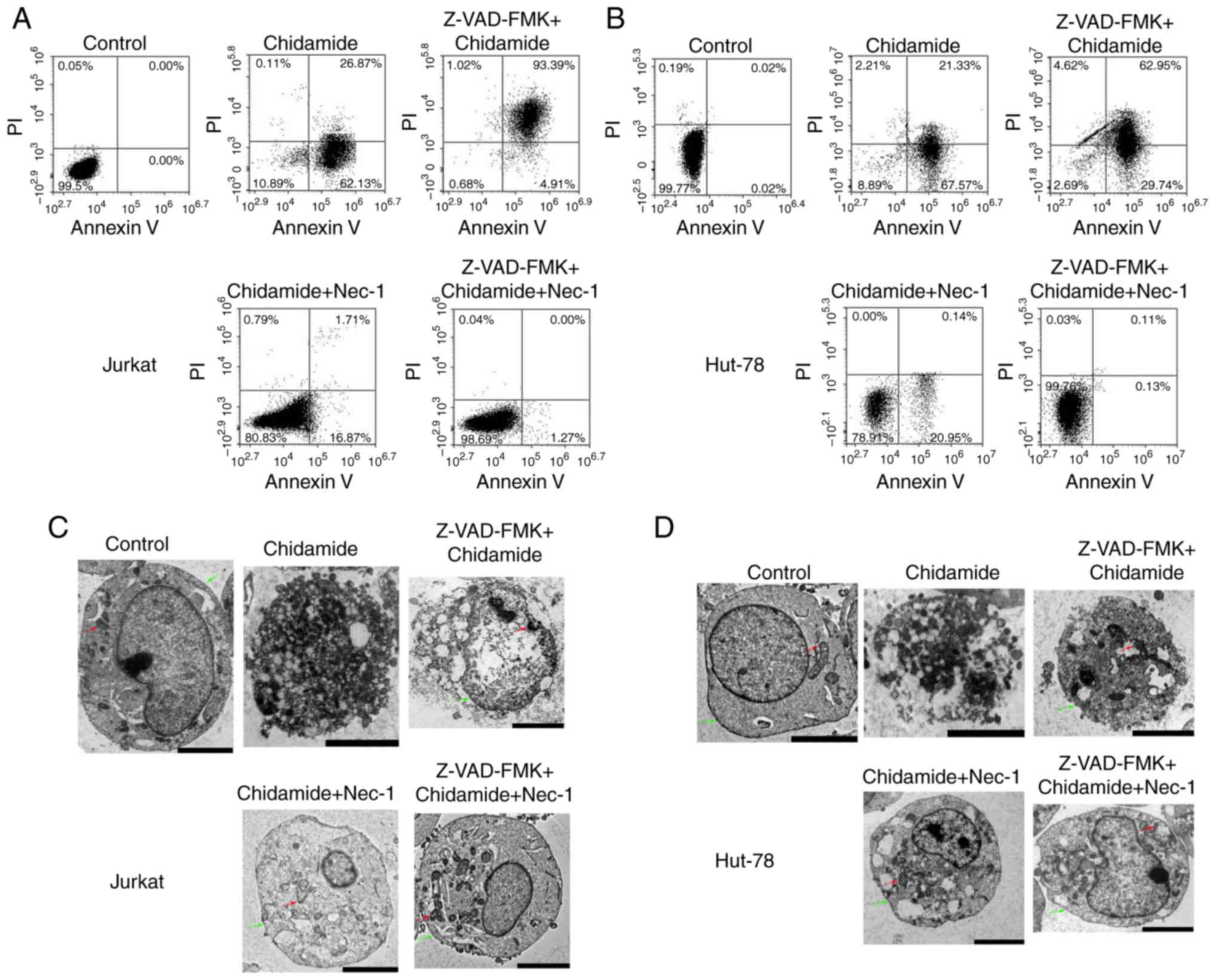
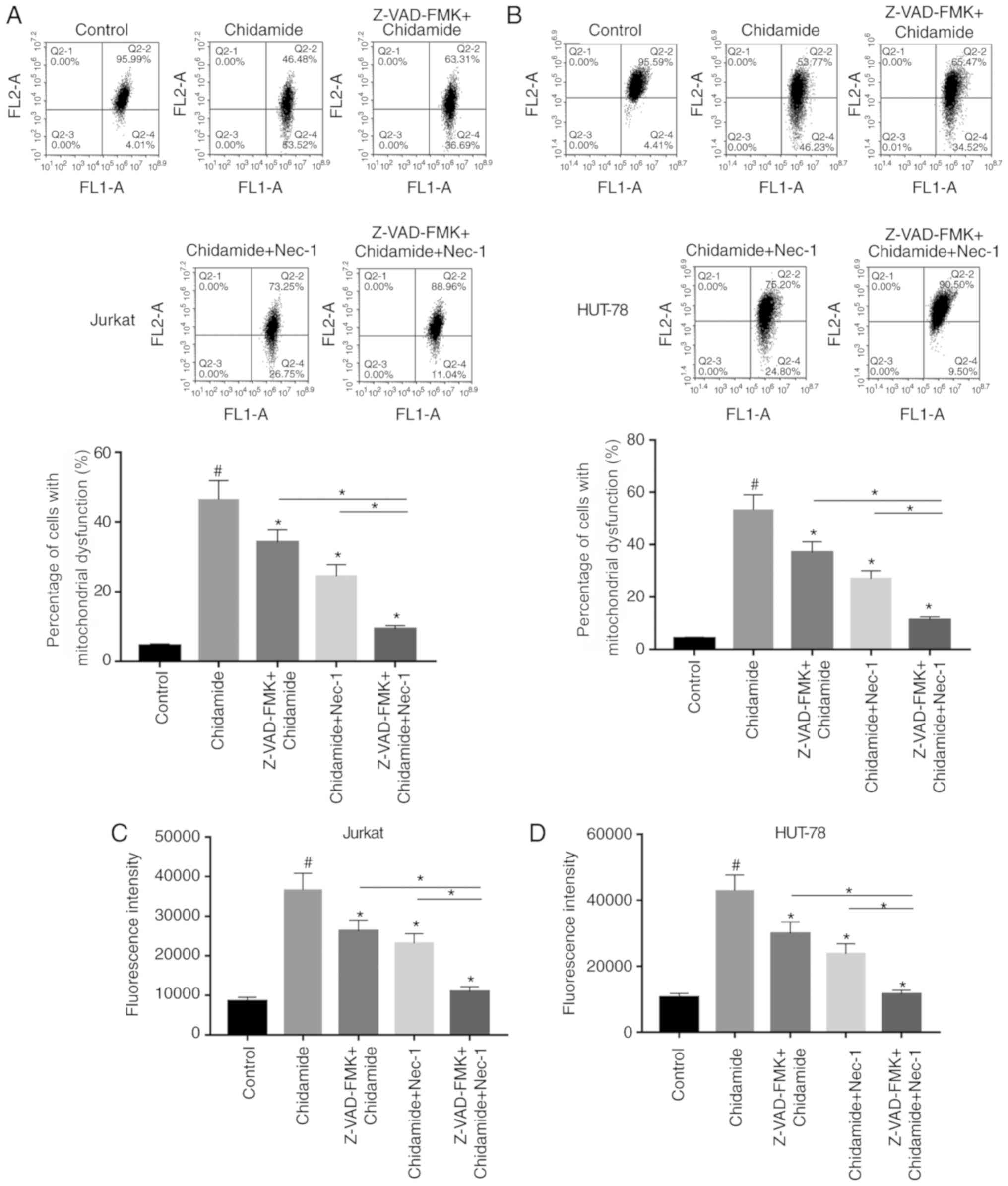
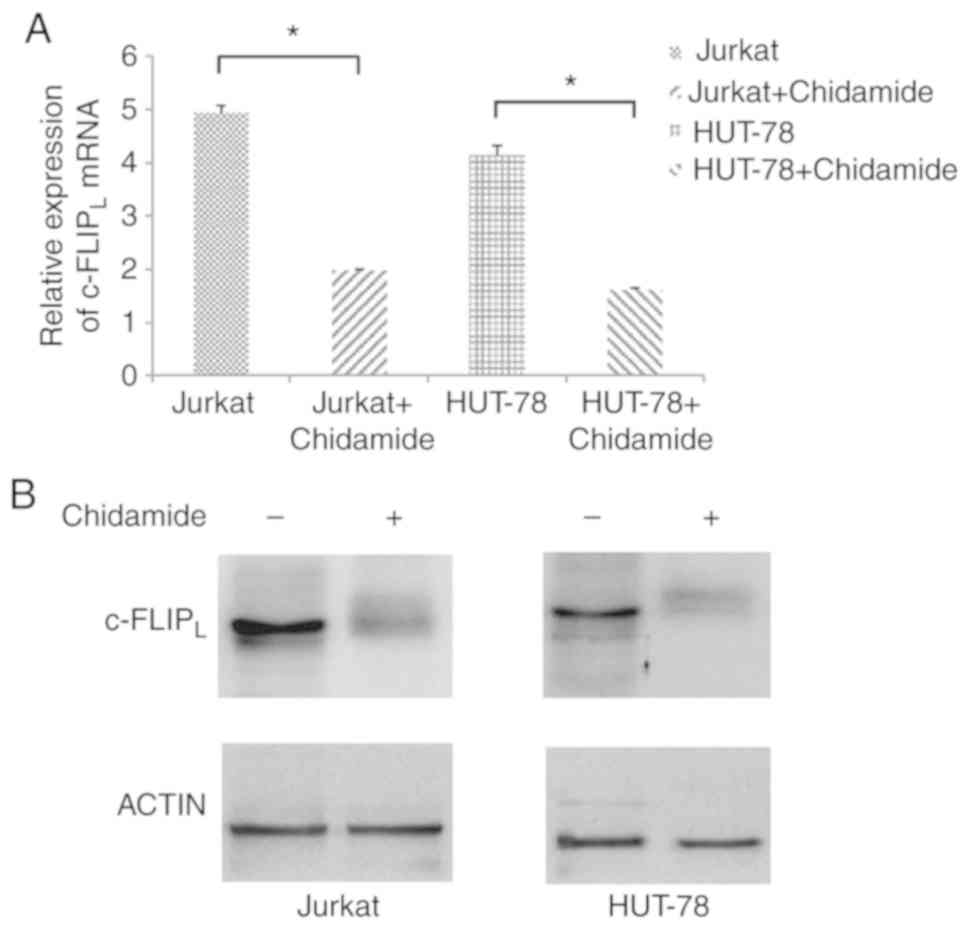
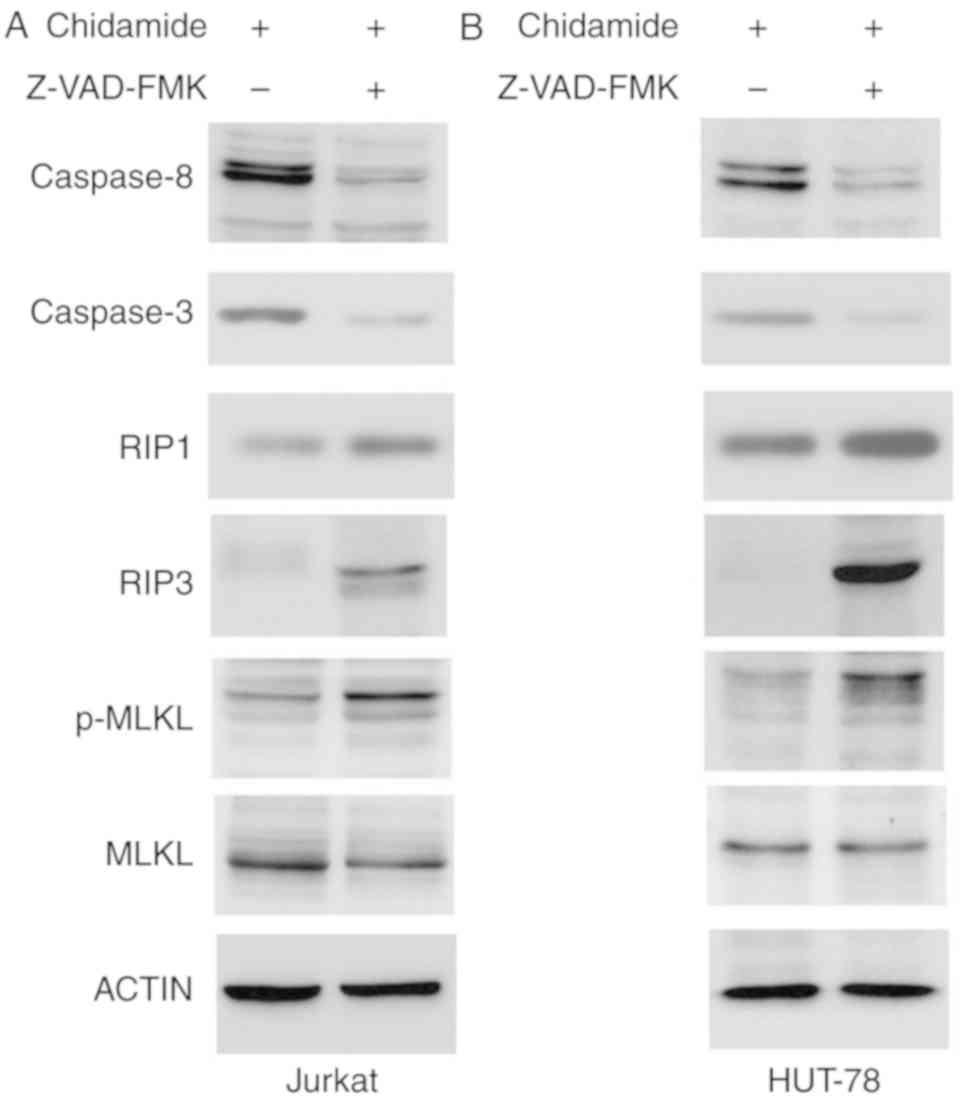
|
1
|
Beesley AH, Firth MJ, Ford J, Weller RE,
Freitas JR, Perera KU and Kees UR: Glucocorticoid resistance in
T-lineage acute lymphoblastic leukaemia is associated with a
proliferative metabolism. Br J Cancer. 100:1926–1936. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
He MX and He YW: CFLAR/c-FLIPL: A star in
the autophagy, apoptosis and necroptosis alliance. Autophagy.
9:791–793. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sachanas S, Levidou G, Angelopoulou MK,
Moschogiannis M, Yiakoumis X, Kalpadakis C, Vassilakopoulos TP,
Kontopidou F, Tsirkinidis P, Dimitrakopoulou A, et al: Apoptotic
and proliferative characteristics of proliferation centers in lymph
node sections of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leuk
Lymphoma. 55:571–582. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Venza I, Visalli M, Oteri R, Teti D and
Venza M: Class I-specific histone deacetylase inhibitor MS-275
overrides TRAIL-resistance in melanoma cells by downregulating
c-FLIP. Int Immunopharmacol. 21:439–446. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zheng Z, Cheng S, Wu W, Wang L, Zhao Y,
Shen Y, Janin A and Zhao WL: C-FLIP is involved in tumor
progression of Peripheral T-cell lymphoma and targeted by histone
deacetylase inhibitors. J Hematol Oncol. 7:882014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Su Z, Yang Z, Xu Y, Chen Y and Yu Q:
Apoptosis, autophagy, necroptosis, and cancer metastasis. Mol
Cancer. 14:482015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Deng XX, Li SS and Sun FY: Necrostatin-1
prevents necroptosis in brains after ischemic stroke via inhibition
of RIPK1-mediated RIPK3/MLKL signaling. Aging Dis. 10:807–817.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Pasparakis M and Vandenabeele P:
Necroptosis and its role in inflammation. Nature. 517:311–320.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhang B, Cao K, Liu Z, Shan W, Wen Q and
Wang R: Receptor interacting protein kinase 3 promotes
cisplatin-induced necroptosis in apoptosis-resistant HepG2/DDP
cells. Neoplasma. 2019:180710N4662019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Fu D, Jordan JJ and Samson LD: Human
ALKBH7 is required for alkylation and oxidation-induced programmed
necrosis. Genes Dev. 27:1089–1100. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Pietkiewicz S, Schmidt JH and Lavrik IN:
Quantification of apoptosis and necroptosis at the single cell
level by a combination of imaging flow cytometry with classical
Annexin V/propidium iodide staining. J Immunol Methods. 423:99–103.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in
Oncology, . Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Version1. 2018
March 12;2018.
|
|
14
|
Hu X and Xuan Y: Bypassing cancer drug
resistance by activating multiple death pathways-A proposal from
the study of circumventing cancer drug resistance by induction of
necroptosis. Cancer Lett. 259:127–137. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Irmler M, Thome M, Hahne M, Schneider P,
Hofmann K, Steiner V, Bodmer JL, Schröter M, Burns K, Mattmann C,
et al: Inhibition of death receptor signals by cellular FLIP.
Nature. 388:190–195. 1997. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hsu TS, Mo ST, Hsu PN and Lai MZ: c-FLIP
is a target of the E3 ligase deltex1 in gastric cancer. Cell Death
Dis. 9:1352018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Park SJ, Kim MJ, Kim HB, Sohn HY, Bae JH,
Kang CD and Kim SH: Trichostatin A sensitizes human ovarian cancer
cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis by down-regulation of c-FLIPL via
inhibition of EGFR pathway. Biochem Pharmacol. 77:1328–1336. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Mclornan D, Hay J, Mclaughlin K, Holohan
C, Burnett AK, Hills RK, Johnston PG, Mills KI, McMullin MF,
Longley DB and Gilkes A: Prognostic and therapeutic relevance of
c-FLIP in acute myeloid leukaemia. Br J Haematol. 160:188–198.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Florean C, Schnekenburger M, Grandjenette
C, Dicato M and Diederich M: Epigenomics of leukemia: From
mechanisms to therapeutic applications. Epigenomics. 3:581–609.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Xiao PF, Tao YF, Hu SY, Cao L, Lu J, Wang
J, Feng X, Pan J and Chai YH: mRNA expression profiling of histone
modifying enzymes in pediatric acute monoblastic leukemia.
Pharmazie. 72:177–186. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Haery L, Mussakhan S, Waxman DJ and
Gilmore TD: Evidence for an oncogenic modifier role for mutant
histone acetyltransferases in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Leuk
Lymphoma. 57:2661–2671. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Valdez BC, Li Y, Murray D, Liu Y, Nieto Y,
Champlin RE and Andersson BS: Combination of a hypomethylating
agent and inhibitors of PARP and HDAC traps PARP1 and DNMT1 to
chromatin, acetylates DNA repair proteins, down-regulates NuRD and
induces apoptosis in human leukemia and lymphoma cells. Oncotarget.
9:3908–3921. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhou H, Cai Y, Liu D, Li M, Sha Y, Zhang
W, Wang K, Gong J, Tang N, Huang A and Xia J: Pharmacological or
transcriptional inhibition of both HDAC1 and 2 leads to cell cycle
blockage and apoptosis via p21 Waf1/Cip1 and p19 INK4d upregulation
in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Prolif. 51:e124472018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Li S, Wang F, Qu Y, Chen X, Gao M, Yang J,
Zhang D, Zhang N, Li W and Liu H: HDAC2 regulates cell
proliferation, cell cycle progression and cell apoptosis in
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma EC9706 cells. Oncol Lett.
13:403–409. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ahn MY and Yoon JH: Histone deacetylase 8
as a novel therapeutic target in oral squamous cell carcinoma.
Oncol Rep. 37:540–546. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yoon S and Eom GH: HDAC and HDAC
Inhibitor: From Cancer to Cardiovascular Diseases. Chonnam Med J.
52:1–11. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chan TS, Tse E and Kwong YL: Chidamide in
the treatment of peripheral T-cell lymphoma. Onco Targets Ther.
10:347–352. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lu CT, Leong PY, Hou TY, Huang SJ, Hsiao
YP and Ko JL: Ganoderma immunomodulatory protein and chidamide
down-regulate integrin-related signaling pathway result in
migration inhibition and apoptosis induction. Phytomedicine.
51:39–47. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yang S, Nan P, Li C, Lin F, Li H, Wang T,
Zhou C, Zhang X, Meng X, Qian H, et al: Inhibitory effect of
chidamide on the growth of human adenoid cystic carcinoma cells.
Biomed Pharmacother. 99:608–614. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Degterev A, Huang Z, Boyce M, Li Y, Jagtap
P, Mizushima N, Cuny GD, Mitchison TJ, Moskowitz MA and Yuan J:
Chemical inhibitor of nonapoptotic cell death with therapeutic
potential for ischemic brain injury. Nat Chem Biol. 1:112–119.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Papaemmanuil E, Hosking FJ, Vijayakrishnan
J, Price A, Olver B, Sheridan E, Kinsey SE, Lightfoot T, Roman E,
Irving JA, et al: Loci on 7p12.2, 10q21.2 and 14q11.2 are
associated with risk of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Nat
Genet. 41:1006–1010. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhang DW, Shao J, Lin J, Zhang N, Lu BJ,
Lin SC, Dong MQ and Han J: RIP3, an energy metabolism regulator
that switches TNF-induced cell death from apoptosis to necrosis.
Science. 325:332–336. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Qiu X, Zhang Y and Han J: RIP3 is an
upregulator of aerobic metabolism and the enhanced respiration by
necrosomal RIP3 feeds back on necrosome to promote necroptosis.
Cell Death Differ. 25:821–824. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Cook WD, Moujalled DM, Ralph TJ, Lock P,
Young SN, Murphy JM and Vaux DL: RIPK1-and RIPK3-induced cell death
mode is determined by target availability. Cell Death Differ.
21:1600–1612. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Xu B, Xu M, Tian Y, Yu Q, Zhao Y, Chen X,
Mi P, Cao H, Zhang B, Song G, et al: Matrine induces RIP3-dependent
necroptosis in cholangiocarcinoma cells. Cell Death Discov.
3:160962017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kim SK, Kim WJ, Yoon JH, Ji JH, Morgan MJ,
Cho H, Kim YC and Kim YS: Upregulated RIP3 Expression Potentiates
MLKL phosphorylation-mediated programmed necrosis in toxic
epidermal Necrolysis. J Invest Dermatol. 135:2021–2030. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Moujalled DM, Cook WD, Murphy JM and Vaux
DL: Necroptosis induced by RIPK3 requires MLKL but not Drp1. Cell
Death Dis. 5:e10862014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|