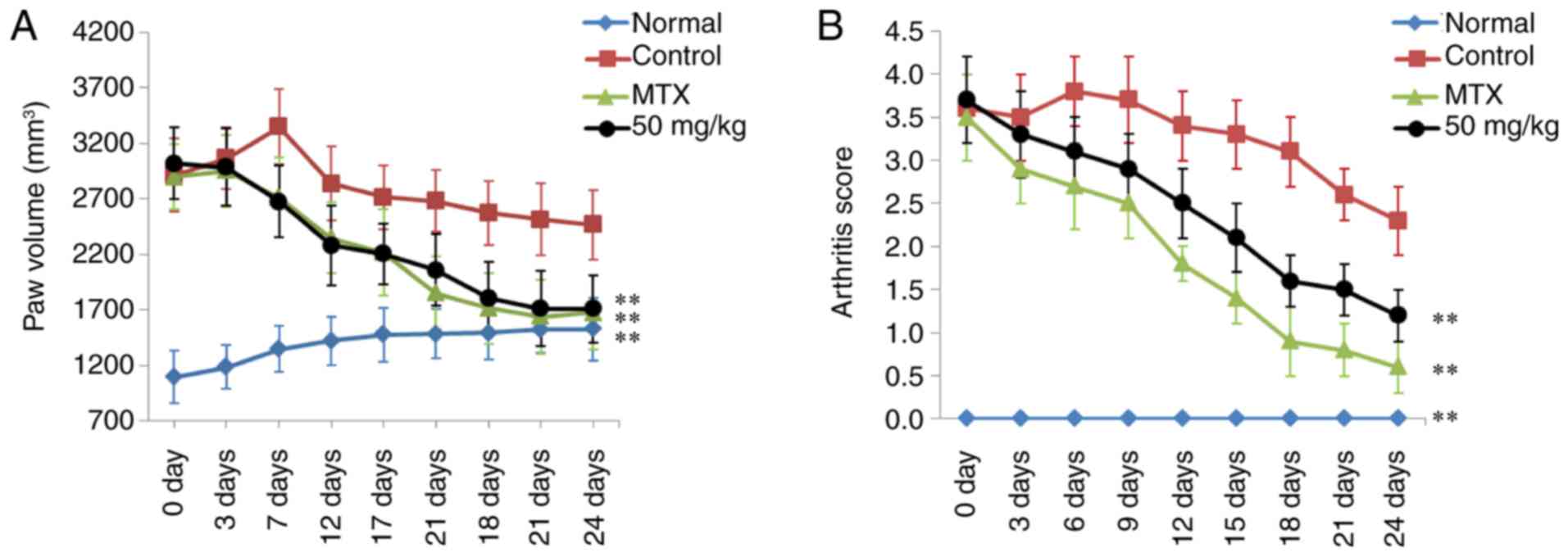
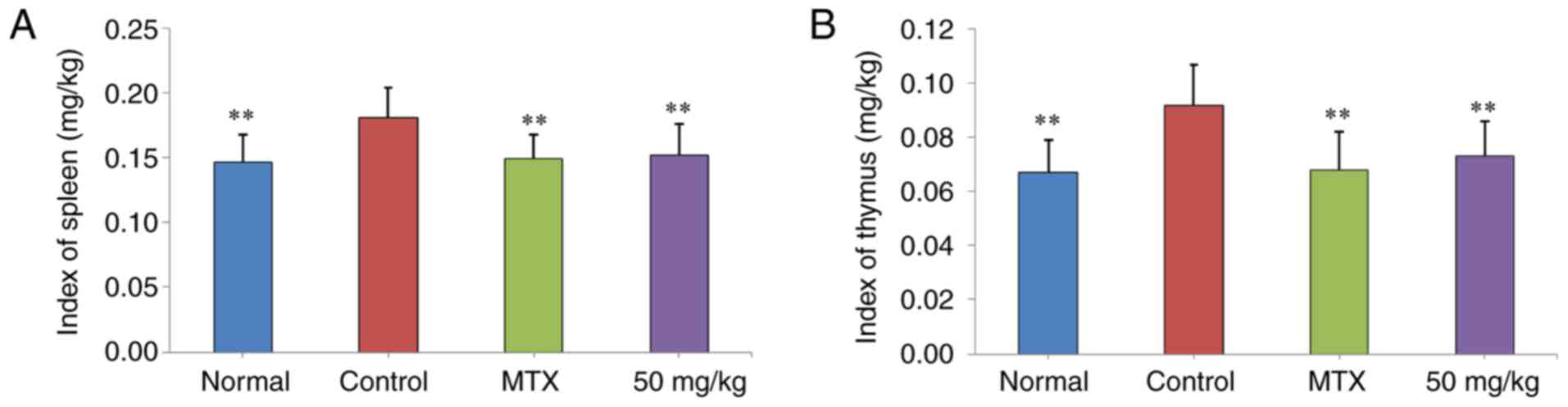
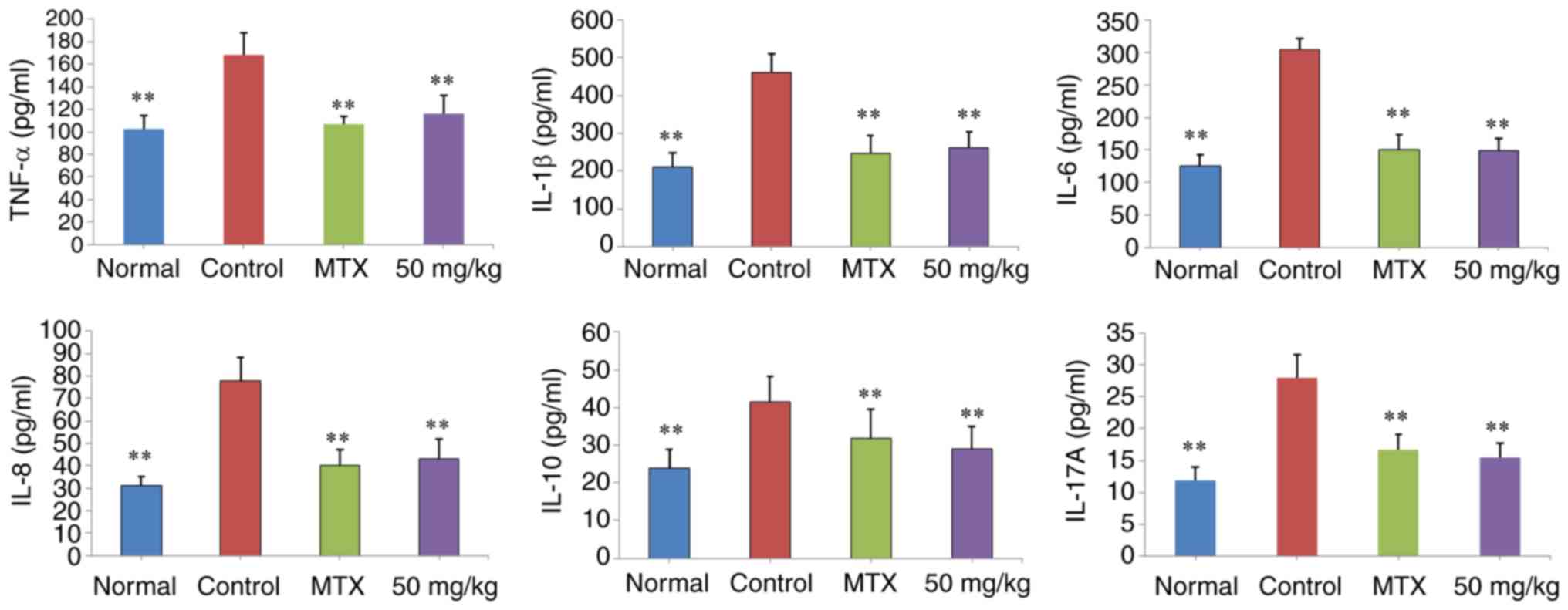
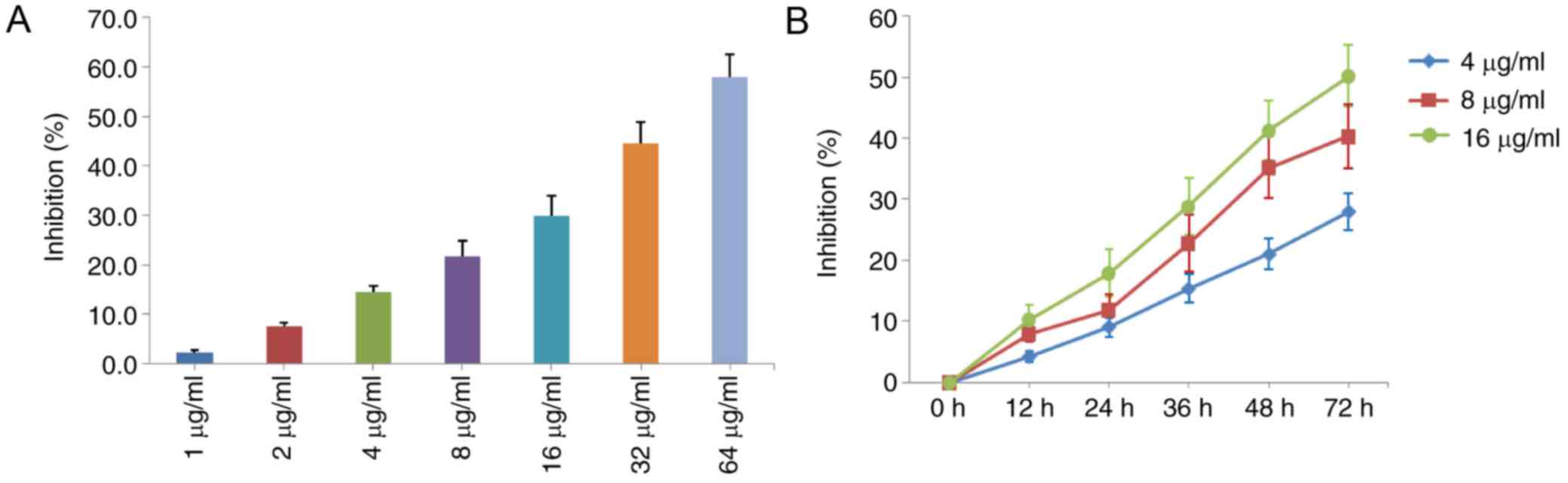
|
1
|
Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission:
Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China Part I. People's
Medical Publishing House. (Beijing). 1022015.
|
|
2
|
Huang YL: Research progress of
Curculiginis orchioides. J Chin Med Mater. 26:225–229.
2003.(In Chinese).
|
|
3
|
Zhang XJ, Sun YH and Wang HoY: Chemical
constituents from Curculigo orchioids. Chin Tradit Pat Med.
29:1869–1872. 2017.(In Chinese).
|
|
4
|
Fan PT, Zhang LM, Heng M, Liu BC, Xie X,
Ning ZS and Xu H: Effects of curculigoside on expressions of
Caspase-3, PARP-1 and estrogen receptor in hippocampus of model
rats with vascular dementia. Chin J Neuroanat. 33:453–458. 2017.(In
Chinese).
|
|
5
|
Lu HW, Zhu BH and Liang YK: Determination
of curculigoside in crude medicine curculigo orchioides by HPLC.
Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 27:192–194. 2002.(In Chinese).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ooi J, Azmi NH, Imam MU, Alitheen NB and
Ismail M: Curculigoside and polyphenol-rich ethyl acetate fraction
of Molineria latifolia rhizome improved glucose uptake via
potential mTOR/AKT activated GLUT4 translocation. J Food Drug Anal.
26:1253–1264. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Pu J, Fang FF, Li XQ, Shu ZH, Jiang YP,
Han T, Peng W and Zheng CJ: Matrine exerts a strong anti-arthritic
effect on type II collagen-induced arthritis in rats by inhibiting
inflammatory responses. Int J Mol Sci. 17(pii): E14102016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Okada Y, Wu D, Trynka G, Raj T, Terao C,
Ikari K, Kochi Y, Ohmura K, Suzuki A, Yoshida S, et al: Genetics of
rheumatoid arthritis contributes to biology and drug discovery.
Nature. 506:376–381. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang Q, Wang L, Wu L, Zhang M, Hu S, Wang
R, Han Y, Wu Y, Zhang L, Wang X, et al: Paroxetine alleviates T
lymphocyte activation and infiltration to joints of
collagen-induced arthritis. Sci Rep. 7:453642017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Firestein GS and McInnes IB:
Immunopathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Immunity. 46:183–196.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Xie QC and Yang YP: Anti-proliferative of
physcion 8-O-β-glucopyranoside isolated from Rumex japonicus Houtt.
on A549 cell lines via inducing apoptosis and cell cycle arrest.
BMC Complement Alter Med. 14:3772014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
National Institute of Health, USA. Public
health service policy on humane care and use of laboratory animals.
2002.
|
|
13
|
Wu XY, Li JZ, Guo JZ and Hou BY:
Ameliorative effects of curculigoside from Curculigo orchioides
Gaertn on learning and memory in aged rats. Molecules.
17:10108–10118. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Fu DX, Lei GQ, Cheng XW, Chen JK and Zhou
TS: Curculigoside C, a new phenolic glucoside from rhizomes of
curculigo orchioides. Acta Bot Sin. 46:621–624. 2004.
|
|
15
|
Peng W, Wang L, Qiu X, Jiang Y, Han T, Pan
L, Jia X, Qin L and Zheng C: Therapeutic effects of Caragana
pruinosa Kom. roots extract on type II collagen-induced arthritis
in rats. J Ethnopharmacol. 191:1–8. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang F, Qiao YH, Niu HM and Zhao H:
Anti-arthritic effect of total anthraquinone from Polygonum
cuspidatum on type II collagen-induced arthritis in rats. Trop J
Pharm Res. 16:2453–2459. 2017.
|
|
17
|
Zheng CJ, Zhao XX, Ai HW, Lin B, Han T,
Jiang YP, Xing X and Qin LP: Therapeutic effects of standardized
Vitex negundo seeds extract on complete Freund's adjuvant induced
arthritis in rats. Phytomedicine. 21:838–846. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang Q, Kuang H, Su Y, Sun Y, Feng J, Guo
R and Chan K: Naturally derived anti-inflammatory compounds from
Chinese medicinal plants. J Ethnopharmacol. 146:9–39. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Peng W, Shen H, Lin B, Han P, Li CH, Zhang
QY, Ye BZ, Rahman K, Xin HL, Qin LP and Han T: Docking study and
antiosteoporosis effects of a dibenzylbutane lignan isolated from
Litsea cubeba targeting Cathepsin K and MEK1. Med Chem Res.
27:2062–2070. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Majithia V and Geraci SA: Rheumatoid
arthritis: Diagnosis and management. Am J Med. 120:936–939. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
McNamee K, Williams R and Seed M: Animal
models of rheumatoid arthritis: How informative are they? Eur J
Pharmacol. 759:278–286. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Luo Y, Liu M, Xia Y, Dai Y, Chou G and
Wang Z: Therapeutic effect of norisoboldine, an alkaloid isolated
from Radix Linderae, on collagen-induced arthritis in mice.
Phytomedicine. 17:726–731. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Trentham DE, McCune WJ, Susman P and David
JR: Autoimmunity to collagen in adjuvant arthritis of rats. J Clin
Investig. 66:1109–1117. 1980. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Imboden JB: The immunopathogenesis of
rheumatoid arthritis. Annu Rev Pathol Mech Dis. 4:417–434. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Sennikov SV, Alshevskaya AA, Shkaruba NS,
Chumasova OA, Sizikov AE and Lopatnikova JA: Expression of TNFα
membrane-bound receptors in the peripheral blood mononuclear cells
(PMBC) in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Cytokine. 73:288–294.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kalden JR: Emerging role of anti-tumor
necrosis factor therapy in rheumatic diseases. Arthritis Res. 4
Suppl 2:S34–S40. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Mariaselvam CM, Aoki M, Salah S, Boukouaci
W, Moins-Teisserenc H, Charron D, Krishnamoorthy R, Tamouza R and
Negi VS: Cytokine expression and cytokine-based T cell profiling in
South Indian rheumatoid arthritis. Immunobiology. 219:772–777.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Roeleveld DM and Koenders MI: The role of
the Th17 cytokines IL-17 and IL-22 in rheumatoid arthritis
pathogenesis and developments in cytokine immunotherapy. Cytokine.
74:101–107. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Rossi D, Modena V, Sciascia S and
Roccatello D: Rheumatoid arthritis: Biological therapy other than
anti-TNF. Int Immunopharmacol. 27:185–188. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Conti P, Kempuraj D, Kandere K, Di
Gioacchino M, Barbacane RC, Castellani ML, Felaco M, Boucher W,
Letourneau R and Theoharides TC: IL-10, an inflammatory/inhibitory
cytokine, but not always. Immunol Lett. 86:123–129. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Tran CN, Lundy SK and Fox DA: Synovial
biology and T cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Pathophysiology.
12:183–189. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Xia Y, Li X, Ou-Yang Z and Chen JW:
Selective modulation of MAPKs contribute to the anti-proliferative
and anti-inflammatory activities of
1,7-dihydroxy-3,4-dimethoxyxanthone in rheumatoid arthritis-derived
fibroblast-like synoviocyte MH7A cells. J Ethnopharmacol.
168:248–254. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
O'Shea JJ and Murray PJ: Cytokine
signaling modules in inflammatory response. Immunity. 28:477–487.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
O'Shea JJ and Plenge R: JAK and STAT
signaling molecules in immunoregulation and immune-mediated
disease. Immunity. 36:542–550. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Migita K, Izumi Y, Torigoshi T, Satomura
K, Izumi M, Nishino Y, Jiuchi Y, Nakamura M, Kozuru H, Nonaka F, et
al: Inhibition of Janus kinase/signal transducer and activator of
transcription (JAK/STAT) signalling pathway in rheumatoid synovial
fibroblasts using small molecule compounds. Clin Exp Immunol.
174:356–363. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Sweeney SE and Firestein GS: Signal
transduction in rheumatoid arthritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol.
16:231–237. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Dutzmann J, Daniel JM, Bauersachs J,
Hilfiker-Kleiner D and Sedding DG: Emerging translational
approaches to target STAT3 signalling and its impact on vascular
dsease. Cardiovasc Res. 106:365–374. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Baker RG, Hayden MS and Ghosh S: NF-κB,
inflammation, and metabolic disease. Cell Metab. 13:11–22. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Vallabhapurapu S and Karin M: Regulation
and function of NF-kappaB transcription factors in the immune
system. Annu Rev Immunol. 27:693–733. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Beg AA and Baldwin AS Jr: The I kappa B
proteins: Multifunctional regulators of Rel/NF-kappa B
transcription factors. Genes Dev. 7:2064–2070. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Lyss G, Knorre A, Schmidt TJ, Pahl HL and
Merfort I: The anti-inflammatory sesquiterpene lactone helenalin
inhibits the transcription factor NF-kappaB by directly targeting
p65. J Biol Chem. 273:33508–33516. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|