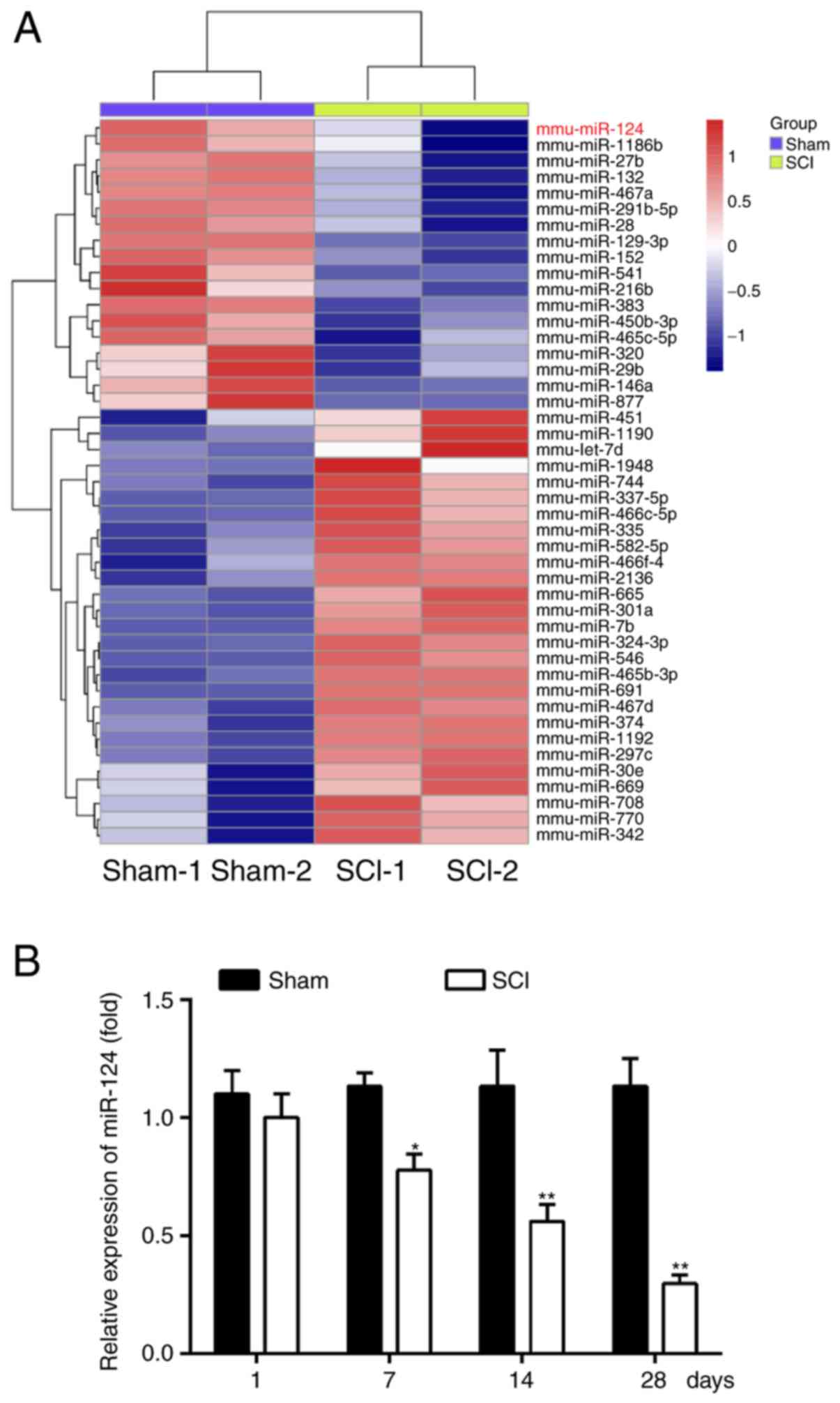
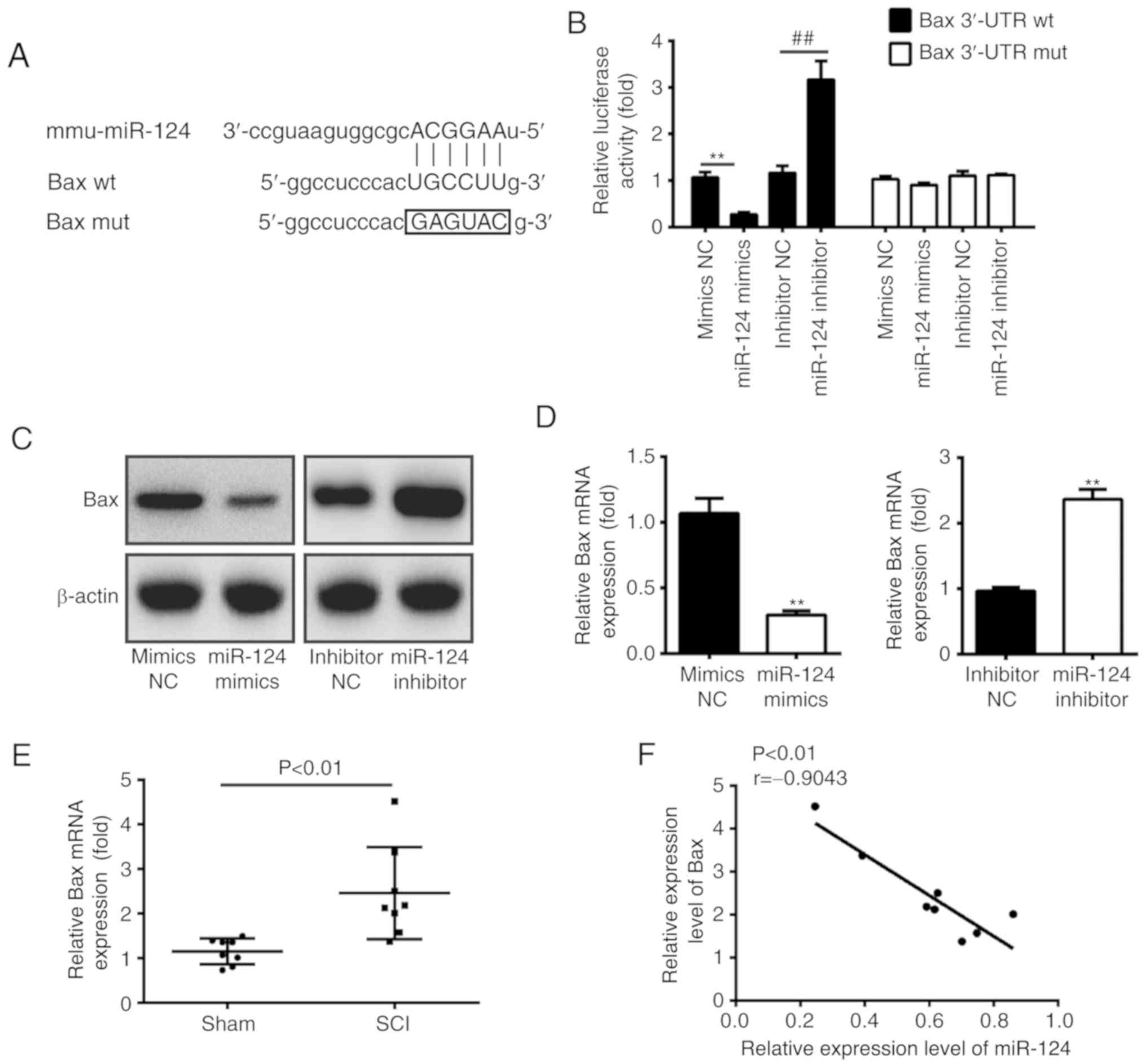
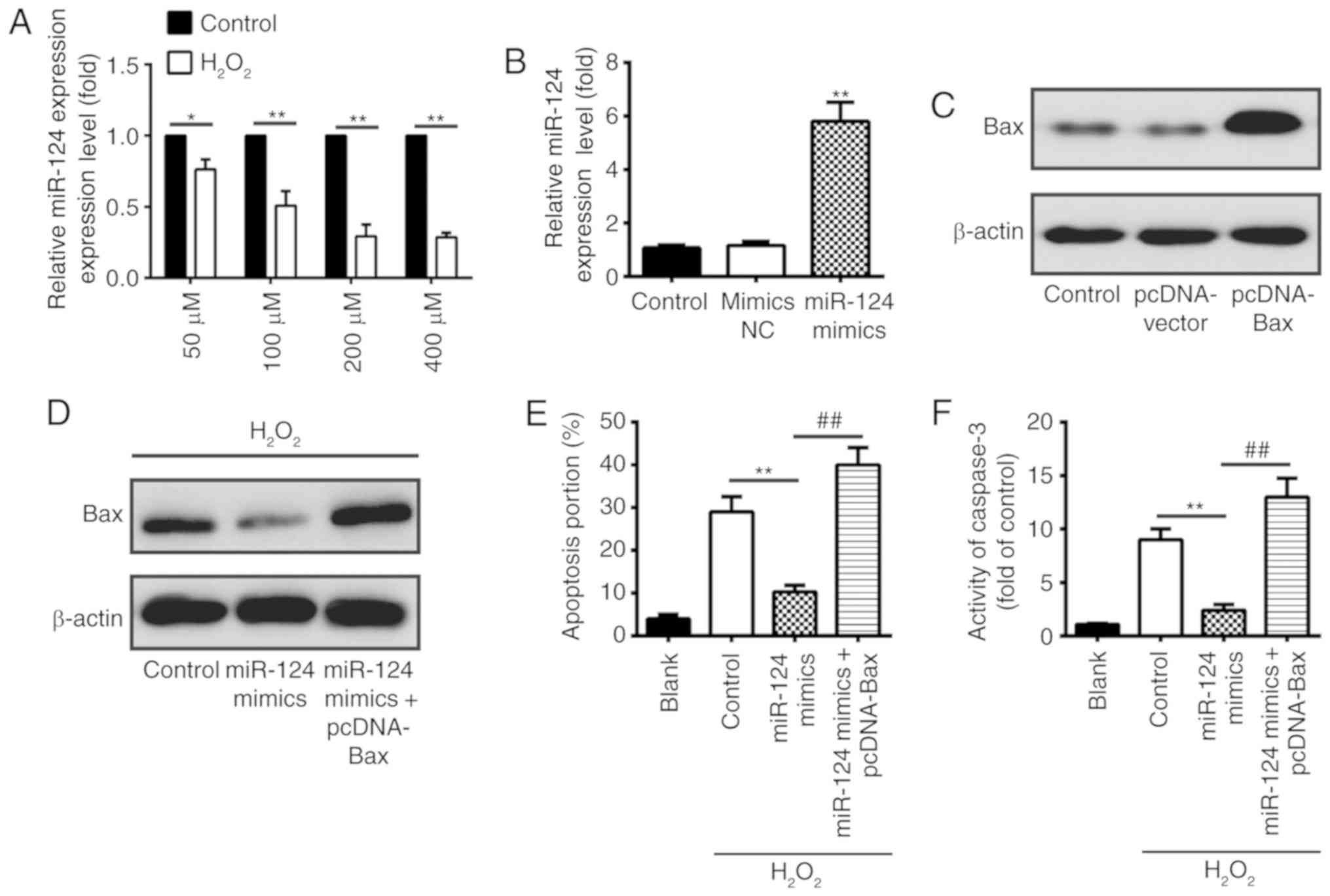
|
1
|
Chen Y, Cao S, Xu P, Han W, Shan T, Pan J,
Lin W, Chen X and Wang X: Changes in the expression of miR-34a and
its target genes following spinal cord injury in rats. Med Sci
Monit. 22:3981–3993. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hu W, Wang H, Liu Z, Liu Y, Wang R, Luo X
and Huang Y: Neuroprotective effects of lycopene in spinal cord
injury in rats via antioxidative and anti-apoptotic pathway.
Neurosci Lett. 642:107–112. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Thuret S, Moon LD and Gage FH: Therapeutic
interventions after spinal cord injury. Nat Rev Neurosci.
7:628–643. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Blight AR: Miracles and molecules-progress
in spinal cord repair. Nat Neurosci. 5 (Suppl 1):S1051–S1054. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Rabchevsky AG, Patel SP and Springer JE:
Pharmacological interventions for spinal cord injury: Where do we
stand? How might we step forward? Pharmacol Ther. 132:15–29.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kawabata H, Setoguchi T, Yone K, Souda M,
Yoshida H, Kawahara K, Maruyama I and Komiya S: High mobility group
box 1 is upregulated after spinal cord injury and is associated
with neuronal cell apoptosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 35:1109–1115.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Li J, Huang C-Y, Zheng RL, Cui KR and Li
JF: Hydrogen peroxide induces apoptosis in human hepatoma cells and
alters cell redox status. Cell Biol Int. 24:9–23. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Reuter S, Eifes S, Dicato M, Aggarwal BB
and Diederich M: Modulation of anti-apoptotic and survival pathways
by curcumin as a strategy to induce apoptosis in cancer cells.
Biochem Pharmacol. 76:1340–1351. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Balaban RS, Nemoto S and Finkel T:
Mitochondria, oxidants, and aging. Cell. 120:483–495. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li P, Nijhawan D and Wang X: Mitochondrial
activation of apoptosis. Cell 116 (2 Suppl). S57–S61. 2004.
|
|
11
|
Nicholson DW and Thornberry NA: Caspases:
Killer proteases. Trends Biochem Sci. 22:299–306. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Croce CM: Causes and consequences of
microRNA dysregulation in cancer. Nat Rev Genet. 10:704–714. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Target recognition
and regulatory functions. Cell. 136:215–233. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Friedman RC, Farh KK, Burge CB and Bartel
DP: Most mammalian mRNAs are conserved targets of microRNAs. Genome
Res. 19:92–105. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Krichevsky AM: MicroRNA profiling: From
dark matter to white matter, or identifying new players in
neurobiology. ScientificWorldJournal. 7:155–166. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kosik KS: The neuronal microRNA system.
Nat Rev Neurosci. 7:911–920. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Bak M, Silahtaroglu A, Møller M,
Christensen M, Rath MF, Skryabin B, Tommerup N and Kauppinen S:
MicroRNA expression in the adult mouse central nervous system. RNA.
14:432–444. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Liu NK, Wang XF, Lu QB and Xu XM: Altered
microRNA expression following traumatic spinal cord injury. Exp
Neurol. 219:424–429. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Liu G, Keeler BE, Zhukareva V and Houlé
JD: Cycling exercise affects the expression of apoptosis-associated
microRNAs after spinal cord injury in rats. Exp Neurol.
226:200–206. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sun Y, Su Q, Li L, Wang X, Lu Y and Liang
J: MiR-486 regulates cardiomyocyte apoptosis by p53-mediated BCL-2
associated mitochondrial apoptotic pathway. BMC Cardiovasc Disord.
17:1192017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Makhdoumi P, Roohbakhsh A and Karimi G:
MicroRNAs regulate mitochondrial apoptotic pathway in myocardial
ischemia-reperfusion-injury. Biomed Pharmacother. 84:1635–1644.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang J, Jiao Y, Cui L and Jiang L: miR-30
functions as an oncomiR in gastric cancer cells through regulation
of P53-mediated mitochondrial apoptotic pathway. Biosci Biotechnol
Biochem. 81:119–126. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yune TY, Lee JY, Jung GY, Kim SJ, Jiang
MH, Kim YC, Oh YJ, Markelonis GJ and Oh TH: Minocycline alleviates
death of oligodendrocytes by inhibiting pro-nerve growth factor
production in microglia after spinal cord injury. J Neurosci.
27:7751–7761. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Saeed AI, Sharov V, White J, Li J, Liang
W, Bhagabati N, Braisted J, Klapa M, Currier T, Thiagarajan M, et
al: TM4: A free, open-source system for microarray data management
and analysis. Biotechniques. 34:374–378. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Basso DM, Beattie MS and Bresnahan JC: A
sensitive and reliable locomotor rating scale for open field
testing in rats. J Neurotrauma. 12:1–21. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yu JY, Chung KH, Deo M, Thompson RC and
Turner DL: MicroRNA miR-124 regulates neurite outgrowth during
neuronal differentiation. Exp Cell Res. 314:2618–2633. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Shao Q, Jiang W and Jin Y: MiR-124 effect
in neurons apoptosis in newborn rat with thyroid hypofunction. Int
J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:14465–14471. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yu DS, Lv G, Mei XF, Cao Y, Wang YF, Wang
YS and Bi YL: MiR-200c regulates ROS-induced apoptosis in murine
BV-2 cells by targeting FAP-1. Spinal Cord. Dec 2–2014.(Epub ahead
of print).
|
|
30
|
Hu F, Min J, Cao X, Liu L, Ge Z, Hu J and
Li X: MiR-363-3p inhibits the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition
and suppresses metastasis in colorectal cancer by targeting Sox4.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 474:35–42. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Nishimura R, Tabata K, Arakawa M, Ito Y,
Kimura Y, Akihisa T, Nagai H, Sakuma A, Kohno H and Suzuki T:
Isobavachalcone, a chalcone constituent of Angelica keiskei,
induces apoptosis in neuroblastoma. Biol Pharm Bull. 30:1878–1883.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
He J, Xiao Y, Casiano CA and Zhang L: Role
of mitochondrial cytochrome c in cocaine-induced apoptosis
in coronary artery endothelial cells. J Pharmacol Experimental
Ther. 295:896–903. 2000.
|
|
33
|
Liu H, Qin CK, Han GQ, Xu HW, Ren WH and
Qin CY: Synthetic chenodeoxycholic acid derivative, HS-1200,
induces apoptosis of human hepatoma cells via a mitochondrial
pathway. Cancer Lett. 270:242–249. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Noguchi K, Kitanaka C, Yamana H, Kokubu A,
Mochizuki T and Kuchino Y: Regulation of c-Myc through
phosphorylation at Ser-62 and Ser-71 by c-Jun N-terminal kinase. J
Biol Chem. 274:32580–32587. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Klapsinou E, Argyri E, Panotopoulou E,
Daskalopoulou D, Patsouris E, Nonni A, Lazaris AC and Thomopoulou
GH: Bax and Bak expression in cervical smears of women with low-and
high-risk HPV types: A study of 120 cases. J Cytol. 32:223–229.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Su CC, Lee KI, Chen MK, Kuo CY, Tang CH
and Liu SH: Cantharidin induced oral squamous cell carcinoma cell
apoptosis via the JNK-regulated mitochondria and endoplasmic
reticulum stress-related signaling pathways. PLoS One.
11:e01680952016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Lu Z, Chen H, Zheng XM and Chen ML:
Experimental study on the apoptosis of cervical cancer Hela cells
induced by juglone through c-Jun N-terminal kinase/c-Jun pathway.
Asian Pac J Trop Med. 10:572–575. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zou H, Li Y, Liu X and Wang X: An
APAF-1.cytochrome c multimeric complex is a functional
apoptosome that activates procaspase-9. J Biol Chem.
274:11549–11556. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Giovanni SD, Knoblach SM, Brandoli C, Aden
SA, Hoffman EP and Faden AI: Gene profiling in spinal cord injury
shows role of cell cycle neuronal death. Ann Neurol. 53:454–468.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
De Biase A, Knoblach SM, Di Giovanni S,
Fan C, Molon A, Hoffman EP and Faden AI: Gene expression profiling
of experimental traumatic spinal cord injury as a function of
distance from impact site and injury severity. Physiol Genomics.
22:368–381. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Hu JZ, Huang JH, Zeng L, Wang G, Cao M and
Lu HB: Anti-apoptotic effect of microRNA-21 after contusion spinal
cord injury in rats. J Neurotrauma. 30:1349–1360. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Lagos-Quintana M, Rauhut R, Yalcin A,
Meyer J, Lendeckel W and Tuschl T: Identification of
tissue-specific MicroRNAs from mouse. Curr Biol. 12:735–739. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Krichevsky AM, King KS, Donahue CP,
Khrapko K and Kosik KS: A microRNA array reveals extensive
regulation of microRNAs during brain development. RNA. 9:1274–1281.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Sempere LF, Freemantle S, Pitha-Rowe I,
Moss E, Dmitrovsky E and Ambros V: Expression profiling of
mammalian microRNAs uncovers a subset of brain-expressed microRNAs
with possible roles in murine and human neuronal differentiation.
Genome Biol. 5:R132004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Miska EA, Alvarez-Saavedra E, Townsend M,
Yoshii A, Sestan N, Rakic P, Constantine-Paton M and Horvitz HR:
Microarray analysis of microRNA expression in the developing
mammalian brain. Genome Biol. 5:R682004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Zhao Y, Zhang H, Zhang D, Yu CY, Zhao XH,
Liu FF, Bian GL, Ju G and Wang J: Loss of microRNA-124 expression
in neurons in the peri-lesion area in mice with spinal cord injury.
Neural Regen Res. 10:1147–1152. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Song JL, Zheng W, Chen W, Qian Y, Ouyang
YM and Fan CY: Lentivirus-mediated microRNA-124 gene-modified bone
marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation promotes the repair of
spinal cord injury in rats. Exp Mol Med. 49:e3322017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Xu W, Wang X, Li P, Qin K and Jiang X:
miR-124 regulates neural stem cells in the treatment of spinal cord
injury. Neurosci Lett. 529:12–17. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Malhotra R, Lin Z, Vincenz C and Brosius
FC III: Hypoxia induces apoptosis via two independent pathways in
Jurkat cells: Differential regulation by glucose. Am J Physiol Cell
Physiol. 281:C1596–C1603. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Susin SA, Lorenzo HK, Zamzami N, Marzo I,
Snow BE, Brothers GM, Mangion J, Jacotot E, Costantini P, Loeffler
M, et al: Molecular characterization of mitochondrial
apoptosis-inducing factor. Nature. 397:441–446. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|