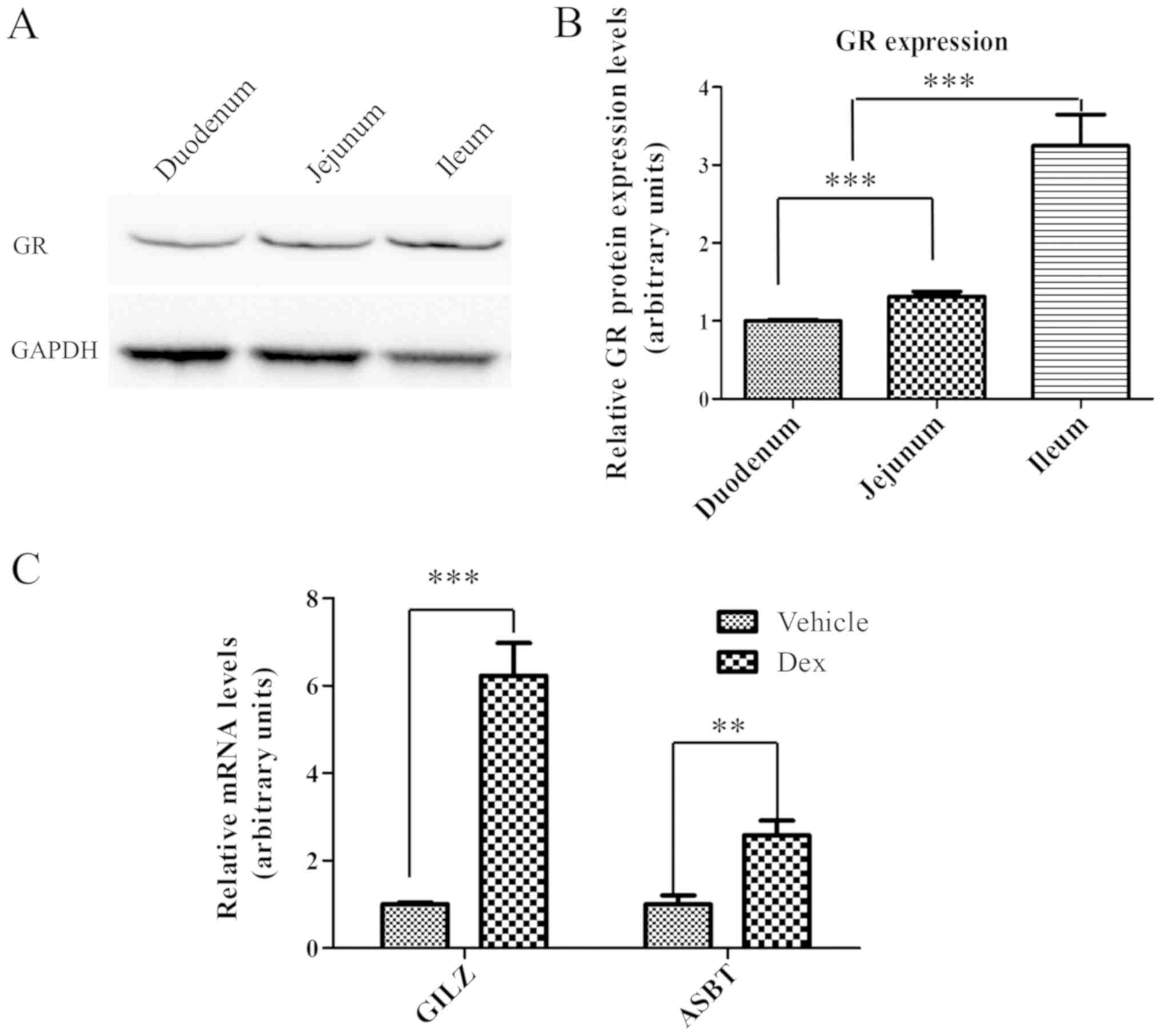
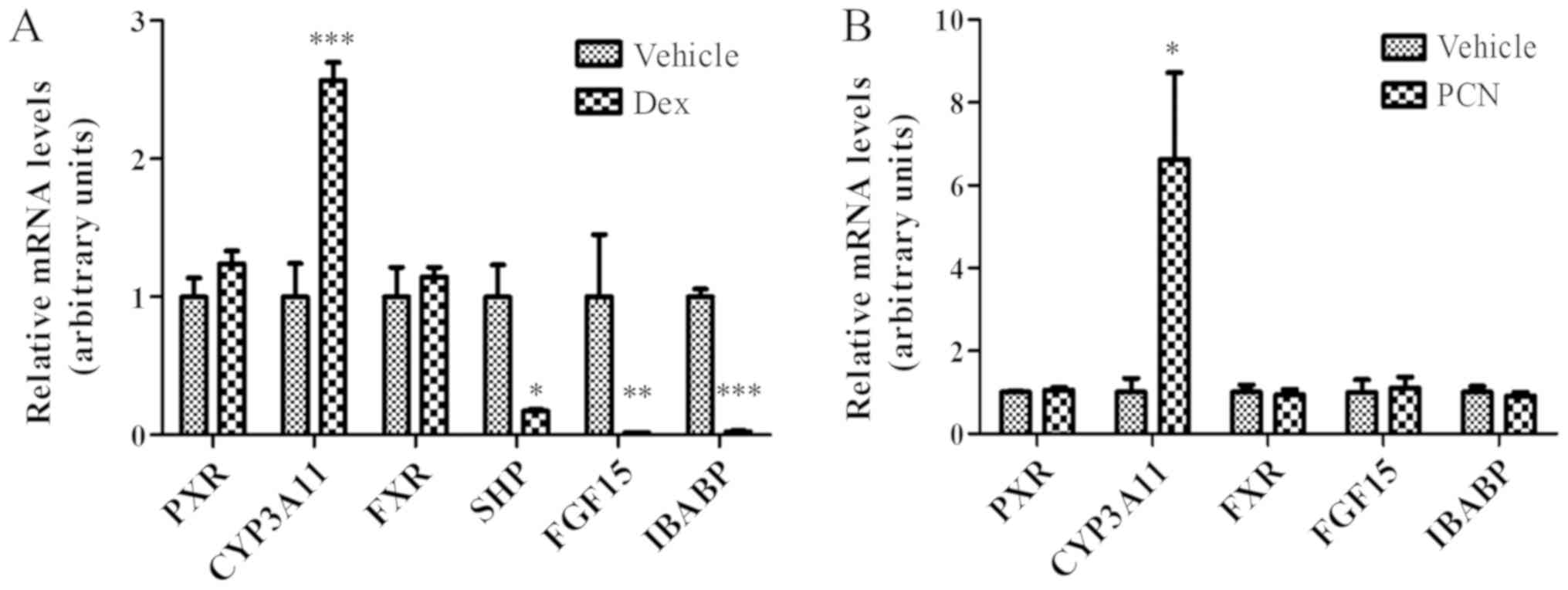
|
1
|
McWhirter JR, Goulding M, Weiner JA, Chun
J and Murre C: A novel fibroblast growth factor gene expressed in
the developing nervous system is a downstream target of the
chimeric homeodomain oncoprotein E2A-Pbx1. Development.
124:3221–3232. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Nishimura T, Utsunomiya Y, Hoshikawa M,
Ohuchi H and Itoh N: Structure and expression of a novel human FGF,
FGF-19, expressed in the fetal brain. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1444:148–151. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Inagaki T, Choi M, Moschetta A, Peng L,
Cummins CL, McDonald JG, Luo G, Jones SA, Goodwin B, Richardson JA,
et al: Fibroblast growth factor 15 functions as an enterohepatic
signal to regulate bile acid homeostasis. Cell Metab. 2:217–225.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Potthoff MJ, Boney-Montoya J, Choi M, He
T, Sunny NE, Satapati S, Suino-Powell K, Xu HE, Gerard RD, Finck
BN, et al: FGF15/19 regulates hepatic glucose metabolism by
inhibiting the CREB-PGC-1α pathway. Cell Metab. 13:729–738. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Fu L, John LM, Adams SH, Yu XX, Tomlinson
E, Renz M, Williams PM, Soriano R, Corpuz R, Moffat B, et al:
Fibroblast growth factor 19 increases metabolic rate and reverses
dietary and leptin-deficient diabetes. Endocrinology.
145:2594–2603. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kir S, Beddow SA, Samuel VT, Miller P,
Previs SF, Suino-Powell K, Xu HE, Shulman GI, Kliewer SA and
Mangelsdorf DJ: FGF19 as a postprandial, insulin-independent
activator of hepatic protein and glycogen synthesis. Science.
331:1621–1624. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Tomlinson E, Fu L, John L, Hultgren B,
Huang X, Renz M, Stephan JP, Tsai SP, Powell-Braxton L, French D
and Stewart TA: Transgenic mice expressing human fibroblast growth
factor-19 display increased metabolic rate and decreased adiposity.
Endocrinology. 143:1741–1747. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Schmidt DR, Holmstrom SR, Fon Tacer K,
Bookout AL, Kliewer SA and Mangelsdorf DJ: Regulation of bile acid
synthesis by fat-soluble vitamins A and D. J Biol Chem.
285:14486–14494. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Reue K, Lee JM and Vergnes L: Diet1 is a
regulator of fibroblast growth factor 15/19-dependent bile acid
synthesis. Dig Dis. 33:307–313. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Baschant U, Lane NE and Tuckermann J: The
multiple facets of glucocorticoid action in rheumatoid arthritis.
Nat Rev Rheumatol. 8:645–655. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Andrews RC and Walker BR: Glucocorticoids
and insulin resistance: Old hormones, new targets. Clin Sci (Lond).
96:513–523. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lemke U, Krones-Herzig A, Berriel Diaz M,
Narvekar P, Ziegler A, Vegiopoulos A, Cato AC, Bohl S, Klingmüller
U, Screaton RA, et al: The glucocorticoid receptor controls hepatic
dyslipidemia through Hes1. Cell Metab. 8:212–223. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yamanishi Y, Nosaka Y, Kawasaki H,
Hirayama C and Ikawa S: Sterol and bile acid metabolism after
short-term prednisolone treatment in patients with chronic active
hepatitis. Gastroenterol Jpn. 20:246–251. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ge H, Zhang J, Gong Y, Gupte J, Ye J,
Weiszmann J, Samayoa K, Coberly S, Gardner J, Wang H, et al:
Fibroblast growth factor receptor 4 (FGFR4) deficiency improves
insulin resistance and glucose metabolism under diet-induced
obesity conditions. J Biol Chem. 289:30470–30480. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Jia K, Li L, Liu Z, Hartog M, Kluetzman K,
Zhang QY and Ding X: Generation and characterization of a novel
CYP2A13-transgenic mouse model. Drug Metab Dispos. 42:1341–1348.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
D'Agostino J, Ding X, Zhang P, Jia K, Fang
C, Zhu Y, Spink DC and Zhang QY: Potential biological functions of
cytochrome P450 reductase-dependent enzymes in small intestine:
Novel link to expression of major histocompatibility complex class
II genes. J Biol Chem. 287:17777–17788. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Schmittgen TD and Livak KJ: Analyszing
real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method. Nat Protoc.
3:1101–1108. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Cariou B, van Harmelen K, Duran-Sandoval
D, van Dijk TH, Grefhorst A, Abdelkarim M, Caron S, Torpier G,
Fruchart JC, Gonzalez FJ, et al: The farnesoid X receptor modulates
adiposity and peripheral insulin sensitivity in mice. J Biol Chem.
281:11039–11049. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Trousson A, Makoukji J, Petit PX, Bernard
S, Slomianny C, Schumacher M and Massaad C: Cross-talk between
oxysterols and glucocorticoids: Differential regulation of secreted
phopholipase A2 and impact on oligodendrocyte death. PLoS One.
4:e80802009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Berrebi D, Bruscoli S, Cohen N, Foussat A,
Migliorati G, Bouchet-Delbos L, Maillot MC, Portier A, Couderc J,
Galanaud P, et al: Synthesis of glucocorticoid-induced leucine
zipper (GILZ) by macrophages: An anti-inflammatory and
immunosuppressive mechanism shared by glucocorticoids and IL-10.
Blood. 101:729–738. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Miyata M, Yamakawa H, Hamatsu M,
Kuribayashi H, Takamatsu Y and Yamazoe Y: Enterobacteria modulate
intestinal bile acid transport and homeostasis through apical
sodium-dependent bile acid transporter (SLC10A2) expression. J
Pharmacol Exp Ther. 336:188–196. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhang QY, Dunbar D and Kaminsky LS:
Characterization of mouse small intestinal cytochrome P450
expression. Drug Metab Dispos. 31:1346–1351. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yamamoto KR: Steroid receptor regulated
transcription of specific genes and gene networks. Annu Rev Genet.
19:209–252. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yamamoto KR, Darimont BD, Wagner RL and
Iñiguez-Lluhí JA: Building transcriptional regulatory complexes:
Signals and surfaces. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 63:587–598.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Weikum ER, Knuesel MT, Ortlund EA and
Yamamoto KR: Glucocorticoid receptor control of transcription:
Precision and plasticity via allostery. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
18:159–174. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ayroldi E and Riccardi C:
Glucocorticoid-induced leucine zipper (GILZ): A new important
mediator of glucocorticoid action. FASEB J. 23:3649–3658. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wang JC, Derynck MK, Nonaka DF,
Khodabakhsh DB, Haqq C and Yamamoto KR: Chromatin
immunoprecipitation (ChIP) scanning identifies primary
glucocorticoid receptor target genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
101:15603–15608. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Jung D, Fantin AC, Scheurer U, Fried M and
Kullak-Ublick GA: Human ileal bile acid transporter gene ASBT
(SLC10A2) is transactivated by the glucocorticoid receptor. Gut.
53:78–84. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Grober J, Zaghini I, Fujii H, Jones SA,
Kliewer SA, Willson TM, Ono T and Besnard P: Identification of a
bile acid-responsive element in the human ileal bile acid-binding
protein gene. Involvement of the farnesoid X
receptor/9-cis-retinoic acid receptor heterodimer. J Biol Chem.
274:29749–29754. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hwang ST, Urizar NL, Moore DD and Henning
SJ: Bile acids regulate the ontogenic expression of ileal bile acid
binding protein in the rat via the farnesoid X receptor.
Gastroenterology. 122:1483–1492. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Huss JM and Kasper CB: Two-stage
glucocorticoid induction of CYP3A23 through both the glucocorticoid
and pregnane X receptors. Mol Pharmacol. 58:48–57. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kliewer SA, Moore JT, Wade L, Staudinger
JL, Watson MA, Jones SA, McKee DD, Oliver BB, Willson TM,
Zetterström RH, et al: An orphan nuclear receptor activated by
pregnanes defines a novel steroid signaling pathway. Cell.
92:73–82. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Dietzman RH, Ersek RA, Bloch JM and
Lilleheir RC: High-output, low-resistance gram-negative septic
shock in man. Angiology. 20:691–700. 1969. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lehmann JM, McKee DD, Watson MA, Willson
TM, Moore JT and Kliewer SA: The human orphan nuclear receptor PXR
is activated by compounds that regulate CYP3A4 gene expression and
cause drug interactions. J Clin Invest. 102:1016–1023. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Schuetz EG and Guzelian PS: Induction of
cytochrome P-450 by glucocorticoids in rat liver. II. Evidence that
glucocorticoids regulate induction of cytochrome P-450 by a
nonclassical receptor mechanism. J Biol Chem. 259:2007–2012.
1984.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Schuetz EG, Wrighton SA, Barwick JL and
Guzelian PS: Induction of cytochrome P-450 by glucocorticoids in
rat liver. I. Evidence that glucocorticoids and pregnenolone 16
alpha-carbonitrile regulate de novo synthesis of a common form of
cytochrome P-450 in cultures of adult rat hepatocytes and in the
liver in vivo. J Biol Chem. 259:1999–2006. 1984.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Lu Y, Zhang Z, Xiong X, Wang X, Li J, Shi
G, Yang J, Zhang X, Zhang H, Hong J, et al: Glucocorticoids promote
hepatic cholestasis in mice by inhibiting the transcriptional
activity of the farnesoid X receptor. Gastroenterology.
143:1630–1640. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|