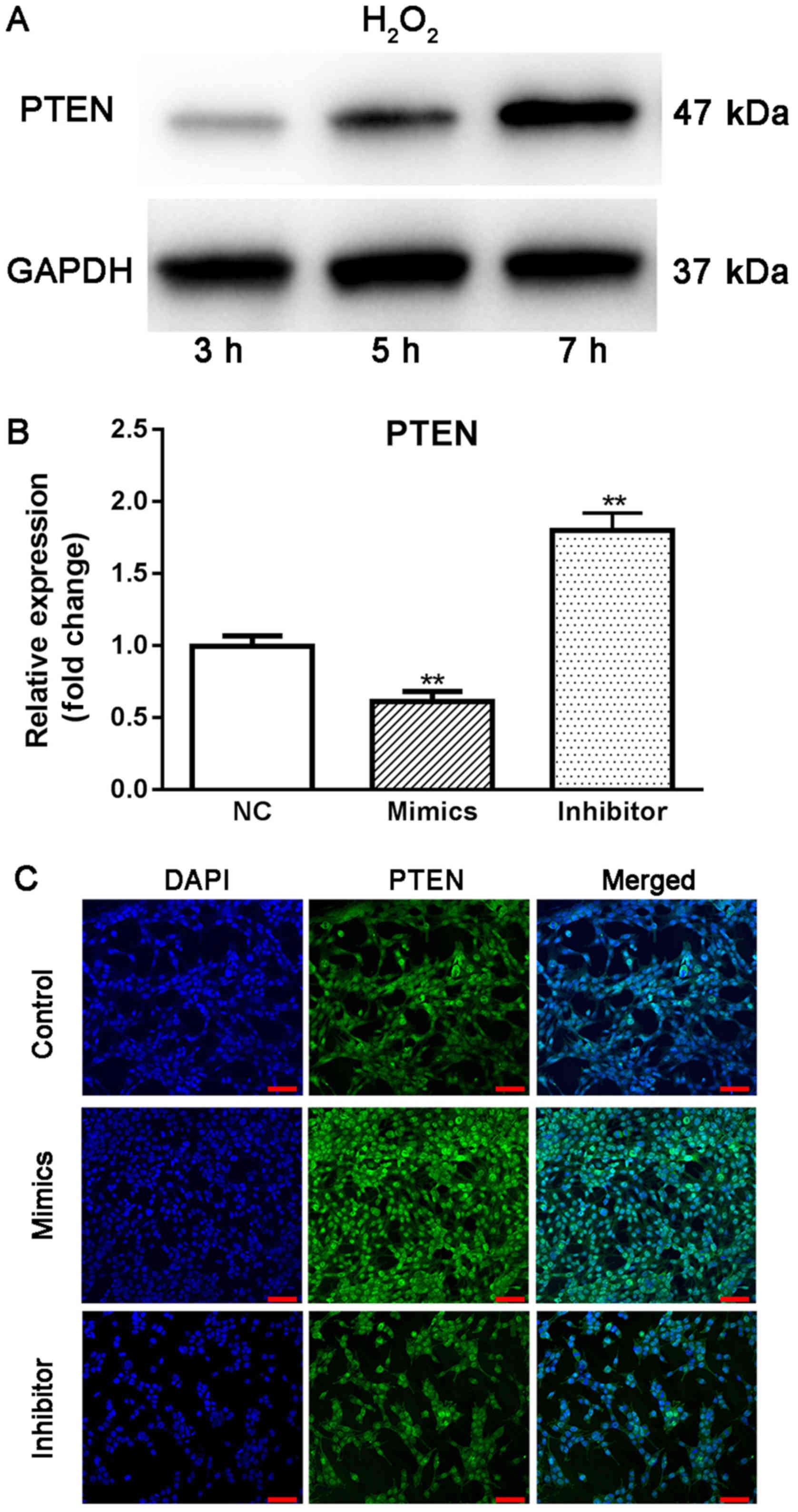
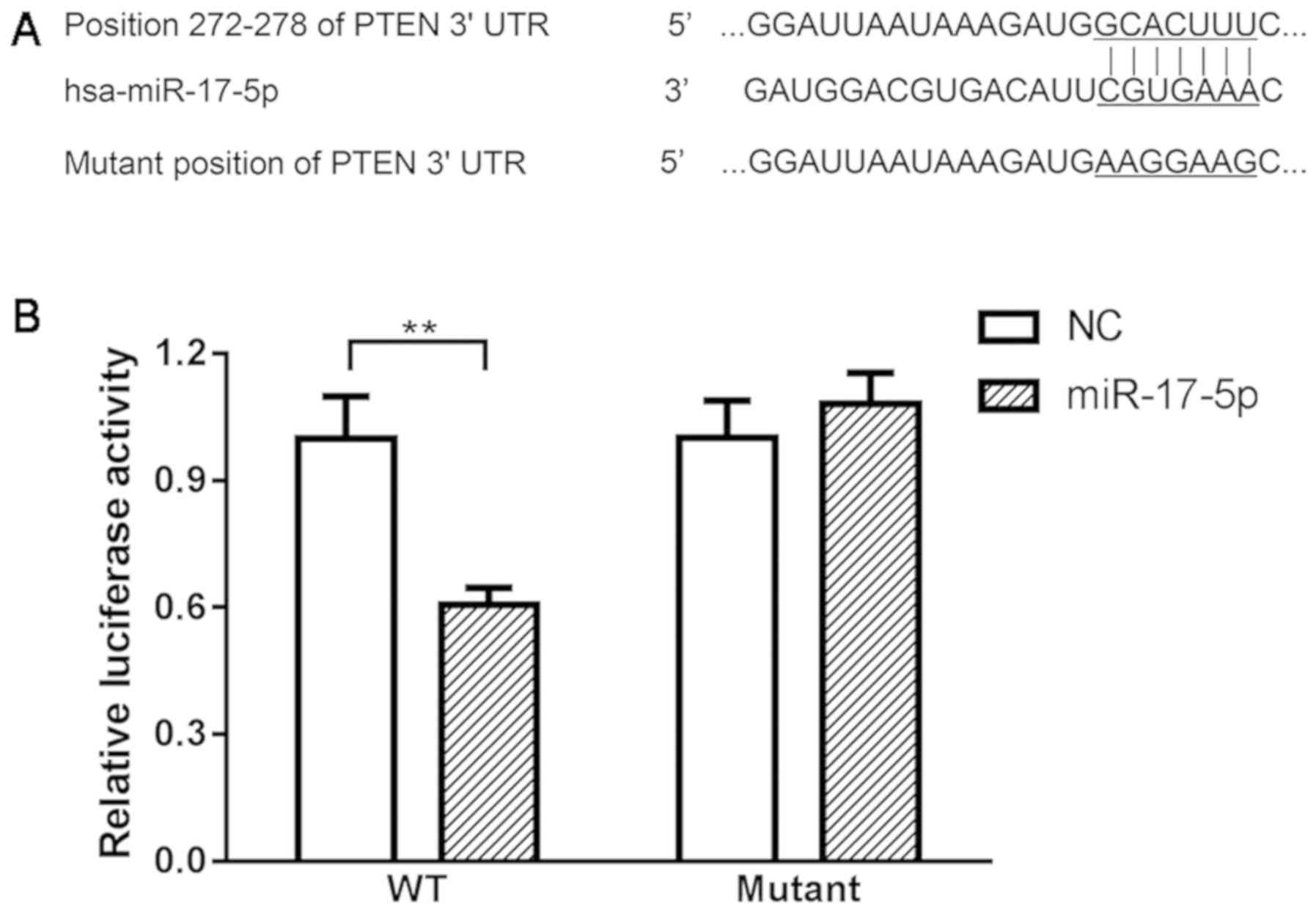
|
1
|
Zhao R, Yin D, Wang E and Si B: The effect
of MTHFR ala222val polymorphism on open-angle glaucoma: a
meta-analysis. Ophthalmic Genet. 36:27–30. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Tham YC, Li X, Wong TY, Quigley HA, Aung T
and Cheng CY: Global prevalence of glaucoma and projections of
glaucoma burden through 2040: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. Ophthalmology. 121:2081–2090. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bailey JN, Loomis SJ, Kang JH, Allingham
RR, Gharahkhani P, Khor CC, Burdon KP, Aschard H, Chasman DI, Igo
RP Jr, et al: Genome-wide association analysis identifies TXNRD2,
ATXN2 and FOXC1 as susceptibility loci for primary open-angle
glaucoma. Nat Genet. 48:189–194. 2016. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Liang YB, Wang NL, Rong SS and Thomas R:
Initial treatment for primary angle-closure glaucoma in China. J
Glaucoma. 24:469–473. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Nongpiur ME, Khor CC, Jia H, Cornes BK,
Chen LJ, Qiao C, Nair KS, Cheng CY, Xu L, George R, et al: ABCC5, a
gene that influences the anterior chamber depth, is associated with
primary angle closure glaucoma. PLoS Genet. 10:e10040892014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Shen W, Han Y, Huang B, Qi Y, Xu L, Guo R,
Wang X and Wang J: MicroRNA-483-3p inhibits extracellular matrix
production by targeting Smad4 in human trabecular meshwork cells.
Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 56:8419–8427. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Xu L, Zhang Y, Guo R, Shen W, Qi Y, Wang
Q, Guo Z, Qi C, Yin H and Wang J: HES1 promotes extracellular
matrix protein expression and inhibits proliferation and migration
in human trabecular meshwork cells under oxidative stress.
Oncotarget. 8:21818–21833. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Feng R, Sang Q, Zhu Y, Fu W, Liu M, Xu Y,
Shi H, Xu Y, Qu R, Chai R, et al: MiRNA-320 in the human follicular
fluid is associated with embryo quality in vivo and affects mouse
embryonic development in vitro. Sci Rep. 5:86892015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Li Y, Cai B, Shen L, Dong Y, Lu Q, Sun S,
Liu S, Ma S, Ma PX and Chen J: MiRNA-29b suppresses tumor growth
through simultaneously inhibiting angiogenesis and tumorigenesis by
targeting Akt3. Cancer Lett. 397:111–119. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Qun L, Wenda X, Weihong S, Jianyang M, Wei
C, Fangzhou L, Zhenyao X and Pingjin G: miRNA-27b modulates
endothelial cell angiogenesis by directly targeting Naa15 in
atherogenesis. Atherosclerosis. 254:184–192. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Falzone L, Candido S, Salemi R, Basile MS,
Scalisi A, McCubrey JA, Torino F, Signorelli SS, Montella M and
Libra M: Computational identification of microRNAs associated to
both epithelial to mesenchymal transition and NGAL/MMP-9 pathways
in bladder cancer. Oncotarget. 7:72758–72766. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bagnoli M, De Cecco L, Granata A,
Nicoletti R, Marchesi E, Alberti P, Valeri B, Libra M, Barbareschi
M, Raspagliesi F, et al: Identification of a chrXq27.3 microRNA
cluster associated with early relapse in advanced stage ovarian
cancer patients. Oncotarget. 2:1265–1278. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Guo R, Shen W, Su C, Jiang S and Wang J:
Relationship between the pathogenesis of glaucoma and miRNA.
Ophthalmic Res. 57:194–199. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Molasy M, Walczak A, Szaflik J, Szaflik JP
and Majsterek I: MicroRNAs in glaucoma and neurodegenerative
diseases. J Hum Genet. 62:105–112. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Paylakhi SH, Yazdani S, April C, Fan JB,
Moazzeni H, Ronaghi M and Elahi E: Non-housekeeping genes expressed
in human trabecular meshwork cell cultures. Mol Vis. 18:241–254.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Tsuchida A, Ohno S, Wu W, Borjigin N,
Fujita K, Aoki T, Ueda S, Takanashi M and Kuroda M: miR-92 is a key
oncogenic component of the miR-17-92 cluster in colon cancer.
Cancer Sci. 102:2264–2271. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhu Y, Gu J, Li Y, Peng C, Shi M, Wang X,
Wei G, Ge O, Wang D, Zhang B, et al: MiR-17-5p enhances pancreatic
cancer proliferation by altering cell cycle profiles via disruption
of RBL2/E2F4-repressing complexes. Cancer Lett. 412:59–68. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Liao XH, Xiang Y, Yu CX, Li JP, Li H, Nie
Q, Hu P, Zhou J and Zhang TC: STAT3 is required for
MiR-17-5p-mediated sensitization to chemotherapy-induced apoptosis
in breast cancer cells. Oncotarget. 8:15763–15774. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Jin T, Wu X, Yang H, Liu M, He Y, He X,
Shi X, Wang F, Du S, Ma Y, et al: Association of the miR-17-5p
variants with susceptibility to cervical cancer in a Chinese
population. Oncotarget. 7:76647–76655. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Shi J, Bei Y, Kong X, Liu X, Lei Z, Xu T,
Wang H, Xuan Q, Chen P, Xu J, et al: miR-17-3p contributes to
exercise-induced cardiac growth and protects against myocardial
ischemia-reperfusion injury. Theranostics. 7:664–676. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tan L, Meng L, Shi X and Yu B: Knockdown
of microRNA-17-5p ameliorates atherosclerotic lesions in ApoE-/-
mice and restores the expression of very low density lipoprotein
receptor. Biotechnol Lett. 39:967–976. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Li G, Luna C, Qiu J, Epstein DL and
Gonzalez P: Alterations in microRNA expression in stress-induced
cellular senescence. Mech Ageing Dev. 130:731–741. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yu AL, Fuchshofer R, Kampik A and
Welge-Lüssen U: Effects of oxidative stress in trabecular meshwork
cells are reduced by prostaglandin analogues. Invest Ophthalmol Vis
Sci. 49:4872–4880. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chen M, Liu B, Gao Q, Zhuo Y and Ge J:
Mitochondria-targeted peptide MTP-131 alleviates mitochondrial
dysfunction and oxidative damage in human trabecular meshwork
cells. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 52:7027–7037. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wang Y, Li F and Wang S: MicroRNA-93 is
overexpressed and induces apoptosis in glaucoma trabecular meshwork
cells. Mol Med Rep. 14:5746–5750. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Luna C, Li G, Qiu J, Epstein DL and
Gonzalez P: MicroRNA-24 regulates the processing of latent TGFβ1
during cyclic mechanical stress in human trabecular meshwork cells
through direct targeting of FURIN. J Cell Physiol. 226:1407–1414.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Reshi L, Wang HV, Hui CF, Su YC and Hong
JR: Anti-apoptotic genes Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL overexpression can block
iridovirus serine/threonine kinase-induced
Bax/mitochondria-mediated cell death in GF-1 cells. Fish Shellfish
Immunol. 61:120–129. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yang J and Yao S: JNK-Bcl-2/Bcl-xL-Bax/Bak
pathway mediates the crosstalk between matrine-induced autophagy
and apoptosis via interplay with Beclin 1. Int J Mol Sci.
16:25744–25758. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Liu H, Pan Y, Han X, Liu J and Li R:
MicroRNA-216a promotes the metastasis and epithelial-mesenchymal
transition of ovarian cancer by suppressing the PTEN/AKT pathway.
Onco Targets Ther. 10:2701–2709. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ronen S, Abbott DW, Kravtsov O, Abdelkader
A, Xu Y, Banerjee A and Iczkowski KA: PTEN loss and p27 loss differ
among morphologic patterns of prostate cancer, including
cribriform. Hum Pathol. 65:85–91. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Feng Y, Zou W, Hu C, Li G, Zhou S, He Y,
Ma F, Deng C and Sun L: Modulation of CASC2/miR-21/PTEN pathway
sensitizes cervical cancer to cisplatin. Arch Biochem Biophys.
623-624:20–30. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Li S, Shen Y, Wang M and Yang J, Lv M, Li
P, Chen Z and Yang J: Loss of PTEN expression in breast cancer:
Association with clinicopathological characteristics and prognosis.
Oncotarget. 8:32043–32054. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Tellios N, Belrose JC, Tokarewicz AC,
Hutnik C, Liu H, Leask A, Motolko M, Iijima M and Parapuram SK:
TGF-β induces phosphorylation of phosphatase and tensin homolog:
Implications for fibrosis of the trabecular meshwork tissue in
glaucoma. Sci Rep. 7:8122017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|