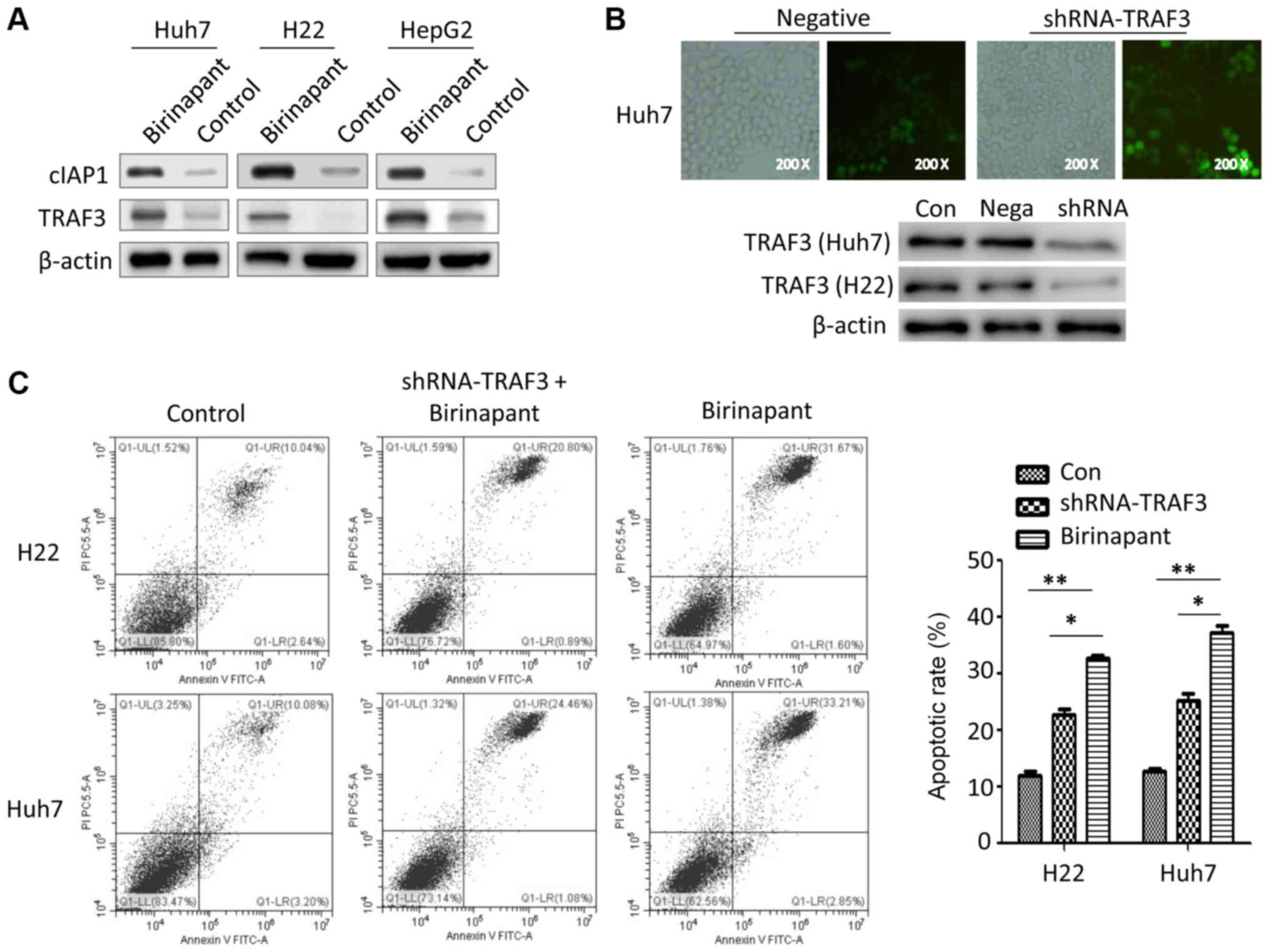
|
1
|
Bruix J, Gores GJ and Mazzaferro V:
Hepatocellular carcinoma: Clinical frontiers and perspectives. Gut.
63:844–855. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hartke J, Johnson M and Ghabril M: The
diagnosis and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Semin Diagn
Pathol. 34:153–159. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Boddu P, Carter BZ, Verstovsek S and
Pemmaraju N: SMAC mimetics as potential cancer therapeutics in
myeloid malignancies. Br J Haematol. 185:219–231. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Cossu F, Milani M, Mastrangelo E and Lecis
D: Targeting the BIR domains of inhibitor of apoptosis (IAP)
proteins in cancer treatment. Comput Struct Biotechnol J.
17:142–150. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Pedersen J, LaCasse EC, Seidelin JB,
Coskun M and Nielsen OH: Inhibitors of apoptosis (IAPs) regulate
intestinal immunity and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD)
inflammation. Trends Mol Med. 20:652–665. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chromik J, Safferthal C, Serve H and Fulda
S: Smac mimetic primes apoptosis-resistant acute myeloid leukaemia
cells for cytarabine-induced cell death by triggering necroptosis.
Cancer Lett. 344:101–109. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Nikkhoo A, Rostami N, Hojjat-Farsangi M,
Azizi G, Yousefi B, Ghalamfarsa G and Jadidi-Niaragh F: Smac
mimetics as novel promising modulators of apoptosis in the
treatment of breast cancer. J Cell Biochem. 120:9300–9314. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Abhari BA, McCarthy N, Le Berre M,
Kilcoyne M, Joshi L, Agostinis P and Fulda S: Smac mimetic
suppresses tunicamycin-induced apoptosis via resolution of ER
stress. Cell Death Dis. 10:1552019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Gerges S, Rohde K and Fulda S: Cotreatment
with Smac mimetics and demethylating agents induces both apoptotic
and necroptotic cell death pathways in acute lymphoblastic leukemia
cells. Cancer Lett. 375:127–132. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Brumatti G, Ma C, Lalaoui N, Nguyen NY,
Navarro M, Tanzer MC, Richmond J, Ghisi M, Salmon JM, Silke N, et
al: The caspase-8 inhibitor emricasan combines with the SMAC
mimetic birinapant to induce necroptosis and treat acute myeloid
leukemia. Sci Transl Med. 8:339ra692016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Shu X, Zhu Z, Cao D, Zheng L, Wang F, Pei
H, Wen J, Yang J, Li D, Bai P, et al: PEG-derivatized birinapant as
a nanomicellar carrier of paclitaxel delivery for cancer therapy.
Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 182:1103562019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Liu H, Liao R, He K, Zhu X, Li P and Gong
J: The SMAC mimetic birinapant attenuates
lipopolysaccharide-induced liver injury by inhibiting the tumor
necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 3 degradation in Kupffer
cells. Immunol Lett. 85:79–83. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Ho PC, Tsui YC, Feng X, Greaves DR and Wei
LN: NF-κB-mediated degradation of the coactivator RIP140 regulates
inflammatory responses and contributes to endotoxin tolerance. Nat
Immunol. 13:379–386. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liu Z, Mar KB, Hanners NW, Perelman SS,
Kanchwala M, Xing C, Schoggins JW and Alto NM: A NIK-SIX signalling
axis controls inflammation by targeted silencing of non-canonical
NF-κB. Nature. 68:249–253. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Mi L, Zhou Y, Wu D, Tao Q, Wang X, Zhu H,
Gao X, Wang J, Ling R, Deng J, et al: ACSS2/AMPK/PCNA
pathway-driven proliferation and chemoresistance of esophageal
squamous carcinoma cells under nutrient stress. Mol Med Rep.
20:5286–5296. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sato Y, Yoshino H, Kazama Y and
Kashiwakura I: Involvement of caspase-8 in apoptosis enhancement by
cotreatment with retinoic acid-inducible gene-I-like receptor
agonist and ionizing radiation in human non-small cell lung cancer.
Mol Med Rep. 18:5286–5294. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Razmkhah M, Abtahi S and Ghaderi A:
Mesenchymal stem cells, immune cells and tumor cells crosstalk: A
sinister triangle in the tumor microenvironment. Curr Stem Cell Res
Ther. 14:43–51. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Jin Y, Meng X, Qiu Z, Su Y, Yu P and Qu P:
Anti-tumor and anti-metastatic roles of cordycepin, one bioactive
compound of Cordyceps militaris. Saudi J Biol Sci.
25:991–995. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Verhagen AM and Vaux DL: Cell death
regulation by the mammalian IAP antagonist Diablo/Smac. Apoptosis.
7:163–166. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Soung YH, Park WS, Nam SW, Lee JY, Yoo NJ
and Lee SH: SMAC/DIABLO mutation is uncommon in gastric and
colorectal carcinomas. Pathology. 38:85–87. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Cekay MJ, Roesler S, Frank T, Knuth AK,
Eckhardt I and Fulda S: Smac mimetics and type II interferon
synergistically induce necroptosis in various cancer cell lines.
Cancer Lett. 410:228–237. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Bhatti IA, Abhari BA and Fulda S:
Identification of a synergistic combination of Smac mimetic and
Bortezomib to trigger cell death in B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma
cells. Cancer Lett. 405:63–72. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Tseng PH, Matsuzawa A, Zhang W, Mino T,
Vignali DA and Karin M: Different modes of ubiquitination of the
adaptor TRAF3 selectively activate the expression of type I
interferons and proinflammatory cytokines. Nat Immunol. 11:70–75.
2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lin WW, Hostager BS and Bishop GA: TRAF3,
ubiquitination, and B-lymphocyte regulation. Immunol Rev.
266:46–55. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wen J, Bai H, Chen N, Zhang W, Zhu X, Li P
and Gong J: USP25 promotes endotoxin tolerance via suppressing
K48-linked ubiquitination and degradation of TRAF3 in Kupffer
cells. Mol Immunol. 106:53–62. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Guan K, Wei C, Zheng Z, Song T, Wu F,
Zhang Y, Cao Y, Ma S, Chen W, Xu Q, et al: MAVS promotes
inflammasome activation by targeting ASC for K63-linked
ubiquitination via the E3 ligase TRAF3. J Immunol. 194:4880–4890.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Muro I, Fang G, Gardella KA, Mahajan IM
and Wright CW: The TRAF3 adaptor protein drives proliferation of
anaplastic large cell lymphoma cells by regulating multiple
signaling pathways. Cell Cycle. 13:1918–1927. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Eytan DF, Snow GE, Carlson S, Derakhshan
A, Saleh A, Schiltz S, Cheng H, Mohan S, Cornelius S, Coupar J, et
al: SMAC Mimetic birinapant plus radiation eradicates human head
and neck cancers with genomic amplifications of cell death genes
FADD and BIRC2. Cancer Res. 76:5442–5454. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhu X, Shen X, Qu J, Straubinger RM and
Jusko WJ: Multi-scale network model supported by proteomics for
analysis of combined gemcitabine and birinapant effects in
pancreatic cancer cells. CPT Pharmacometrics Syst Pharmacol.
7:549–561. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|