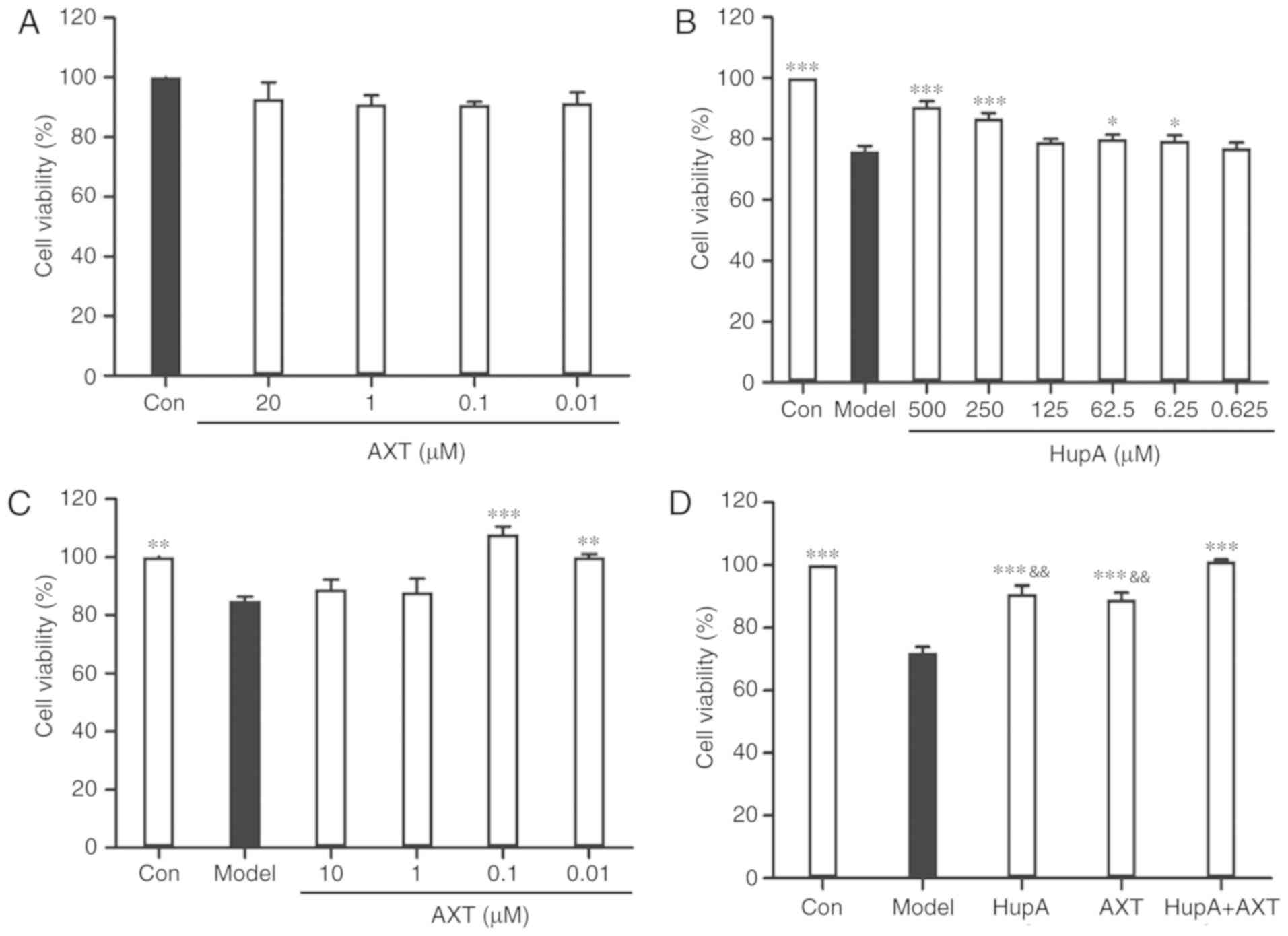
|
1
|
Migdal C and Serres M: Reactive oxygen
species and oxidative stress. Med Sci (Paris). 27:405–412. 2011.(In
French). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Byun EB, Park WY, Kim WS, Song HY, Sung NY
and Byun EH: Neuroprotective effect of Capsicum annuum var.
Abbreviatum against hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative stress in
HT22 hippocampus cells. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 82:2149–2157.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sullivan PG, Rabchevsky AG, Waldmeier PC
and Springer JE: Mitochondrial permeability transition in CNS
trauma: Cause or effect of neuronal cell death? J Neurosci Res.
79:231–239. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Namioka N, Hanyu H, Hirose D, Hatanaka H,
Sato T and Shimizu S: Oxidative stress and inflammation are
associated with physical frailty in patients with Alzheimer's
disease. Geriater Gerontol Int. 17:913–918. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Sankhla CS: Oxidative stress and
Parkinson's disease. Neurol India. 65:269–270. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Uttara B, Singh AV, Zamboni P and Mahajan
RT: Oxidative stress and neurodegenerative diseases: A review of
upstream and downstream antioxidant therapeutic options. Curr
Neuropharmacol. 7:65–74. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wadhwa R, Gupta R and Maurya PK: Oxidative
stress and accelerated aging in neurodegenerative and
neuropsychiatric disorder. Curr Pharm Des. 24:4711–4725. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Shinotoh H, Namba H, Fukushi K, Nagatsuka
S, Tanaka N, Aotsuka A, Ota T, Tanada S and Irie T: Progressive
loss of cortical acetylcholinesterase activity in association with
cognitive decline in Alzheimer's disease: A positron emission
tomography study. Ann Neurol. 48:194–200. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Mimica N and Presecki P: Side effects of
approved antidementives. Psychiat Danub. 21:108–113. 2009.
|
|
10
|
Cheng DH, Ren H and Tang XC: Huperzine A,
a novel promising acetylcholinesterase inhibitor. Neuroreport.
8:97–101. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang R, Zhang HY and Tang XC: Huperzine A
attenuates cognitive dysfunction and neuronal degeneration caused
by beta-amyloid protein-(1–40) in rat. Eur J Pharmacol.
421:149–156. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Mei Z, Zheng P, Tan X, Wang Y and Situ B:
Huperzine A alleviates neuroinflammation, oxidative stress and
improves cognitive function after repetitive traumatic brain
injury. Metab Brain Dis. 32:1861–1869. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Xu Z and Wang Y: Huperzine A attenuates
hepatic ischemia reperfusion injury via anti-oxidative and
anti-apoptotic pathways. Mol Med Rep. 10:701–706. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Shi Q, Fu J, Ge D, He Y, Ran J, Liu Z, Wei
J, Diao T and Lu Y: Huperzine A ameliorates cognitive deficits and
oxidative stress in the hippocampus of rats exposed to acute
hypobaric hypoxia. Neurochem Res. 37:2042–2052. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Pohanka M, Zemek F, Bandouchova H and
Pikula J: Toxicological scoring of Alzheimer's disease drug
huperzine in a guinea pig model. Toxicol Mech Methods. 22:231–235.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhang HY, Zheng CY, Yan H, Wang ZF, Tang
LL, Gao X and Tang XC: Potential therapeutic targets of huperzine A
for Alzheimer's disease and vascular dementia. Chem Biol Interact.
175:396–402. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Gao X and Tang XC: Huperzine A attenuates
mitochondrial dysfunction in beta-amyloid-treated PC12 cells by
reducing oxygen free radicals accumulation and improving
mitochondrial energy metabolism. J Neurosci Res. 83:1048–1057.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Xiao XQ, Wang R and Tang XC: Huperzine A
and tacrine attenuate beta-amyloid peptide-induced oxidative
injury. J Neurosci Res. 61:564–569. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Xiao XQ, Wang R, Han YF and Tang XC:
Protective effects of huperzine A on beta-amyloid(25–35) induced
oxidative injury in rat pheochromocytoma cells. Neurosci Lett.
286:155–158. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Saxena G, Singh SP, Agrawal R and Nath C:
Effect of donepezil and tacrine on oxidative stress in
intracerebral streptozotocin-induced model of dementia in mice. Eur
J Pharmacol. 581:283–289. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ambati RR, Phang SM, Ravi S and
Aswathanarayana RG: Astaxanthin: Sources, extraction, stability,
biological activities and its commercial applications-a review. Mar
Drugs. 12:128–152. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Naguib YM: Antioxidant activities of
astaxanthin and related carotenoids. J Agric Food Chem.
48:1150–1154. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yang Y, Liu X, Huang J, Zhong Y, Mao Z,
Xiao H, Li M and Zhuo Y: Inhibition of p38 mitogen-activated
protein kinase phosphorylation decrease tert-butyl
hydroperoxide-induced apoptosis in human trabecular meshwork cells.
Mol Vis. 18:2127–2136. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Brookmeyer R, Johnson E, Ziegler-Graham K
and Arrighi HM: Forecasting the global burden of Alzheimer's
disease. Alzheimers Dement. 3:186–191. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wu W, Liu BH, Xie CL, Xia XD and Zhang YM:
Neuroprotective effects of N-acetyl cysteine on primary hippocampus
neurons against hydrogen peroxide-induced injury are mediated via
inhibition of mitogen-activated protein kinases signal transduction
and antioxidative action. Mol Med Rep. 17:6647–6654.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lee JH, Park SY, Shin YW, Kim CD, Lee WS
and Hong KW: Concurrent administration of cilostazol with donepezil
effectively improves cognitive dysfunction with increased
neuroprotection after chronic cerebral hypoperfusion in rats. Brain
Res. 1185:246–255. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Cachard-Chastel M, Devers S, Sicsic S,
Langlois M, Lezoualc'H F, Gardier AM and Belzung C: Prucalopride
and donepezil act synergistically to reverse scopolamine-induced
memory deficit in C57Bl/6j mice. Behav Brain Res. 187:455–461.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ma S, Liu X, Xun Q and Zhang X:
Neuroprotective effect of Ginkgolide K against H2O2-induced PC12
cell cytotoxicity by ameliorating mitochondrial dysfunction and
oxidative stress. Biol Pharm Bull. 37:217–225. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhang Z, Lv Z, Shao Y, Qiu Q, Zhang W,
Duan X, Li Y and Li C: Microsomal glutathione transferase 1
attenuated ROS-induced lipid peroxidation in Apostichopus
japonicus. Dev Comp Immunol. 73:79–87. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Suzuki S, Miyachi Y, Niwa Y and Isshiki N:
Significance of reactive oxygen species in distal flap necrosis and
its salvage with liposomal SOD. Br J Plast Surg. 42:559–564. 1989.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|