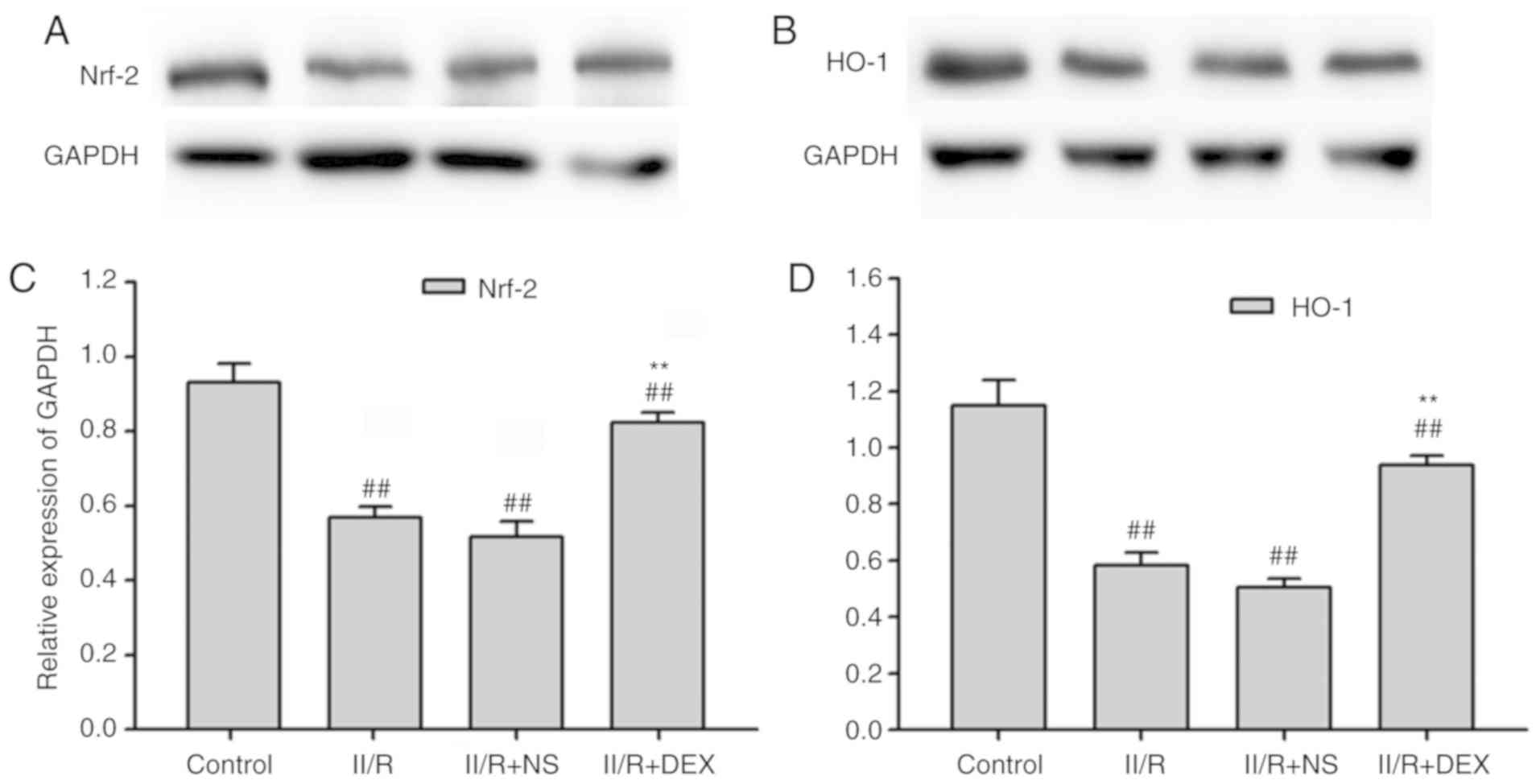
|
1
|
Chen LW, Egan L, Li ZW, Greten FR, Kagnoff
MF and Karin M: The two faces of IKK and NF-kappaB inhibition:
Prevention of systemic inflammation but increased local injury
following intestinal ischemia-reperfusion. Nat Med. 9:575–581.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Mallick IH, Yang W, Winslet MC and
Seifalian AM: Ischemia-reperfusion injury of the intestine and
protective strategies against injury. Dig Dis Sci. 49:1359–1377.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Li Y, Wen S, Yao X, Liu W, Shen J, Deng W,
Tang J, Li C and Liu K: MicroRNA-378 protects against intestinal
ischemia/reperfusion injury via a mechanism involving the
inhibition of intestinal mucosal cell apoptosis. Cell Death Dis.
8:e31272017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Tadros T, Traber DL, Heggers JP and
Herndon DN: Effects of interleukin-1alpha administration on
intestinal ischemia and reperfusion injury, mucosal permeability,
and bacterial translocation in burn and sepsis. Ann Surg.
237:101–109. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Higuchi S, Wu R, Zhou M, Marini CP,
Ravikumar TS and Wang P: Gut hyperpermiability after ischemia and
reperfusion: Attenuation with adrenomedullin and its binding
protein treatment. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 1:409–418.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Isik A, Peker K, Gursul C, Sayar I, Firat
D, Yilmaz I and Demiryilmaz I: The effect of ozone and naringin on
intestinal ischemia/reperfusion injury in an experimental model.
Int J Surg. 21:38–44. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chiang CH, Pai HI and Liu SL:
Ventilator-induced lung injury (VILI) promotes ischemia/reperfusion
lung injury (I/R) and NF-kappaB antibody attenuates both injuries.
Resuscitation. 79:147–154. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Rahman I, Marwick J and Kirkham P: Redox
modulation of chromatin remodeling: Impact on histone acetylation
and deacetylation, NF-kappaB and pro-inflammatory gene expression.
Biochem Pharmacol. 68:1255–1267. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Li A, Yuen VM, Goulay-Dufay S and Kwok PC:
Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of dexmedetomidine. Drug Dev
Ind Pharm. 42:1917–1927. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sha J, Zhang H, Zhao Y, Feng X, Hu X, Wang
C, Song M and Fan H: Dexmedetomidine attenuates
lipopolysaccharide-induced liver oxidative stress and cell
apoptosis in rats by increasing GSK-3β/MKP-1/Nrf2 pathway activity
via the a2 adrenergic receptor. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol.
364:144–152. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Han J, Wang M, Jing X, Shi H, Ren M and
Lou H: (−)-Epigallocatechin gallate protects against cerebral
ischemia-induced oxidative stress via Nrf2/ARE signaling. Neurochem
Res. 39:1292–1299. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Li L, Dong H, Song E, Xu X, Liu L and Song
Y: Nrf2/ARE pathway activation, HO-1 and NQO1 induction by
polychlorinated biphenyl quinone is associated with reactive oxygen
species and PI3K/AKT signaling. Chem Biol Interact. 209:56–67.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sies H, Berndt C and Jones DP: Oxidative
atress. Annu Rev Biochem. 86:715–748. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Athale J, Ulrich A, MacGarvey NC, Bartz
RR, Welty-Wolf KE, Suliman HB and Piantadosi CA: Nrf2 promotes
alveolar mitochondrial biogenesis and resolution of lung injury in
Staphylococcus aureus pneumonia in mice. Free Radic Biol Med.
53:1584–1294. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
National Research Council (US) Committee
for the Update of the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory
Animals. Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. 8th.
Washington (DC): National Academies Press (US); 2011
|
|
16
|
Zhang XY, Liu ZM, Wen SH, Li YS, Li Y, Yao
X, Huang WQ and Liu KX: Dexmedetomidine administration before, but
not after, ischemia attenuates intestinal injury induced by
intestinal ischemia-reperfusion in rats. Anesthesiology.
116:1035–1046. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Stefanutti G, Pierro A, Parkinson EJ,
Smith VV and Eaton S: Moderate hypothermia as a rescue therapy
against intestinal ischemia and reperfusion injury in the rat. Crit
Care Med. 36:1564–1572. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Li J, Chen Q, He X, Alam A, Ning J, Yi B,
Lu K and Gu J: Dexmedetomidine attenuates lung apoptosis induced by
renal ischemia-reperfusion injury through a2AR/PI3K/Akt pathway. J
Transl Med. 16:782018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Fu C, Dai X, Yang Y, Lin M, Cai Y and Cai
S: Dexmedetomidine attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung
injury by inhibiting oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction
and apoptosis in rats. Mol Med Rep. 15:131–138. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Xue BB, Chen BH, Tang YN, Weng CW and Lin
LN: Dexmedetomidine protects against lung injury induced by limb
ischemia-reperfusion via the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB pathway. Kaohsiung J
Med Sci. 35:672–678. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang W and Zhang J: Dexmedetomidine
preconditioning protects against lung injury induced by
ischemia-reperfusion through inhibition of autophagy. Exp Ther Med.
14:973–980. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Liang S, Wang Y and Liu Y: Dexmedetomidine
alleviates lung ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats by activating
PI3K/Akt pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 23:370–377.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Dong WW, Liu YJ, Lv Z, Mao YF, Wang YW,
Zhu XY and Jiang L: Lung endothelial barrier protection by
resveratrol involves inhibition of HMGB1 release and HMGB1-induced
mitochondrial oxidative damage via an Nrf2-dependent mechanism.
Free Radic Biol Med. 88:404–416. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Pryor WA and Stanley JP: Letter: A
suggested mechanism for the production of malonaldehyde during the
autoxidation of polyunsaturated fatty acids. Nonenzymatic
production of prostaglandin endoperoxides during autoxidation. J
Org Chem. 40:3615–3617. 1975. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hayyan M, Hashim MA and AlNashef IM:
Superoxide Ion: Generation and chemical implications. Chem Rev.
116:3029–3085. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Eltzschig HK and Eckle T: Ischemia and
reperfusion-from mechanism to translation. Nat Med. 17:1391–1401.
2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Toth B, Alexander M, Daniel T, Chaudry IH,
Hubbard WJ and Schwacha MG: The role of gammadelta T cells in the
regulation of neutrophil-mediated tissue damage after thermal
injury. J Leukoc Biol. 76:545–552. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Coursin DB, Coursin DB and Maccioli GA:
Dexmedetomidine. Curr Opin Crit Care. 7:221–226. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chen Z, Ding T and Ma CG: Dexmedetomidine
(DEX) protects against hepatic ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury by
suppressing inflammation and oxidative stress in NLRC5 deficient
mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 493:1143–1150. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Si Y, Bao H, Han L, Chen L, Zeng L, Jing
L, Xing Y and Geng Y: Dexmedetomidine attenuation of renal
ischaemia-reperfusion injury requires sirtuin 3 activation. Br J
Anaesth. 121:1260–1271. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Fang B, Li XQ, Bi B, Tan WF, Liu G, Zhang
Y and Ma H: Dexmedetomidine attenuates blood-spinal cord barrier
disruption induced by spinal cord ischemia reperfusion injury in
rats. Cell Physiol Biochem. 36:373–383. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yuan F, Fu H, Sun K, Wu S and Dong T:
Effect of dexmedetomidine on cerebral ischemia-reperfusion rats by
activating mitochondrial ATP-sensitive potassium channel. Metab
Brain Dis. 32:539–546. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Cheng X, Hu J, Wang Y, Ye H, Li X, Gao Q
and Li Z: Effects of dexmedetomidine postconditioning on myocardial
Ischemia/Reperfusion injury in diabetic rats: Role of the
PI3K/Akt-dependent signaling pathway. J Diabetes Res.
2018:30719592018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Cui J, Zhao H, Wang C, Sun JJ, Lu K and Ma
D: Dexmedetomidine attenuates oxidative stress induced lung
alveolar epithelial cell apoptosis in vitro. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2015:3583962015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Gao S, Wang Y, Zhao J and Su A: Effects of
dexmedetomidine pretreatment on heme oxygenase-1 expression and
oxidative stress during one-lung ventilation. Int J Clin Exp
Pathol. 8:3144–3149. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ward PA: Oxidative stress: Acute and
progressive lung injury. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1203:53–59. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Lei J, Wei Y, Song P, Li Y, Zhang T, Feng
Q and Xu G: Cordycepin inhibits LPS-induced acute lung injury by
inhibiting inflammation and oxidative stress. Eur J Pharmacol.
818:110–114. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
McCord JM and Edeas MA: SOD, oxidative
stress and human pathologies: A brief history and a future vision.
Biomed Pharmacother. 59:139–142. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Paris A and Tonner PH: Dexmedetomidine in
anaesthesia. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 18:412–418. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Carollo DS, Nossaman BD and Ramadhyani U:
Dexmedetomidine: A review of clinical applications. Curr Opin
Anaesthesiol. 21:457–461. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Poljsak B, Suput D and Milisav I:
Achieving the balance between ROS and antioxidants: When to use the
synthetic antioxidants. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2013:9567922013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Zhao W, Gan X, Su G, Wanling G, Li S, Hei
Z, Yang C and Wang H: The interaction between oxidative stress and
mast cell activation plays a role in acute lung injuries induced by
intestinal ischemia-reperfusion. J Surg Res. 187:542–552. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Hybertson BM and Gao B: Role of the Nrf2
signaling system in health and disease. Clin Genet. 86:447–452.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
de Roos B and Duthie GG: Role of dietary
pro-oxidants in the maintenance of health and resilience to
oxidative stress. Mol Nutr Food Res. 59:1229–1248. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Tkachev VO, Menshchikova EB and Zenkov NK:
Mechanism of the Nrf2/Keap1/ARE signaling system. Biochemistry
(Mosc). 76:407–422. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Yan X, Cheng X, Zhou L, He X, Zheng W and
Chen H: Dexmedetomidine alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced lung
injury in Wistar rats. Oncotarget. 8:44410–44417. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Nadatani Y, Watanabe T, Shimada S, Otani
K, Tanigawa T and Fujiwara Y: Microbiome and intestinal
ischemia/reperfusion injury. J Clin Biochem Nutr. 63:26–32. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Bellingan GJ: The pulmonary physician in
critical care* 6: The pathogenesis of ALI/ARDS. Thorax. 57:540–546.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Souza DG, Vieira AT, Soares AC, Pinho V,
Nicoli JR, Vieira LQ and Teixeira MM: The essential role of the
intestinal microbiota in facilitating acute inflammatory responses.
J Immunol. 173:4137–4146. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Tamion F, Richard V, Lyoumi S, Daveau M,
Bonmarchand G, Leroy J, Thuillez C and Lebreton JP: Gut ischemia
and mesenteric synthesis of inflammatory cytokines after
hemorrhagic or endotoxic shock. Am J Physiol. 273:G314–G321.
1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Ware LB and Matthay MA: The acute
respiratory distress syndrome. N Engl J Med. 342:1334–1349. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Cui T, Miksa M, Wu R, Komura H, Zhou M,
Dong W, Wang Z, Higuchi S, Chaung W, Blau SA, et al: Milk fat
globule epidermal growth factor 8 attenuates acute lung injury in
mice after intestinal ischemia and reperfusion. Am J Respir Crit
Care Med. 181:238–246. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Chen H, Bai C and Wang X: The value of the
lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury model in respiratory
medicine. Expert Rev Respir Med. 4:773–783. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Zu G, Zhou T, Che N and Zhang X:
Salvianolic acid A protects against oxidative stress and apoptosis
induced by intestinal ischemia-reperfusion injury through
activation of Nrf2/HO-1 pathways. J Biol Chem. 49:2320–2332.
2018.
|
|
56
|
Fan J, Xu G, Jiang T and Qin Y:
Pharmacologic induction of heme oxygenase-1 plays a protective role
in diabetic retinopathy in rats. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci.
53:6541–6556. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|