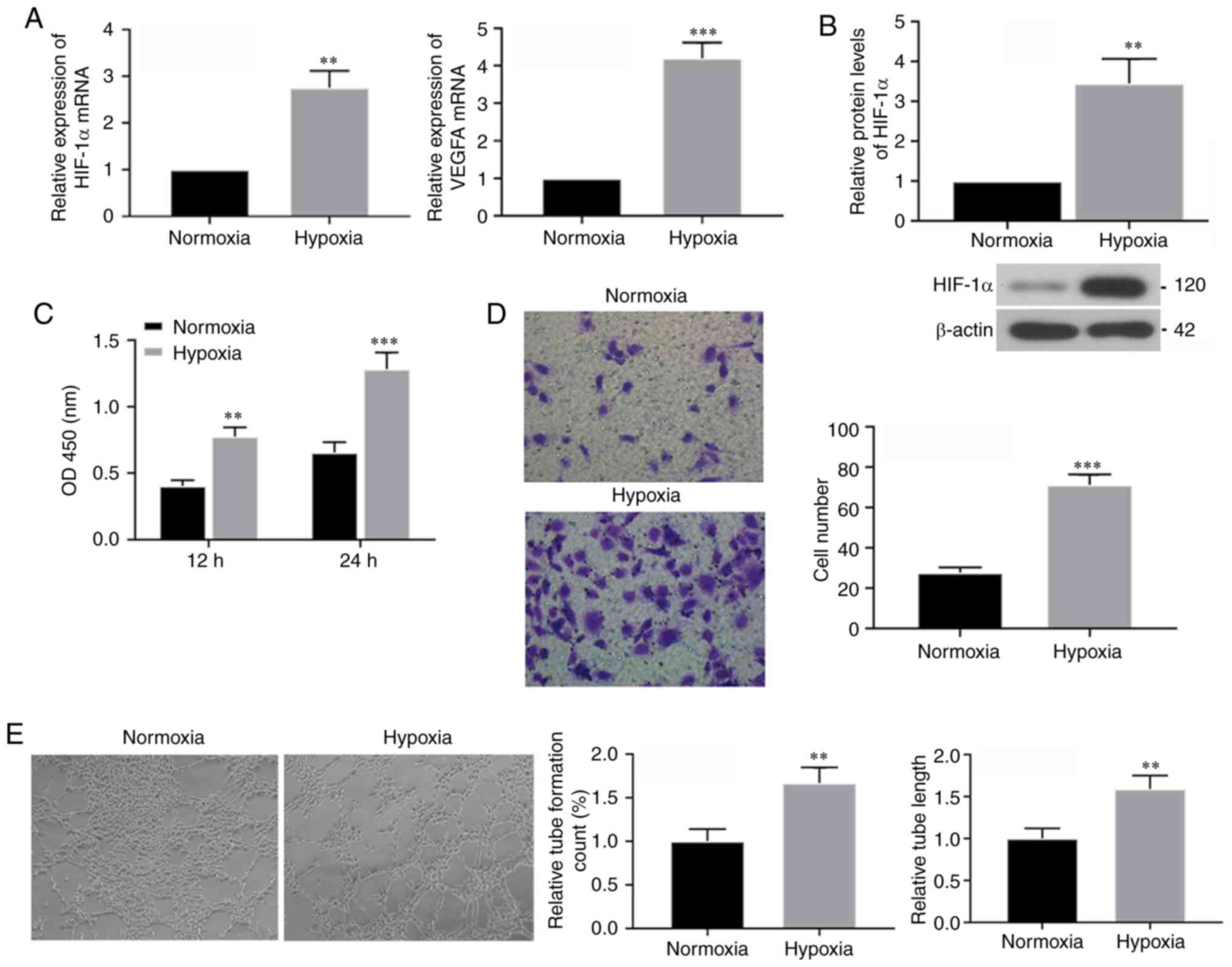
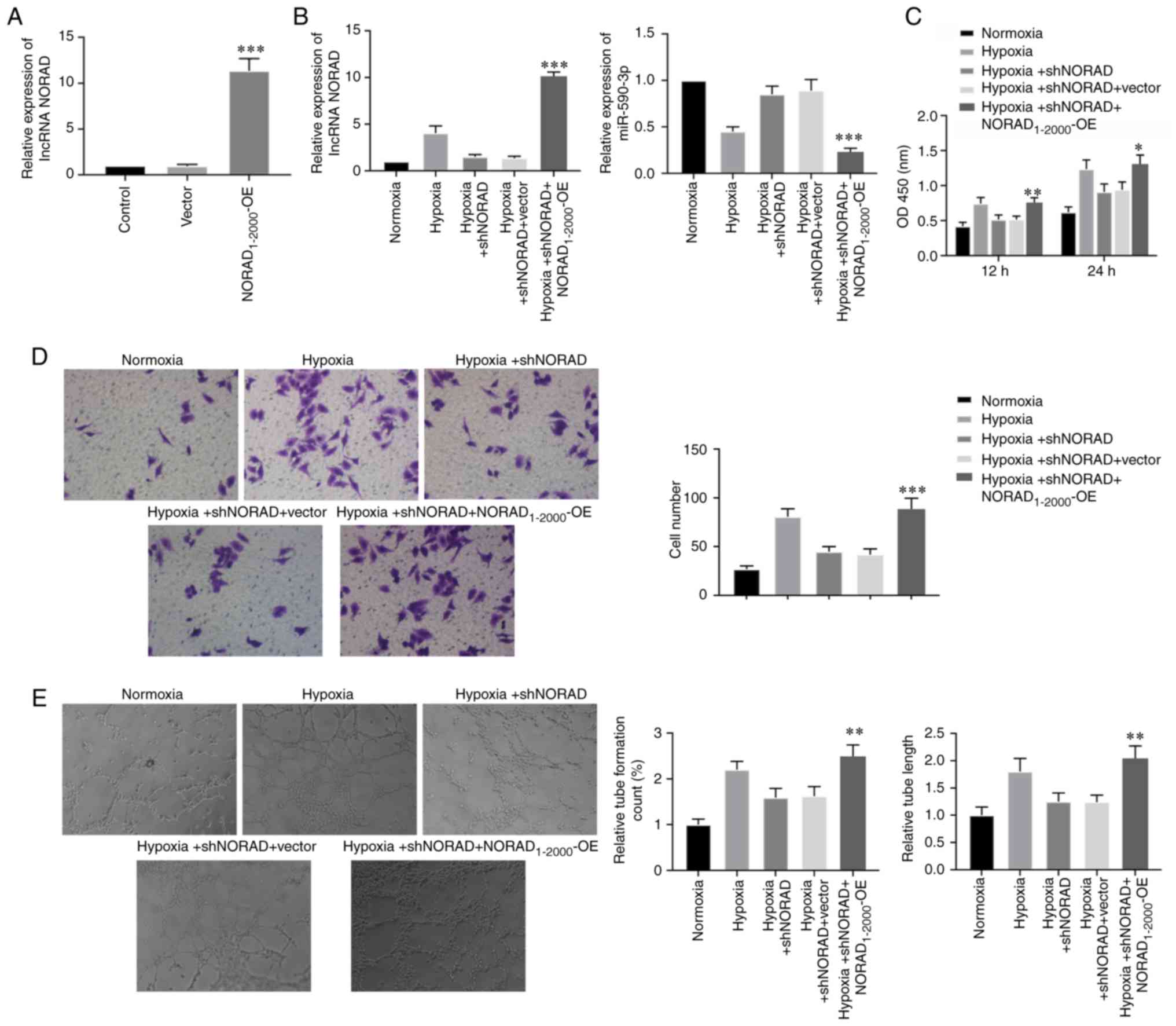
|
1
|
Carmeliet P: Mechanisms of angiogenesis
and arteriogenesis. Nat Med. 6:389–395. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Risau W: Mechanisms of angiogenesis.
Nature. 386:671–674. 1997. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yancopoulos GD, Davis S, Gale NW, Rudge
JS, Wiegand SJ and Holash J: Vascular-specific growth factors and
blood vessel formation. Nature. 407:242–248. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ferrara N: Vascular endothelial growth
factor: Molecular and biological aspects. Curr Top Microbiol
Immunol. 237:1–30. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zimna A and Kurpisz M: Hypoxia-inducible
factor-1 in physiological and pathophysiological angiogenesis:
Applications and therapies. Biomed Res Int. 2015:5494122015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Greijer AE, van der Groep P, Kemming D,
Shvarts A, Semenza GL, Meijer GA, van de Wiel MA, Belien JA, van
Diest PJ and van der Wall E: Up-regulation of gene expression by
hypoxia is mediated predominantly by hypoxia-inducible factor 1
(HIF-1). J Pathol. 206:291–304. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Semenza GL: Angiogenesis in ischemic and
neoplastic disorders. Annu Rev Med. 54:17–28. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Mori S, Tran V, Nishikawa K, Kaneda T,
Hamada Y, Kawaguchi N, Fujita M, Saegusa J, Takada YK, Matsuura N,
et al: A dominant-negative FGF1 mutant (the R50E mutant) suppresses
tumorigenesis and angiogenesis. PLoS One. 8:e579272013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Semenza GL: Oxygen sensing,
hypoxia-inducible factors, and disease pathophysiology. Annu Rev
Pathol. 9:47–71. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Go AS, Mozaffarian D, Roger VL, Benjamin
EJ, Berry JD, Borden WB, Bravata DM, Dai S, Ford ES, Fox CS, et al:
Heart disease and stroke statistics-2013 update: A report from the
American heart association. Circulation. 127:e6–e245. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Murray CJ and Lopez AD: Mortality by cause
for eight regions of the world: Global burden of disease study.
Lancet. 349:1269–1276. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lavine KJ, Kovacs A, Weinheimer C and Mann
DL: Repetitive myocardial ischemia promotes coronary growth in the
adult mammalian heart. J Am Heart Assoc. 2:e0003432013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Fatica A and Bozzoni I: Long non-coding
RNAs: New players in cell differentiation and development. Nat Rev
Genet. 15:7–21. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kung JT, Colognori D and Lee JT: Long
noncoding RNAs: Past, present, and future. Genetics. 193:651–669.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Han P, Li W, Lin CH, Yang J, Shang C,
Nuernberg ST, Jin KK, Xu W, Lin CY, Lin CJ, et al: A long noncoding
RNA protects the heart from pathological hypertrophy. Nature.
514:102–106. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang K, Long B, Zhou LY, Liu F, Zhou QY,
Liu CY, Fan YY and Li PF: CARL lncRNA inhibits anoxia-induced
mitochondrial fission and apoptosis in cardiomyocytes by impairing
miR-539-dependent PHB2 downregulation. Nat Commun. 5:35962014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lee S, Kopp F, Chang TC, Sataluri A, Chen
B, Sivakumar S, Yu H, Xie Y and Mendell JT: Noncoding RNA NORAD
regulates genomic stability by sequestering PUMILIO proteins. Cell.
164:69–80. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Liu H, Li J, Koirala P, Ding X, Chen B,
Wang Y, Wang Z, Wang C, Zhang X and Mo YY: Long non-coding RNAs as
prognostic markers in human breast cancer. Oncotarget.
7:20584–20596. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Li H, Wang X, Wen C, Huo Z, Wang W, Zhan
Q, Cheng D, Chen H, Deng X, Peng C and Shen B: Long noncoding RNA
NORAD, a novel competing endogenous RNA, enhances the
hypoxia-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition to promote
metastasis in pancreatic cancer. Mol Cancer. 16:1692017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Miao Z, Guo X and Tian L: The long
noncoding RNA NORAD promotes the growth of gastric cancer cells by
sponging miR-608. Gene. 687:116–124. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kawasaki N, Miwa T, Hokari S, Sakurai T,
Ohmori K, Miyauchi K, Miyazono K and Koinuma D: Long noncoding RNA
NORAD regulates transforming growth factor-β signaling and
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition-like phenotype. Cancer Sci.
109:2211–2220. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ekhteraei-Tousi S, Mohammad-Soltani B,
Sadeghizadeh M, Mowla SJ, Parsi S and Soleimani M: Inhibitory
effect of hsa-miR-590-5p on cardiosphere-derived stem cells
differentiation through downregulation of TGFβ signaling. J Cell
Biochem. 116:179–191. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Jafarzadeh M and Soltani BM:
Hsa-miR-590-5p interaction with SMAD3 transcript supports its
regulatory effect on The TGFβ signaling pathway. Cell J. 18:7–12.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Nallamshetty S, Chan SY and Loscalzo J:
Hypoxia: A master regulator of microRNA biogenesis and activity.
Free Radic Biol Med. 64:20–30. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kumar MM and Goyal R: LncRNA as a
therapeutic target for angiogenesis. Curr Top Med Chem.
17:1750–1757. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Rehmsmeier M, Steffen P, Hochsmann M and
Giegerich R: Fast and effective prediction of microRNA/target
duplexes. RNA. 10:1507–1517. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory
Animals. Institute for Laboratory Animal Research. National
Academies Press. (Washington, DC). 2011.
|
|
29
|
Yang Z, Zhao Y, Lin G, Zhou X, Jiang X and
Zhao H: Noncoding RNA activated by DNA damage (NORAD): Biologic
function and mechanisms in human cancers. Clin Chim Acta. 489:5–9.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Madanecki P, Kapoor N, Bebok Z, Ochocka R,
Collawn JF and Bartoszewski R: Regulation of angiogenesis by
hypoxia: The role of microRNA. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 18:47–57. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Folkman J and Shing Y: Angiogenesis. J
Biol Chem. 267:10931–10934. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Geng L, Chaudhuri A, Talmon G, Wisecarver
JL and Wang J: TGF-Beta suppresses VEGFA-mediated angiogenesis in
colon cancer metastasis. PLoS One. 8:e599182013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Aplin AC and Nicosia RF: Hypoxia
paradoxically inhibits the angiogenic response of isolated vessel
explants while inducing overexpression of vascular endothelial
growth factor. Angiogenesis. 19:133–146. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Noren Hooten N, Abdelmohsen K, Gorospe M,
Ejiogu N, Zonderman AB and Evans MK: microRNA expression patterns
reveal differential expression of target genes with age. PLoS One.
5:e107242010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|