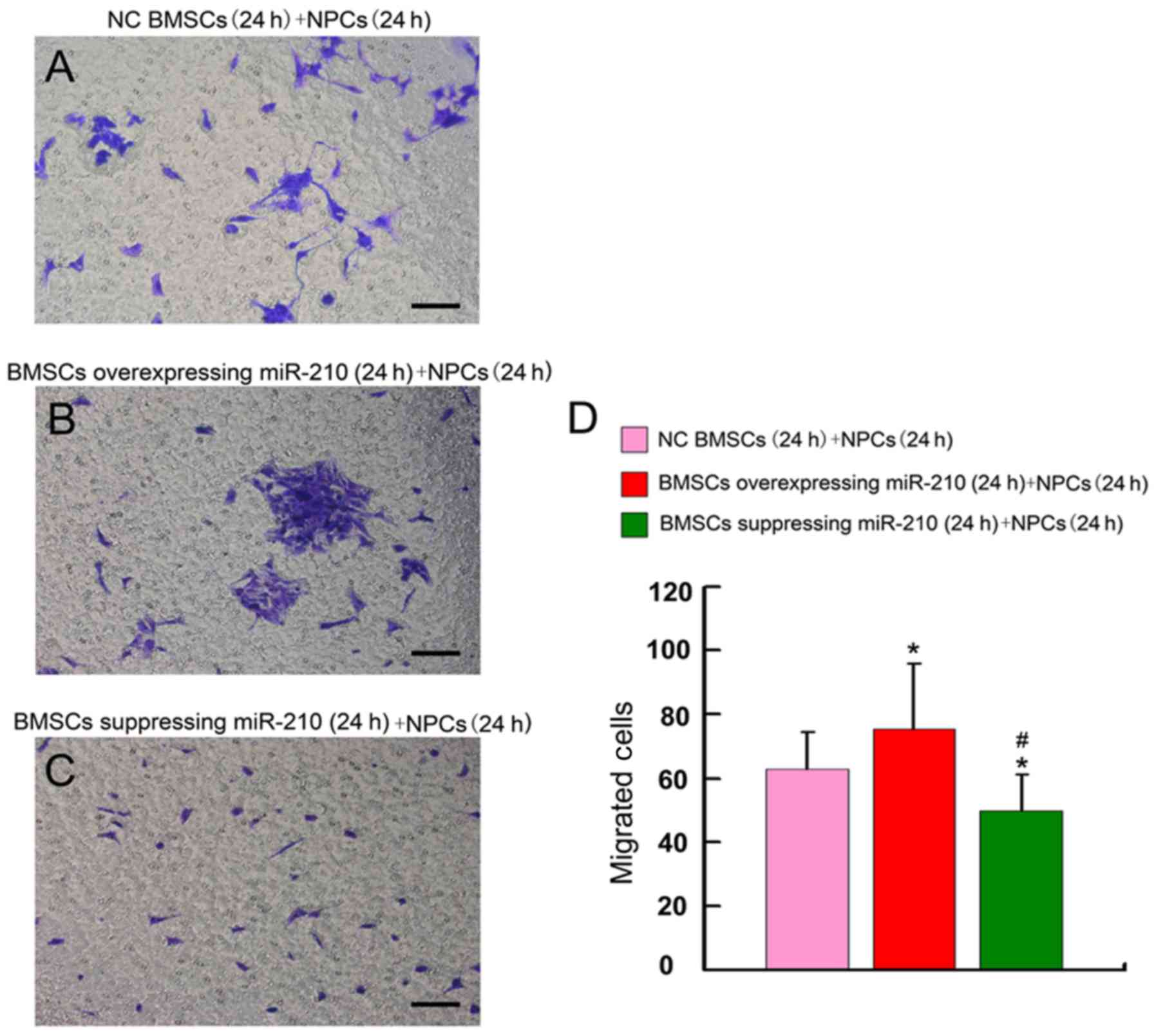
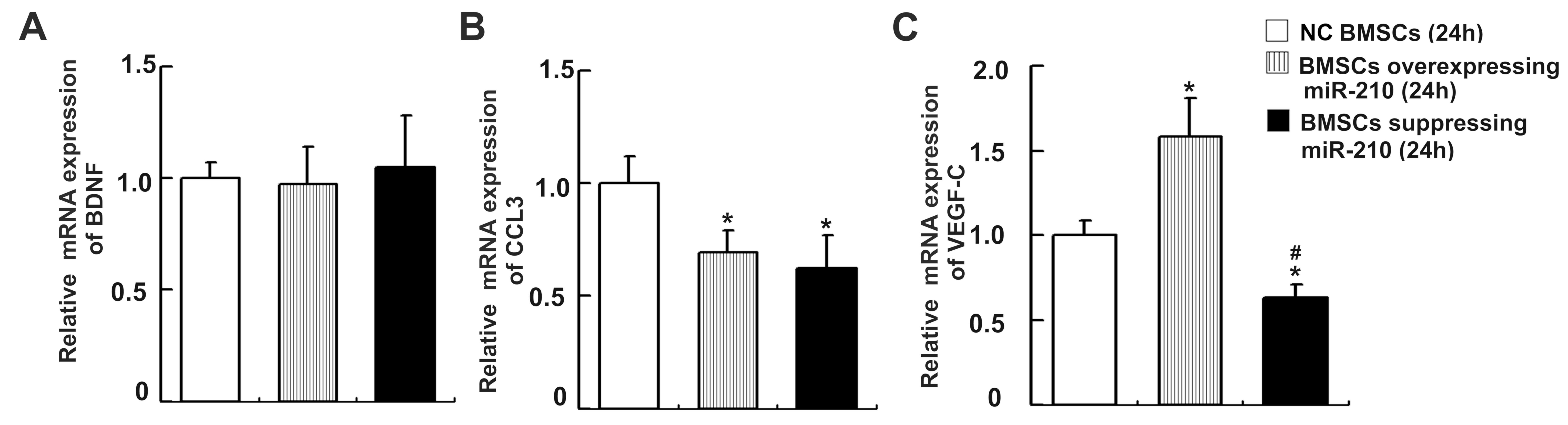
|
1
|
Khatri R, McKinney AM, Swenson B and
Janardhan V: Blood-brain barrier, reperfusion injury, and
hemorrhagic transformation in acute ischemic stroke. Neurology. 79
(13 Suppl 1):S52–S57. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Blesch A: Human ESC-derived interneurons
improve major consequences of spinal cord injury. Cell Stem Cell.
19:423–424. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Davoust C, Plas B, Béduer A, Demain B,
Salabert AS, Sol JC, Vieu C, Vaysse L and Loubinoux I: Regenerative
potential of primary adult human neural stem cells on
micropatterned bio-implants boosts motor recovery. Stem Cell Res
Ther. 8:2532017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Feng Y, Ju Y, Cui J and Wang L: Bone
marrow stromal cells promote neuromotor functional recovery, via
upregulation of neurotrophic factors and synapse proteins following
traumatic brain injury in rats. Mol Med Rep. 16:654–660. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hsueh YY, Chang YJ, Huang CW, Handayani F,
Chiang YL, Fan SC, Ho CJ, Kuo YM, Yang SH, Chen YL, et al: Synergy
of endothelial and neural progenitor cells from adipose-derived
stem cells to preserve neurovascular structures in rat
hypoxic-ischemic brain injury. Sci Rep. 5:149852015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Park KJ, Park E, Liu E and Baker AJ: Bone
marrow-derived endothelial progenitor cells protect postischemic
axons after traumatic brain injury. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab.
34:357–366. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Gennai S, Monsel A, Hao Q, Liu J, Gudapati
V, Barbier EL and Lee JW: Cell-based therapy for traumatic brain
injury. Br J Anaesth. 115:203–212. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Banerjee S, Williamson DA, Habib N and
Chataway J: The potential benefit of stem cell therapy after
stroke: An update. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 8:569–580. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Steinberg GK, Kondziolka D, Wechsler LR,
Lunsford LD, Coburn ML, Billigen JB, Kim AS, Johnson JN, Bates D,
King B, et al: Clinical outcomes of transplanted modified bone
marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells in stroke: A phase 1/2a
study. Stroke. 47:1817–1824. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hao L, Zou Z, Tian H, Zhang Y, Zhou H and
Liu L: Stem cell-based therapies for ischemic stroke. Biomed Res
Int. 2014:4687482014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
An SS, Jin HL, Kim KN, Kim DS, Cho J, Liu
ML, Oh JS, Yoon DH, Lee MH and Ha Y: Neuroprotective effect of
combined hypoxia-induced VEGF and bone marrow-derived mesenchymal
stem cell treatment. Childs Nerv Syst. 26:323–331. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Eckert MA, Vu Q, Xie K, Yu J, Liao W,
Cramer SC and Zhao W: Evidence for high translational potential of
mesenchymal stromal cell therapy to improve recovery from ischemic
stroke. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 33:1322–1334. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hsuan YC, Lin CH, Chang CP and Lin MT:
Mesenchymal stem cell-based treatments for stroke, neural trauma,
and heat stroke. Brain Behav. 6:e005262016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Doetsch F: A niche for adult neural stem
cells. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 13:543–550. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Koh SH and Lo EH: The role of the PI3K
pathway in the regeneration of the damaged brain by neural stem
cells after cerebral infarction. J Clin Neurol. 11:297–304. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Temple S: Division and differentiation of
isolated CNS blast cells in microculture. Nature. 340:471–473.
1989. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Gage FH: Mammalian neural stem cells.
Science. 287:1433–1438. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Liu ZH, Yang G, Zhao T, Cao GJ, Xiong L,
Xia W, Huang X, Wu LY, Wu K, Fan M, et al: Small ncRNA expression
and regulation under hypoxia in neural progenitor cells. Cell Mol
Neurobiol. 31:1–5. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yao L and Li Y: The role of direct current
electric field-guided stem cell migration in neural regeneration.
Stem Cell Rev. 12:365–375. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Abe M and Bonini NM: MicroRNAs and
neurodegeneration: Role and impact. Trends Cell Biol. 23:30–36.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ivan M and Huang X: miR-210: Fine-tuning
the hypoxic response. Adv Exp Med Biol. 772:205–227. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Pulkkinen K, Malm T, Turunen M, Koistinaho
J and Ylä-Herttuala S: Hypoxia induces microRNA miR-210 in vitro
and in vivo ephrin-A3 and neuronal pentraxin 1 are potentially
regulated by miR-210. FEBS Lett. 582:2397–2401. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Qiu J, Zhou XY, Zhou XG, Cheng R, Liu HY
and Li Y: Neuroprotective effects of microRNA-210 against
oxygen-glucose deprivation through inhibition of apoptosis in PC12
cells. Mol Med Rep. 7:1955–1959. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lou YL, Guo F, Liu F, Gao FL, Zhang PQ,
Niu X, Guo SC, Yin JH, Wang Y and Deng ZF: miR-210 activates notch
signaling pathway in angiogenesis induced by cerebral ischemia. Mol
Cell Biochem. 370:45–51. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Volný O, Kašičková L, Coufalová D,
Cimflová P and Novák J: microRNAs in cerebrovascular disease. Adv
Exp Med Biol. 888:155–195. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Rink C and Khanna S: MicroRNA in ischemic
stroke etiology and pathology. Physiol Genomics. 43:521–528. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhu J, Zhou Z, Liu Y and Zheng J:
Fractalkine and CX3CR1 are involved in the migration of
intravenously grafted human bone marrow stromal cells toward
ischemic brain lesion in rats. Brain Res. 1287:173–183. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhang Y, Zheng J, Zhou Z, Zhou H, Wang Y,
Gong Z and Zhu J: Fractalkine promotes chemotaxis of bone
marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells towards ischemic brain
lesions through Jak2 signaling and cytoskeletal reorganization.
FEBS J. 282:891–903. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Jiang Y, Li L, Tan X, Liu B, Zhang Y and
Li C: miR-210 mediates vagus nerve stimulation-induced antioxidant
stress and anti-apoptosis reactions following cerebral
ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. J Neurochem. 134:173–181.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhang D, Cao X, Li J and Zhao G: MiR-210
inhibits NF-κB signaling pathway by targeting DR6 in
osteoarthritis. Sci Rep. 5:127752015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Cao L, Zhang X, Cao F, Wang Y, Shen Y,
Yang C, Uzan G, Peng B and Zhang D: Inhibiting inducible miR-223
further reduces viable cells in human cancer cell lines MCF-7 and
PC3 treated by celastrol. BMC Cancer. 15:8732015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Brown JP, Couillard-Després S, Cooper-Kuhn
CM, Winkler J, Aigner L and Kuhn HG: Transient expression of
doublecortin during adult neurogenesis. J Comp Neurol. 467:1–10.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Croft AP and Przyborski SA: Mesenchymal
stem cells expressing neural antigens instruct a neurogenic cell
fate on neural stem cells. Exp Neurol. 216:329–341. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kuroda S: Current opinion of bone marrow
stromal cell transplantation for ischemic stroke. Neurol Med Chir
(Tokyo). 56:293–301. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Alexanian AR: Neural stem cells induce
bone-marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells to generate neural
stem-like cells via juxtacrine and paracrine interactions. Exp Cell
Res. 310:383–391. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Bai L, Caplan A, Lennon D and Miller RH:
Human mesenchymal stem cells signals regulate neural stem cell
fate. Neurochem Res. 32:353–362. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Liu X, Ye R, Yan T, Yu SP, Wei L, Xu G,
Fan X, Jiang Y, Stetler RA, Liu G and Chen J: Cell based therapies
for ischemic stroke: From basic science to bedside. Prog Neurobiol.
115:92–115. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Lu J, Manaenko A and Hu Q: Targeting adult
neurogenesis for poststroke therapy. Stem Cells Int.
2017:58686322017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Haragopal H, Yu D, Zeng X, Kim SW, Han IB,
Ropper AE, Anderson JE and Teng YD: Stemness enhancement of human
neural stem cells following bone marrow MSC coculture. Cell
Transplant. 24:645–659. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Wang Y, Tu W, Lou Y, Xie A, Lai X, Guo F
and Deng Z: Mesenchymal stem cells regulate the proliferation and
differentiation of neural stem cells through Notch signaling. Cell
Biol Int. 33:1173–1179. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Hackstein H, Tschipakow I, Bein G, Nold P,
Brendel C and Baal N: Contact-dependent abrogation of bone
marrow-derived plasmacytoid dendritic cell differentiation by
murine mesenchymal stem cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
476:15–20. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Yamada T, Yuasa M, Masaoka T, Taniyama T,
Maehara H, Torigoe I, Yoshii T, Shinomiya K, Okawa A and Sotome S:
After repeated division, bone marrow stromal cells express
inhibitory factors with osteogenic capabilities, and EphA5 is a
primary candidate. Bone. 57:343–354. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Wang PP, Xie DY, Liang XJ, Peng L, Zhang
GL, Ye YN, Xie C and Gao ZL: HGF and direct mesenchymal stem cells
contact synergize to inhibit hepatic stellate cells activation
through TLR4/NF-kB pathway. PLoS One. 7:e434082012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Huang X, Ding L, Bennewith KL, Tong RT,
Welford SM, Ang KK, Story M, Le QT and Giaccia AJ:
Hypoxia-inducible mir-210 regulates normoxic gene expression
involved in tumor initiation. Mol Cell. 35:856–867. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Xiong L, Wang F, Huang X, Liu ZH, Zhao T,
Wu LY, Wu K, Ding X, Liu S, Wu Y, et al: DNA demethylation
regulates the expression of miR-210 in neural progenitor cells
subjected to hypoxia. FEBS J. 279:4318–4326. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Nie Y, Han BM, Liu XB, Yang JJ, Wang F,
Cong XF and Chen X: Identification of MicroRNAs involved in
hypoxia- and serum deprivation-induced apoptosis in mesenchymal
stem cells. Int J Biol Sci. 7:762–768. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Sun G and Peng H: HIF-1α-induced
microRNA-210 reduces hypoxia-induced osteoblast MG-63 cell
apoptosis. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 79:1232–1239. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Wang F, Xiong L, Huang X, Zhao T, Wu LY,
Liu ZH, Ding X, Liu S, Wu Y, Zhao Y, et al: miR-210 suppresses
BNIP3 to protect against the apoptosis of neural progenitor cells.
Stem Cell Res. 11:657–667. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Zhang C, Tian W, Meng L, Qu L and Shou C:
PRL-3 promotes gastric cancer migration and invasion through a
NF-κB-HIF-1α-miR-210 axis. J Mol Med (Berl). 94:401–415. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Qu A, Du L, Yang Y, Liu H, Li J, Wang L,
Liu Y, Dong Z, Zhang X, Jiang X, et al: Hypoxia-inducible MiR-210
is an independent prognostic factor and contributes to metastasis
in colorectal cancer. PLoS One. 9:e909522014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Zeng L, He X, Wang Y, Tang Y, Zheng C, Cai
H, Liu J, Wang Y, Fu Y and Yang GY: MicroRNA-210 overexpression
induces angiogenesis and neurogenesis in the normal adult mouse
brain. Gene Ther. 21:37–43. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Liu F, Lou YL, Wu J, Ruan QF, Xie A, Guo
F, Cui SP, Deng ZF and Wang Y: Upregulation of microRNA-210
regulates renal angiogenesis mediated by activation of VEGF
signaling pathway under ischemia/perfusion injury in vivo and in
vitro. Kidney Blood Press Res. 35:182–191. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Kawanishi Y, Nakasa T, Shoji T, Hamanishi
M, Shimizu R, Kamei N, Usman MA and Ochi M: Intra-articular
injection of synthetic microRNA-210 accelerates avascular meniscal
healing in rat medial meniscal injured model. Arthritis Res Ther.
16:4882014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Díaz-Coránguez M, Segovia J, López-Ornelas
A, Puerta-Guardo H, Ludert J, Chávez B, Meraz-Cruz N and
González-Mariscal L: Transmigration of neural stem cells across the
blood brain barrier induced by glioma cells. PLoS One.
8:e606552013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|