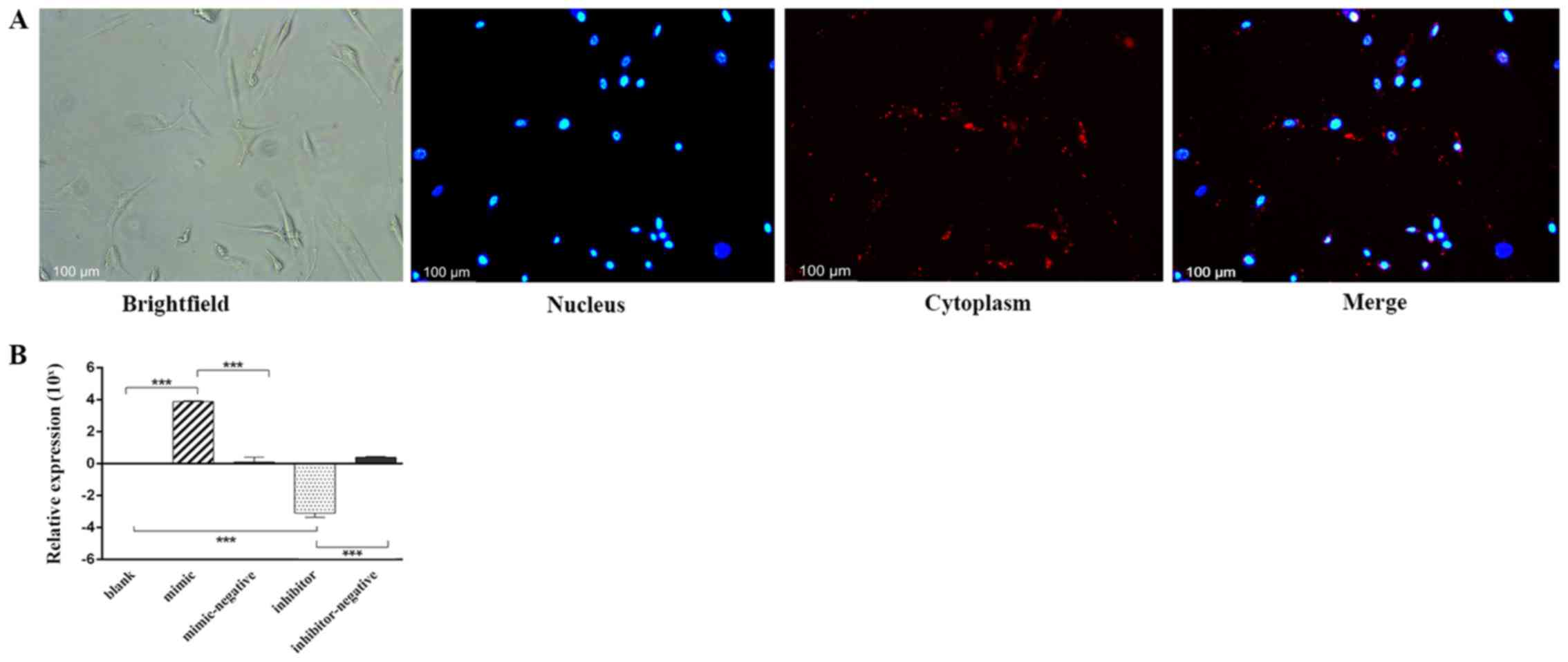
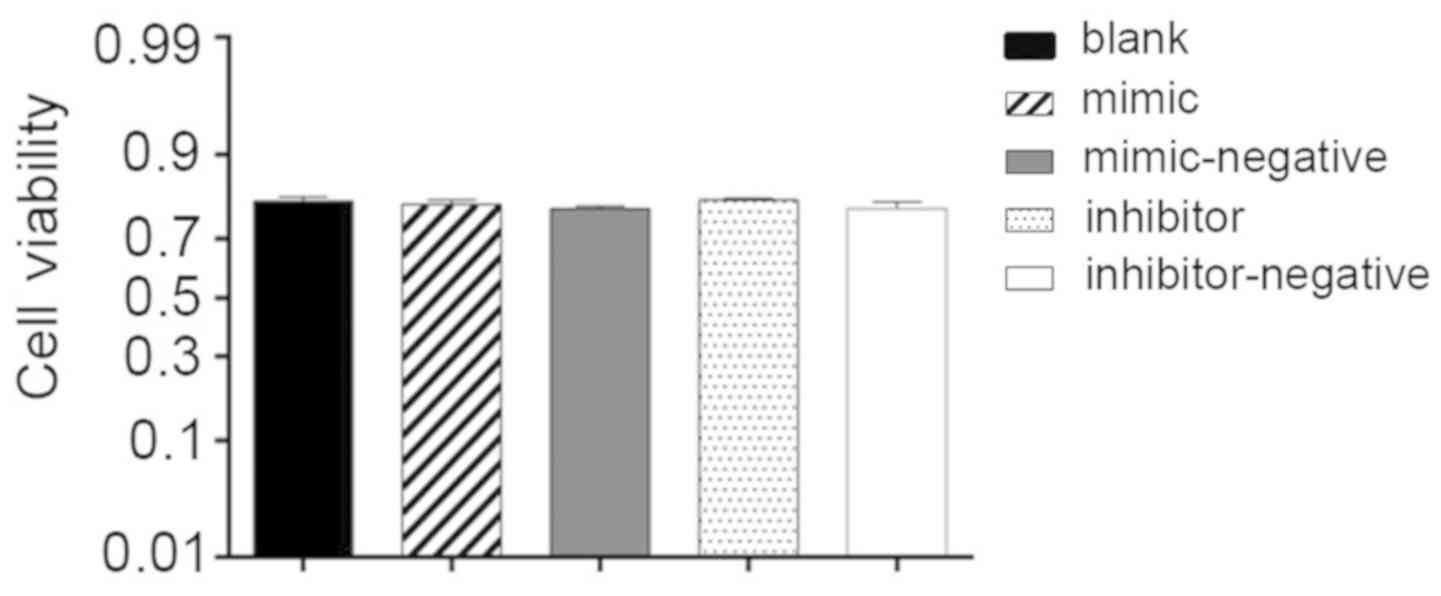
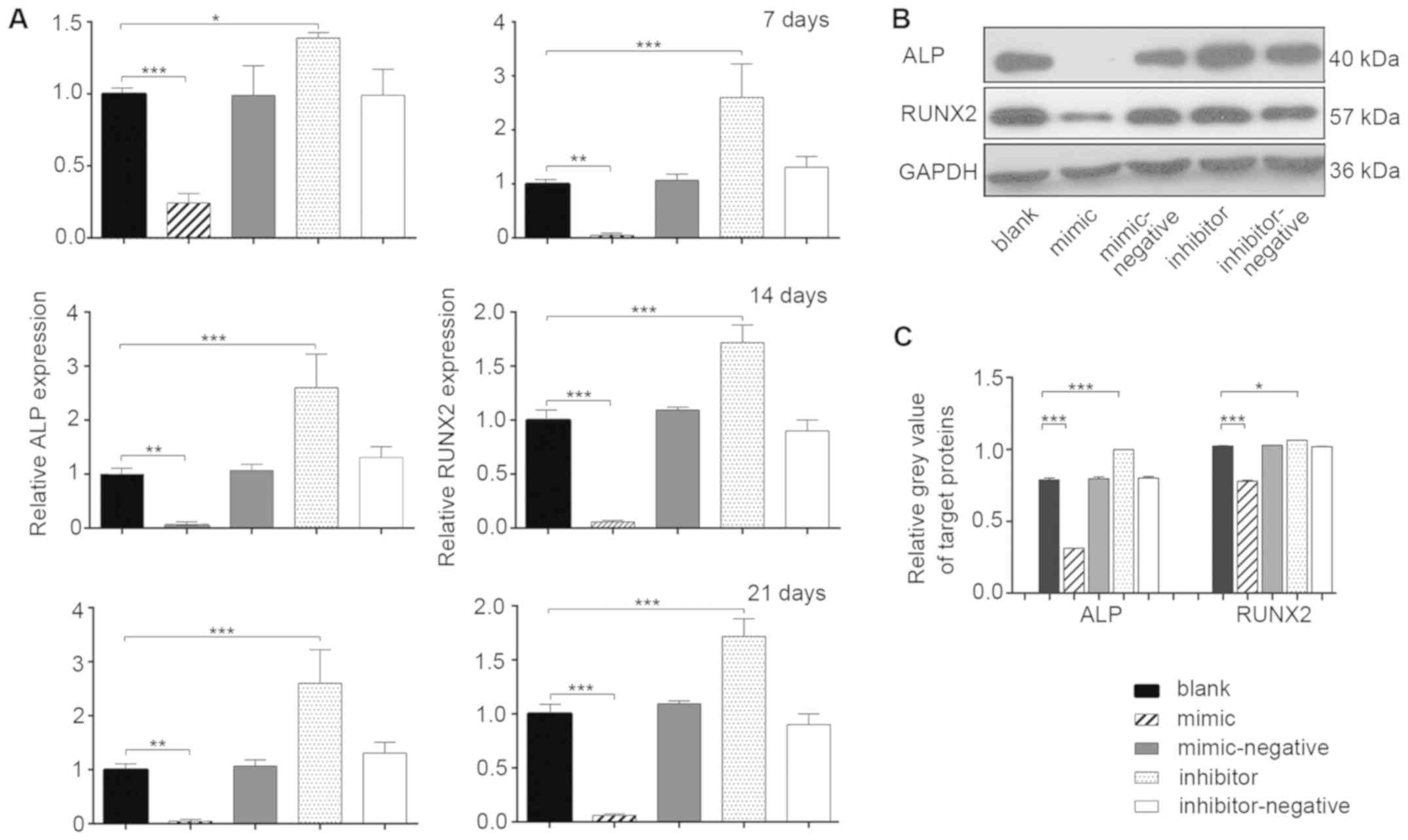
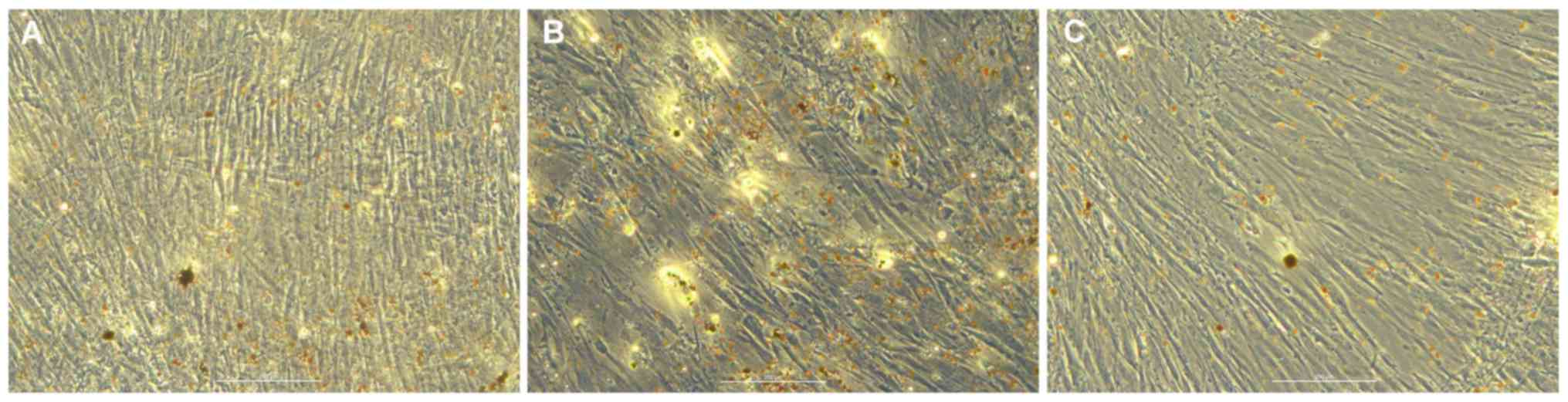
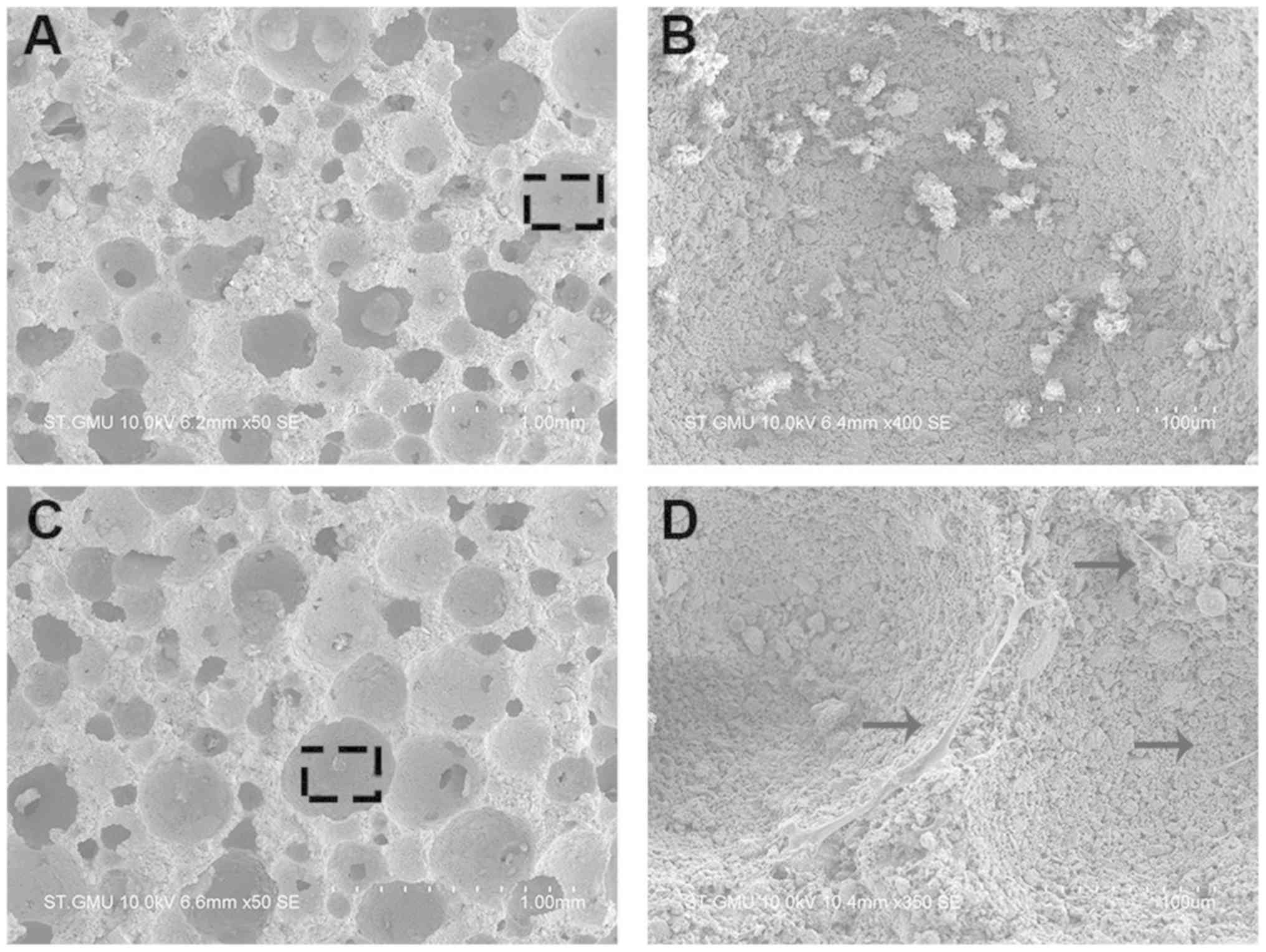
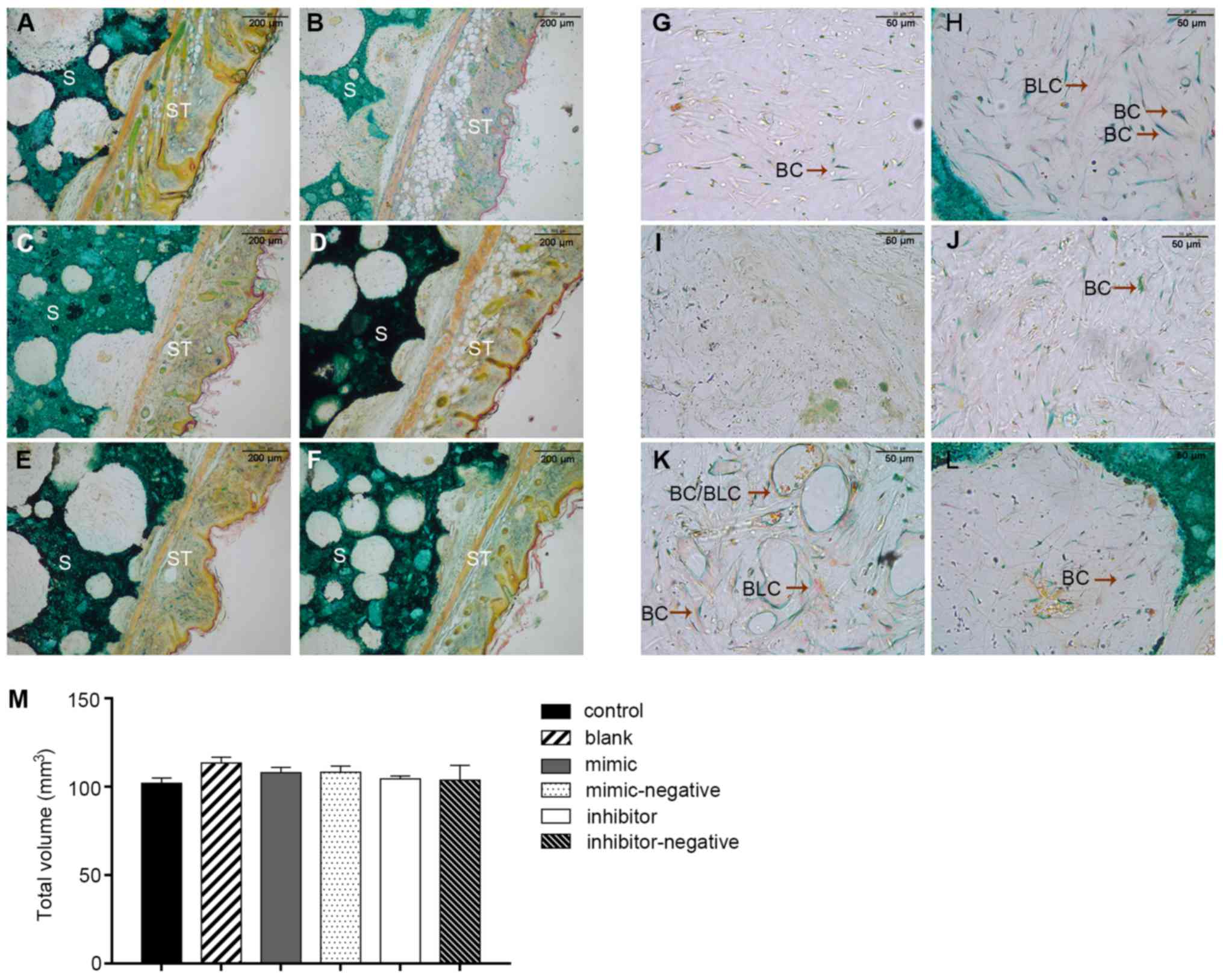
|
1
|
Pichler K, Loreto C, Leonardi R, Reuber T,
Weinberg AM and Musumeci G: Rankl is downregulated in bone cells by
physical activity (treadmill and vibration stimulation training) in
rat with glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis. Histol Histopathol.
28:1185–1196. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Castrogiovanni P, Trovato FM, Szychlinska
MA, Nsir H, Imbesi R and Musumeci G: The importance of physical
activity in osteoporosis. From the molecular pathways to the
clinical evidence. Histol Histopathol. 31:1183–1194.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Cardinale M and Bosco C: The use of
vibration as an exercise intervention. Exerc Sport Sci Rev. 31:3–7.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Srinivasaiah S, Musumeci G, Mohan T,
Castrogiovanni P, Absenger-Novak M, Zefferer U, Mostofi S, Bonyadi
Rad E, Grün NG, Weinberg AM and Schäfer U: A 300 µm organotypic
bone slice culture model for temporal investigation of endochondral
osteogenesis. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 25:197–212. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Pittenger MF, Mackay AM, Beck SC, Jaiswal
RK, Douglas R, Mosca JD, Moorman MA, Simonetti DW, Craig S and
Marshak DR: Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem
cells. Science. 284:143–147. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Szychlinska MA, Castrogiovanni P, Nsir H,
Di Rosa MD, Guglielmino C, Parenti R, Calabrese G, Pricoco E,
Salvatorelli L, Magro G, et al: Engineered cartilage regeneration
from adipose tissue derived-mesenchymal stem cells: A
morphomolecular study on osteoblast, chondrocyte and apoptosis
evaluation. Exp Cell Res. 357:222–235. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yamada Y, Ueda M, Hibi H and Nagasaka T:
Translational research for injectable tissue-engineered bone
regeneration using mesenchymal stem cells and platelet-rich plasma:
From basic research to clinical case study. Cell Transplant.
13:343–355. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yamada Y, Nakamura S, Ito K, Kohgo T, Hibi
H, Nagasaka T and Ueda M: Injectable tissue-engineered bone using
autogenous bone marrow-derived stromal cells for maxillary sinus
augmentation: Clinical application report from a 2-6-year
follow-up. Tissue Eng Part A. 14:1699–1707. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lau NC, Lim LP, Weinstein EG and Bartel
DP: An abundant class of tiny RNAs with probable regulatory roles
in Caenorhabditis elegans. Science. 294:858–862. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Rana TM: Illuminating the silence:
Understanding the structure and function of small RNAs. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 8:23–36. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Tanzer A, Amemiya CT, Kim CB and Stadler
PF: Evolution of microRNAs located within hox gene clusters. J Exp
Zool B Mol Dev Evol. 304:75–85. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Woltering JM and Durston AJ: Mir-10
represses hoxb1a and hoxb3a in zebrafish. PLoS One. 3:e13962008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Mu N, Gu J, Huang T, Zhang C, Shu Z, Li M,
Hao Q, Li W, Zhang W, Zhao J, et al: A novel NF-κB/YY1/MicroRNA-10a
regulatory circuit in fibroblast-like synoviocytes regulates
inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. Sci Rep. 6:200592016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Liang D, Zhen L, Yuan T, Huang J, Deng F,
Wuyahan, Zhang H, Pan L, Liu Y, The E, et al: miR-10a regulates
proliferation of human cardiomyocyte progenitor cells by targeting
GATA6. PLoS One. 9:e1030972014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Xiong G, Huang H, Feng M, Yang G, Zheng S,
You L, Zheng L, Hu Y, Zhang T and Zhao Y: miR-10a-5p targets TFAP2C
to promote gemcitabine resistance in pancreatic ductal
adenocarcinoma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 37:762018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Huang J, Zhao L, Xing L and Chen D:
MicroRNA-204 regulates Runx2 protein expression and mesenchymal
progenitor cell differentiation. Stem Cells. 28:357–364.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Inose H, Ochi H, Kimura A, Fujita K, Xu R,
Sato S, Iwasaki M, Sunamura S, Takeuchi Y, Fukumoto S, et al: A
microRNA regulatory mechanism of osteoblast differentiation. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:20794–20799. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative pcr and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
National Research Council, . Guide for the
Care and Use of Laboratory Animals: Eighth Edition. The National
Academies Press. (Washington, DC). 2011.
|
|
20
|
Kanczler JM, Ginty PJ, Barry JJ, Clarke
NM, Howdle SM, Shakesheff KM and Oreffo RO: The effect of
mesenchymal populations and vascular endothelial growth factor
delivered from biodegradable polymer scaffolds on bone formation.
Biomaterials. 29:1892–1900. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Reiser J, Zhang XY, Hemenway CS, Mondal D,
Pradhan L and La Russa VF: Potential of mesenchymal stem cells in
gene therapy approaches for inherited and acquired diseases. Expert
Opin Biol Ther. 5:1571–1584. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chen L, Xu Y, Zhao J, Zhang Z, Yang R, Xie
J, Liu X and Qi S: Conditioned medium from hypoxic bone
marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells enhances wound healing in
mice. PLoS One. 9:e961612014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Bernstein E, Caudy AA, Hammond SM and
Hannon GJ: Role for a bidentateribonuclease in the initiation step
of RNA interference. Nature. 409:363–366. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Fire A, Xu S, Montgomery MK, Kostas SA,
Driver SE and Mello CC: Potent and specific genetic interference by
double-stranded RNA in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature. 391:806–811.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Morris KV and Mattick JS: The rise of
regulatory RNA. Nat Rev Genet. 15:423–437. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Van Wijnen AJ, Stein GS, Gergen JP, Groner
Y, Hiebert SW, Ito Y, Liu P, Neil JC, Ohki M and Speck N:
Nomenclature for Runt-related (RUNX) proteins. Oncogene.
23:4209–4210. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Rosen CJ: Bone remodeling, energy
metabolism, and the molecular clock. Cell Metab. 7:7–10. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Musumeci G, Mobasheri A, Trovato FM,
Szychlinska MA, Graziano AC, Lo Furno D, Avola R, Mangano S,
Giuffrida R and Cardile V: Biosynthesis of collagen I, II, RUNX2
and lubricin at different time points of chondrogenic
differentiation in a 3D in vitro model of human mesenchymal stem
cells derived from adipose tissue. Acta Histochem. 116:1407–1417.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Izu Y, Sun M, Zwolanek D, Veit G, Williams
V, Cha B, Jepsen KJ, Koch M and Birk DE: Type XII collagen
regulates osteoblast polarity and communication during bone
formation. J Cell Biol. 193:1115–1130. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Liu Y, Xu F, Pei HX, Zhu X, Lin X, Song
CY, Liang QH, Liao EY and Yuan LQ: Vaspin regulates the osteogenic
differentiation of MC3T3-E1 through the Pi3K-Akt/miR-34c loop. Sci
Rep. 6:255782016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Bonyadi Rad E, Musumeci G, Pichler K,
Heidary M, Szychlinska MA, Castrogiovanni P, Marth E, Böhm C,
Srinivasaiah S, Krönke G, et al: Runx2 mediated induction of novel
targets ST2 and Runx3 leads to cooperative regulation of
hypertrophic differentiation in ATDC5 chondrocytes. Sci Rep.
7:179472017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhang Y, Xie RL, Croce CM, Stein JL, Lian
JB, Van Wijnen AJ and Stein GS: A program of microRNAs controls
osteogenic lineage progression by targeting transcription factor
Runx2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 108:9863–9868. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Tian F, Ji XL, Xiao WA, Wang B and Wang F:
CXCL13 promotes osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem
cells by inhibiting miR-23a expression. Stem Cells Int.
2015:6323052015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Chang CH, Fan TC, Yu JC, Liao GS, Lin YC,
Shih AC, Li WH and Yu AL: The prognostic significance of RUNX2 and
miR-10a/10b and their inter-relationship in breast cancer. J Transl
Med. 12:2572014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Saltiel AR: Structural and functional
roles of glycosylphosphoinositides. Subcell Biochem. 26:65–185.
1996.
|
|
36
|
Wang X, Guo B, Li Q, Peng J, Yang Z, Wang
A, Li D, Hou Z, Lv K, Kan G, et al: miR-214 targets ATF4 to inhibit
bone formation. Nat Med. 19:93–100. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Liu XD, Cai F, Liu L, Zhang Y and Yang AL:
MicroRNA-210 is involved in the regulation of postmenopausal
osteoporosis through promotion of VEGF expression and osteoblast
differentiation. Biol Chem. 396:339–347. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Shen E, Diao X, Wei C, Wu Z, Zhang L and
Hu B: MicroRNAs target gene and signaling pathway by bioinformatics
analysis in the cardiac hypertrophy. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
397:380–385. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Cao Q, Li YY, He WF, Zhang ZZ, Zhou Q, Liu
X, Shen Y and Huang TT: Interplay between microRNAs and the STAT3
signaling pathway in human cancers. Physiol Genomics. 45:1206–1214.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zhang W, Xie Y, Xu L, Wang Y, Zhu X, Wang
R, Zhang Y, Muleke EM and Liu L: Identification of microRNAs and
their target genes explores miRNA-mediated regulatory network of
cytoplasmic male sterility occurrence during anther development in
radish (Raphanus sativus L.). Front Plant Sci.
7:10542016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Otto F, Lübbert M and Stock M: Upstream
and downstream targets of RUNX proteins. J Cell Biochem. 89:9–18.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Park J, Wada S, Ushida T and Akimoto T:
The microRNA-23a has limited roles in bone formation and
homeostasis in vivo. Physiol Res. 64:711–719. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Taipaleenmä H, Eskildsen T, Stenvang J,
Abdallah MB, Ditzel N, Säämäne AM, Kauppine S and Kasse M: Mir-138
is a novel regulator of in vivo bone formation. Bone. 47 (Suppl
1):S462010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Chen L, Holmstrøm K, Qiu W, Ditzel N, Shi
K, Hokland L and Kassem M: MicroRNA-34a inhibits osteoblast
differentiation and in vivo bone formation of human stromal stem
cells. Stem Cells. 32:902–912. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Liu L, Liu M, Li R, Liu H, Du L, Chen H,
Zhang Y, Zhang S and Liu D: MicroRNA-503-5p inhibits
stretch-induced osteogenic differentiation and bone formation. Cell
Biol Int. 41:112–123. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Hattori S: Structural features of ectopic
bone-like tissue in porous hydroxyapatite blocks. Kokubyo Gakkai
Zasshi. 75:120–137. 2008.(In Japanese). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Mayr H, Schlüfter S, Detsch R and Ziegler
G: Influence of phase composition on degradation and resorption of
biphasic calcium phosphate ceramics. Key Eng Mater 361-363.
1043–1046. 2008.
|
|
48
|
Daculsi G, Laboux O, Malard O and Weiss P:
Current state of the art of biphasic calcium phosphate bioceramics.
J Mater Sci Mater Med. 14:195–200. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Yamada S, Heymann D, Bouler JM and Daculsi
G: Osteoclasticresorption of calcium phosphate ceramics with
different hydroxyapatite/beta-tricalcium phosphate ratios.
Biomaterials. 18:1037–1041. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Rentsch C, Schneiders W, Manthey S,
Rentsch B and Rammelt S: Comprehensive histological evaluation of
bone implants. Biomatter. 4:e279932014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Eskildsen T, Taipaleenmäki H, Stenvang J,
Abdallah BM, Ditzel N, Nossent AY, Bak M, Kauppinen S and Kassem M:
MicroRNA-138 regulates osteogenic differentiation of human stromal
(mesenchymal) stem cells in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
108:6139–6144. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Qadir AS, Um S, Lee H, Baek K, Seo BM, Lee
G, Kim GS, Woo KM, Ryoo HM and Baek JH: miR-124 negatively
regulates osteogenic differentiation and in vivo bone formation of
mesenchymal stem cells. J Cell Biochem. 116:730–742. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Liu S, Liu D, Chen C, Hamamura K,
Moshaverinia A, Yang R, Liu Y, Jin Y and Shi S: MSC transplantation
improves osteopenia via epigenetic regulation of notch signaling in
lupus. Cell Metab. 22:606–618. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Luo Y, Chen GL, Hannemann N, Ipseiz N,
Krönke G, Bäuerle T, Munos L, Wirtz S, Schett G and Bozec A:
Microbiota from obese mice regulate hematopoietic stem cell
differentiation by altering the bone niche. Cell Metab. 22:886–894.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Zou W, Greenblatt MB, Brady N, Lotinun S,
Zhai B, de Rivera H, Singh A, Sun J, Gygi SP, Baron R, et al: The
microtubule-associated protein DCAMKL1 regulates osteoblast
function via repression of Runx2. J Exp Med. 210:1793–1806. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Sureban SM, May R, Lightfoot SA, Hoskins
AB, Lerner M, Brackett DJ, Postier RG, Ramanujam R, Mohammed A, Rao
CV, et al: DCAMKL-1 regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition in
human pancreatic cells through a miR-200a-dependent mechanism.
Cancer Res. 71:2328–2338. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Sureban SM, May R, Ramalingam S,
Subramaniam D, Natarajan G, Anant S and Houchen CW: Selective
blockade of DCAMKL-1 results in tumor growth arrest by a Let-7a
MicroRNA-dependent mechanism. Gastroenterology. 137:649–659. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Cao T, Li H, Hu Y, Ma D and Cai X: miR-144
suppresses the proliferation and metastasis of hepatocellular
carcinoma by targeting E2F3. Tumour Biol. 35:10759–10764. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Fan Y, Hanai JI, Le PT, Bi R, Maridas D,
DeMambro V, Figueroa CA, Kir S, Zhou X, Mannstadt M, et al:
Parathyroid hormone directs bone marrow mesenchymal cell fate. Cell
Metab. 25:661–672. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Li JY, D'Amelio P, Robinson J, Walker LD,
Vaccaro C, Luo T, Tyagi AM, Yu M, Reott M, Sassi F, et al: IL-17A
is increased in humans with primary hyperparathyroidism and
mediates PTH-induced bone loss in mice. Cell Metab. 22:799–810.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|