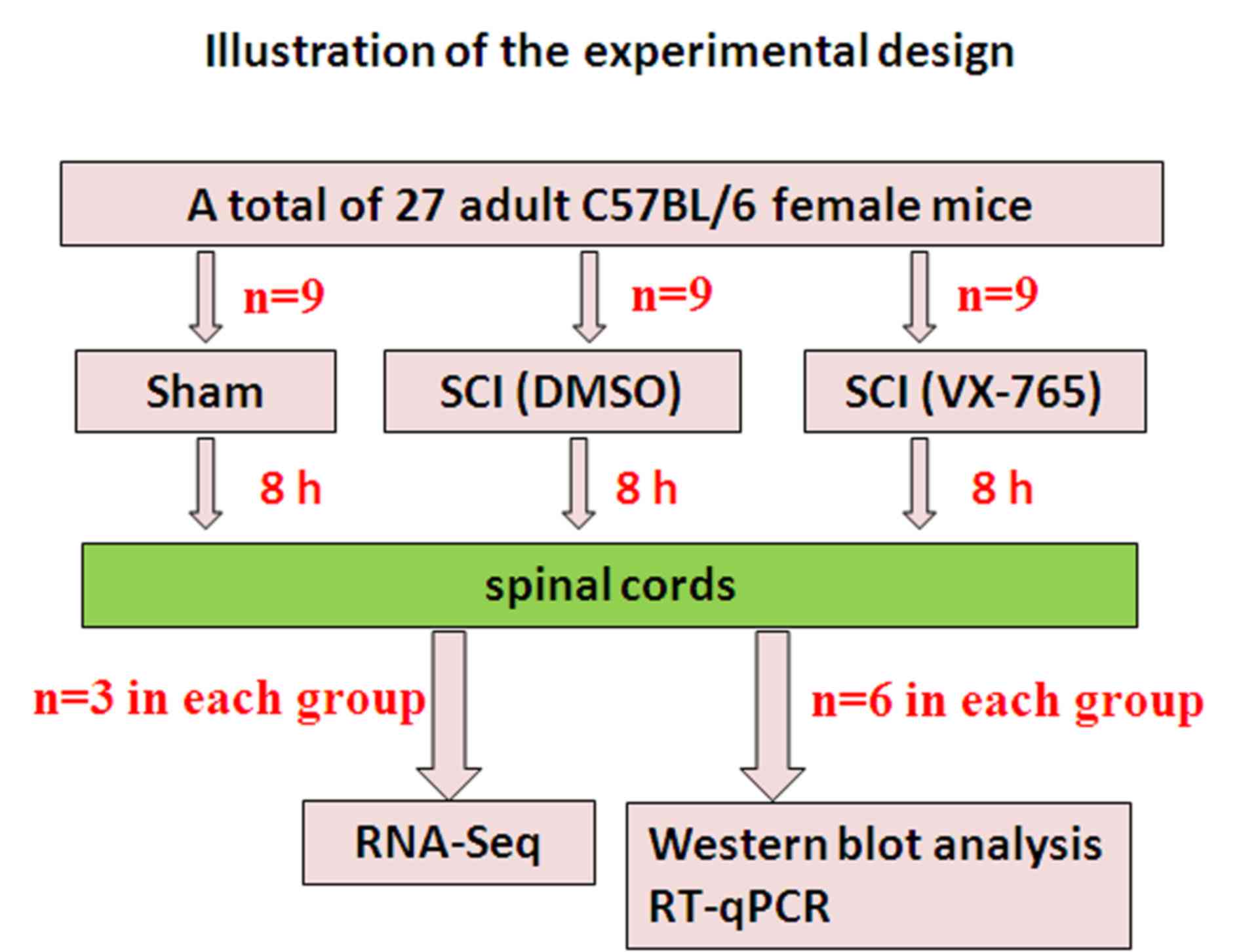
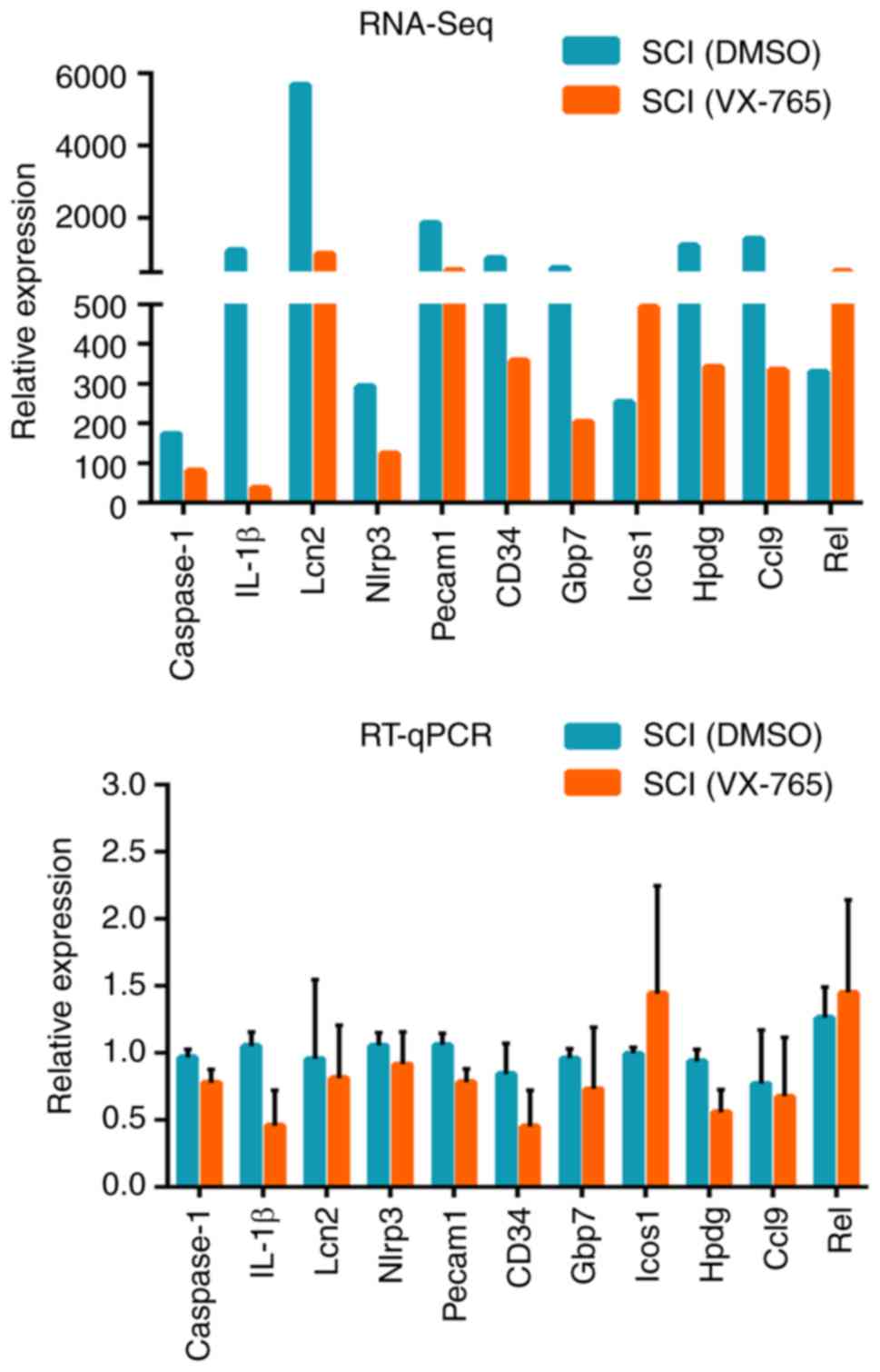
|
1
|
Friedli L, Rosenzweig ES, Barraud Q,
Schubert M, Dominici N, Awai L, Nielson JL, Musienko P, Nout-Lomas
Y, Zhong H, et al: Pronounced species divergence in corticospinal
tract reorganization and functional recovery after lateralized
spinal cord injury favors primates. Sci Transl Med. 7:302ra1342015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
de Rivero Vaccari JP, Dietrich WD and
Keane RW: Activation and regulation of cellular inflammasomes: Gaps
in our knowledge for central nervous system injury. J Cereb Blood
Flow Metab. 34:369–375. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Krakauer T: Inflammasomes, autophagy, and
cell death: The trinity of innate host defense against
intracellular bacteria. Mediators Inflamm. 2019:24712152019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Li L, Tang W and Yi F: Role of
inflammasome in chronic kidney disease. Adv Exp Med Biol.
1165:407–421. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Stack JH, Beaumont K, Larsen PD, Straley
KS, Henkel GW, Randle JC and Hoffman HM: IL-converting
enzyme/caspase-1 inhibitor VX-765 blocks the hypersensitive
response to an inflammatory stimulus in monocytes from familial
cold autoinflammatory syndrome patients. J Immunol. 175:2630–2634.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhang Y and Zheng Y: Effects and
mechanisms of potent caspase-1 inhibitor VX765 treatment on
collagen-induced arthritis in mice. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 34:111–118.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Flores J, Noel A, Foveau B, Lynham J,
Lecrux C and LeBlanc AC: Caspase-1 inhibition alleviates cognitive
impairment and neuropathology in an Alzheimer's disease mouse
model. Nat Commun. 9:39162018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Maroso M, Balosso S, Ravizza T, Iori V,
Wright CI, French J and Vezzani A: Interleukin-1β biosynthesis
inhibition reduces acute seizures and drug resistant chronic
epileptic activity in mice. Neurotherapeutics. 8:304–315. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wu J, Zhao Z, Kumar A, Lipinski MM, Loane
DJ, Stoica BA and Faden AI: Endoplasmic reticulum stress and
disrupted neurogenesis in the brain are associated with cognitive
impairment and depressive-like behavior after spinal cord injury. J
Neurotrauma. 33:1919–1935. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Horiuchi H, Oshima Y, Ogata T, Morino T,
Matsuda S, Miura H and Imamura T: Evaluation of injured axons using
two-photon excited fluorescence microscopy after spinal cord
contusion injury in YFP-H line mice. Int J Mol Sci. 16:15785–15799.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Galvan MD, Luchetti S, Burgos AM, Nguyen
HX, Hooshmand MJ, Hamers FP and Anderson AJ: Deficiency in
complement C1q improves histological and functional locomotor
outcome after spinal cord injury. J Neurosci. 28:13876–13888. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Liu JQ, Yang D and Folz RJ: A novel
bronchial ring bioassay for the evaluation of small airway smooth
muscle function in mice. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol.
291:L281–L288. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Song XY, Zhou FH, Zhong JH, Wu LL and Zhou
XF: Knockout of p75(NTR) impairs re-myelination of injured sciatic
nerve in mice. J Neurochem. 96:833–842. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Mehto S, Jena KK, Nath P and Chauhan S,
Kolapalli SP, Das SK, Sahoo PK, Jain A, Taylor GA and Chauhan S:
The Crohn's disease risk factor IRGM limits NLRP3 inflammasome
activation by impeding its assembly and by mediating its selective
autophagy. Mol Cell. 73:429–445.e27. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lin YH, Wu Y, Wang Y, Yao ZF, Tang J, Wang
R, Shen L, Ding SQ, Hu JG and Lü HZ: Spatio-temporal expression of
Hexokinase-3 in the injured female rat spinal cords. Neurochem Int.
113:23–33. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Shi LL, Zhang N, Xie XM, Chen YJ, Wang R,
Shen L, Zhou JS, Hu JG and Lü HZ: Transcriptome profile of rat
genes in injured spinal cord at different stages by RNA-sequencing.
BMC Genomics. 18:1732017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Martinon F, Burns K and Tschopp J: The
inflammasome: A molecular platform triggering activation of
inflammatory caspases and processing of proIL-beta. Mol Cell.
10:417–426. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Latz E, Xiao TS and Stutz A: Activation
and regulation of the inflammasomes. Nat Rev Immunol. 13:397–411.
2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Mortezaee K, Khanlarkhani N, Beyer C and
Zendedel A: Inflammasome: Its role in traumatic brain and spinal
cord injury. J Cell Physiol. 233:5160–5169. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zendedel A, Monnink F, Hassanzadeh G,
Zaminy A, Ansar MM, Habib P, Slowik A, Kipp M and Beyer C: Estrogen
attenuates local inflammasome expression and activation after
spinal cord injury. Mol Neurobiol. 55:1364–1375. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chen K, Deng S, Lu H, Zheng Y, Yang G, Kim
D, Cao Q and Wu JQ: RNA-seq characterization of spinal cord injury
transcriptome in acute/subacute phases: A resource for
understanding the pathology at the systems level. PLoS One.
8:e725672013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Huang Q, Wu LY, Wang Y and Zhang XS: GOMA:
Functional enrichment analysis tool based on GO modules. Chin J
Cancer. 32:195–204. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Burridge K: Focal adhesions: A personal
perspective on a half century of progress. FEBS J. 284:3355–3361.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
LaFlamme SE, Mathew-Steiner S, Singh N,
Colello-Borges D and Nieves B: Integrin and microtubule crosstalk
in the regulation of cellular processes. Cell Mol Life Sci.
75:4177–4185. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
De Pascalis C and Etienne-Manneville S:
Single and collective cell migration: The mechanics of adhesions.
Mol Biol Cell. 28:1833–1846. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Rabelink TJ, van den Berg BM, Garsen M,
Wang G, Elkin M and van der Vlag J: Heparanase: Roles in cell
survival, extracellular matrix remodelling and the development of
kidney disease. Nat Rev Nephrol. 13:201–212. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Bonnans C, Chou J and Werb Z: Remodelling
the extracellular matrix in development and disease. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 15:786–801. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yue B: Biology of the extracellular
matrix: An overview. J Glaucoma. 23 (8 Suppl 1):S20–S23. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Roy S, Rizvi ZA and Awasthi A: Metabolic
checkpoints in differentiation of helper T cells in tissue
inflammation. Front Immunol. 9:30362019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ridiandries A, Tan JTM and Bursill CA: The
role of chemokines in wound healing. Int J Mol Sci. 19(pii):
E32172018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wang JG, Williams JC, Davis BK, Jacobson
K, Doerschuk CM, Ting JP and Mackman N: Monocytic microparticles
activate endothelial cells in an IL-1β-dependent manner. Blood.
118:2366–2374. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Prendergast CT and Anderton SM: Immune
cell entry to central nervous system-current understanding and
prospective therapeutic targets. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug
Targets. 9:315–327. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Shechter R, London A and Schwartz M:
Orchestrated leukocyte recruitment to immune-privileged sites:
Absolute barriers versus educational gates. Nat Rev Immunol.
13:206–218. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Demeestere D, Libert C and Vandenbroucke
RE: Clinical implications of leukocyte infiltration at the choroid
plexus in (neuro)inflammatory disorders. Drug Discov Today.
20:928–941. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Vergadi E, Ieronymaki E, Lyroni K,
Vaporidi K and Tsatsanis C: Akt signaling pathway in macrophage
activation and M1/M2 polarization. J Immunol. 198:1006–1014. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kim C, Ye F and Ginsberg MH: Regulation of
integrin activation. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 27:321–345. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Pollan SG, Huang F, Sperger JM, Lang JM,
Morrissey C, Cress AE, Chu CY, Bhowmick NA, You S, Freeman MR, et
al: Regulation of inside-out β1-integrin activation by CDCP1.
Oncogene. 37:2817–2836. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Dehne N, Fuhrmann D and Brune B:
Hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) in hormone signaling during health
and disease. Cardiovasc Hematol Agents Med Chem. 11:125–135. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Risbud MV and Shapiro IM: Notochordal
cells in the adult intervertebral disc: New perspective on an old
question. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 21:29–41. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|