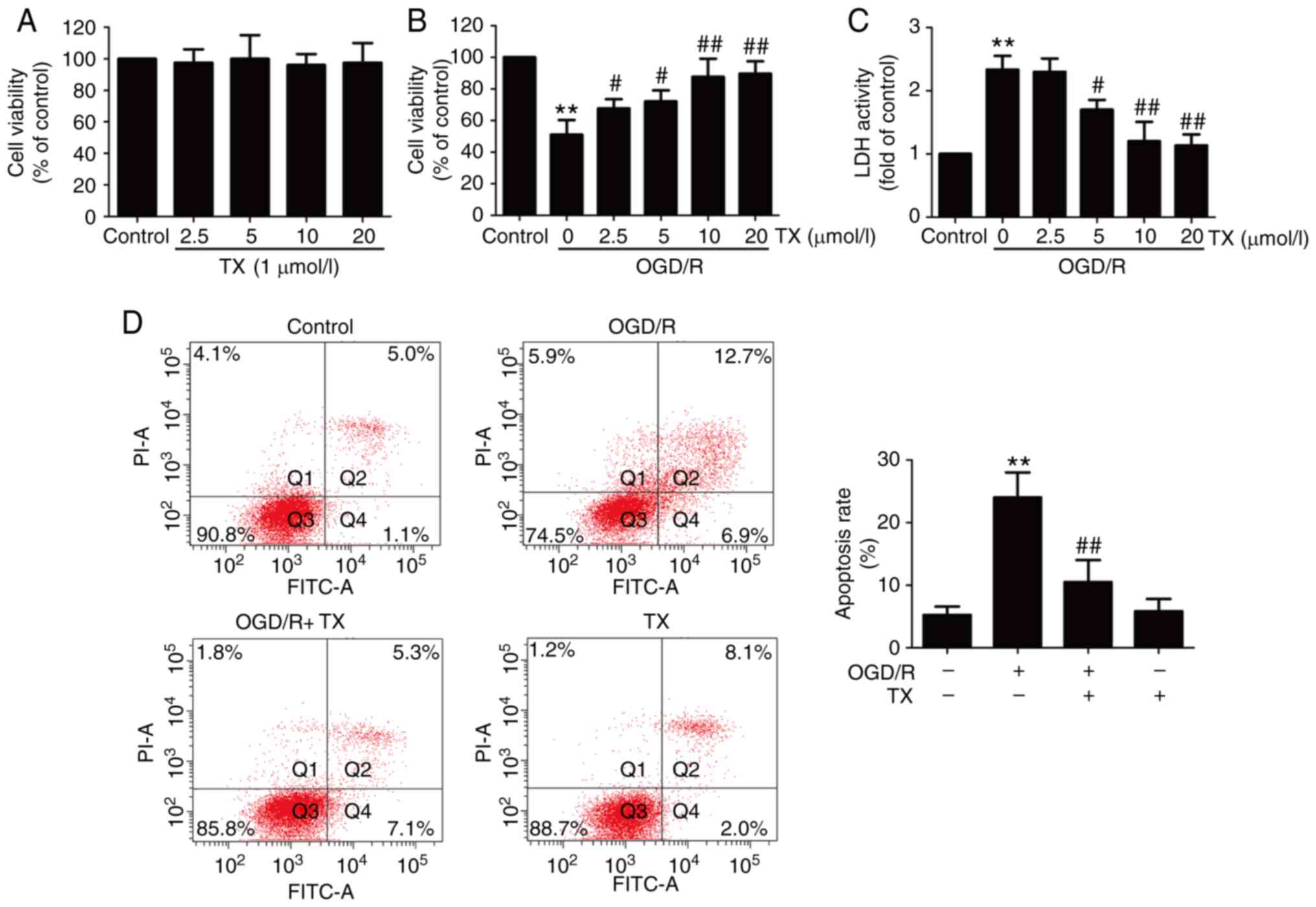
|
1
|
Kalogeris T, Baines CP, Krenz M and
Korthuis RJ: Ischemia/reperfusion. Compr Physiol. 7:113–170. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Yang CF: Clinical manifestations and basic
mechanisms of myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. Ci Ji Yi Xue
Za Zhi. 30:209–215. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hausenloy DJ and Yellon DM: Myocardial
ischemia-reperfusion injury: A neglected therapeutic target. J Clin
Invest. 123:92–100. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Donato M, Evelson P and Gelpi RJ:
Protecting the heart from ischemia/reperfusion injury: An update on
remote ischemic preconditioning and postconditioning. Curr Opin
Cardiol. 32:784–790. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hentia C, Rizzato A, Camporesi E, Yang Z,
Muntean DM, Săndesc D and Bosco G: An overview of protective
strategies against ischemia/reperfusion injury: The role of
hyperbaric oxygen preconditioning. Brain Behav. 8:e009592018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Huang Z, Zhang L, Wang Y, Gao H, Li X,
Huang X and Huang T: Effects of rutin and its derivatives on
citrinin production by Monascus aurantiacus Li AS3.4384 in liquid
fermentation using different types of media. Food Chem.
284:205–212. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zavvari Oskuye Z, Mirzaei Bavil F,
Hamidian GR, Mehri K, Qadiri A, Ahmadi M, Oghbaei H, Vatankhah AM
and Keyhanmanesh R: Troxerutin affects the male fertility in
prepubertal type 1 diabetic male rats. Iran J Basic Med Sci.
22:197–205. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Raja B, Saranya D and Prabhu R: Role of
flavonoid troxerutin on blood pressure, oxidative stress and
regulation of lipid metabolism. Front Biosci (Elite Ed).
11:121–129. 2019. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Xin X, Zhang M, Li X, Lai F and Zhao G:
Biocatalytic synthesis of acylated derivatives of troxerutin: Their
bioavailability and antioxidant properties in vitro. Microb Cell
Fact. 17:1302018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Najafi M, Noroozi E, Javadi A and
Badalzadeh R: Anti-arrhythmogenic and anti-inflammatory effects of
troxerutin in ischemia/reperfusion injury of diabetic myocardium.
Biomed Pharmacother. 102:385–391. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yu Y and Zheng G: Troxerutin protects
against diabetic cardiomyopathy through NFkappaB/AKT/IRS1 in a rat
model of type 2 diabetes. Mol Med Rep. 15:3473–3478. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Mokhtari B, Badalzadeh R, Alihemmati A and
Mohammadi M: Phosphorylation of GSK-3β and reduction of apoptosis
as targets of troxerutin effect on reperfusion injury of diabetic
myocardium. Eur J Pharmacol. 765:316–321. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Badalzadeh R, Baradaran B, Alihemmati A,
Yousefi B and Abbaszadeh A: Troxerutin preconditioning and ischemic
postconditioning modulate inflammatory response after myocardial
ischemia/reperfusion injury in rat model. Inflammation. 40:136–143.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Gielis JF, Beckers PAJ, Briede JJ, Cos P
and Van Schil PE: Oxidative and nitrosative stress during pulmonary
ischemia-reperfusion injury: From the lab to the OR. Ann Transl
Med. 5:1312017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hernandez-Resendiz S, Chinda K, Ong SB,
Cabrera-Fuentes H, Zazueta C and Hausenloy DJ: The role of redox
dysregulation in the inflammatory response to Acute myocardial
ischaemia-reperfusion injury-adding fuel to the fire. Curr Med
Chem. 25:1275–1293. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Cadenas S: ROS and redox signaling in
myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury and cardioprotection. Free
Radic Biol Med. 117:76–89. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Gonzalez-Montero J, Brito R, Gajardo AI
and Rodrigo R: Myocardial reperfusion injury and oxidative stress:
Therapeutic opportunities. World J Cardiol. 10:74–86. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Katsuki S, Matoba T, Koga JI, Nakano K and
Egashira K: Anti-inflammatory nanomedicine for cardiovascular
disease. Front Cardiovasc Med. 4:872017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sinning C, Westermann D and Clemmensen P:
Oxidative stress in ischemia and reperfusion: Current concepts,
novel ideas and future perspectives. Biomark Med. 11:11031–11040.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sun XH, Wang X, Zhang Y and Hui J:
Exosomes of bone-marrow stromal cells inhibit cardiomyocyte
apoptosis under ischemic and hypoxic conditions via miR-486-5p
targeting the PTEN/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Thromb Res.
177:23–32. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yao H and Han X and Han X: The
cardioprotection of the insulin-mediated PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling
pathway. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 14:433–442. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Agani F and Jiang BH: Oxygen-independent
regulation of HIF-1: Novel involvement of PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in
cancer. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 13:245–251. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Brocato J, Chervona Y and Costa M:
Molecular responses to hypoxia-inducible factor 1α and beyond. Mol
Pharmacol. 85:651–657. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Jianqiang P, Ping Z, Xinmin F, Zhenhua Y,
Ming Z and Ying G: Expression of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha
ameliorate myocardial ischemia in rat. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
465:691–695. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Li M, Cui Y, He W, Deng X, Wang Y, Cai M,
Wang Y, Pei J, Mei X and Wu P: Effects of triple-mutated
hypoxia-inducible factor-1α on angiogenesis and cardiac function
improvement in rats with myocardial infarction. Cell Physiol
Biochem. 50:2329–2340. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Man S, Chai H, Cui J, Yao J, Ma L and Gao
W: Antitumor and anti-metastatic mechanisms of Rhizoma paridis
saponins in Lewis mice. Environ Toxicol. 33:149–155. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Movafagh S, Crook S and Vo K: Regulation
of hypoxia-inducible factor-1a by reactive oxygen species: New
developments in an old debate. J Cell Biochem. 116:696–703. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Liang S, Wang Y and Liu Y: Dexmedetomidine
alleviates lung ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats by activating
PI3K/Akt pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 23:370–377.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Liang Z, Chi YJ, Lin GQ, Luo SH, Jiang QY
and Chen YK: MiRNA-26a promotes angiogenesis in a rat model of
cerebral infarction via PI3K/AKT and MAPK/ERK pathway. Eur Rev Med
Pharmacol Sci. 22:3485–3492. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wei J and Wu J, Xu W, Nie H, Zhou R, Wang
R, Liu Y, Tang G and Wu J: Salvianolic acid B inhibits glycolysis
in oral squamous cell carcinoma via targeting PI3K/AKT/HIF-1α
signaling pathway. Cell Death Dis. 9:5992018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Shu L, Zhang W, Huang G, Huang C, Zhu X,
Su G and Xu J: Troxerutin attenuates myocardial cell apoptosis
following myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury through inhibition
of miR-146a-5p expression. J Cell Physiol. 234:9274–9282. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Liu J, Sui H, Zhao J and Wang Y: Osmotin
protects H9c2 cells from simulated ischemia-reperfusion injury
through AdipoR1/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Front Physiol.
8:6112017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Liu Q, Li J, Wang J, Li J, Janicki JS and
Fan D: Effects and mechanisms of chinese herbal medicine in
ameliorating myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. Evid Based
Complement Alternat Med. 2013:9256252013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Shu L, Zhang W, Huang C, Huang G and Su G:
Troxerutin protects against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury
Via Pi3k/Akt pathway in rats. Cell Physiol Biochem. 44:1939–1948.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Lee SH, Wolf PL, Escudero R, Deutsch R,
Jamieson SW and Thistlethwaite PA: Early expression of angiogenesis
factors in acute myocardial ischemia and infarction. N Engl J Med.
342:626–633. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Semenza GL: HIF-1: Mediator of
physiological and pathophysiological responses to hypoxia. J Appl
Physiol (1985). 88:1474–1480. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Sun N, Meng F, Xue N, Pang G, Wang Q and
Ma H: Inducible miR-145 expression by HIF-1a protects
cardiomyocytes against apoptosis via regulating SGK1 in simulated
myocardial infarction hypoxic microenvironment. Cardiol J.
25:268–278. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Yu L, Zhang W, Huang C, Liang Q, Bao H,
Gong Z, Xu M, Wang Z, Wen M and Cheng X: FoxO4 promotes myocardial
ischemia-reperfusion injury: The role of oxidative stress-induced
apoptosis. Am J Transl Res. 10:2890–2900. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Ma W, Wang S, Liu X, Tang F, Zhao P, Cheng
K, Zheng Q, Zhuo Y, Zhao X, Li X and Feng W: Protective effect of
troxerutin and cerebroprotein hydrolysate injection on cerebral
ischemia through inhibition of oxidative stress and promotion of
angiogenesis in rats. Mol Med Rep. 19:3148–3158. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Geetha R, Sathiya Priya C and Anuradha CV:
Troxerutin abrogates mitochondrial oxidative stress and myocardial
apoptosis in mice fed calorie-rich diet. Chem Biol Interact.
278:74–83. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Sies H: Oxidative stress: A concept in
redox biology and medicine. Redox Biol. 4:180–183. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Czerska M, Mikołajewska K, Zieliński M,
Gromadzińska J and Wąsowicz W: Today's oxidative stress markers.
Med Pr. 66:393–405. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Ong SB, Hernández-Reséndiz S,
Crespo-Avilan GE, Mukhametshina RT, Kwek XY, Cabrera-Fuentes HA and
Hausenloy DJ: Inflammation following acute myocardial infarction:
Multiple players, dynamic roles, and novel therapeutic
opportunities. Pharmacol Ther. 186:73–87. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Zhào H, Liu Y, Zeng J, Li D, Zhang W and
Huang Y: Troxerutin and cerebroprotein hydrolysate injection
protects neurovascular units from oxygen-glucose deprivation and
reoxygenation-induced injury in vitro. Evid Based Complement
Alternat Med. 2018:98596722018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Shan Q, Zheng GH, Han XR, Wen X, Wang S,
Li MQ, Zhuang J, Zhang ZF, Hu B, Zhang Y and Zheng YL: Troxerutin
protects kidney tissue against BDE-47-induced inflammatory damage
through CXCR4-TXNIP/NLRP3 signaling. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2018:98654952018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Shan Q, Zhuang J, Zheng G, Zhang Z, Zhang
Y, Lu J and Zheng Y: Troxerutin reduces kidney damage against
BDE-47-induced apoptosis via inhibiting NOX2 activity and
increasing Nrf2 activity. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017.6034692.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Qiu Z, Lei S, Zhao B, Wu Y, Su W, Liu M,
Meng Q, Zhou B, Leng Y and Xia ZY: NLRP3 inflammasome
activation-mediated pyroptosis aggravates myocardial
ischemia/reperfusion injury in diabetic rats. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2017:97432802017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Shen Y, Liu X, Shi J and Wu X: Involvement
of Nrf2 in myocardial ischemia and reperfusion injury. Int J Biol
Macromol. 125:496–502. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|