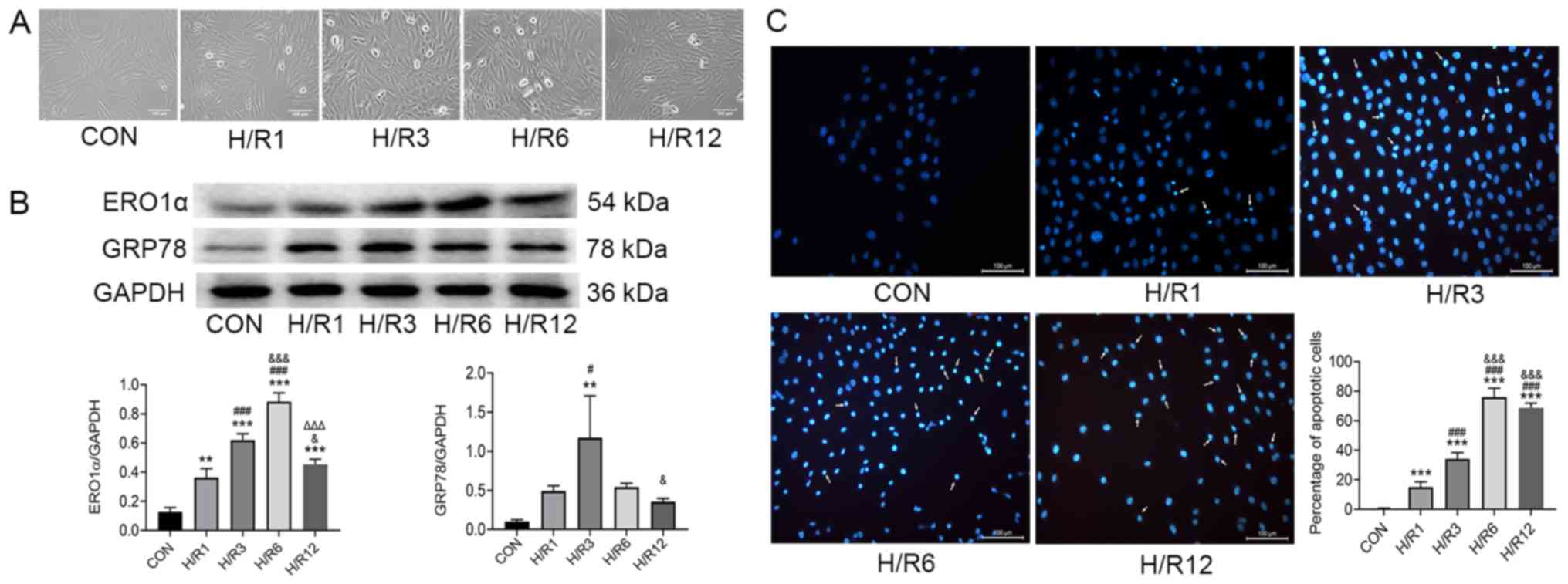
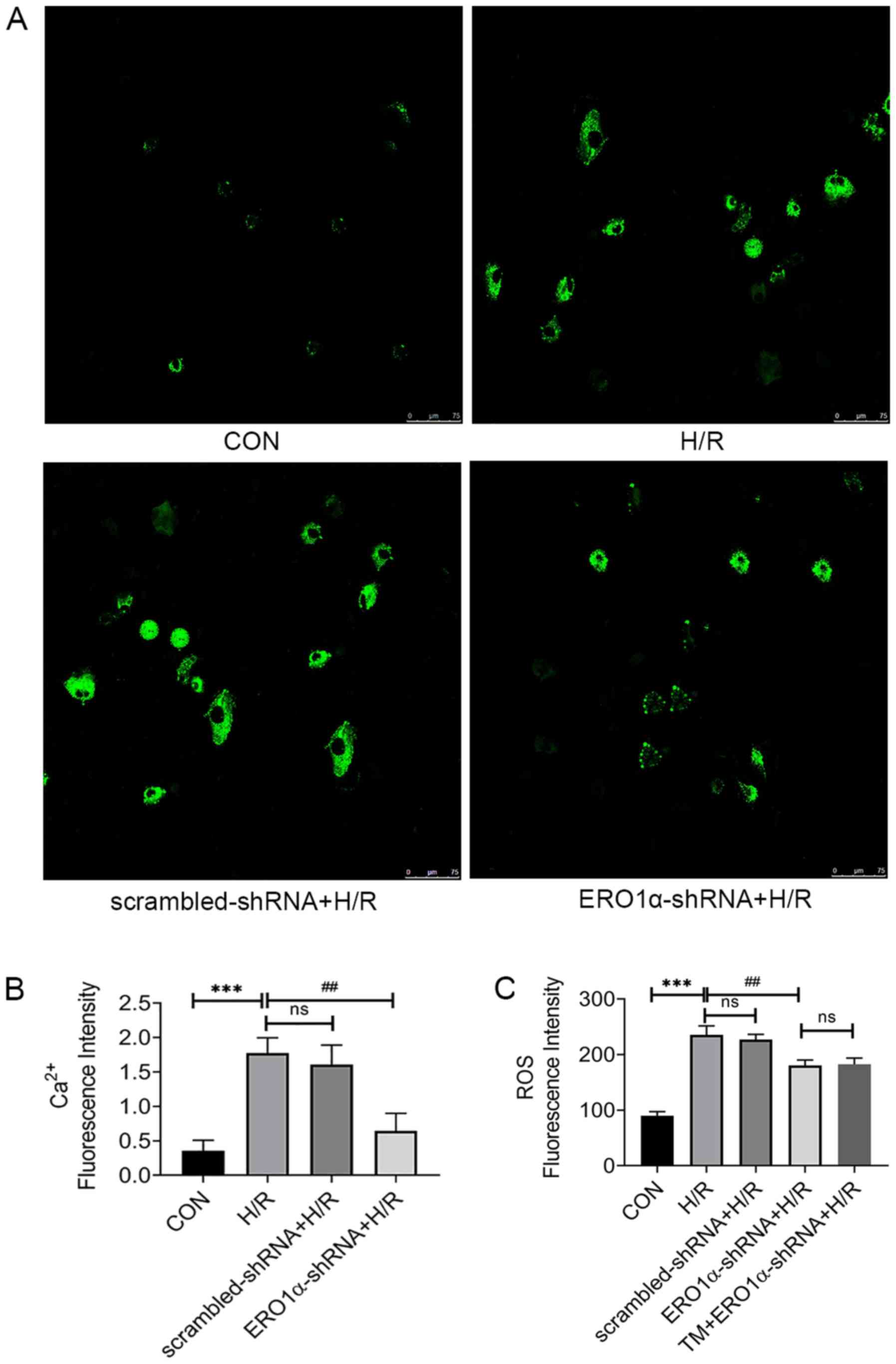
|
1
|
Braunwald E and Kloner RA: Myocardial
reperfusion: A double-edged sword? J Clin Invest. 76:1713–1719.
1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hausenloy DJ and Yellon DM: Ischaemic
conditioning and reperfusion injury. Nat Rev Cardiol. 13:193–209.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hausenloy DJ and Yellon DM: Myocardial
ischemia-reperfusion injury: A neglected therapeutic target. J Clin
Invest. 123:92–100. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Dhalla NS, Elmoselhi AB, Hata T and Makino
N: Status of myocardial antioxidants in ischemia-reperfusion
injury. Cardiovasc Res. 47:446–456. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chang JC, Lien CF, Lee WS, Chang HR, Hsu
YC, Luo YP, Jeng JR, Hsieh JC and Yang KT: Intermittent hypoxia
prevents myocardial mitochondrial Ca2+ overload and cell
death during ischemia/reperfusion: The role of reactive oxygen
species. Cells. 8:E5642019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Farrukh MR, Nissar UA, Afnan Q, Rafiq RA,
Sharma L, Amin S, Kaiser P, Sharma PR and Tasduq SA: Oxidative
stress mediated Ca (2+) release manifests endoplasmic reticulum
stress leading to unfolded protein response in UV-B irradiated
human skin cells. J Dermatol Sci. 75:24–35. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Martindale JJ, Fernandez R, Thuerauf D,
Whittaker R, Gude N, Sussman MA and Glembotski CC: Endoplasmic
reticulum stress gene induction and protection from
ischemia/reperfusion injury in the hearts of transgenic mice with a
tamoxifen-regulated form of ATF6. Circ Res. 98:1186–1193. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Jian L, Lu Y, Lu S and Lu C: Chemical
chaperone 4-phenylbutyric acid reduces cardiac ischemia/reperfusion
injury by alleviating endoplasmic reticulum stress and oxidative
stress. Med Sci Monit. 22:5218–5227. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kerkhofs M, Giorgi C, Marchi S, Seitaj B,
Parys JB, Pinton P, Bultynck G and Bittremieux M: Alterations in
Ca2+ signalling via ER-mitochondria contact site
remodelling in cancer. Adv Exp Med Biol. 997:225–254. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kerkhofs M, Bittremieux M, Morciano G,
Giorgi C, Pinton P, Parys JB and Bultynck G: Emerging molecular
mechanisms in chemotherapy: Ca2+ signaling at the
mitochondria-associated endoplasmic reticulum membranes. Cell Death
Dis. 9:3342018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Morciano G, Marchi S, Morganti C, Sbano L,
Bittremieux M, Kerkhofs M, Corricelli M, Danese A,
Karkucinska-Wieckowska A, Wieckowski MR, et al: Role of
mitochondria-associated ER membranes in calcium regulation in
cancer-specific settings. Neoplasia. 20:510–523. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Dias-Gunasekara S, Gubbens J, van Lith M,
Dunne C, Williams JA, Kataky R, Scoones D, Lapthorn A, Bulleid NJ
and Benham AM: Tissue specific expression and dimerization of the
endoplasmic reticulum oxidoreductase Ero1beta. J Biol Chem.
280:33066–33075. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zito E, Chin KT, Blais J, Harding HP and
Ron D: ERO1-beta, a pancreas-specific disulfide oxidase, promotes
insulin biogenesis and glucose homeostasis. J Cell Biol.
188:821–832. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Pagani M, Fabbri M, Benedetti C, Fassio A,
Pilati S, Bulleid NJ, Cabibbo A and Sitia R: Endoplasmic reticulum
oxidoreductin 1-Lbeta (ERO1-Lbeta), a human gene induced in the
course of the unfolded protein response. J Biol Chem.
275:23685–23692. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Gess B, Hofbauer KH, Wenger RH, Lohaus C,
Meyer HE and Kurtz A: The cellular oxygen tension regulates
expression of the endoplasmic oxidoreductase ERO1-Lalpha. Eur J
Biochem. 270:2228–2235. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sevier CS and Kaiser CA: Ero1 and redox
homeostasis in the endoplasmic reticulum. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1783:549–556. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Seervi M, Sobhan PK, Joseph J, Ann Mathew
K and Santhoshkumar TR: ERO1α-dependent endoplasmic
reticulum-mitochondrial calcium flux contributes to ER stress and
mitochondrial permeabilization by procaspase-activating compound-1
(PAC-1). Cell Death Dis. 4:e9682013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Nakamura K, Tamaki H, Kang MS, Mochimaru
H, Lee ST, Nakamura K and Kamagata Y: A six-well plate method: Less
laborious and effective method for cultivation of obligate
anaerobic microorganisms. Microbes Environ. 26:301–306. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Li J, Xia X, Ke Y, Nie H, Smith MA and Zhu
X: Trichosanthin induced apoptosis in HL-60 cells via mitochondrial
and endoplasmic reticulum stress signaling pathways. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1770:1169–1180. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lai LN, Zhang XJ, Zhang XY, Song LH, Guo
CH, Lei JW and Song XL: Lazaroid U83836E protects the heart against
ischemia reperfusion injury via inhibition of oxidative stress and
activation of PKC. Mol Med Rep. 13:3993–4000. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lai L, Chen Y, Tian X, Li X, Zhang X, Lei
J, Bi Y, Fang B and Song X: Artesunate alleviates hepatic fibrosis
induced by multiple pathogenic Factors and inflammation through the
inhibition of LPS/TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway in rats. Eur J
Pharmacol. 765:234–241. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wu H, Ye M, Yang J and Ding J: Modulating
endoplasmic reticulum stress to alleviate myocardial ischemia and
reperfusion injury from basic research to clinical practice: A long
way to go. Int J Cardiol. 223:630–631. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yu L, Li S, Tang X, Li Z, Zhang J, Xue X,
Han J, Liu Y, Zhang Y, Zhang Y, et al: Diallyl trisulfide
ameliorates myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury by reducing
oxidative stress and endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated
apoptosis in type 1 diabetic rats: Role of SIRT1 activation.
Apoptosis. 22:942–954. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yoon S, Park SJ, Han JH, Kang JH, Kim JH,
Lee J, Park S, Shin HJ, Kim K, Yun M and Chwae YJ:
Caspase-dependent cell death-associated release of nucleosome and
damage-associated molecular patterns. Cell Death Dis. 5:e14942014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Groenendyk J, Sreenivasaiah PK, Kim DH,
Agellon LB and Michalak M: Biology of endoplasmic reticulum stress
in the heart. Circ Res. 107:1185–1197. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Weiss JN, Korge P, Honda HM and Ping P:
Role of the mitochondrial permeability transition in myocardial
disease. Circ Res. 93:292–301. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kalogeris T, Baines CP, Krenz M and
Korthuis RJ: Cell biology of ischemia/reperfusion injury. Int Rev
Cell Mol Biol. 298:229–317. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Gelebart P, Opas M and Michalak M:
Calreticulin, a Ca2+-binding chaperone of the
endoplasmic reticulum. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 37:260–266. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Doroudgar S and Glembotski CC: New
concepts of endoplasmic reticulum function in the heart: Programmed
to conserve. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 55:85–91. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Guan G, Zhang J, Liu S, Huang W, Gong Y
and Gu X: Glucagon-like peptide-1 attenuates endoplasmic reticulum
stress-induced apoptosis in H9c2 cardiomyocytes during
hypoxia/reoxygenation through the GLP-1R/PI3K/Akt pathways. Naunyn
Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 392:715–722. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wang XB, Huang XM, Ochs T, Li XY, Jin HF,
Tang CS and Du JB: Effect of sulfur dioxide preconditioning on rat
myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury by inducing endoplasmic
reticulum stress. Basic Res Cardiol. 106:865–878. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Xu J, Hu H, Chen B, Yue R, Zhou Z, Liu Y,
Zhang S, Xu L, Wang H and Yu Z: Lycopene protects against
hypoxia/reoxygenation injury by alleviating ER stress induced
apoptosis in neonatal mouse cardiomyocytes. PLoS One.
10:e01364432015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zito E: ERO1: A protein disulfide oxidase
and H2O2 producer. Free Radic Biol Med. 83:299–304. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zeeshan HM, Lee GH, Kim HR and Chae HJ:
Endoplasmic reticulum stress and associated ROS. Int J Mol Sci.
17:3272016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Yang X, Xu H, Hao Y, Zhao L, Cai X, Tian
J, Zhang M, Han X, Ma S, Cao J and Jiang Y: Endoplasmic reticulum
oxidoreductin 1α mediates hepatic endoplasmic reticulum stress in
homocysteine-induced atherosclerosis. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin
(Shanghai). 46:902–910. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Neuber C, Uebeler J, Schulze T, Sotoud H,
El-Armouche A and Eschenhagen T: Guanabenz interferes with ER
stress and exerts protective effects in cardiac myocytes. PLoS One.
9:e988932014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zhu X, Zhang ZL, Li P, Liang WY, Feng XR
and Liu ML: Shenyuan, an extract of American ginseng and corydalis
tuber formula, attenuates cardiomyocyte apoptosis via inhibition of
endoplasmic reticulum stress and oxidative stress in a porcine
model of myocardial infarction. J Ethnopharmacol. 150:672–681.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Mei Y, Thompson MD, Shiraishi Y, Cohen RA
and Tong X: Sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+
ATPase C674 promotes ischemia- and hypoxia-induced angiogenesis via
coordinated endothelial cell and macrophage function. J Mol Cell
Cardiol. 76:275–282. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Szegezdi E, Fitzgerald U and Samali A:
Caspase-12 and ER-stress-mediated apoptosis: The story so far. Ann
NY Acad Sci. 1010:186–194. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Giorgi C, De Stefani D, Bononi A, Rizzuto
R and Pinton P: Structural and functional link between the
mitochondrial network and the endoplasmic reticulum. Int J Biochem
Cell Biol. 41:1817–1827. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Park SJ, Lee SB, Suh Y, Kim SJ, Lee N,
Hong JH, Park C, Woo Y, Ishizuka K, Kim JH, et al: DISC1 modulates
neuronal stress responses by gate-keeping ER-mitochondria
Ca2+ transfer through the MAM. Cell Rep. 21:2748–2759.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Marchi S, Bittremieux M, Missiroli S,
Morganti C, Patergnani S, Sbano L, Rimessi A, Kerkhofs M, Parys JB,
Bultynck G, et al: Endoplasmic reticulum-mitochondria communication
through Ca2+ signaling: The importance of
mitochondria-associated membranes (MAMs). Adv Exp Med Biol.
997:49–67. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Yang L, Guan G, Lei L, Liu J, Cao L and
Wang X: Oxidative and endoplasmic reticulum stresses are involved
in palmitic acid-induced H9c2 cell apoptosis. Biosci Rep.
39:BSR201902252019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Kang S, Kang J, Kwon H, Frueh D, Yoo SH,
Wagner G and Park S: Effects of redox potential and Ca2+
on the inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor L3-1 loop region:
Implications for receptor regulation. J Biol Chem. 283:25567–25575.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Li G, Mongillo M, Chin KT, Harding H, Ron
D, Marks AR and Tabas I: Role of ERO1-alpha-mediated stimulation of
inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate receptor activity in endoplasmic
reticulum stress-induced apoptosis. J Cell Biol. 186:783–792. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|