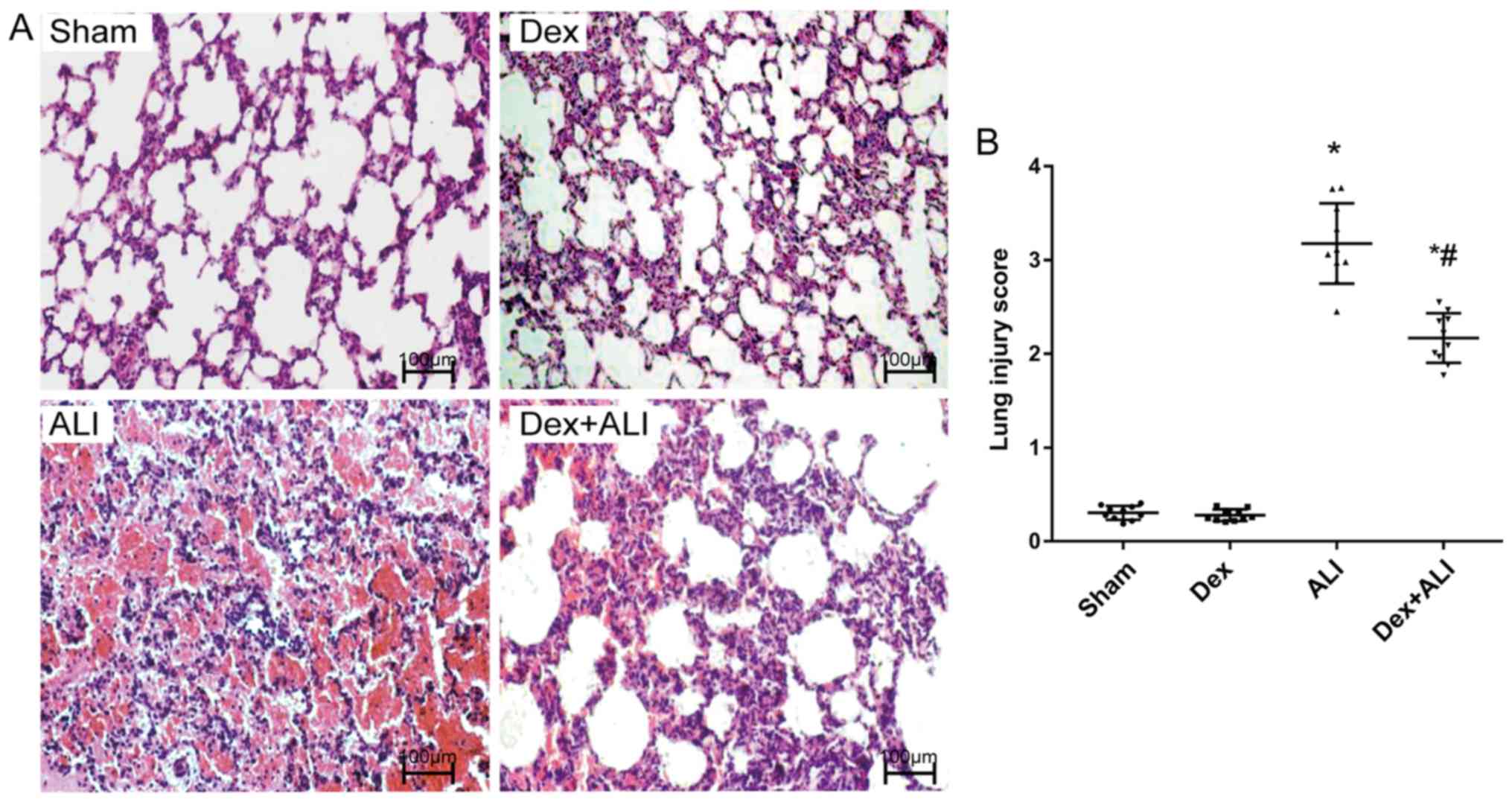
|
1
|
Ehrnthaller C, Flierl M, Perl M, Denk S,
Unnewehr H, Ward PA, Radermacher P, Ignatius A, Gebhard F,
Chinnaiyan A and Huber-Lang M: The molecular fingerprint of lung
inflammation after blunt chest trauma. Eur J Med Res. 20:702015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kauvar DS and Wade CE: The epidemiology
and modern management of traumatic hemorrhage: US and international
perspectives. Crit Care 9 Suppl. 5 (Suppl 5):S1–S9. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Sauaia A, Moore EE, Johnson JL, Chin TL,
Banerjee A, Sperry JL, Maier RV and Burlew CC: Temporal trends of
postinjury multiple-organ failure: Still resource intensive,
morbid, and lethal. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 76:582–593. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Angele MK, Schneider CP and Chaudry IH:
Bench-to-bedside review: Latest results in hemorrhagic shock. Crit
Care. 12:2182008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Eltzschig HK and Eckle T: Ischemia and
reperfusion-from mechanism to translation. Nat Med. 17:1391–1401.
2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Shah CV, Localio AR, Lanken PN, Kahn JM,
Bellamy S, Gallop R, Finkel B, Gracias VH, Fuchs BD and Christie
JD: The impact of development of acute lung injury on hospital
mortality in critically ill trauma patients. Crit Care Med.
36:2309–2315. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Villar J, Blanco J and Kacmarek RM:
Current incidence and outcome of the acute respiratory distress
syndrome. Curr Opin Crit Care. 22:1–6. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Xu P, Wen Z, Shi X, Li Y, Fan L, Xiang M,
Li A, Scott MJ, Xiao G, Li S, et al: Hemorrhagic shock augments
Nlrp3 inflammasome activation in the lung through impaired pyrin
induction. J Immunol. 190:5247–5255. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Grailer JJ, Canning BA, Kalbitz M,
Haggadone MD, Dhond RM, Andjelkovic AV, Zetoune FS and Ward PA:
Critical role for the NLRP3 inflammasome during acute lung injury.
J Immunol. 192:5974–5983. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Mangan MSJ, Olhava EJ, Roush WR, Seidel
HM, Glick GD and Latz E: Targeting the NLRP3 inflammasome in
inflammatory diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 17:588–606. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lee HM, Kim JJ, Kim HJ, Shong M, Ku BJ and
Jo EK: Upregulated NLRP3 inflammasome activation in patients with
type 2 diabetes. Diabetes. 62:194–204. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Duewell P, Kono H, Rayner KJ, Sirois CM,
Vladimer G, Bauernfeind FG, Abela GS, Franchi L, Nuñez G, Schnurr
M, et al: NLRP3 inflammasomes are required for atherogenesis and
activated by cholesterol crystals. Nature. 464:1357–1361. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhen Y and Zhang H: NLRP3 inflammasome and
inflammatory bowel disease. Front Immunol. 10:2762019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Primiano MJ, Lefker BA, Bowman MR, Bree
AG, Hubeau C, Bonin PD, Mangan M, Dower K, Monks BG, Cushing L, et
al: Efficacy and pharmacology of the NLRP3 inflammasome inhibitor
CP-456,773 (CRID3) in murine models of dermal and pulmonary
inflammation. J Immunol. 197:2421–2433. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Mizushina Y, Karasawa T, Aizawa K, Kimura
H, Watanabe S, Kamata R, Komada T, Mato N, Kasahara T, Koyama S, et
al: Inflammasome-independent and atypical processing of IL-1β
contributes to acid aspiration-induced acute lung injury. J
Immunol. 203:236–246. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Afonso J and Reis F: Dexmedetomidine:
Current role in anesthesia and intensive care. Rev Bras Anestesiol.
62:118–133. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Carollo DS, Nossaman BD and Ramadhyani U:
Dexmedetomidine: A review of clinical applications. Curr Opin
Anaesthesiol. 21:457–461. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Xu Y, Zhang R, Li C, Yin X, Lv C, Wang Y,
Zhao W and Zhang X: Dexmedetomidine attenuates acute lung injury
induced by lipopolysaccharide in mouse through inhibition of MAPK
pathway. Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 29:462–471. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhang Q, Wu D, Yang Y, Liu T and Liu H:
Dexmedetomidine alleviates hyperoxia-induced acute lung injury via
inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Cell Physiol Biochem.
42:1907–1919. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kang K, Gao Y, Wang SC, Liu HT, Kong WL,
Zhang X, Huang R, Qi ZD, Zheng JB, Qu JD, et al: Dexmedetomidine
protects against lipopolysaccharide-induced sepsis-associated acute
kidney injury via an α7 nAChR-dependent pathway. Biomed
Pharmacother. 106:210–216. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Jiang Y, Xia M, Huang Q, Ding D, Li Y,
Zhang Z and Zhang X: Protective effect of dexmedetomidine against
organ dysfunction in a two-hit model of hemorrhage/resuscitation
and endotoxemia in rats. Braz J Med Biol Res. 52:e79052019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Cheng F, Yan FF, Liu YP, Cong Y, Sun KF
and He XM: Dexmedetomidine inhibits the NF-κB pathway and NLRP3
inflammasome to attenuate papain-induced osteoarthritis in rats.
Pharm Biol. 57:649–659. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yin D, Zhou S, Xu X, Gao W, Li F, Ma Y,
Sun D, Wu Y, Guo Q, Liu H, et al: Dexmedetomidine attenuated early
brain injury in rats with subarachnoid haemorrhage by suppressing
the inflammatory response: The TLR4/NF-κB pathway and the NLRP3
inflammasome may be involved in the mechanism. Brain Res.
1698:1–10. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
National Research Council (US) Committee
for the Update of the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory
Animals, . Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals (8th).
National Academies Press (US). Washington (DC): 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Seitz DH, Perl M, Liener UC, Tauchmann B,
Braumüller ST, Brückner UB, Gebhard F and Knöferl MW: Inflammatory
alterations in a novel combination model of blunt chest trauma and
hemorrhagic shock. J Trauma. 70:189–196. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wu XJ, Liu HM, Song XM, Zhao B, Leng Y,
Wang EY, Zhan LY, Meng QT and Xia ZY: Penehyclidine hydrochloride
inhibits TLR4 signaling and inflammation, and attenuates blunt
chest trauma and hemorrhagic shock-induced acute lung injury in
rats. Mol Med Rep. 17:6327–6336. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wu X, Song X, Li N, Zhan L, Meng Q and Xia
Z: Protective effects of dexmedetomidine on blunt chest
trauma-induced pulmonary contusion in rats. J Trauma Acute Care
Surg. 74:524–530. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Belperio JA, Keane MP, Burdick MD, Londhe
V, Xue YY, Li K, Phillips RJ and Strieter RM: Critical role for
CXCR2 and CXCR2 ligands during the pathogenesis of
ventilator-induced lung injury. J Clin Invest. 110:1703–1716. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Sun K, Fan J and Han J: Ameliorating
effects of traditional Chinese medicine preparation, Chinese
materia medica and active compounds on ischemia/reperfusion-induced
cerebral microcirculatory disturbances and neuron damage. Acta
Pharm Sin B. 5:8–24. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kao RL, Huang W, Martin CM and Rui T: The
effect of aerosolized indomethacin on lung inflammation and injury
in a rat model of blunt chest trauma. Can J Surg. 61:S208–S218.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Rendeki S and Molnár TF: Pulmonary
contusion. J Thorac Dis. 11 (Suppl 2):S141–S151. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Liu X and Chen Z: The pathophysiological
role of mitochondrial oxidative stress in lung diseases. J Transl
Med. 15:2072017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Torun AC, Tutuncu S, Ustun B and Akdemir
HU: A study of the therapeutic effects of resveratrol on blunt
chest trauma-induced acute lung injury in rats and the potential
role of endocan as a biomarker of inflammation. Inflammation.
40:1803–1810. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Lamkanfi M and Dixit VM: Mechanisms and
functions of inflammasomes. Cell. 157:1013–1022. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Pedraza-Alva G, Pérez-Martínez L,
Valdez-Hernández L, Meza-Sosa KF and Ando-Kuri M: Negative
regulation of the inflammasome: Keeping inflammation under control.
Immunol Rev. 265:231–257. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhang Y and Li X, Grailer JJ, Wang N, Wang
M, Yao J, Zhong R, Gao GF, Ward PA, Tan DX and Li X: Melatonin
alleviates acute lung injury through inhibiting the NLRP3
inflammasome. J Pineal Res. 60:405–414. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zhang H, Chen S, Zeng M, Lin D, Wang Y,
Wen X, Xu C, Yang L, Fan X, Gong Y, et al: Apelin-13 administration
protects against LPS-induced acute lung injury by inhibiting NF-κB
pathway and NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Cell Physiol Biochem.
49:1918–1932. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Li Z, Jia Y, Feng Y, Cui R, Miao R, Zhang
X, Qu K, Liu C and Zhang J: Methane alleviates sepsis-induced
injury by inhibiting pyroptosis and apoptosis: In vivo and in vitro
experiments. Aging (Albany NY). 11:1226–1239. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Deletombe B, Trouve-Buisson T, Godon A,
Falcon D, Giorgis-Allemand L, Bouzat P, Bosson JL and Payen JF:
Dexmedetomidine to facilitate non-invasive ventilation after blunt
chest trauma: A randomised, double-blind, crossover,
placebo-controlled pilot study. Anaesth Crit Care Pain Med.
38:477–483. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Fu C, Dai X, Yang Y, Lin M, Cai Y and Cai
S: Dexmedetomidine attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung
injury by inhibiting oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction
and apoptosis in rats. Mol Med Rep. 15:131–138. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Meng L, Li L, Lu S, Li K, Su Z, Wang Y,
Fan X, Li X and Zhao G: The protective effect of dexmedetomidine on
LPS-induced acute lung injury through the HMGB1-mediated TLR4/NF-κB
and PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathways. Mol Immunol. 94:7–17. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Li Y, Pan Y, Gao L, Lu G, Zhang J, Xie X,
Tong Z, Li B, Li G and Li W: Dexmedetomidine attenuates pancreatic
injury and inflammatory response in mice with pancreatitis by
possible reduction of NLRP3 activation and up-regulation of NET
expression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 495:2439–2447. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Yang CL, Tsai PS and Huang CJ: Effects of
dexmedetomidine on regulating pulmonary inflammation in a rat model
of ventilator-induced lung injury. Acta Anaesthesiol Taiwan.
46:151–159. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Tasdogan M, Memis D, Sut N and Yuksel M:
Results of a pilot study on the effects of propofol and
dexmedetomidine on inflammatory responses and intraabdominal
pressure in severe sepsis. J Clin Anesth. 21:394–400. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|