|
1
|
Jung M, Lee TH, Oh HJ, Kim H, Son Y, Lee
EH and Kim J: Inhibitory effect of 5,6-dihydroergosteol-glucoside
on atopic dermatitis-like skin lesions via suppression of NF-kappaB
and STAT activation. J Dermatol Sci. 79:2878–261. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Lim SJ, Kim M, Randy A, Nam EJ and Nho CW:
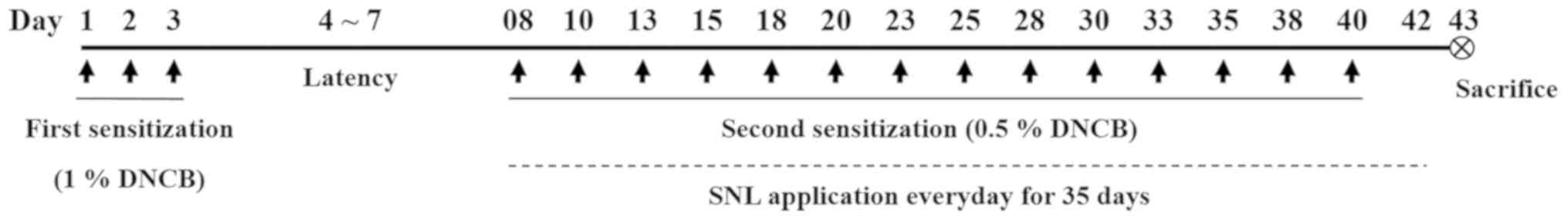
Effects of Hovenia dulcis Thunb. Extract and methyl vanillate on
atopic dermatitis-like skin lesions and TNF-α/IFN-γ-induced
chemokines production in HaCaT cells. J Pharm Pharmacol.
68:1465–1479. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
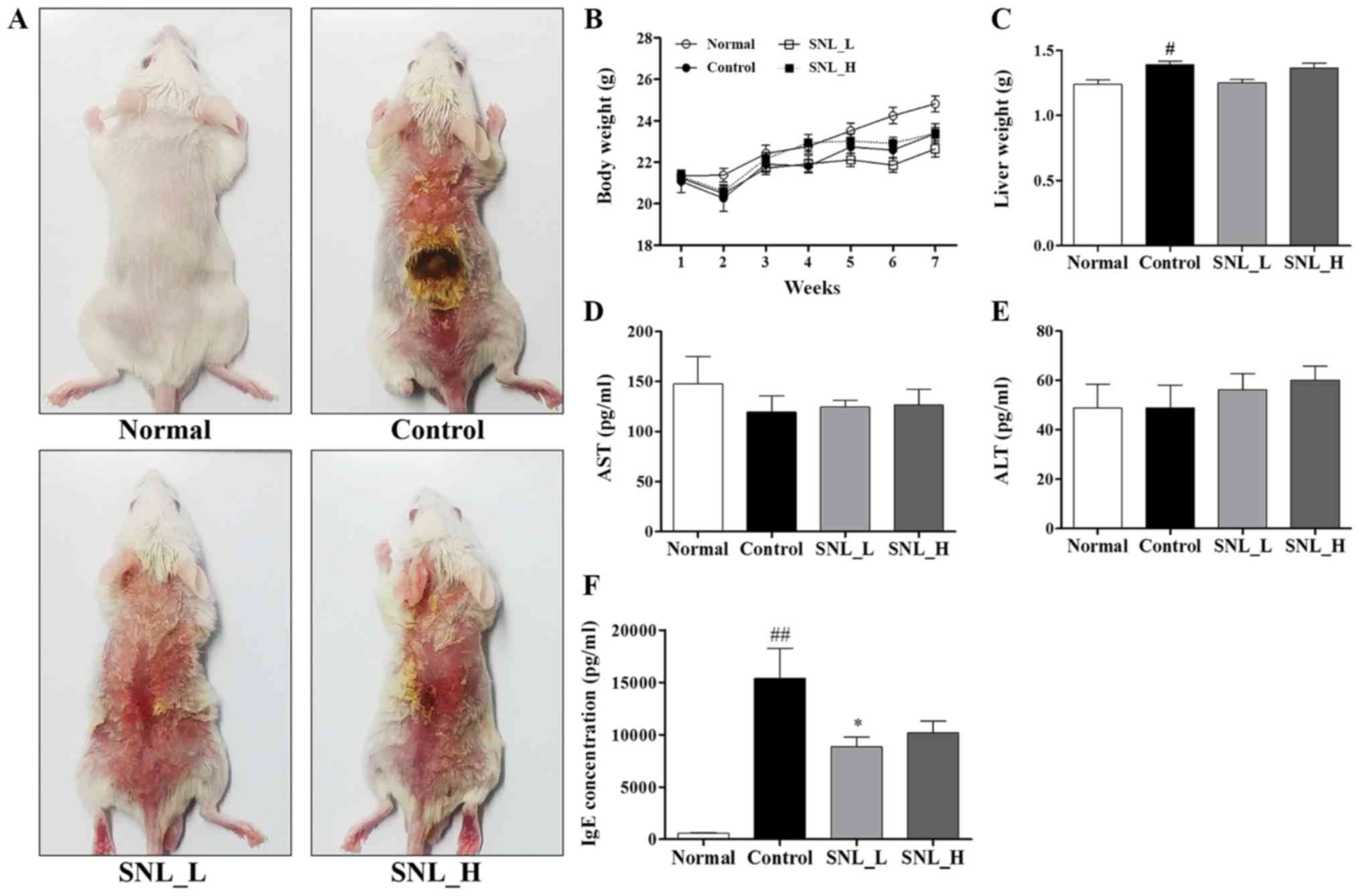
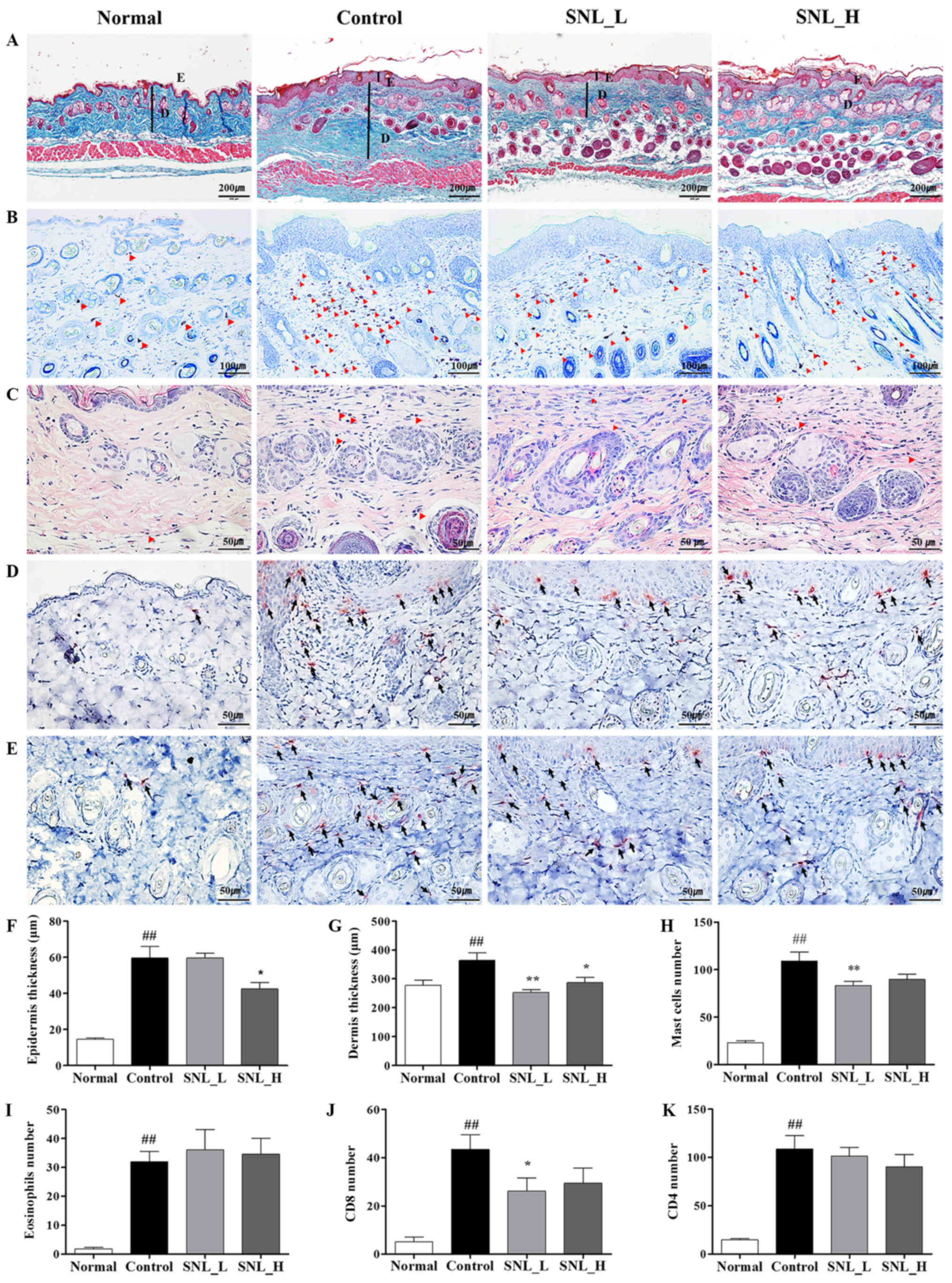
Spergel JM and Paller AS: Atopic
dermatitis and the atopic march. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 112 (Suppl
6):S118–S127. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
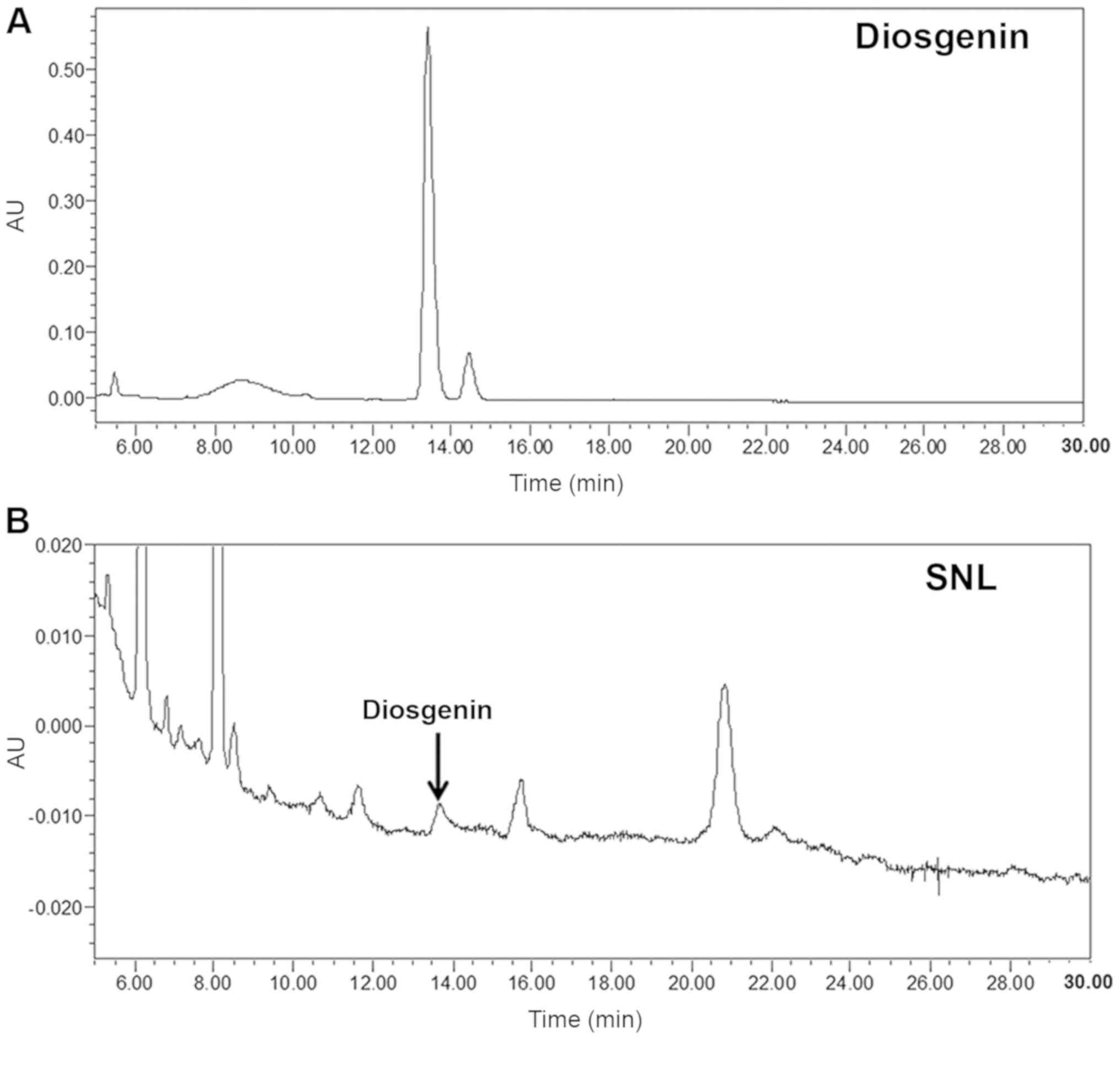
|
|
4
|
Nutten S: Atopic dermatitis: Global
epidemiology and risk factors. Ann Nutr Metab. 66 (Suppl 1):S8–S16.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Charman CR, Morris AD and Williams HC:
Topical corticosteroid phobia in patients with atopic eczema. Br J
Dermatol. 142:931–936. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Leung DYM, Boguniewicz M, Howell MD,
Nomura I and Hamid OA: New insights into atopic dermatitis. J Clin
Invest. 113:651–657. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kleiman A and Tuckermann JP:
Glucocorticoid receptor action in beneficial and side effects of
steroid therapy: Lessons from conditional knockout mice. Mol Cell
Endocrinol. 275:98–108. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Galli SJ, Tsai M and Piliponsky AM: The
development of allergic inflammation. Nature. 454:445–454. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kraneveld AD, Sagar S, Garssen J and
Folkerts G: The two faces of mast cells in food allergy and
allergic asthma: The possible concept of Yin Yang. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1822:93–99. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Dahl C, Hoffmann HJ, Saito H and Schiotz
PO: Human mast cells express receptors for IL-3, IL-5 and GM-CSF; a
partial map of receptors on human mast cells cultured in vitro.
Allergy. 59:1087–1096. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Liu YJ: Thymic stromal lymphopoietin:
Master switch for allergic inflammation. J Exp Med. 203:269–273.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Fujii Y, Takeuchi H, Sakuma S, Sengoku T
and Takakura S: Characterization of a
2,4-dinitrochlorobenzene-induced chronic dermatitis model in rats.
Skin Pharmacol Physiol. 22:240–247. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Inagaki N, Shiraishi N, Igeta K, Itoh T,
Chikumoto T, Nagao M, Kim JF and Nagai H: Inhibition of scratching
behavior associated with allergic dermatitis in mice by tacrolimus,
but not by dexamethasone. Eur J Pharmacol. 546:189–196. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yang CT, Yang ZL, Zhang MF, Dong Q, Wang
XY, Lan AP, Zeng FQ, Chen PX, Wang CH and Feng JQ: Hydrogen sulfide
protects against chemical hypoxia-induced cytotoxicity and
inflammation in HaCaT cells through inhibition of ROS/NF-κB/COX-2
pathway. PLoS One. 6:e219712011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chodorowska G: Plasma concentrations of
IFN-gamma and TNF-alpha in psoriatic patients before and after
local treatment with dithranol ointment. J Eur Acad Dermatol
Venereol. 10:147–151. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Loganayaki N, Siddhuraju P and Manian S:
Antioxidant activity of two traditional Indian vegetables:
Solanum nigrum L. and Solanum torvum L. Food Sci
Biotechnol. 19:121–127. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Proksch E, Folster-Holst R and Jensen JM:
Skin barrier function, epidermal proliferation and differentiation
in eczema. J Dermatol Sci. 43:159–169. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lambrecht BN and Hammad H: The role of
dendritic and epithelial cells as master regulators of allergic
airway inflammation. Lancet. 376:835–843. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Galli SJ: The Mast Cell-IgE Paradox: From
homeostasis to anaphylaxis. Am J Pathol. 186:212–224. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kim SY, Yohannes SB, Damte D, Lee SJ,
Hossain MA, Kim JY, Rhee MH, Suh JW and Park SC: Effect of
fermented rhus verniciflua extract on DNCB induced-atopy like
dermatitis in BALB/c mice. Pak Vet J. 34:333–336. 2014.
|
|
21
|
Choi YY, Kim MH, Ahn KS, Um JY, Lee SG and
Yang WM: Immunomodulatory effects of Pseudostellaria heterophylla
(Miquel) Pax on regulation of Th1/Th2 levels in mice with atopic
dermatitis. Mol Med Rep. 15:649–656. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lee HG, Cho NC, Jeong AJ, Li YC, Rhie SJ,
Choi JS, Lee KH, Kim Y, Kim YN, Kim MH, et al: Immunomodulatory
activities of the benzoxathiole derivative BOT-4-one ameliorate
pathogenic skin inflammation in mice. J Invest Dermatol.
136:107–116. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Suthar AC and Mulani RM: A high
performance thin layer chromatography method for quantitative
estimation of Diosgenin in Solanum nigrum Linn. Pharmacog
Magazine. 4:112–115. 2008.
|
|
24
|
Desai S, Tatke P and Gabhe SY:
Quantification of diosgenin in extracts and formulations containing
Solanum Nigrum. Int J Pharm Sci Res. 6:676–681. 2015.
|
|
25
|
Matsuda H, Watanabe N, Geba GP, Sperl J,
Tsudzuki M, Hiroi J, Matsumoto M, Ushio H, Saito S, Askenase PW and
Ra C: Development of atopic dermatitis-like skin lesion with IgE
hyperproduction in NC/Nga mice. Int Immunol. 9:461–466. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kabashima K: New concept of the
pathogenesis of atopic dermatitis: Interplay among the barrier,
allergy, and pruritus as a trinity. J Dermatol Sci. 70:3–11. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wang G, Savinko T, Wolff H, Dieu-Nosjean
MC, Kemeny L, Homey B, Lauerma AI and Alenius H: Repeated
epicutaneous exposures to ovalbumin progressively induce atopic
dermatitis-like skin lesions in mice. Clin Exp Allergy. 37:151–161.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Skoner DR: Allergic rhinitis: Definition,
epidemiology, detection, and pathophysiology, diagnosis. J Allergy
Clin Immun. 108 (Suppl 1):S2–S8. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Amarasekera M: Immunoglobulin E in health
and disease. Asia Pac Allergy. 1:12–15. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
De Filippo K, Dudeck A, Hasenberg M, Nye
E, van Rooijen N, Hartmann K, Gunzer M, Roers A and Hogg N: Mast
cell and macrophage chemokines CXCL1/CXCL2 control the early stage
of neutrophil recruitment during tissue inflammation. Blood.
121:4930–4937. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Stone KD, Prussin C and Metcalfe DD: IgE,
mast cells, basophils, and eosinophils. J Allergy Clin Immun. 125
(2 Suppl 2):S73–S80. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Janeway CA Jr: The T cell receptor as a
multicomponent signalling machine: CD4/CD8 coreceptors and CD45 in
T cell activation. Annu Rev Immunol. 10:645–674. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Nagata T and Koide Y: Induction of
specific CD8(+) T cells against intracellular bacteria by CD8(+)
T-cell-oriented immunization approaches. J Biomed Biotechnol.
2010:7645422010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Roesner LM, Heratizadeh A, Wieschowski S,
Mittermann I, Valenta R, Eiz-Vesper B, Hennig C, Hansen G, Falk CS
and Werfel T: α-NAC-specific autoreactive CD8+ T cells in atopic
dermatitis are of an effector memory type and secrete IL-4 and
IFN-γ. J Immunol. 196:3245–3252. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Hijnen D, Knol EF, Gent YY, Giovannone B,
Beijn SJ, Kupper TS, Bruijnzeel-Koomen CA and Clark RA: CD8(+) T
cells in the lesional skin of atopic dermatitis and psoriasis
patients are an important source of IFN-γ, IL-13, IL-17, and IL-22.
J Invest Dermatol. 133:973–979. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Gordon JR, Burd PR and Galli SJ: Mast
cells as a source of multifunctional cytokines. Immunol Today.
11:458–464. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Baggiolini M and Clark-Lewis I:
Interleukin-8, a chemotactic and inflammatory cytokine. FEBS Lett.
307:97–101. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Hedges JC, Singer CA and Gerthoffer WT:
Mitogen-activated protein kinases regulate cytokine gene expression
in human airway myocytes. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 23:86–94.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Jacobsen EA, Lee NA and Lee JJ:
Re-defining the unique roles for eosinophils in allergic
respiratory inflammation. Clin Exp Allergy. 44:1119–1136. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Barnes PJ and Stockley RA: COPD: Current
therapeutic interventions and future approaches. Eur Respir J.
25:1084–1106. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Kwon DJ, Bae YS, Ju SM, Goh AR, Youn GS,
Choi SY and Park J: Casuarinin suppresses TARC/CCL17 and MDC/CCL22
production via blockade of NF-κB and STAT1 activation in HaCaT
cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 417:1254–1259. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Ju SM, Song HY, Lee SJ, Seo WY, Sin DH,
Goh AR, Kang YH, Kang IJ, Won MH, Yi JS, et al: Suppression of
thymus- and activation-regulated chemokine (TARC/CCL17) production
by 1,2,3,4,6-penta-O-galloyl-beta-D-glucose via blockade of
NF-kappaB and STAT1 activation in the HaCaT cells. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 387:115–120. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|