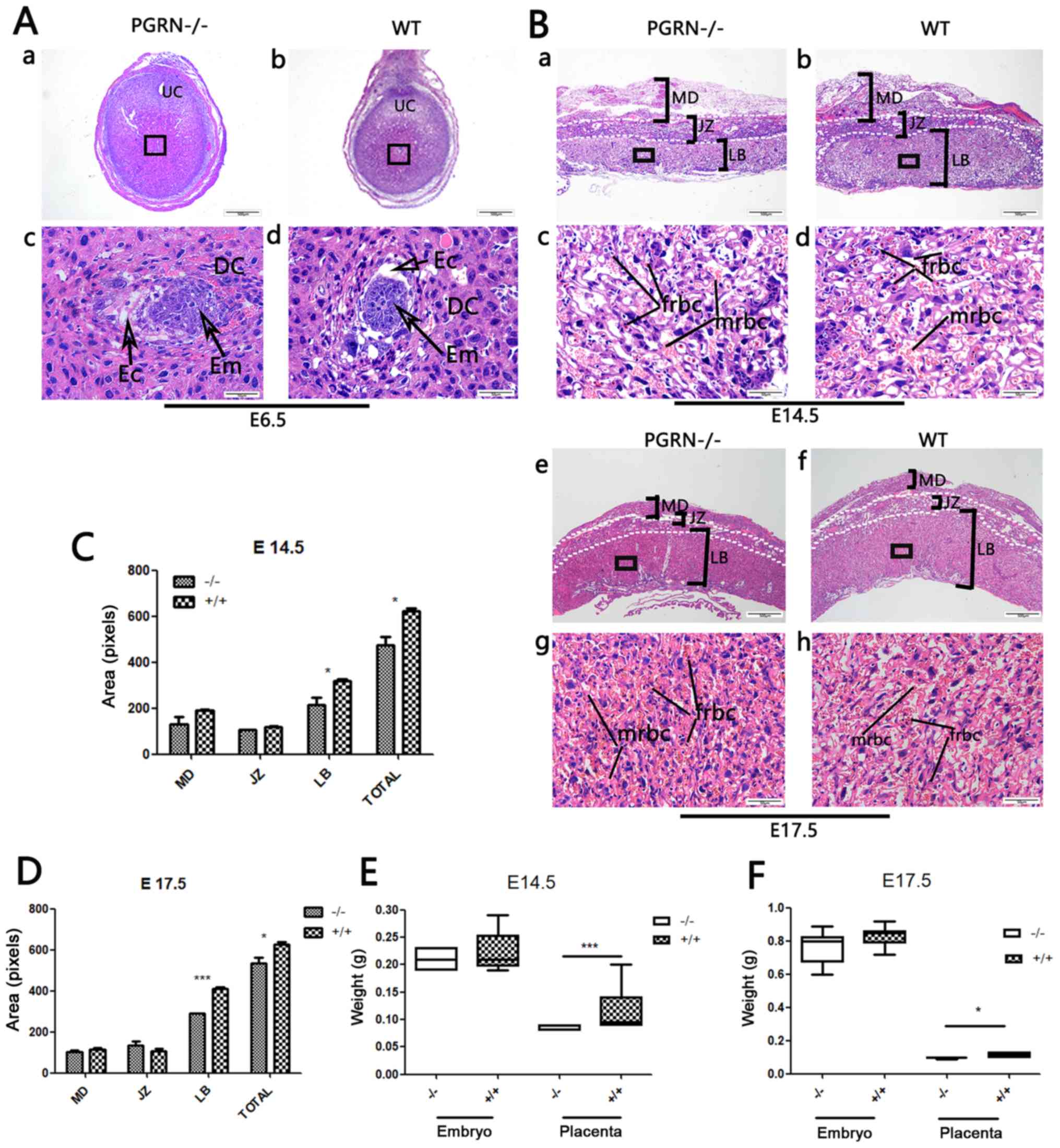
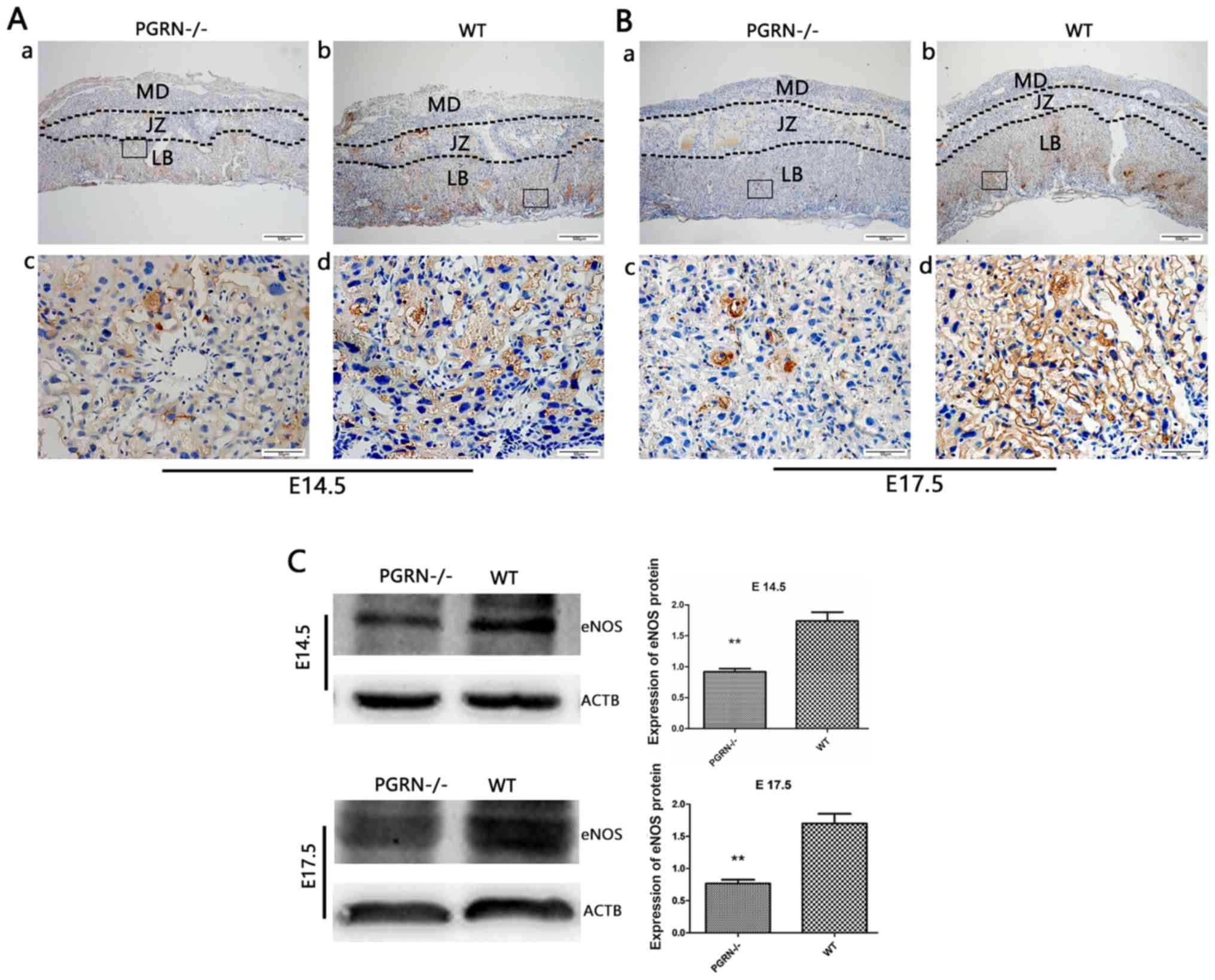
|
1
|
Sibley CP, Brownbill P, Glazier JD and
Greenwood SL: Knowledge needed about the exchange physiology of the
placenta. Placenta. 64 (Suppl 1):3482–S15. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Muntener M and Hsu YC: Development of
trophoblast and placenta of the mouse. A reinvestigation with
regard to the in vitro culture of mouse trophoblast and placenta.
Acta Anat (Basel). 98:241–252. 1977.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Adamson SL, Lu Y, Whiteley KJ, Holmyard D,
Hemberger M, Pfarrer C and Cross JC: Interactions between
trophoblast cells and the maternal and fetal circulation in the
mouse placenta. Dev Biol. 250:358–373. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Malassine A, Frendo JL and Evain-Brion D:
A comparison of placental development and endocrine functions
between the human and mouse model. Hum Reprod Update. 9:531–539.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Carmeliet P and Jain RK: Angiogenesis in
cancer and other diseases. Nature. 407:249–257. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Carmeliet P and Collen D: Role of vascular
endothelial growth factor and vascular endothelial growth factor
receptors in vascular development. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol.
237:133–158. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Risau W: Mechanisms of angiogenesis.
Nature. 386:671–674. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Carmeliet P and Conway EM: Growing better
blood vessels. Nat Biotechnol. 19:1019–1020. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Leach L, Lammiman MJ, Babawale MO, Hobson
SA, Bromilou B, Lovat S and Simmonds MJ: Molecular organization of
tight and adherens junctions in the human placental vascular tree.
Placenta. 21:547–557. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
He Z, Ong CH, Halper J and Bateman A:
Progranulin is a mediator of the wound response. Nat Med.
9:225–229. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Jian J, Konopka J and Liu C: Insights into
the role of progranulin in immunity, infection, and inflammation. J
Leukoc Biol. 93:199–208. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yin F, Banerjee R, Thomas B, Zhou P, Qian
L, Jia T, Ma X, Ma Y, Iadecola C, Beal MF, et al: Exaggerated
inflammation, impaired host defense, and neuropathology in
progranulin-deficient mice. J Exp Med. 207:117–128. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Eguchi R, Nakano T and Wakabayashi I:
Progranulin and granulin-like protein as novel VEGF-independent
angiogenic factors derived from human mesothelioma cells. Oncogene.
36:714–722. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Desmarais JA, Cao M, Bateman A and Murphy
BD: Spatiotemporal expression pattern of progranulin in embryo
implantation and placenta formation suggests a role in cell
proliferation, remodeling, and angiogenesis. Reproduction.
136:247–257. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Winther H, Leiser R, Pfarrer C and Dantzer
V: Localization of micro- and intermediate filaments in
non-pregnant uterus and placenta of the mink suggests involvement
of maternal endothelial cells and periendothelial cells in blood
flow regulation. Anat Embryol (Berl). 200:253–263. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Tangkeangsirisin W and Serrero G: PC
cell-derived growth factor (PCDGF/GP88, progranulin) stimulates
migration, invasiveness and VEGF expression in breast cancer cells.
Carcinogenesis. 25:1587–1592. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tangkeangsirisin W, Hayashi J and Serrero
G: PC cell-derived growth factor mediates tamoxifen resistance and
promotes tumor growth of human breast cancer cells. Cancer Res.
64:1737–1743. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Daniel R, He Z, Carmichael KP, Halper J
and Bateman A: Cellular localization of gene expression for
progranulin. J Histochem Cytochem. 48:999–1009. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Stubert J, Richter DU, Gerber B and Briese
V: Expression pattern of progranulin in the human placenta and its
effect on cell proliferation in the choriocarcinoma cell line BeWo.
J Reprod Dev. 57:229–235. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Qin J, Diaz-Cueto L, Schwarze JE,
Takahashi Y, Imai M, Isuzugawa K, Yamamoto S, Chang KT, Gerton GL
and Imakawa K: Effects of progranulin on blastocyst hatching and
subsequent adhesion and outgrowth in the mouse. Biol Reprod.
73:434–442. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Díaz-Cueto L, Stein P, Jacobs A, Schultz
RM and Gerton GL: Modulation of mouse preimplantation embryo
development by acrogranin (epithelin/granulin precursor). Dev Biol.
217:406–418. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Açıkgöz AS, Tüten A, Öncül M, Eskalen S,
Dinçgez BC, Şimşek A, Yüksel MA and Guralp O: Evaluation of
maternal serum progranulin levels in normotensive pregnancies, and
pregnancies with early- and late-onset preeclampsia. J Matern Fetal
Neonatal Med. 29:2658–2664. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Stubert J, Schattenberg F, Richter DU,
Dieterich M and Briese V: Trophoblastic progranulin expression is
upregulated in cases of fetal growth restriction and preeclampsia.
J Perinat Med. 40:475–481. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kadyrov M, Kingdom JC and Huppertz B:
Divergent trophoblast invasion and apoptosis in placental bed
spiral arteries from pregnancies complicated by maternal anemia and
early-onset preeclampsia/intrauterine growth restriction. Am J
Obstet Gynecol. 194:557–563. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Tal R: The role of hypoxia and
hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha in preeclampsia pathogenesis. Biol
Reprod. 87:1342012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Aghaeepour N, Lehallier B, Baca Q, Ganio
EA, Wong RJ, Ghaemi MS, Culos A, El-Sayed YY, Blumenfeld YJ, Druzin
ML, et al: A proteomic clock of human pregnancy. Am J Obstet
Gynecol. 218:347.e1–347.e14. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Stubert J, Szewczyk M, Spitschak A, Knoll
S, Richter DU and Pützer BM: Adenoviral mediated expression of
anti-inflammatory progranulin by placental explants modulates
endothelial cell activation by decrease of ICAM-1 expression.
Placenta. 90:109–117. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Honma M, Koizumi F, Wakaki K and Ochiai H:
Co-expression of fibroblastic, histiocytic and smooth muscle cell
phenotypes on cultured adherent cells derived from human palatine
tonsils: A morphological and immunocytochemical study. Pathol Int.
45:903–913. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Jackson DE, Gully LM, Henshall TL, Mardell
CE and Macardle PJ: Platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1
(PECAM-1/CD31) is associated with a naive B-cell phenotype in human
tonsils. Tissue Antigens. 56:105–116. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kulandavelu S, Whiteley KJ, Qu D, Mu J,
Bainbridge SA and Adamson SL: Endothelial nitric oxide synthase
deficiency reduces uterine blood flow, spiral artery elongation,
and placental oxygenation in pregnant mice. Hypertension.
60:231–238. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhixin S, Xuemei Z, Liping Z, Xu F, Tao X,
Zhang H, Lin X, Kang L, Xiang Y, Lai X, et al: Progranulin plays a
central role in host defense during sepsis by promoting macrophage
recruitment. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 194:1219–1232. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Portilho NA and Pelajo-Machado M:
Mechanism of hematopoiesis and vasculogenesis in mouse placenta.
Placenta. 69:140–145. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Daniel R, Daniels E, He Z and Bateman A:
Progranulin (acrogranin/PC cell-derived growth
factor/granulin-epithelin precursor) is expressed in the placenta,
epidermis, microvasculature, and brain during murine development.
Dev Dyn. 227:593–599. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Enders AC: A comparative study of the fine
structure of the trophoblast in several hemochorial placentas. Am J
Anat. 116:29–67. 1965. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Walentin K, Hinze C and Schmidt-Ott KM:
The basal chorionic trophoblast cell layer: An emerging coordinator
of placenta development. Bioessays. 38:254–265. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Beltowski J: Role of progranulin in the
regulation of vascular tone: (patho)physiological implications.
Acta Physiol (Oxf). 219:706–708. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Hwang HJ, Jung TW, Hong HC, Choi HY, Seo
JA, Kim SG, Kim NH, Choi KM, Choi DS, Baik SH and Yoo HJ:
Progranulin protects vascular endothelium against atherosclerotic
inflammatory reaction via Akt/eNOS and nuclear factor-κB pathways.
PLoS One. 8:e766792013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Toh H, Cao M, Daniels E and Bateman A:
Expression of the growth factor progranulin in endothelial cells
influences growth and development of blood vessels: A novel mouse
model. PLoS One. 8:e649892013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Yamaguchi YL, Tanaka SS, Oshima N,
Kiyonari H, Asashima M and Nishinakamura R: Translocon-associated
protein subunit Trap-γ/Ssr3 is required for vascular network
formation in the mouse placenta. Dev Dyn. 240:394–403. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Kanazawa M, Kawamura K, Takahashi T, Miura
M, Tanaka Y, Koyama M, Toriyabe M, Igarashi H, Nakada T, Nishihara
M, et al: Multiple therapeutic effects of progranulin on
experimental acute ischaemic stroke. Brain. 138:1932–1948. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Toh H, Daniels E and Bateman A: Methods to
investigate the roles of progranulin in angiogenesis using in vitro
strategies and transgenic mouse models. Methods Mol Biol.
1806:329–360. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Kazama K, Hoshino K, Kodama T, Okada M and
Yamawaki H: Adipocytokine, progranulin, augments
acetylcholine-induced nitric oxide-mediated relaxation through the
increases of cGMP production in rat isolated mesenteric artery.
Acta Physiol (Oxf). 219:781–789. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Jiang F, Wang H, Bao S, Zhou H, Zhang Y,
Yan Y, Lai Y, Teng W and Shan Z: Thyrotropin regulates eNOS
expression in the endothelium by PGRN through Akt pathway. Front
Endocrinol (Lausanne). 9:3532018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Stilley JAW and Segaloff DL: Deletion of
fetoplacental Fshr inhibits fetal vessel angiogenesis in the mouse
placenta. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 476:79–83. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Kwee L, Baldwin HS, Shen HM, Stewart CL,
Buck C, Buck CA and Labow MA: Defective development of the
embryonic and extraembryonic circulatory systems in vascular cell
adhesion molecule (VCAM-1) deficient mice. Development.
121:489–503. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Li Y and Behringer RR: Esx1 is an
X-chromosome-imprinted regulator of placental development and fetal
growth. Nat Genet. 20:309–311. 1998. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Krüger O, Plum A, Kim JS, Winterhager E,
Maxeiner S, Hallas G, Kirchhoff S, Traub O, Lamers WH and Willecke
K: Defective vascular development in connexin 45-deficient mice.
Development. 127:4179–4193. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Ohlsson R, Falck P, Hellström M, Lindahl
P, Boström H, Franklin G, Ahrlund-Richter L, Pollard J, Soriano P
and Betsholtz C: PDGFB regulates the development of the
labyrinthine layer of the mouse fetal placenta. Dev Biol.
212:124–136. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Kozak KR, Abbott B and Hankinson O:
ARNT-deficient mice and placental differentiation. Dev Biol.
191:297–305. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Wendling O, Chambon P and Mark M: Retinoid
X receptors are essential for early mouse development and
placentogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 96:547–551. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Junaid TO, Brownbill P, Chalmers N,
Johnstone ED and Aplin JD: Fetoplacental vascular alterations
associated with fetal growth restriction. Placenta. 35:808–815.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Jackman K, Kahles T, Lane D,
Garcia-Bonilla L, Abe T, Capone C, Hochrainer K, Voss H, Zhou P,
Ding A, et al: Progranulin deficiency promotes post-ischemic
blood-brain barrier disruption. J Neurosci. 33:19579–19589. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Fu Y, Sun Y, Zhou M, Wang X, Wang Z, Wei
X, Zhang Y, Su Z, Liang K, Tang W and Yi F: Therapeutic potential
of progranulin in hyperhomocysteinemia-induced cardiorenal
dysfunction. Hypertension. 69:259–266. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|