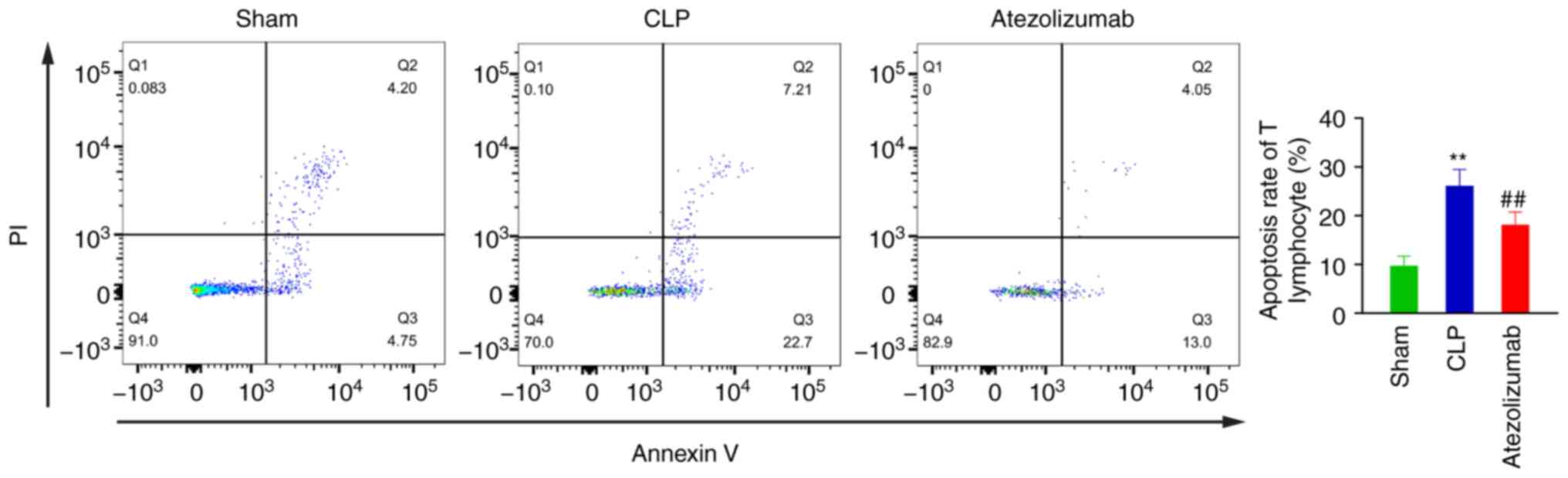
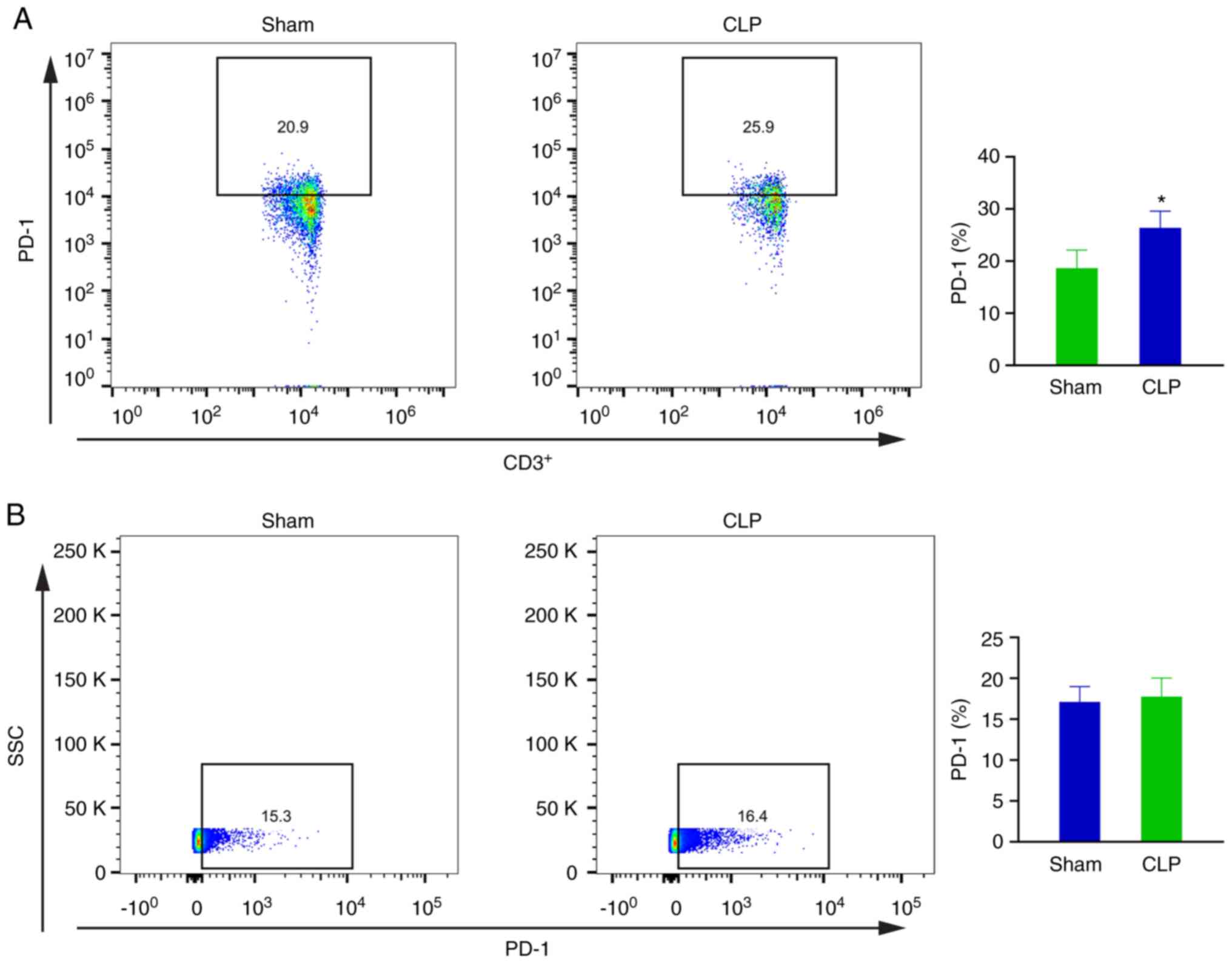
|
1
|
Singer M, Deutschman CS, Seymour CW,
Shankar-Hari M, Annane D, Bauer M, Bellomo R, Bernard GR, Chiche
JD, Coopersmith CM, et al: The third international consensus
definitions for sepsis and septic shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA.
315:801–810. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Florian B: Mayr, Sachin Yende and Derek C
Angus: Epidemiology of severe sepsis. Virulence. 5:4–11. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Patil NK, Bohannon JK, Luan L, Guo Y,
Fensterheim B, Hernandez A, Wang J and Sherwood ER: Flt3 ligand
treatment attenuates T cell dysfunction and improves survival in a
murine model of burn wound sepsis. Shock. 47:40–51. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ramonell KM, Zhang W, Hadley A, Chen CW,
Fay KT, Lyons JD, Klingensmith NJ, McConnell KW, Coopersmith CM and
Ford ML: CXCR4 blockade decreases CD4+ T cell exhaustion
and improves survival in a murine model of polymicrobial sepsis.
PLoS One. 12:e01888822017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Boomer JS, To K, Chang KC, Takasu O,
Osborne DF, Walton AH, Bricker TL, Jarman SD II, Kreisel D,
Krupnick AS, et al: Immunosuppression in patients who die of sepsis
and multiple organ failure. Surv Anesthesiol. 56:272–273. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Cao C, Chai Y, Shou S, Wang J, Huang Y and
Ma T: Toll-like receptor 4 deficiency increases resistance in
sepsis-induced immune dysfunction. Int Immunopharmacol. 54:169–176.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Oami T, Watanabe E, Hatano M, Sunahara S,
Fujimura L, Sakamoto A, Ito C, Toshimori K and Oda S: Suppression
of T cell autophagy results in decreased viability and function of
T cells through accelerated apoptosis in a murine sepsis model.
Crit Care Med. 45:e77–e85. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hotchkiss RS, Osmon SB, Chang KC, Wagner
TH, Coopersmith CM and Karl IE: Accelerated lymphocyte death in
sepsis occurs by both the death receptor and mitochondrial
pathways. J Immunol. 174:5110–5118. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang JF, Li JB, Zhao YJ, Yi WJ, Bian JJ,
Wan XJ, Zhu KM and Deng XM: Up-regulation of programmed cell death
1 ligand 1 on neutrophils may be involved in sepsis-induced
immunosuppression: An animal study and a prospective case-control
study. Anesthesiology. 122:852–863. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Dougall WC, Aguilera AR and Smyth MJ: Dual
targeting of RANKL and PD-1 with a bispecific antibody improves
anti-tumor immunity. Clin Transl Immunology. 8:e010812019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Oliver AJ, Davey AS, Keam SP, Mardiana S,
Chan JD, von Scheidt B, Beavis PA, House IG, Van Audernaerde JR,
Darcy PK, et al: Tissue-specific tumor microenvironments influence
responses to immunotherapies. Clin Transl Immunology. 8:e10942019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Walker DG, Shakya R, Morrison B, Neller
MA, Matthews KK, Nicholls J, Smith C and Khanna R: Impact of
pre-therapy glioblastoma multiforme microenvironment on clinical
response to autologous CMV-specific T-cell therapy. Clin Transl
Immunology. 8:e010882019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Herbst RS, Soria JC, Kowanetz M, Fine GD,
Hamid O, Gordon MS, Sosman JA, McDermott DF, Powderly JD, Gettinger
SN, et al: Predictive correlates of response to the anti-PD-L1
antibody MPDL3280A in cancer patients. Nature. 515:563–567. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Powles T, Eder JP, Fine GD, Braiteh FS,
Loriot Y, Cruz C, Bellmunt J, Burris HA, Petrylak DP, Teng SL, et
al: MPDL3280A (anti-PD-L1) treatment leads to clinical activity in
metastatic bladder cancer. Nature. 515:558–562. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Balar AV, Galsky MD, Rosenberg JE, Powles
T, Petrylak DP, Bellmunt J, Loriot Y, Necchi A, Hoffman-Censits J,
Perez-Gracia JL, et al IMvigor210 Study Group, : Atezolizumab as
first-line treatment in cisplatin-ineligible patients with locally
advanced and metastatic urothelial carcinoma: A single-arm,
multicentre, phase 2 trial. Lancet. 389:67–76. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Fehrenbacher L, Spira A, Ballinger M,
Kowanetz M, Vansteenkiste J, Mazieres J, Park K, Smith D,
Artal-Cortes A, Lewanski C, et al POPLAR Study Group, :
Atezolizumab versus docetaxel for patients with previously treated
non-small-cell lung cancer (POPLAR): A multicentre, open-label,
phase 2 randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 387:1837–1846. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
McDermott DF, Sosman JA, Sznol M, Massard
C, Gordon MS, Hamid O, Powderly JD, Infante JR, Fassò M, Wang YV,
et al: Atezolizumab, an anti-programmed death-ligand 1 antibody, in
metastatic renal cell carcinoma: Long-term safety, clinical
activity, and immune correlates from a phase ia study. J Clin
Oncol. 34:833–842. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hotchkiss RS, Monneret G and Payen D:
Sepsis-induced immunosuppression: From cellular dysfunctions to
immunotherapy. Nat Rev Immunol. 13:862–874. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Rittirsch D, Huber-Lang MS, Flierl MA and
Ward PA: Immunodesign of experimental sepsis by cecal ligation and
puncture. Nat Protoc. 4:31–36. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yoseph BP, Klingensmith NJ, Liang Z, Breed
ER, Burd EM, Mittal R, Dominguez JA, Petrie B, Ford ML and
Coopersmith CM: Mechanisms of intestinal barrier dysfunction in
sepsis. Shock. 46:52–59. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bouboulis G, Bonatsos VG, Katsarou AI,
Karameris A, Galanos A, Zacharioudaki A, Theodoropoulos G, Zografos
G, Papalois AE and Toutouzas K: Experimental hemorrhagic shock
protocol in swine models: The effects of 21-aminosteroid on the
small intestine. Curr Ther Res Clin Exp. 88:18–25. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chiu CJ, McArdle AH, Brown R, Scott HJ and
Gurd FN: Intestinal mucosal lesion in low-flow states. Exp Surg.
101:478–483. 1970.
|
|
23
|
Seemann S, Zohles F and Lupp A:
Comprehensive comparison of three different animal models for
systemic inflammation. J Biomed Sci. 24:602017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Skirecki T, Kawiak J, Machaj E, Pojda Z,
Wasilewska D, Czubak J and Hoser G: Early severe impairment of
hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells from the bone marrow caused
by CLP sepsis and endotoxemia in a humanized mice model. Stem Cell
Res Ther. 6:1422015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Boomer JS, To K, Chang KC, Takasu O,
Osborne DF, Walton AH, Bricker TL, Jarman SD II, Kreisel D,
Krupnick AS, et al: Immunosuppression in patients who die of sepsis
and multiple organ failure. JAMA. 306:2594–2605. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lang JD and Matute-Bello G: Lymphocytes,
apoptosis and sepsis: Making the jump from mice to humans. Crit
Care. 13:1092009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hotchkiss RS, Swanson PE, Freeman BD,
Tinsley KW, Cobb JP, Matuschak GM, Buchman TG and Karl IE:
Apoptotic cell death in patients with sepsis, shock, and multiple
organ dysfunction. Crit Care Med. 27:1230–1251. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Tsukamoto H, Fujieda K, Miyashita A,
Fukushima S, Iked T, Kubo Y, Senju S, Ihn H, Nishimura Y and
Oshiumi H: Combined blockade of IL6 and PD-1/PD-L1 signaling
abrogates mutual regulation of their immunosuppressive effects in
the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Res. 78:5011–5022. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zeng Y, Li B, Liang Y, Reeves PM, Qu X,
Ran C, Liu Q, Callahan MV, Sluder AE, Gelfand JA, et al: Dual
blockade of CXCL12-CXCR4 and PD-1-PD-L1 pathways prolongs survival
of ovarian tumor-bearing mice by prevention of immunosuppression in
the tumor microenvironment. FASEB J. 33:6596–6608. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Passariello M, D'Alise AM, Esposito A,
Vetrei C, Froechlich G, Scarselli E, Nicosia A and De Lorenzo C:
Novel human anti-PD-L1 mAbs inhibit immune-independent tumor cell
growth and PD-L1 associated intracellular signalling. Sci Rep.
9:131252019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Huang X, Venet F, Wang YL, Lepape A, Yuan
Z, Chen Y, Swan R, Kherouf H, Monneret G, Chung CS, et al: PD-1
expression by macrophages plays a pathologic role in altering
microbial clearance and the innate inflammatory response to sepsis.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:6303–6308. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Bjarnason I, MacPherson A and Hollander D:
Intestinal permeability: An overview. Gastroenterology.
108:1566–1581. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Turner JR: Intestinal mucosal barrier
function in health and disease. Nat Rev Immunol. 9:799–809. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Perrone EE, Jung E, Breed E, Dominguez JA,
Liang Z, Clark AT, Dunne WM, Burd EM and Coopersmith CM: Mechanisms
of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus pneumonia-induced
intestinal epithelial apoptosis. Shock. 38:68–75. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Li Q, Zhang Q, Wang C, Liu X, Li N and Li
J: Disruption of tight junctions during polymicrobial sepsis in
vivo. J Pathol. 218:210–221. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Suzuki T: Regulation of intestinal
epithelial permeability by tight junctions. Cell Mol Life Sci.
70:631–659. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Haussner F, Chakraborty S, Halbgebauer R
and Huber-Lang M: Challenge to the intestinal mucosa during sepsis.
Front Immunol. 10:8912019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
De-Souza DA and Greene LJ: Intestinal
permeability and systemic infections in critically ill patients:
Effect of glutamine. Crit Care Med. 33:1125–1135. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Schulz K, Sommer O, Jargon D, Utzolino S,
Clement HW, Strate T and von Dobschuetz E: Cytokine and radical
inhibition in septic intestinal barrier failure. J Surg Res.
193:831–840. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Piton G and Capellier G: Biomarkers of gut
barrier failure in the ICU. Curr Opin Crit Care. 22:152–160.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Dial EJ, Romero JJ, Villa X, Mercer DW and
Lichtenberger LM: Lipopolysaccharide-induced gastrointestinal
injury in rats: Role of surface hydrophobicity and bile salts.
Shock. 17:77–80. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zhang Y, Zhou Y, Lou J, Li J, Bo L, Zhu K,
Wan X, Deng X and Cai Z: PD-L1 blockade improves survival in
experimental sepsis by inhibiting lymphocyte apoptosis and
reversing monocyte dysfunction. Crit Care. 14:R2202010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Brahmamdam P, Inoue S, Unsinger J, Chang
KC, McDunn JE and Hotchkiss RS: Delayed administration of anti-PD-1
antibody reverses immune dysfunction and improves survival during
sepsis. J Leukoc Biol. 88:233–240. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|