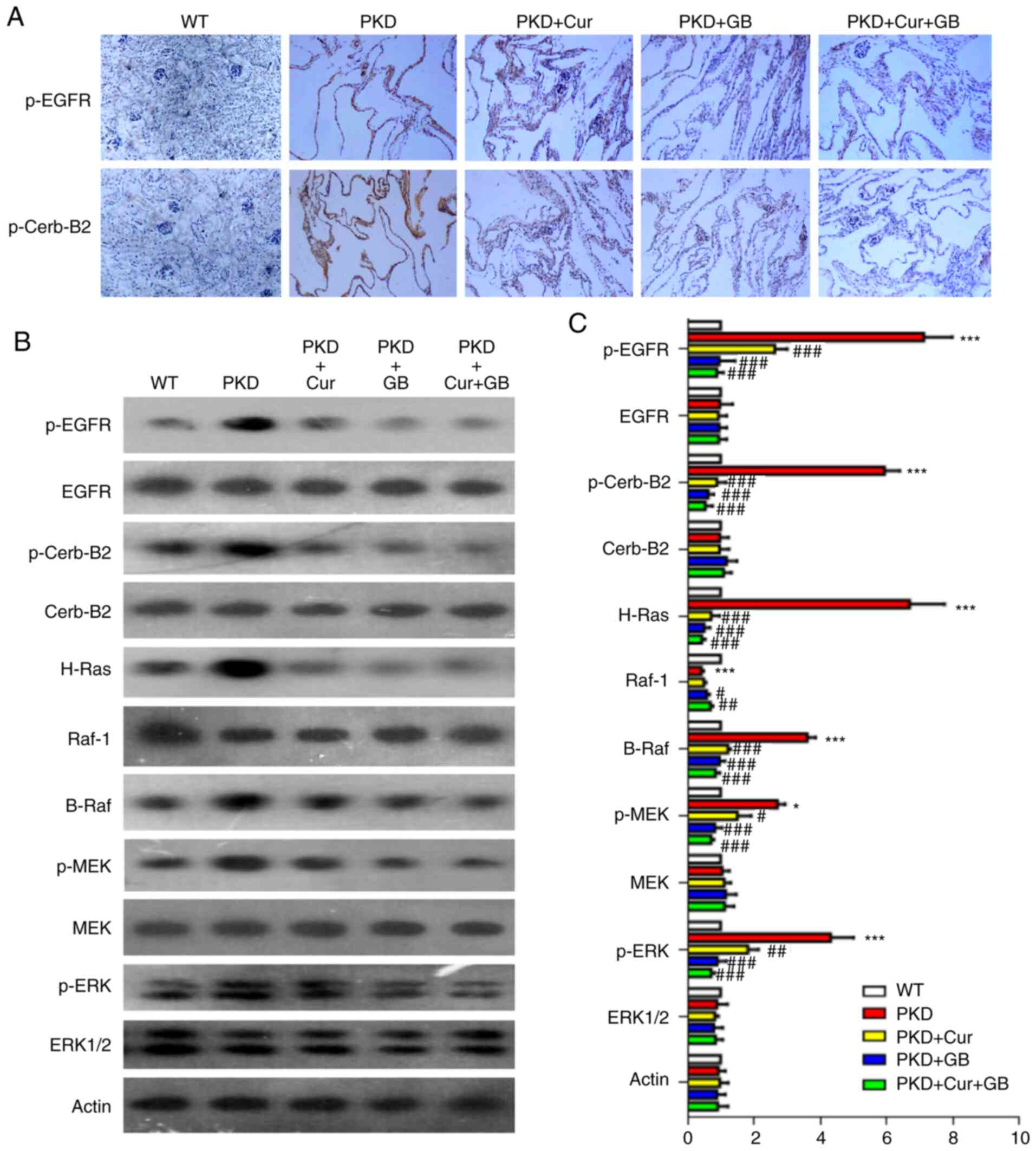
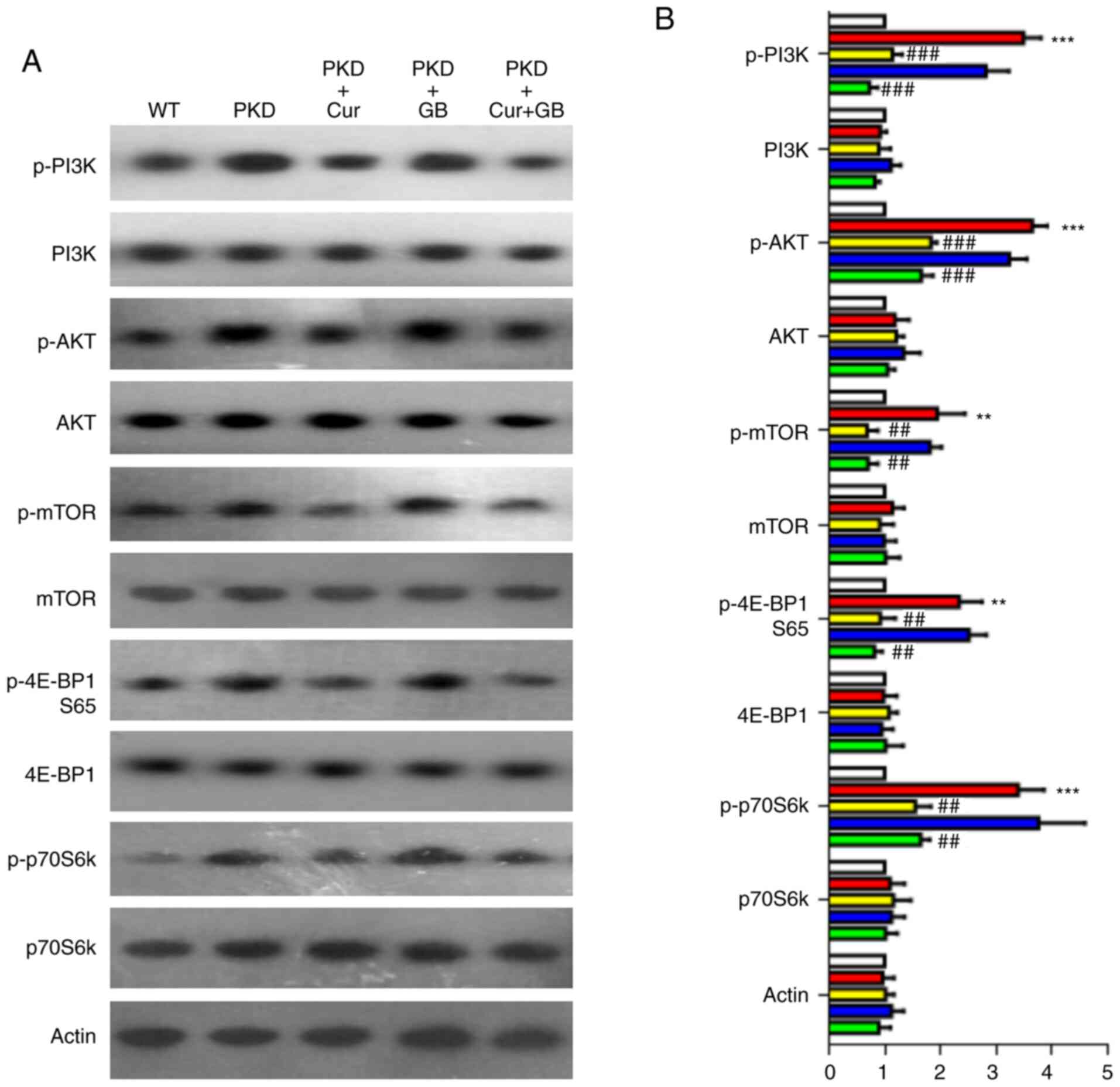
|
1
|
Corradi V, Gastaldon F, Caprara C,
Giuliani A, Martino F, Ferrari F and Ronco C: Predictors of rapid
disease progression in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney
disease. Minerva Med. 108:43–56. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chebib FT, Sussman CR, Wang X, Harris PC
and Torres VE: Vasopressin and disruption of calcium signalling in
polycystic kidney disease. Nat Rev Nephrol. 11:451–464. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Harris PC and Torres VE: Genetic
mechanisms and signaling pathways in autosomal dominant polycystic
kidney disease. J Clin Invest. 124:2315–2324. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Su Q, Hu F, Ge X, Lei J, Yu S, Wang T,
Zhou Q, Mei C and Shi Y: Structure of the human PKD1/PKD2 complex.
Science. 361:eaat98192018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Douguet D, Patel A and Honoré E: Structure
and function of polycystins: Insights into polycystic kidney
disease. Nat Rev Nephrol. 15:412–422. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Malekshahabi T, Khoshdel Rad N, Serra AL
and Moghadasali R: Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease:
Disrupted pathways and potential therapeutic interventions. J Cell
Physiol. 234:12451–12470. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Gattone VH, Chen NX, Sinders RM, Seifert
MF, Duan D, Martin D, Henley C and Moe SM: Calcimimetic inhibits
late-stage cyst growth in ADPKD. J Am Soc Nephrol. 20:1527–1532.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Torres VE: Cyclic AMP, at the hub of the
cystic cycle. Kidney Int. 66:1283–1285. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Calvet JP: Strategies to inhibit cyst
formation in ADPKD. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 3:1205–1211. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Shibazaki S, Yu Z, Nishio S, Tian X,
Thomson RB, Mitobe M, Louvi A, Velazquez H, Ishibe S, Cantley LG,
et al: Cyst formation and activation of the extracellular regulated
kinase pathway after kidney specific inactivation of Pkd1. Hum Mol
Genet. 17:1505–1516. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Pandey P, Brors B, Srivastava PK, Bott A,
Boehn SNE, Groene HJ and Gretz N: Microarray-based approach
identifies microRNAs and their target functional patterns in
polycystic kidney disease. BMC Genomics. 9:6242008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yang B, Sonawane ND, Zhao D, Somlo S and
Verkman AS: Small-molecule CFTR inhibitors slow cyst growth in
polycystic kidney disease. J Am Soc Nephrol. 19:1300–1310. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
He J, Zhou H, Meng J, Zhang S, Wang S,
Shao G, Jin W, Geng X, Zhu S and Yang B: Cardamonin retards
progression of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease via
inhibiting renal cyst growth and interstitial fibrosis. Pharmacol
Res. 155:1047512020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Raman A, Reif GA, Dai Y, Khanna A, Li X,
Astleford L, Parnell SC, Calvet JP and Wallace DP: Integrin-linked
kinase signaling promotes cyst growth and fibrosis in polycystic
kidney disease. J Am Soc Nephrol. 28:2708–2719. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Gao J, Zhou H, Lei T, Zhou L, Li W, Li X
and Yang B: Curcumin inhibits renal cyst formation and enlargement
in vitro by regulating intracellular signaling pathways. Eur J
Pharmacol. 654:92–99. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Higashihara E, Nutahara K, Okegawa T,
Tanbo M, Mori H, Miyazaki I, Nitatori T and Kobayashi K: Safety
study of somatostatin analogue octreotide for autosomal dominant
polycystic kidney disease in Japan. Clin Exp Nephrol. 19:746–752.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhou H, Gao J, Zhou L, Li X, Li W, Li X,
Xia Y and Yang B: Ginkgolide B inhibits renal cyst development in
in vitro and in vivo cyst models. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol.
302:F1234–F1242. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Torres VE, Chapman AB, Devuyst O,
Gansevoort RT, Perrone RD, Koch G, Ouyang J, McQuade RD, Blais JD,
Czerwiec FS, et al: Tolvaptan in later-stage autosomal dominant
polycystic kidney disease. N Engl J Med. 377:1930–1942. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Reif GA, Yamaguchi T, Nivens E, Fujiki H,
Pinto CS and Wallace DP: Tolvaptan inhibits ERK-dependent cell
proliferation, Cl-secretion, and in vitro cyst growth of human
ADPKD cells stimulated by vasopressin. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol.
301:F1005–F1013. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Tesar V, Ciechanowski K, Pei Y, Barash I,
Shannon M, Li R, Williams JH, Levisetti M, Arkin S and Serra A:
Bosutinib versus placebo for autosomal dominant polycystic kidney
disease. J Am Soc Nephrol. 28:3404–3413. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Li A, Xu Y, Fan S, Meng J, Shen X, Xiao Q,
Li Y, Zhang L, Zhang X, Wu G, et al: Canonical Wnt inhibitors
ameliorate cystogenesis in a mouse ortholog of human ADPKD. JCI
Insight. 3:e958742018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Cabrera-López C, Bullich G, Martí T,
Català V, Ballarín J, Bissler JJ, Harris PC, Ars E and Torra R:
Insight into response to mTOR inhibition when PKD1 and TSC2 are
mutated. BMC Med Genet. 16:392015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Muto S, Aiba A, Saito Y, Nakao K, Nakamura
K, Tomita K, Kitamura T, Kurabayashi M, Nagai R, Higashihara E, et
al: Pioglitazone improves the phenotype and molecular defects of a
targeted Pkd1 mutant. Hum Mol Genet. 11:1731–1742. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Raphael KL, Strait KA, Stricklett PK,
Baird BC, Piontek K, Germino GG and Kohan DE: Effect of
pioglitazone on survival and renal function in a mouse model of
polycystic kidney disease. Am J Nephrol. 30:468–473. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Leuenroth SJ, Bencivenga N, Chahboune H,
Hyder F and Crews CM: Triptolide reduces cyst formation in a
neonatal to adult transition Pkd1 model of ADPKD. Nephrol Dial
Transplant. 25:2187–2194. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Su L, Liu L, Jia Y, Lei L, Liu J, Zhu S,
Zhou H, Chen R, Lu HAJ and Yang B: Ganoderma triterpenes retard
renal cyst development by downregulating Ras/MAPK signaling and
promoting cell differentiation. Kidney Int. 92:1404–1418. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhu Y, Teng T, Wang H, Guo H, Du L, Yang
B, Yin X and Sun Y: Quercetin inhibits renal cyst growth in vitro
and via parenteral injection in a polycystic kidney disease mouse
model. Food Funct. 9:389–396. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chebib FT, Perrone RD, Chapman AB, Dahl
NK, Harris PC, Mrug M, Mustafa RA, Rastogi A, Watnick T, Yu ASL and
Torres VE: A practical guide for treatment of rapidly progressive
ADPKD with tolvaptan. J Am Soc Nephrol. 29:2458–2470. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yan FS, Sun JL, Xie WH, Shen L and Ji HF:
Neuroprotective effects and mechanisms of curcumin-cu(II) and
-zn(II) complexes systems and their pharmacological implications.
Nutrients. 10:282017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Zhao NJ, Liao MJ, Wu JJ and Chu KX:
Curcumin suppresses Notch1 signaling: Improvements in fatty liver
and insulin resistance in rats. Mol Med Rep. 17:819–826.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Bandgar BP, Hote BS, Jalde SS and Gacche
RN: Synthesis and biological evaluation of novel curcumin analogues
as anti-inflammatory, anti-cancer and anti-oxidant agents. Med Chem
Res. 21:3006–3014. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Adahoun MA, AlAkhras MH, Jaafar MS and
Bououdina M: Enhanced anti-cancer and antimicrobial activities of
curcumin nanoparticles. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 45:98–107.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yu W, Cao L, Zhao Y, Xiao W and Xiao B:
Comparing the role of Ginkgolide B and Ginkgolide K on cultured
astrocytes exposed to oxygen?glucose deprivation. Mol Med Rep.
18:4417–4427. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Li R, Chen B, Wu W, Bao L, Li J and Qi R:
Ginkgolide B suppresses intercellular adhesion molecule-1
expression via blocking nuclear factor-kappaB activation in human
vascular endothelial cells stimulated by oxidized low-density
lipoprotein. J Pharmacol Sci. 110:362–369. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Shu ZM, Shu XD, Li HQ, Sun Y, Shan H, Sun
XY, Du RH, Lu M, Xiao M, Ding JH and Hu G: Ginkgolide B protects
against ischemic stroke via modulating microglia polarization in
mice. CNS Neurosci Ther. 22:729–739. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhou YY, Wang HY, Tang ZG and Ma DL: Two
new formulae for evaluating the effectiveness of drug combinations
and the revision of Bürgi's and Jin's modified Bürgi's formulae.
Zhongguo Yao Li Xue Bao. 5:217–221. 1984.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Pan YY, Xu SP and Wei W: Effect of
combined nimesulide and adriamycin on proliferation and apoptosis
in hepatocellular carcinoma cell line HepG_2. Chin Pharmacol Bull.
22:884–887. 2006.
|
|
38
|
Liu Y, Pejchinovski M, Wang X, Fu X,
Castelletti D, Watnick TJ, Arcaro A, Siwy J, Mullen W, Mischak H
and Serra AL: Dual mTOR/PI3K inhibition limits PI3K-dependent
pathways activated upon mTOR inhibition in autosomal dominant
polycystic kidney disease. Sci Rep. 8:55842018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ng TP, Chiam P, Lee T, Chua H, Lim L and
Kua EH: Curry consumption and cognitive function in the elderly. Am
J Epidemiol. 164:898–906. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Van Nong H, Hung LX, Thang PN, Chinh VD,
Vu LV, Dung PT, Van Trung T and Nga PT: Fabrication and vibration
characterization of curcumin extracted from turmeric (Curcuma
longa) rhizomes of the northern Vietnam. Springerplus.
5:11472016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Basnet P and Skalko-Basnet N: Curcumin: An
anti-inflammatory molecule from a curry spice on the path to cancer
treatment. Molecules. 6:4567–4598. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Youngjoo K: Estimation of curcumin intake
in Korea based on the Korea national health and nutrition
examination survey (2008–2012). Nutr Res Pract. 8:589–594. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Maheshwari RK, Singh AK, Gaddipati J and
Srimal RC: Multiple biological activities of curcumin: A short
review. Life Sci. 78:2081–2087. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Guan R, Zhao Y, Zhang H, Fan G, Liu X,
Zhou W, Shi C, Wang J, Liu W, Liang X, et al: Draft genome of the
living fossil Ginkgo biloba. Gigascience. 5:492016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Wang S, Ouyang B, Aa J, Geng J, Fei F,
Wang P, Wang J, Peng Y, Geng T, Li Y, et al: Pharmacokinetics and
tissue distribution of ginkgolide A, ginkgolide B, and ginkgolide K
after intravenous infusion of ginkgo diterpene lactones in a rat
model. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 126:109–116. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Zheng PD, Mungur R, Zhou HJ, Hassan M,
Jiang SN and Zheng JS: Ginkgolide B promotes the proliferation and
differentiation of neural stem cells following cerebral
ischemia/reperfusion injury, both in vivo and in vitro. Neural
Regen Res. 13:1204–1211. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Agrawal S: Curcumin and its protective and
therapeutic uses. Natl J Physiol Pharm Pharmacol. 6:1–8. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Anroopb N and Shery J: A simple practice
guide for dose conversion between animals and human. J Basic Clin
Pharm. 7:27–31. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Chandran B and Goel A: A randomized, pilot
study to assess the efficacy and safety of curcumin in patients
with active rheumatoid arthritis. Phytother Res. 26:1719–1725.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Lyu H, Han A, Polsdofer E, Liu S and Liu
B: Understanding the biology of HER3 receptor as a therapeutic
target in human cancer. Acta Pharm Sin B. 8:503–510. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Zeng F and Harris RC: The ErbB receptors
and their ligands in PKD, an overview. Curr Signal Trans Ther.
5:170–180. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Zheleznova NN, Wilson PD and Staruschenko
A: Epidermal growth factor-mediated proliferation and sodium
transport in normal and PKD epithelial cells. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1812:1301–1313. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Wilson SJ, Amsler K, Hyink DP, Li X, Lu W,
Zhou J, Burrow CR and Wilson PD: Inhibition of HER-2(neu/ErbB2)
restores normal function and structure to polycystic kidney disease
(PKD) epithelia. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1762:647–655. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Streets AJ, Magayr TA, Huang L, Vergoz L,
Rossetti S, Simms RJ, Harris PC, Peters DJM and Ong ACM: Parallel
microarray profiling identifies ErbB4 as a determinant of cyst
growth in ADPKD and a prognostic biomarker for disease progression.
Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 312:F577–F588. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Torres VE, Sweeney WE, Wang X, Qian Q,
Harris PC, Frost P and Avner ED: EGF receptor tyrosine kinase
inhibition attenuates the development of PKD in Han:SPRD rats.
Kidney Int. 64:1573–1579. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Yamaguchi T, Reif GA, Calvet JP and
Wallace DP: Sorafenib inhibits cAMP-dependent ERK activation, cell
proliferation, and in vitro cyst growth of human ADPKD cyst
epithelial cells. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 299:F944–F951. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Spirli C, Okolicsanyi S, Fiorotto R,
Fabris L, Cadamuro M, Lecchi S, Tian X, Somlo S and Strazzabosco M:
ERK1/2-dependent vascular endothelial growth factor signaling
sustains cyst growth in polycystin-2 defective mice.
Gastroenterology. 138:360–371. e367. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
De Stephanis L, Bonon A, Varani K, Lanza
G, Gafà R, Pinton P, Pema M, Somlo S, Boletta A and Aguiari G:
Double inhibition of cAMP and mTOR signalling may potentiate the
reduction of cell growth in ADPKD cells. Clin Exp Nephrol.
21:203–211. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Uzgare AR, Kaplan PJ and Greenberg NM:
Differential expression and/or activation of P38MAPK, erk1/2, and
jnk during the initiation and progression of prostate cancer.
Prostate. 55:128–139. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Hui L, Bakiri L, Mairhorfer A, Schweifer
N, Haslinger C, Kenner L, Komnenovic V, Scheuch H, Beug H and
Wagner EF: p38alpha suppresses normal and cancer cell proliferation
by antagonizing the JNK-c-Jun pathway. Nat Genet. 39:741–749. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Nishio S, Hatano M, Nagata M, Horie S,
Koike T, Tokuhisa T and Mochizuki T: Pkd1 regulates immortalized
proliferation of renal tubular epithelial cells through p53
induction and JNK activation. J Clin Invest. 115:910–918. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Liu Y, Dai B, Xu C, Fu L, Hua Z and Mei C:
Rosiglitazone inhibits transforming growth factor-β1 mediated
fibrogenesis in ADPKD cyst-lining epithelial cells. PLoS One.
6:e289152011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Leonhard WN, Der Wal AV, Novalic Z, Kunnen
SJ, Gansevoort RT, Breuning MH, Heer ED and Peters DJ: Curcumin
inhibits cystogenesis by simultaneous interference of multiple
signaling pathways: In vivo evidence from a Pkd1-deletion model. Am
J Physiol Renal Physiol. 300:F1193–F1202. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Aguiari G, Catizone L and Senno LD:
Multidrug therapy for polycystic kidney disease: A review and
perspective. Am J Nephrol. 37:175–182. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Lieberman HR, Kellogg MD, Fulgoni VL III
and Agarwal S: Moderate doses of commercial preparations of Ginkgo
biloba do not alter markers of liver function but moderate alcohol
intake does: A new approach to identify and quantify biomarkers of
‘adverse effects’ of dietary supplements. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol.
84:45–53. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Shiao N and Chan W: Injury effects of
ginkgolide B on maturation of mouse oocytes, fertilization, and
fetal development in vitro and in vivo. Toxicol Lett. 188:63–69.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Hu Y, Mou L, Yang F, Tu H and Lin W:
Curcumin attenuates cyclosporine Ainduced renal fibrosis by
inhibiting hypermethylation of the klotho promoter. Mol Med Rep.
14:3229–3236. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Chen W, Liang Y, Xie L, Lu T, Liu X and
Wang G: Pharmacokintics of the ginkgo bfollowing intravenous
administration of ginkgo B emulsion in rats. Biol Pharm Bull.
30:1–5. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Fadus MC, Lau C, Bikhchandani J and Lynch
HT: Curcumin: An age-old anti-inflammatory and anti-neoplastic
agent. J Tradit Complement Med. 7:339–346. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Norman JT: Fibrosis and progression of
autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD). Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1812:1327–1336. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|