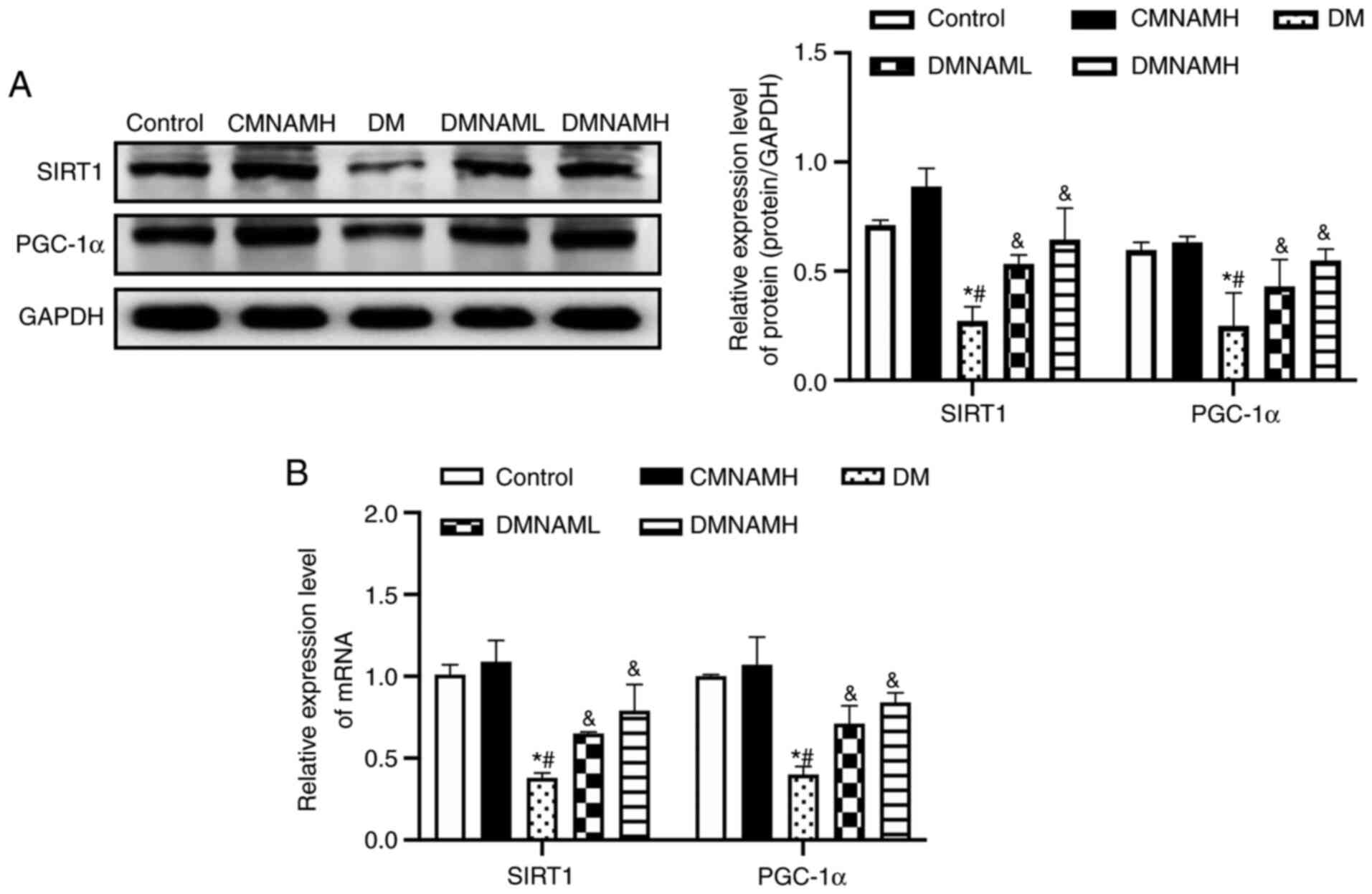
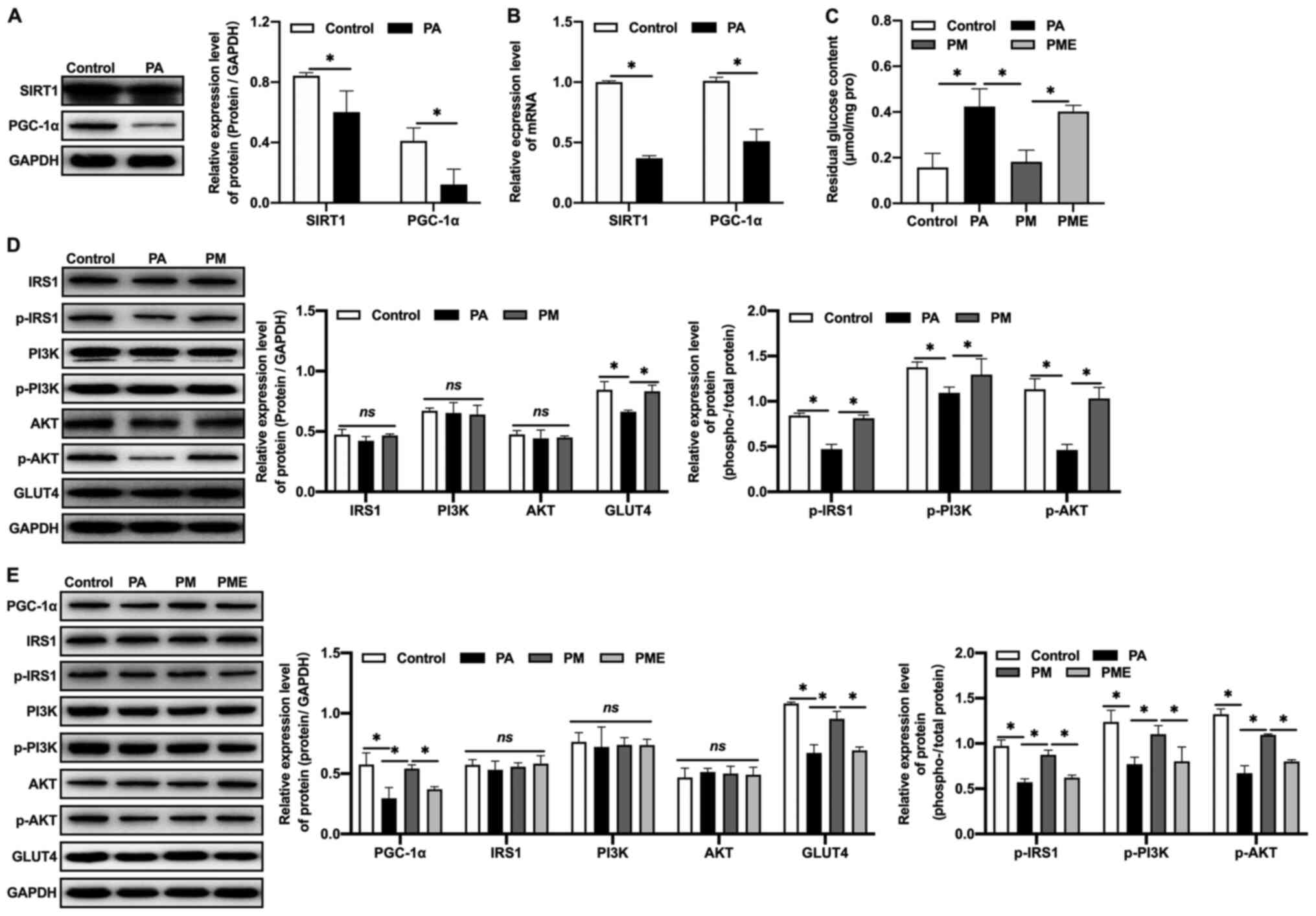
|
1
|
Barnett R: Type 2 diabetes. Lancet.
394:5572019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Saeedi P, Petersohn I, Salpea P, Malanda
B, Karuranga S, Unwin N, Colagiuri S, Guariguata L, Motala AA,
Ogurtsova K, et al: Global and regional diabetes prevalence
estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: Results from
the international diabetes federation diabetes atlas, 9(th)
edition. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 157:1078432019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Weyer C, Tataranni PA, Bogardus C and
Pratley RE: Insulin resistance and insulin secretory dysfunction
are independent predictors of worsening of glucose tolerance during
each stage of type 2 diabetes development. Diabetes Care. 24:89–94.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hernandez-Carretero A, Weber N, LaBarge
SA, Peterka V, Doan NYT, Schenk S and Osborn O: Cysteine- and
glycine-rich protein 3 regulates glucose homeostasis in skeletal
muscle. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 315:E267–E78. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Amati F: Revisiting the
diacylglycerol-induced insulin resistance hypothesis. Obes Rev. 13
(Suppl 2):S40–S50. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Esteves JV, Enguita FJ and Machado UF:
MicroRNAs-mediated regulation of skeletal muscle GLUT4 expression
and translocation in insulin resistance. J Diabetes Res.
2017:72679102017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Guo X, Sun W, Luo G, Wu L, Xu G, Hou D,
Hou Y, Guo X, Mu X, Qin L and Liu T: Panax notoginseng saponins
alleviate skeletal muscle insulin resistance by regulating the
IRS1-PI3K-AKT signaling pathway and GLUT4 expression. FEBS Open
Bio. 9:1008–1019. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Nikas IP, Paschou SA and Ryu HS: The role
of nicotinamide in cancer chemoprevention and therapy.
Biomolecules. 10:4772020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Knip M, Douek IF, Moore WP, Gillmor HA,
McLean AE, Bingley PJ and Gale EA; European Nicotinamide Diabetes
Intervention Trial Group, : Safety of high-dose nicotinamide: A
review. Diabetologia. 43:1337–1345. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Nejabati HR, Mihanfar A, Pezeshkian M,
Fattahi A, Latifi Z, Safaie N, Valiloo M, Jodati AR and Nouri M:
N1-methylnicotinamide (MNAM) as a guardian of cardiovascular
system. J Cell Physiol. 233:6386–6394. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hong S, Moreno-Navarrete JM, Wei X,
Kikukawa Y, Tzameli I, Prasad D, Lee Y, Asara JM, Fernandez-Real
JM, Maratos-Flier E and Pissios P: Nicotinamide N-methyltransferase
regulates hepatic nutrient metabolism through Sirt1 protein
stabilization. Nat Med. 21:887–894. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhang J, Chen Y, Liu C, Li L and Li P:
N(1)-methylnicotinamide improves hepatic insulin sensitivity via
activation of SIRT1 and inhibition of FOXO1 acetylation. J Diabetes
Res. 2020:10801522020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Gu C, Zeng Y, Tang Z, Wang C, He Y, Feng X
and Zhou L: Astragalus polysaccharides affect insulin resistance by
regulating the hepatic SIRT1-PGC-1α/PPARα-FGF21 signaling pathway
in male Sprague Dawley rats undergoing catch-up growth. Mol Med
Rep. 12:6451–6460. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Waldman M, Nudelman V, Shainberg A,
Abraham NG, Kornwoski R, Aravot D, Arad M and Hochhauser E: PARP-1
inhibition protects the diabetic heart through activation of
SIRT1-PGC-1α axis. Exp Cell Res. 373:112–118. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Cheng CF, Ku HC and Lin H: PGC-1α as a
pivotal factor in lipid and metabolic regulation. Int J Mol Sci.
19:34472018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Guilford BL, Parson JC, Grote CW, Vick SN,
Ryals JM and Wright DE: Increased FNDC5 is associated with insulin
resistance in high fat-fed mice. Physiol Rep. 5:e133192017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lagouge M, Argmann C, Gerhart-Hines Z,
Meziane H, Lerin C, Daussin F, Messadeq N, Milne J, Lambert P,
Elliott P, et al: Resveratrol improves mitochondrial function and
protects against metabolic disease by activating SIRT1 and
PGC-1alpha. Cell. 127:1109–1122. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Drel VR, Mashtalir N, Ilnytska O, Shin J,
Li F, Lyzogubov VV and Obrosova IG: The leptin-deficient (ob/ob)
mouse: A new animal model of peripheral neuropathy of type 2
diabetes and obesity. Diabetes. 55:3335–3343. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Tang Q, Li X, Song P and Xu L: Optimal
cut-off values for the homeostasis model assessment of insulin
resistance (HOMA-IR) and pre-diabetes screening: Developments in
research and prospects for the future. Drug Discov Ther. 9:380–385.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Shojaeian Z, Sadeghi R and Latifnejad
Roudsari R: Calcium and vitamin D supplementation effects on
metabolic factors, menstrual cycles and follicular responses in
women with polycystic ocvary syndrome: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. Caspian J Intern Med. 10:359–369. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yaffe D and Saxel O: Serial passaging and
differentiation of myogenic cells isolated from dystrophic mouse
muscle. Nature. 270:725–727. 1977. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Shin JJ, Lee EK, Park TJ and Kim W:
Damage-associated molecular patterns and their pathological
relevance in diabetes mellitus. Ageing Res Rev. 24:66–76. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ortega Á, Berná G, Rojas A, Martín F and
Soria B: Gene-diet interactions in type 2 diabetes: The chicken and
egg debate. Int J Mol Sci. 18:11882017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Carnagarin R, Dharmarajan AM and Dass CR:
Molecular aspects of glucose homeostasis in skeletal muscle-A focus
on the molecular mechanisms of insulin resistance. Mol Cell
Endocrinol. 417:52–62. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Beaudry KM and Devries MC: Sex-based
differences in hepatic and skeletal muscle triglyceride storage and
metabolism (1). Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 44:805–813. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yu N, Fang X, Zhao D, Mu Q, Zuo J, Ma Y,
Zhang Y, Mo F, Zhang D, Jiang G, et al: Anti-diabetic effects of
Jiang Tang Xiao Ke granule via PI3K/Akt signalling pathway in type
2 diabetes KKAy mice. PLoS One. 12:e01689802017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Gao Y, Zhang M, Zhang R, You L, Li T and
Liu RH: Whole grain brown rice extrudate ameliorates the symptoms
of diabetes by activating the IRS1/PI3K/AKT insulin pathway in
db/db mice. J Agric Food Chem. 67:11657–11664. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Huang X, Liu G, Guo J and Su Z: The
PI3K/AKT pathway in obesity and type 2 diabetes. Int J Biol Sci.
14:1483–1496. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Richter EA and Hargreaves M: Exercise,
GLUT4, and skeletal muscle glucose uptake. Physiol Rev.
93:993–1017. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Piątkiewicz P, Bernat-Karpińska M, Miłek
T, Rabijewski M and Rosiak E: NK cell count and glucotransporter 4
(GLUT4) expression in subjects with type 2 diabetes and colon
cancer. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 8:382016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yu L, Chen JF, Shuai X, Xu Y, Ding Y,
Zhang J, Yang W, Liang X, Su D and Yan C: Artesunate protects
pancreatic beta cells against cytokine-induced damage via SIRT1
inhibiting NF-κB activation. J Endocrinol Invest. 39:83–91. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhou S, Tang X and Chen HZ: Sirtuins and
insulin resistance. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 9:7482018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kitada M, Ogura Y, Monno I and Koya D:
Sirtuins and type 2 diabetes: Role in inflammation, oxidative
stress, and mitochondrial function. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne).
10:1872019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lee D and Goldberg AL: SIRT1 protein, by
blocking the activities of transcription factors FoxO1 and FoxO3,
inhibits muscle atrophy and promotes muscle growth. J Biol Chem.
288:30515–30526. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Sin TK, Yu AP, Yung BY, Yip SP, Chan LW,
Wong CS, Rudd JA and Siu PM: Effects of long-term
resveratrol-induced SIRT1 activation on insulin and apoptotic
signalling in aged skeletal muscle. Acta Diabetol. 52:1063–1075.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Manna P, Achari AE and Jain SK:
1,25(OH)(2)-vitamin D(3) upregulates glucose uptake mediated by
SIRT1/IRS1/GLUT4 signaling cascade in C2C12 myotubes. Mol Cell
Biochem. 444:103–108. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|