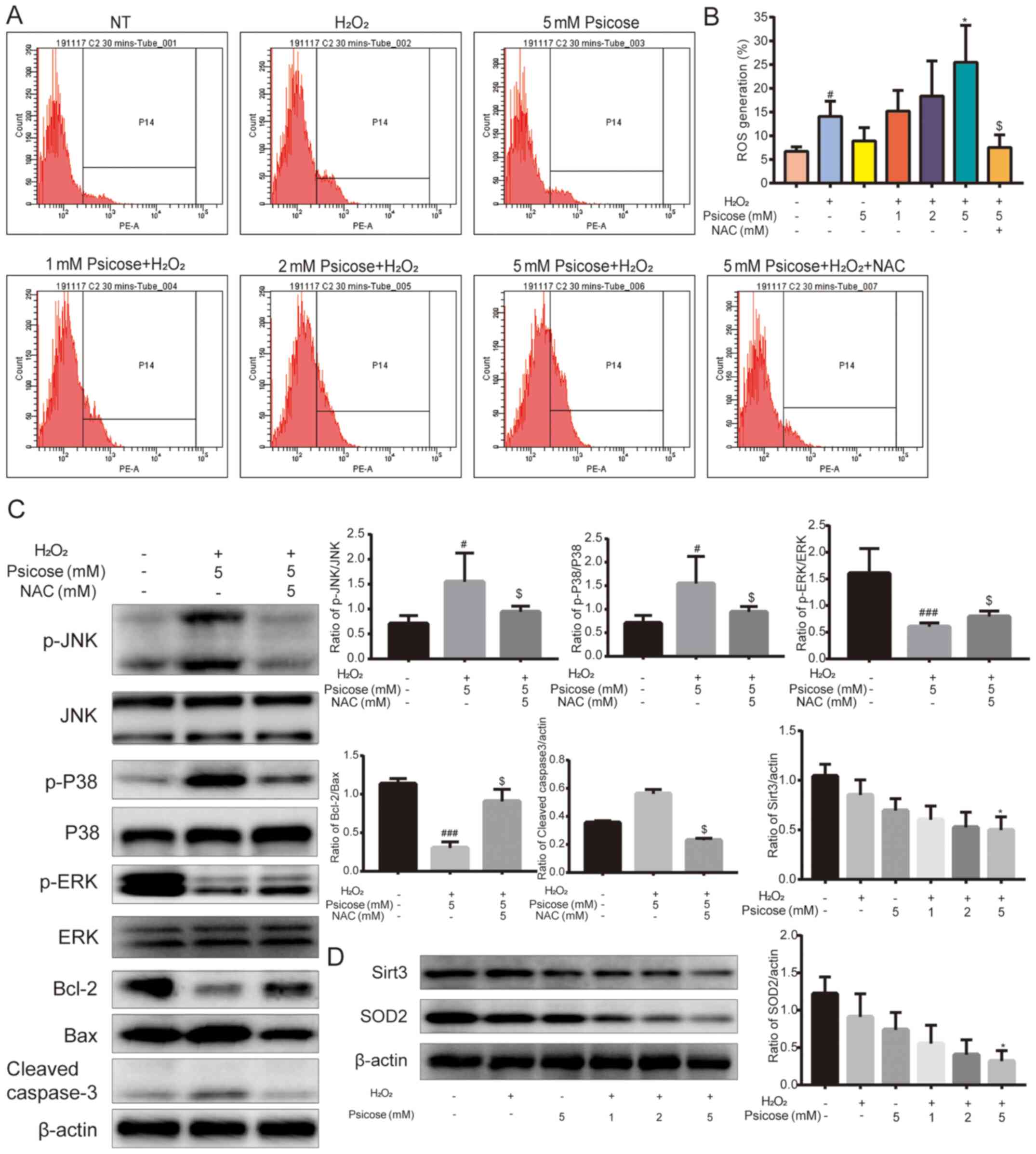
|
1
|
Chu DT, Minh Nguyet NT, Dinh TC, Thai Lien
NV, Nguyen KH, Nhu Ngoc VT, Tao Y, Son LH, Le DH, Nga VB, et al: An
update on physical health and economic consequences of overweight
and obesity. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 12:1095–1100. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sylvetsky AC and Rother KI: Trends in the
consumption of low-calorie sweeteners. Physiol Behav. 164:446–450.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Swithers SE: Artificial sweeteners produce
the counterintuitive effect of inducing metabolic derangements.
Trends Endocrinol Metab. 24:431–441. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
He W, Mu W, Jiang B, Yan X and Zhang T:
Construction of a food grade recombinant bacillus subtilis based on
replicative plasmids with an auxotrophic marker for
biotransformation of d-Fructose to d-Allulose. J Agric Food Chem.
64:3243–3250. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sui L, Dong Y, Watanabe Y, Yamaguchi F,
Hatano N, Tsukamoto I, Izumori K and Tokuda M: The inhibitory
effect and possible mechanisms of D-allose on cancer cell
proliferation. Int J Oncol. 27:907–912. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sui L, Dong Y, Watanabe Y, Yamaguchi F,
Hatano N, Izumori K and Tokuda M: Growth inhibitory effect of
D-allose on human ovarian carcinoma cells in vitro. Anticancer Res.
25:2639–2644. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Mitani T, Hoshikawa H, Mori T, Hosokawa T,
Tsukamoto I, Yamaguchi F, Kamitori K, Tokuda M and Mori N: Growth
inhibition of head and neck carcinomas by D-allose. Head Neck.
31:1049–1055. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tsukamoto I, Hossain A, Yamaguchi F,
Hirata Y, Dong Y, Kamitori K, Sui L, Nonaka M, Ueno M, Nishimoto K,
et al: Intestinal absorption, organ distribution, and urinary
excretion of the rare sugar D-psicose. Drug Des Devel Ther.
8:1955–1964. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Qaisar R, Bhaskaran S and Van Remmen H:
Muscle fiber type diversification during exercise and regeneration.
Free Radic Biol Med. 98:56–67. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Derbre F, Ferrando B, Gomez-Cabrera MC,
Sanchis-Gomar F, Martinez-Bello VE, Olaso-Gonzalez G, Diaz A,
Gratas-Delamarche A, Cerda M and Viña J: Inhibition of xanthine
oxidase by allopurinol prevents skeletal muscle atrophy: role of
p38 MAPKinase and E3 ubiquitin ligases. PLoS One. 7:e466682012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Fan X, Hussien R and Brooks GA:
H2O2-induced mitochondrial fragmentation in C2C12 myocytes. Free
Radic Biol Med. 49:1646–1654. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Siu PM, Wang Y and Alway SE: Apoptotic
signaling induced by H2O2-mediated oxidative stress in
differentiated C2C12 myotubes. Life Sci. 84:468–481. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sandri M and Carraro U: Apoptosis of
skeletal muscles during development and disease. Int J Biochem Cell
Biol. 31:1373–1390. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Jackson MJ, Edwards RH and Symons MC:
Electron spin resonance studies of intact mammalian skeletal
muscle. Biochim Biophys Acta. 847:185–190. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Goldar S, Khaniani MS, Derakhshan SM and
Baradaran B: Molecular mechanisms of apoptosis and roles in cancer
development and treatment. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 16:2129–2144.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zakki SA, Muhammad JS, Li JL, Sun L, Li
ML, Feng QW, Li YL, Cui ZG and Inadera H: Melatonin triggers the
anticancer potential of phenylarsine oxide via induction of
apoptosis through ROS generation and JNK activation. Metallomics.
12:396–407. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hertveldt K, Philippe J, Thierens H,
Cornelissen M, Vral A and De Ridder L: Flow cytometry as a
quantitative and sensitive method to evaluate low dose radiation
induced apoptosis in vitro in human peripheral blood lymphocytes.
Int J Radiat Biol. 71:429–433. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wu J, Liu T, Rios Z, Mei Q, Lin X and Cao
S: Heat shock proteins and cancer. Trends Pharmacol Sci.
38:226–256. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Li M, Kondo T, Zhao QL, Li FJ, Tanabe K,
Arai Y, Zhou ZC and Kasuya M: Apoptosis induced by cadmium in human
lymphoma U937 cells through Ca2+-calpain and
caspase-mitochondria-dependent pathways. J Biol Chem.
275:39702–39709. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Goodyear LJ, Chang PY, Sherwood DJ,
Dufresne SD and Moller DE: Effects of exercise and insulin on
mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathways in rat skeletal
muscle. Am J Physiol. 271:E403–E408. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ronda AC, Vasconsuelo A and Boland R:
Extracellular-regulated kinase and p38 mitogen-activated protein
kinases are involved in the antiapoptotic action of
17beta-estradiol in skeletal muscle cells. J Endocrinol.
206:235–246. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Caporossi D, Ciafre SA, Pittaluga M,
Savini I and Farace MG: Cellular responses to H(2)O(2) and
bleomycin-induced oxidative stress in L6C5 rat myoblasts. Free
Radic Biol Med. 35:1355–1364. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lu J, Cheng K, Zhang B, Xu H, Cao Y, Guo
F, Feng X and Xia Q: Novel mechanisms for superoxide-scavenging
activity of human manganese superoxide dismutase determined by the
K68 key acetylation site. Free Radic Biol Med. 85:114–126. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Coffey VG, Zhong Z, Shield A, Canny BJ,
Chibalin AV, Zierath JR and Hawley JA: Early signaling responses to
divergent exercise stimuli in skeletal muscle from well-trained
humans. FASEB J. 20:190–192. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Reid MB, Shoji T, Moody MR and Entman ML:
Reactive oxygen in skeletal muscle. II. Extracellular release of
free radicals. J Appl Physiol (1985). 73:1805–1809. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Bailey DM, Lawrenson L, McEneny J, Young
IS, James PE, Jackson SK, Henry RR, Mathieu-Costello O, McCord JM
and Richardson RS: Electron paramagnetic spectroscopic evidence of
exercise-induced free radical accumulation in human skeletal
muscle. Free Radic Res. 41:182–190. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Nemes R, Koltai E, Taylor AW, Suzuki K,
Gyori F and Radak Z: Reactive oxygen and nitrogen species regulate
key metabolic, anabolic, and catabolic pathways in skeletal muscle.
Antioxidants (Basel). 7:852018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Medved I, Brown MJ, Bjorksten AR and
McKenna MJ: Effects of intravenous N-acetylcysteine infusion on
time to fatigue and potassium regulation during prolonged cycling
exercise. J Appl Physiol (1985). 96:211–217. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
McKenna MJ, Medved I, Goodman CA, Brown
MJ, Bjorksten AR, Murphy KT, Petersen AC, Sostaric S and Gong X:
N-acetylcysteine attenuates the decline in muscle Na+,K+-pump
activity and delays fatigue during prolonged exercise in humans. J
Physiol. 576:279–288. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hollander J, Fiebig R, Gore M, Ookawara T,
Ohno H and Ji LL: Superoxide dismutase gene expression is activated
by a single bout of exercise in rat skeletal muscle. Pflugers Arch.
442:426–434. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kim YS, Gupta Vallur P, Phaeton R,
Mythreye K and Hempel N: Insights into the Dichotomous Regulation
of SOD2 in Cancer. Antioxidants (Basel). 6:862017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Magnuson BA, Carakostas MC, Moore NH,
Poulos SP and Renwick AG: Biological fate of low-calorie
sweeteners. Nutr Rev. 74:670–689. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yagi K and Matsuo T: The study on
long-term toxicity of d-psicose in rats. J Clin Biochem Nutr.
45:271–277. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Cho YC, Park JE, Park BC, Kim JH, Jeong
DG, Park SG and Cho S: Cell cycle-dependent Cdc25C phosphatase
determines cell survival by regulating apoptosis signal-regulating
kinase 1. Cell Death Differ. 22:1605–1617. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|