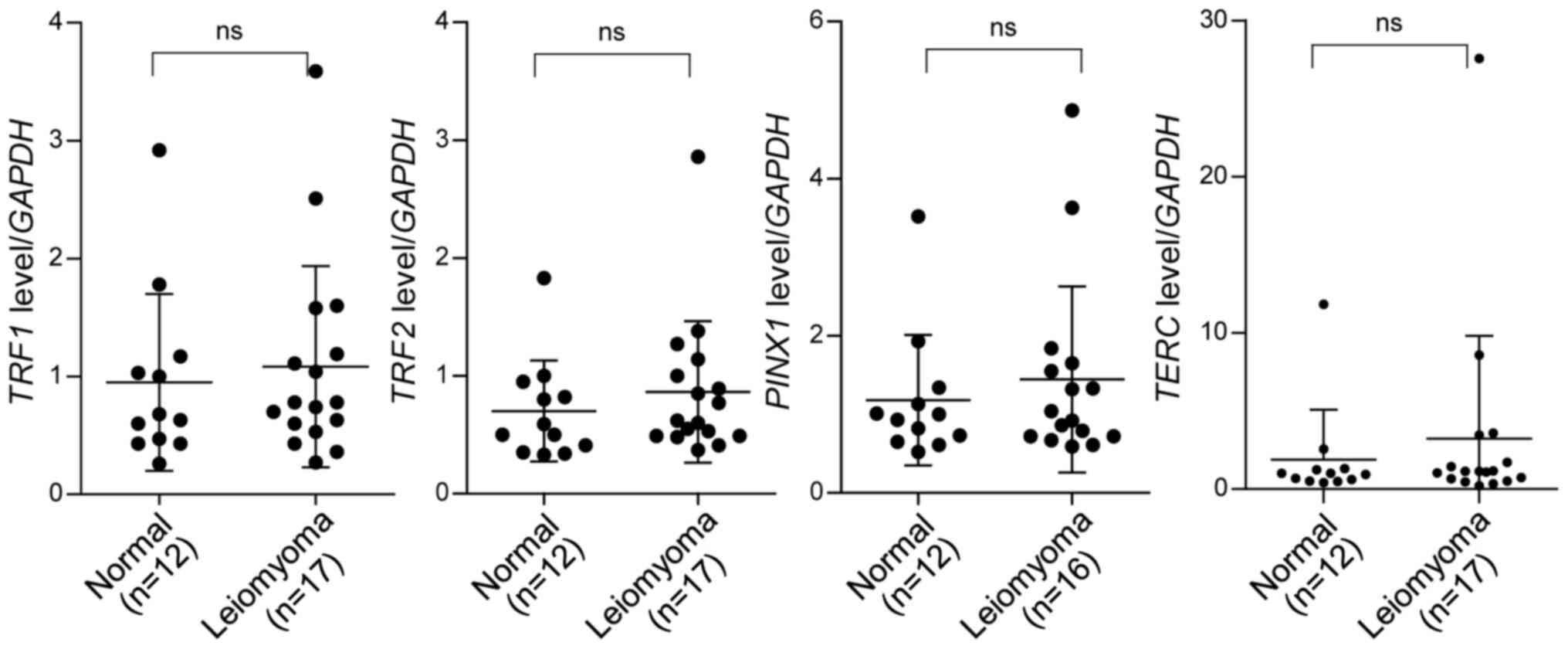
|
1
|
Bulun SE: Uterine fibroids. N Engl J Med.
369:1344–1355. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Al-Hendy A, Myers ER and Stewart E:
Uterine Fibroids: Burden and Unmet Medical Need. Semin Reprod Med.
35:473–480. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
de Lange T: Shelterin-Mediated Telomere
Protection. Annu Rev Genet. 52:223–247. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kim NW, Piatyszek MA, Prowse KR, Harley
CB, West MD, Ho PL, Coviello GM, Wright WE, Weinrich SL and Shay
JW: Specific association of human telomerase activity with immortal
cells and cancer. Science. 266:2011–2015. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Shay JW and Wright WE: Role of telomeres
and telomerase in cancer. Semin Cancer Biol. 21:349–353. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Counter CM, Hirte HW, Bacchetti S and
Harley CB: Telomerase activity in human ovarian carcinoma. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 91:2900–2904. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Nakayama J, Tahara H, Tahara E, Saito M,
Ito K, Nakamura H, Nakanishi T, Tahara E, Ide T and Ishikawa F:
Telomerase activation by hTRT in human normal fibroblasts and
hepatocellular carcinomas. Nat Genet. 18:65–68. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Avilion AA, Piatyszek MA, Gupta J, Shay
JW, Bacchetti S and Greider CW: Human telomerase RNA and telomerase
activity in immortal cell lines and tumor tissues. Cancer Res.
56:645–650. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
van Steensel B and de Lange T: Control of
telomere length by the human telomeric protein TRF1. Nature.
385:740–743. 1997. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
van Steensel B, Smogorzewska A and de
Lange T: TRF2 protects human telomeres from end-to-end fusions.
Cell. 92:401–413. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Oh BK, Kim YJ, Park C and Park YN:
Up-regulation of telomere-binding proteins, TRF1, TRF2, and TIN2 is
related to telomere shortening during human multistep
hepatocarcinogenesis. Am J Pathol. 166:73–80. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Pal D, Sharma U, Singh SK, Kakkar N and
Prasad R: Over-expression of telomere binding factors (TRF1 &
TRF2) in renal cell carcinoma and their inhibition by using SiRNA
induce apoptosis, reduce cell proliferation and migration invitro.
PLoS One. 10:e01156512015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Nakanishi K, Kawai T, Kumaki F, Hiroi S,
Mukai M, Ikeda E, Koering CE and Gilson E: Expression of mRNAs for
telomeric repeat binding factor (TRF)-1 and TRF2 in atypical
adenomatous hyperplasia and adenocarcinoma of the lung. Clin Cancer
Res. 9:1105–1111. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Grun LK, Teixeira ND Jr, Mengden LV, de
Bastiani MA, Parisi MM, Bortolin R, Lavandoski P, Pierdoná V, Alves
LB, Moreira JC, et al: TRF1 as a major contributor for telomeres'
shortening in the context of obesity. Free Radic Biol Med.
129:286–295. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Saito K, Yagihashi A, Nasu S, Izawa Y,
Nakamura M, Kobayashi D, Tsuji N and Watanabe N: Gene expression
for suppressors of telomerase activity (telomeric-repeat binding
factors) in breast cancer. Jpn J Cancer Res. 93:253–258. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Schneider RP, Garrobo I, Foronda M,
Palacios JA, Marión RM, Flores I, Ortega S and Blasco MA: TRF1 is a
stem cell marker and is essential for the generation of induced
pluripotent stem cells. Nat Commun. 4:19462013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Bejarano L, Schuhmacher AJ, Méndez M,
Megías D, Blanco-Aparicio C, Martínez S, Pastor J, Squatrito M and
Blasco MA: Inhibition of TRF1 Telomere Protein Impairs Tumor
Initiation and Progression in Glioblastoma Mouse Models and
Patient-Derived Xenografts. Cancer Cell. 32:590–607.e4. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhou XZ, Huang P, Shi R, Lee TH, Lu G,
Zhang Z, Bronson R and Lu KP: The telomerase inhibitor PinX1 is a
major haploinsufficient tumor suppressor essential for chromosome
stability in mice. J Clin Invest. 121:1266–1282. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Deng W, Jiao N, Li N, Wan X, Luo S and
Zhang Y: Decreased expression of PinX1 protein predicts poor
prognosis of colorectal cancer patients receiving 5-FU adjuvant
chemotherapy. Biomed Pharmacother. 73:1–5. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Cai MY, Zhang B, He WP, Yang GF, Rao HL,
Rao ZY, Wu QL, Guan XY, Kung HF, Zeng YX, et al: Decreased
expression of PinX1 protein is correlated with tumor development
and is a new independent poor prognostic factor in ovarian
carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 101:1543–1549. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Qian D, Zhang B, He LR, Cai MY, Mai SJ,
Liao YJ, Liu YH, Lin MC, Bian XW, Zeng YX, et al: The
telomere/telomerase binding factor PinX1 is a new target to improve
the radiotherapy effect of oesophageal squamous cell carcinomas. J
Pathol. 229:765–774. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Bai J, Chen YS, Mei PJ, Liu QH, Du Y and
Zheng JN: PinX1 is up-regulated and associated with poor patients'
survival in gliomas. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:6952–6959.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Oliva E, Carcangiu M, Carinelli SG, Ip P,
Loening T and Longacre TA: Mesenchymal tumours. WHO Classification
of Tumours of Female Reproductive Organs. 4th edition. Kurman RJ,
Carcangiu ML, Herrington CS and Young RH: IARC Press; Lyon: pp.
135–138. 2014
|
|
24
|
Bonatz G, Frahm SO, Andreas S, Heidorn K,
Jonat W and Parwaresch R: Telomere shortening in uterine
leiomyomas. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 179:591–596. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Rogalla P, Rohen C, Hennig Y, Deichert U,
Bonk U and Bullerdiek J: Telomere repeat fragment sizes do not
limit the growth potential of uterine leiomyomas. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 211:175–182. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kruk PA, Rampino NJ and Bohr VA: DNA
damage and repair in telomeres: Relation to aging. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 92:258–262. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Scheibe M, Arnoult N, Kappei D, Buchholz
F, Decottignies A, Butter F and Mann M: Quantitative interaction
screen of telomeric repeat-containing RNA reveals novel TERRA
regulators. Genome Res. 23:2149–2157. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Park IH, Zhao R, West JA, Yabuuchi A, Huo
H, Ince TA, Lerou PH, Lensch MW and Daley GQ: Reprogramming of
human somatic cells to pluripotency with defined factors. Nature.
451:141–146. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lundberg AS, Randell SH, Stewart SA,
Elenbaas B, Hartwell KA, Brooks MW, Fleming MD, Olsen JC, Miller
SW, Weinberg RA, et al: Immortalization and transformation of
primary human airway epithelial cells by gene transfer. Oncogene.
21:4577–4586. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Deng Z, Wang Z, Stong N, Plasschaert R,
Moczan A, Chen HS, Hu S, Wikramasinghe P, Davuluri RV, Bartolomei
MS, et al: A role for CTCF and cohesin in subtelomere chromatin
organization, TERRA transcription, and telomere end protection.
EMBO J. 31:4165–4178. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−ΔΔC(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Jeffreys AJ, Wilson V and Thein SL:
Hypervariable ‘minisatellite’ regions in human DNA. Nature.
314:67–73. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Karlseder J, Broccoli D, Dai Y, Hardy S
and de Lange T: p53- and ATM-dependent apoptosis induced by
telomeres lacking TRF2. Science. 283:1321–1325. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Celli GB and de Lange T: DNA processing is
not required for ATM-mediated telomere damage response after TRF2
deletion. Nat Cell Biol. 7:712–718. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Martínez P, Thanasoula M, Muñoz P, Liao C,
Tejera A, McNees C, Flores JM, Fernández-Capetillo O, Tarsounas M
and Blasco MA: Increased telomere fragility and fusions resulting
from TRF1 deficiency lead to degenerative pathologies and increased
cancer in mice. Genes Dev. 23:2060–2075. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Zhou XZ and Lu KP: The
Pin2/TRF1-interacting protein PinX1 is a potent telomerase
inhibitor. Cell. 107:347–359. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Laganà AS, Vergara D, Favilli A, La Rosa
VL, Tinelli A, Gerli S, Noventa M, Vitagliano A, Triolo O,
Rapisarda AM, et al: Epigenetic and genetic landscape of uterine
leiomyomas: A current view over a common gynecological disease.
Arch Gynecol Obstet. 296:855–867. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Yang Q, Mas A, Diamond MP and Al-Hendy A:
The mechanism and function of epigenetics in uterine leiomyoma
development. Reprod Sci. 23:163–175. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Cawthon RM: Telomere measurement by
quantitative PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 30:e472002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Tarik M, Ramakrishnan L, Sachdev HS,
Tandon N, Roy A, Bhargava SK and Pandey RM: Validation of
quantitative polymerase chain reaction with Southern blot method
for telomere length analysis. Future Sci OA. 4:FSO2822018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Sun Y, Zhang L, Zhao L, Wu X and Gu J:
Association of leukocyte telomere length in peripheral blood
leukocytes with endometrial cancer risk in Caucasian Americans.
Carcinogenesis. 36:1327–1332. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Benati M, Montagnana M, Danese E, Mazzon
M, Paviati E, Garzon S, Laganà AS, Casarin J, Giudici S, Raffaelli
R, et al: Aberrant telomere length in circulating cell-free DNA as
possible blood biomarker with high diagnostic performance in
endometrial cancer. Pathol Oncol Res. 26:2281–2289. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Blasco MA, Rizen M, Greider CW and Hanahan
D: Differential regulation of telomerase activity and telomerase
RNA during multi-stage tumorigenesis. Nat Genet. 12:200–204. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Yashima K, Milchgrub S, Gollahon LS,
Maitra A, Saboorian MH, Shay JW and Gazdar AF: Telomerase enzyme
activity and RNA expression during the multistage pathogenesis of
breast carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 4:229–234. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Yi X, Tesmer VM, Savre-Train I, Shay JW
and Wright WE: Both transcriptional and posttranscriptional
mechanisms regulate human telomerase template RNA levels. Mol Cell
Biol. 19:3989–3997. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Gazzaniga FS and Blackburn EH: An
antiapoptotic role for telomerase RNA in human immune cells
independent of telomere integrity or telomerase enzymatic activity.
Blood. 124:3675–3684. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|